Immunology and Serology
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Which of the following is paired correctly?
1) Louis Pasteur - Live attenuated, chicken cholera and anthrax vaccine
2) Metchnikoff - Cellular theory of immunity through phagocytosis
3) Jean Dausset - Antibody formation theory
4) Sabin - Development of polio vaccine
A. 1,2
B. 1,2,3
C. 1,2,4
D. 1,2,3,4
C
______ refers to the ability to respond to pathogens in a similar fashion without any exposure needed
A. Specificity
B. Acquired
C. Non-adaptiveness
D. None of these
C
1) Detection of PAMPs by adaptive immune cells occurs via soluble and cell-associated germline-encoded pattern recognition receptors.
2) B and T cells express somatically generated antigen-specific receptors that are not germline encoded but are translational products of multiple genes that are pieced together by gene rearrangements.
A. Only the first statement is correct
B. Only the second statement is correct
C. Both statements are correct
D. Both statements are incorrect
B
Which of the following correctly describe Pattern Recognition Receptors
A. Recognize PAMPS on microorganisms
B. Link to IgM on B-cell surfaces
C. Link to the antigen receptor on T cells
D. Both A and C
A
Processing of antigens to be presented to the T cells is primarily accomplished by what type of cells?
1) Macrophage
2) Basophils
3) Eosinophils
4) B cells
5) Dendritic cells
6) T cells
A. 1, 5
B. 1,2,3
C. 1,4,5
D. 1,5,6
E. 1,4,5,6
C
1) Adaptive immunity play a role in the elimination of extracellular microbes.
2) Adaptive immunity is a consequence of an encounter with a foreign substance
A. Only the first statement is correct
B. Only the second statement is correct
C. Both statements are correct
D. Both statements are incorrect
C
Which statement correctly describe Phagocytosis?
1) Phagocytosis is the ingestion by individual cells of invading foreign particles
2) Haptens like antibodies and complement proteins enhance phagocytosis
3) Phagocytes generate toxic products in a process known as respiratory burst
4) Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils and Macrophages are phagocytes
A. 1,2
B. 1,2,3
C. 1,3,4
D. 1,2,3,4
C
Which of the following APRs are paired incorrectly with its immune function?
A. C-reactive protein - Opsonization
B. Hepcidin - Degradation of blood clots
C. Ceruloplasmin - Oxidizes iron
D. Complement factors - Opsonization, lysis
B
A team of immunlogists is studying the adaptive immune responses of patients infected with different classes of pathogens. They are particularly interested in understanding which helper T cell subsets are activated in response to each type of infection. Based on the information provided, which helper T cell subset is most associated with the immune response to each of these infections?
● Patient 1 has a severe parasitic worm infection, presenting with gastrointestinal discomfort and elevated levels of eosinophils in the blood. The immune response involves the activation of cells that promote antibody production and recruit other immune cells to combat the parasite.
● Patient 2 is dealing with a fungal infection localized in the mucosal surfaces, resulting in persistent inflammation and the recruitment of neutrophils to the infected area.
● Patient 3 is suffering from an intracellular bacterial infection, causing prolonged fever and the activation of macrophages to help contain the bacteria hidden inside host cells.
A. Patient 1 - Th2; Patient 2 - Th17; Patient 3 - Th1
B. Patient 1 - Th1; Patient 2 - Th2; Patient 3 - Th17
C. Patient 1 - Th1; Patient 2 - Th17; Patient 3 - Th2
D. None of these
A
Refer to item #9, which of the following molecules released by activated macrophages contributes to the prolonged fever during an intracellular bacterial infection?
A. IL-10
B. TNF-a
C. IFN-a
D. IL-4
B
The antibody idiopathy refers to:
A. The hypervariable region of the light chain
B. The hypervariable region of the heavy chain
C. The hypervariable region of both the heavy and light chains
D. The complement binding region on the heavy chain
C
In the development of B cells, the process of V(D)J recombination is crucial for generating diversity. What does V(D)J recombinant primarily affect?
A. The constant region of the heavy chain
B. The variable region of the heavy and light chains
C. The hinge region of the antibody
D. The Fc region of the antibody
B
Which antibody is most effective at crossing the placenta to provide passive immunity to a fetus?
A. IgM
B. IgE
C. IgA
D. IgG
E. Both A and D
D
Th1 cells synthesize & needed in the activation
of macrophages, CD8+ T cells, and NK cells.
A. IL-2 & TGF-B
B. IFN-y & IL-2
C. IL-10 & TGF-B
D. IL-4 & IL-5
E. None of these
B
When IL-2 is secreted by antigen-specific T cells activated due to presentation of antigen by APCs, what happens to naive antigen-nonspecific T cells in the vicinity?
A. They proliferate due to their exposure to IL-2.
B. They often undergo apoptosis.
C. They secrete cytokines associated with their Th phenotypes.
D. Nothing happens.
D
Individuals with certain inherited genetic diseases lack a thymus. These individuals have reduced immune function and are most likely to be deficient in a number of functions of which of the following cell types?
A. B cell only
B. T cell only
C. B cell & T cell
D. Dendritic cell
C
1) Naive T cells require costimulation for activation.
2) Effector T cells do not require costimulation to perform their effector functions.
A. Only the first statement is correct.
B. Only the second statement is correct.
C. Both statements are correct.
D. Both statements are incorrect.
C
The chemical composition of an antigen affects its immunogenicity. Which of the following is more likely to be highly immunogenic?
A. Simple polysaccharides
B. Non-repetitive proteins
C. Nucleic acids
D. Lipid bilayers
E. None of these
B
All of the following describe an epitope, except:
A. Same as an antigenic determinant site
B. Area of immunogen recognized by T cells
C. Consists of sequential amino acids only
D. Key portion of the immunogen
C
MHC molecules are associated with which of the following?
A. Graft rejection
B. Autoimmune diseases
C. Determining to which Ag an individual responds
D. All of these
D
Which of the following is true of MHC (HLA) class II antigens?
A. They are found on all nucleated cells
B. They are found on B cells and macrophages
C. They all originate at one locus
D. They are coded for on chromosome 9
B
MHC class I molecules are regarded important for which of the following?
A. Binding of CD8 molecules on T cells
B. Binding to CD4 molecules on T cells
C. Presenting exogenous antigen to B cells
D. Presenting intact viral proteins to T cells
A
This is the most primitive antibody class:
A. IgG
B. IgA
C. IgM
D. IgD
E. IgE
C
The properties of an antibody class are defined by:
A. The size of the antigen-antibody complexes
B. Nature of the stimulating antigen
C. Fab end of the molecule
D. Fc end of the molecule
D
The light chains of an immunoglobulin molecule possess:
A. Alpha or beta
B. Alpha or lambda
C. Kappa or beta
D. Kappa or lambda
D
Which of the following are functions of immunoglobulins, except:
A. Neutralizing toxic substances
B. Facilitating phagocytosis through opsonization
C. Interacting with Tc cells to lyse viruses
D. Combining with the complement to destroy cellular antigens
C
Papain digestion of an IgG preparation of antibody specific for the antigen hen egg HEA will:
A. Lose it antigen specificity
B. Precipitate with HEA
C. Lose all interchain disulfide bonds
D. Produce two Fab molecules and one Fc fragment
D
A multilineage cytokine among the following cytokine is:
A. IL-1
B. IL-2
C. IL-3
D. IL-4
C
Toxic Shock Syndrome is initiated by the release of superantigens like the enterotoxins of S. aureus or S. pyogenes. These antigens, when processed may trigger the activation of T cells leading to systemic reactions including fever, blood clotting, hypotension, diarrhea and shock. Which of the following cytokine/s are the ultimate cause of this dysregulation in TSS?
A. IL-1 & TNF-a
B. TNF-a & IL-10
C. IFN-Y & IL-4
D. IL-4 & TGF-B
A
1) Th2 secrete IL-2 and IFN-Y, but not IL-4 or IL-5;
2) Th1 secrete IL-4 and IL-5, but not IL-2 or IFN-Y.
A. Only the first statement is correct.
B. Only the second statement is correct.
C. Both statements are correct.
D. Both statements are incorrect.
D
The alternative pathway of complement activation is characterized by all of the following statements, except:
A. activation of C' components beyond C3 in the cascade
B. participation of properdin
C. generation of anaphylatoxins
D. activation of C4
D
1) In the first phase, the complement protein, C1, which consists of the C1q, C1r, and C1s subunits, binds to antigen-antibody complexes.
2) In the second ase, fragments of C4, C2, and C3 combine to form the activation unit, which cleaves the C5 component of complement.
A. Only the first statement is correct
B. Only the second statement is correct
C. Both statements are correct
D. Both statements are incorrect
C
Patient Bogart presents with a history of frequent infections. You perform a complement assay measuring the activity of the terminal pathway Imponents (C5 to C9). The results indicate a marked decrease in C5 and C6 levels, while other complement components appear normal. What is the most likely outcome of a C5 to C6 deficiency in the patient?
A. He will have normal opsonization but impaired immune clearance
B. He will have a higher susceptibility to Neisseria spp. infections
C. He has to be checked for autoimmune disease
D. None of these
B
Which of the following statements about cytokines and subsets of CD4+ T cells is incorrect?
A. Th1 cells secrete cytokines that induce macrophage and NK cell activation
B. Cytokines produced by Th2 cells are important in allergic responses
C. The presence of IL-12 during the activation and differentiation of CD4+ T cells favors the development of Th1 cells
D. Cytokines synthesized by Th1 and Th2 cells inhibit the action of Treg cells
D
Which of the following correctly describes the characteristics of T cells that leave the thymus?
A. They lack CD4 and CD8 but have a TCR with high affinity for MHC plus self-antigen
B. They express both CD4 and CD8, lack a TCR, and have low affinity for MHC plus self-antigen
C. They express either CD4 and CD8, and have a TCR, and have high affinity for MHC plus self-antigen
D. They express either CD4 or CD8 and have a TCR with low to moderate affinity for MHC plus self-antigen
D
Which of the following cytokines is measured in the QuantiFERON-TB Gold test to assess a response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
A. IL-1
B. TNF-a
C. IFN-Y
D. IL-6
E. Both B & C
C
The test that will give a positive result in Secondary Syphilis:
A. RPR
B. FTA-ABS
C. Darkfield Microscopy
D. Both A & C
E. Both A & B
E
Which one is recommended for testing CSF for the detection of neurosyphilis?
A. RPR
B. VDRL
C. MHA-TP
D. Microscopy
B
A 7-year-old child presents with joint pain and swelling after a recent sore throat. The physician suspects rheumatic fever and orders an ASO neutralization test. The childʼs ASO titer is significantly elevated. Why is the ASO neutralization test particularly useful in pediatric patients?
A. It helps in identifying Streptococcus pneumoniae infections, which are common in children.
B. It allows for early diagnosis of sequelae of Group A Streptococcus infections in children.
C. It detects the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes in throat cultures.
D. It provides information on the patientʼs immune system function, which is often underdeveloped in children.
B
In the laboratory, heterophile antibodies are routinely detected by their reaction with
A. B lymphocytes
B. Bovine erythrocyte antigens
C. Sheep erythrocyte antigens
D. Epstein-Barr virus antigens
B
The serum of a person who received all doses of the Hepatitis B vaccine should have?
A. Anti-HBs
B. Anti-HBe
C. Anti-HBc
D. All of these
A
Which of the following immune cells are likely to be involved in the immune response to HCV?
A. Cytotoxic T cells
B. Helper T cells
C. B cells
D. Dendritic cells
E. All of these
E
Hepatitis B is considered most infectious when which of the following heap marker/s is detected:
A. HBsAg
B. HBeAg
C. HBcAg
D. Anti-HBc IgG
B
Heterophile antibodies in IM will react to all cells, EXCEPT:
A. Sheep Cells
B. Horse Cells
C. Beef Cells
D. Guinea Pig Cells
D
The Circumoval Precipitin Test is used to diagnose:
A. Schistosomiasis
B. Malaria
C. Filariasis
D. Toxoplasmosis
A
Which of the following serological tests detects the polysaccharide capsule antigen in serum and CSF of patients with suspected infection with Cryptococcus neoformans?
A. Complement fixation
B. India ink test
C. Latex agglutination
D. RAST
C
The Widal Reaction is used primarily to detect which disease?
A. Q fever
B. Typhoid fever
C. Rickettsia
D. Group A Strep
B
TEST: IgG and IgM to viral capsid antigen are found to be positive. Interpret the EBV serological test:
A. Current infection
B. Past infection
C. HIV infection
D. Invalid; Cross reaction
A
Which of the following correctly describes the increased susceptibility to infection among AIDS patients?
A. Decreased CD4+ cells
B. Decreased CD8+ cells
C. Decreased HIV Ag
D. Cytotoxic T cells are main targets
A
The emergence of autoimmune disease is a result of the breakdown of the immune system ability to discriminate between self and non self. Autoantibodies are always unique to autoimmune diseases.
A. Only the first statement is correct
B. Only the second statement is correct
C. Both statements are correct
D. Both statements are incorrect
A
A 24 y/o female patient has had increasing malaise; facial skin lesions are exacerbated by sunlight exposure; and arthralgias and myalgias for the past month. Laboratory results include pancytopenia and serum creatinine 3 mg/dL. Urinalysis shows hematuria and proteinuria. A renal biopsy shows granular deposits of IgG and complement in the glomerular basement membrane. Which of the following condition is likely to be ruled in?
A. SLE
B. She is completely normal
C. RA
D. Waldenstromʼs
A
SLE can be distinguished from RA on the basis of:
A. Presence of anti-dsDNA and anti-Sm
B. Joint pain
C. Presence of antinuclear antibodies
D. Cross-reactivity with latex agglutination tests
A
Rheumatoid factor if typically an IgM autoantibody with specificity for which of the following?
A. Fc portion of IgG
B. SS-B
C. dsDNA
D. RNP
A
1) Antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor of the neuromuscular junction are known to cause of myasthenia gravis.
2) Antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction block the binding of acetylcholine to the receptor, resulting muscle weakness.
A. Only the first statement is correct
B. Only the second statement is correct
C. Both statements are correct
D. Both statements are incorrect
C
Nephelometry is based on the principle:
A. The measurement of turbidity resulting from specific antigen-coated latex particles agglutinated by corresponding antibody
B. Agglutination resulting from physical attachment of antibody molecules to antigens on an erythrocyte membrane
C. Agglutination of host antibody to antigenic determinant on a bacterial agent
D. Precipitation of immune-related proteins in agarose gel
A
Avidity may be defined as the
A. Strength of a reacting antibody
B. Degree of hemolysis
C. Titer of an antigen
D. Dilution of an antibody
A
It refers to the qualitative gel precipitation technique in which both antigen and antibody diffuse out from well cut in the gel
A. Countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis
B. Ouchterlony double immunodiffusion
C. Rocket electrophoresis
D. Flocculation testing
B
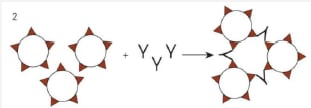
The image below is that type of agglutination?
B
________ is the agglutination of erythrocytes in tests for antibody detection
A. Precipitation
B. Latex agglutination
C. Coagglutination
D. Hemagglutination
D
The insert instructions for a slide agglutination test informs the RMT that after mixing the patientʼs serum and latex particles, the slide must be rotated for 2 minutes. What would happen if the slide were rotated for 10 mins?
A. Possible false-positive result
B. Possible false-negative result
C. No effect
A
How much diluent needs to be added to 0.1 mL of serum to make a 1:15 dilution?
A. 1.4 mL
B. 1.5 mL
C. 5.0 mL
D. 15 mL
A
A nasopharyngeal sample is processed and fixed onto a microscope slide. Next, fluorescein-conjugated antibody is added to the slide. The sample is then incubated with a labeled antibody. This is followed with washing and then observed for fluorescence. Which of the following techniques best describes this procedure?
A. Indirect fluorescent antibody test
B. Direct fluorescent antibody test
C. Latex agglutination
D. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
B
Turgeon, a 25 y/o female patient presents with a fever, a malar facial rash, alopecia, and ulcerations on her two fingertips. Her urinalysis last shows proteinuria. Which one of the following is the most likely explanation for her proteinuria given that you are suspecting for an SLE case?
A. Cytotoxic T cells attack the glomerular basement membrane
B. A delayed hypersensitivity response consisting of macrophages and CD4-positive T cells damages the glomeruli
C. Immune complexes are trapped in the glomeruli and activate complement, then C5a attracts neutrophils that damage the glomeruli.
D. None of these
C
Hemolytic transfusion reaction and hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn are example of what type of hypersensitivity reaction?
A. Type 1
B. Type 2
C. Type 3
D. Type 4
B
Estrogen and progesterone receptors are tumor markers most commonly employed to provide prognostic information for:
A. Colorectal cancer
B. Hepatocellular cancer
C. Breast cancer
D. Uterine cancer
C
Rejection of a tumor may involve which of the following?
A. T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity
B. ADCC
C. Complement-dependent cytotoxicity
D. Tumor destruction by phagocytic cells
E. All of these
E
In CGD:
1) there is an inability of phagocytic cells to produce a microbicidal effect to catalase-negative bacteria and this leads to infections such as pneumonitis, infectious dermatitis, and perianal abscesses.
2) Microbial proliferation and WBC accumulation will lead to the formation of abscess and granulomas
A. Only the first statement is correct
B. Only the second statement is correct
C. Both statements are correct
D. Both statements are incorrect
B
Which of the following immune deficiency disorders is associated exclusively with an abnormality of the humoral immune response?
A. X-linked agammaglobulinemia
B. DiGeorge syndrome
C. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
D. ataxia telangiectasia
A
In clinical transplantation, preformed cytotoxic antibodies reactive against MHC antigens expressed on the grafted tissue cause:
A. Chronic rejection
B. Hyperacute rejection
C. Acute rejection
D. Type IV hypersensitivity
B
Transplant rejections may involve
A. Cell-mediated immunity
B. Activation of TH17 cells
C. Complement-dependent cytotoxicity
D. The release of IFN-y by alloreactive TH1 cells
E. All of the statements are correct
E