Structure and Function of Living Organisms
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Explain why no droplets are seen after bile and lipase solution is added to the oil and water mixture
Bile emulsification
Smaller drops / increased surface area
Optimum pH
Lipase is an enzyme
Digests
Into fatty acids / glycerol
Explain how this structure (villus) is adapted to absorb glucose
Large surface area
Microvilli
Capillaries
Movement of blood to maintain concentration gradient
One cell thick
So diffusion easy
Active transport
Describe the role of chloroplasts in leaf cells
Trap/absorb light
Using chlorophyll
For photosynthesis to produce glucose/starch
Explain what happens in a leaf when it is destarched?
Starch is removed /used etc
converted to glucose
For respiration/energy
Describe how the green pigment is removed safely before testing a leaf for the presence of starch
Starch is removed /used etc
converted to glucose
For respiration/energy
Design an investigation to find out the effect of statins on blood cholesterol levels.
Change to type of statin used
Organism -- needs to be kept the same gender / age / mass / height / level of cholesterol
Repeat the test three times / use several people (group of people)
M1 measure cholesterol level
M2 at start and end
S1 + S2 same diet / mass of food / same stress / exercise / smoking
Describe how magnesium ions are used to help trees grow
For the chlorophyll in chloroplasts
To absorb light in photosynthesis
Which type of meat would provide the most energy?
The one with the most fat
Uses of fat in the human body
Energy
Protection/padding
Insulation
Cell membranes
Myelin sheath
Complete the table
Safety precautions for Benedict’s test
water bath / avoid direct heat / point away / eq;
goggles / lab coat / tongs / tie hair / tuck tie away / gloves;
(ii) Gazelles cannot maintain their top speed for a long time because a change in the type of respiration takes place in their muscle cells. Explain how this change in respiration stops gazelles from running at a top speed for a long time.
Anaerobic respiration
Uses less oxygen
Building up lactic acid
Denaturing the organism's enzymes
Providing less energy
Lion eyes have a layer of cells behind the retina that reflects light which has passed through the retina. Suggest how this would help a lion see in low light intensities.
Light passes through retina twice / more light through retina / more detection by retina / stimulation
Suggest adaption in structure of lion’s eye that helps the lion to see in low light intensities.
Light passes through retina twice / more light through retina / more detection by retina / stimulation
Suggest another adaption in structure of lion’s eye that helps the lion to see in low light intensities.
Dilated/larger pupil/ expanded pupil / more rods / larger hole in iris / radial muscles contract more
Suggest why saliva released into lion’s mouth does not contain amylase
Lion eats protein
Amylase cannot digest protein
Explain why there are no plasma proteins in urine
Protein molecules large /too big
Leave glomerulus /capillaries and enter Bowman's/renal capsule
Explain why there is no glucose in urine
Reabsorbed into blood
Through proximal/first/convoluted tubule
Through active transport
Name substances you would find in urine
Salts/minerals/ions/named mineral ion/hormones/vitamins
Urea
water
Suggest why a person with diabetes has glucose in their urine
No insulin
High blood glucose levels
Cannot reabsorb all glucose
ingestion
food enters the mouth
digestion
breaks down large insoluble molecules into smaller insoluble molecules
absorption
small food molecules move from small intestine into blood
assimilation
small food molecules are used to build large molecules
egestion
removal of undigested food / faeces / waste from anus
Draw + label phagocyte
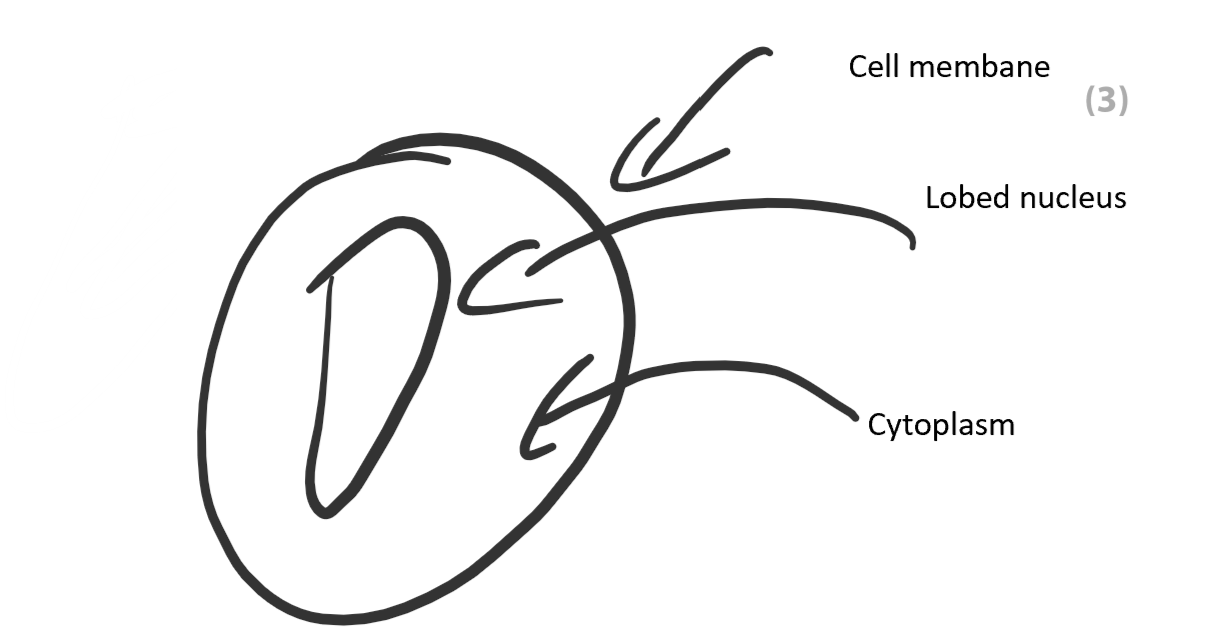
Way structure of phagocyte differs from red blood cell
Nucleus/bigger/irregular/not biconcave
Describe how white blood cells are used by the body to defend against infection
1 ingest / engulf / surround / phagocytosis / eq;
2 enzymes;
3 digest / breakdown / eq;
4 lymphocytes;
5 antibodies / antitoxins;
6 specific / eq;
7 antigen:
8 memory / memory cell / eq;
Name A + B
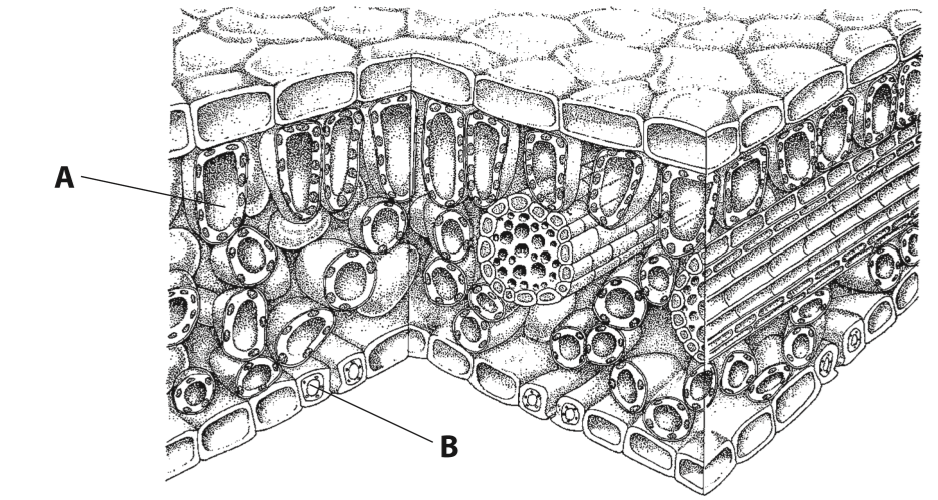
Function of waxy cuticle
Reduce water loss / transpiration / evaporation / prevent entry of microorganisms
Explain how the excretory product of photosynthesis is removed from the leaf
Diffuses
Through stomata/pores/holes
Along concentration gradient
Reasons plants lose their leaves in cooler months
Reduce water loss
Less light
Less photosynthesis
Conserve energy
Which hormone repairs the uterus lining, and where is it produced?
oestrogen, ovaries
Suggest why cells do not store glucose
soluble
osmotic effect
Do fungi have a cell wall?
Yes
muscles that operate penguin’s feet located in penguin’s body rather than in feet. How does this benefit the penguin?
Muscles kept warm
Contract
Respiration
Enzymes at optimum tempearture
Describe how growth hormone could be destroyed in the stomach
hydrochloric acid
enzymes such as protease/pepsin
breakdown
and denature growth hormone
Describe how levels of blood glucose are kept constant in human plasma after eating a meal
Islets of langerhans in the pancreas
Release insulin
To lower levels of glucose
Storing it in form of glycogen
Ways in which nervous communication differs from hormonal communication
Neurones versus blood
Shorter lasting
Target cells (versus all around body)
Faster
Electrical vs chemical
Describe response of roots to gravity and explain how response benefits the plant
Positively geotropic (downward)
This allows roots to anchor the plant
Obtain water / mineral ions nutrients etc
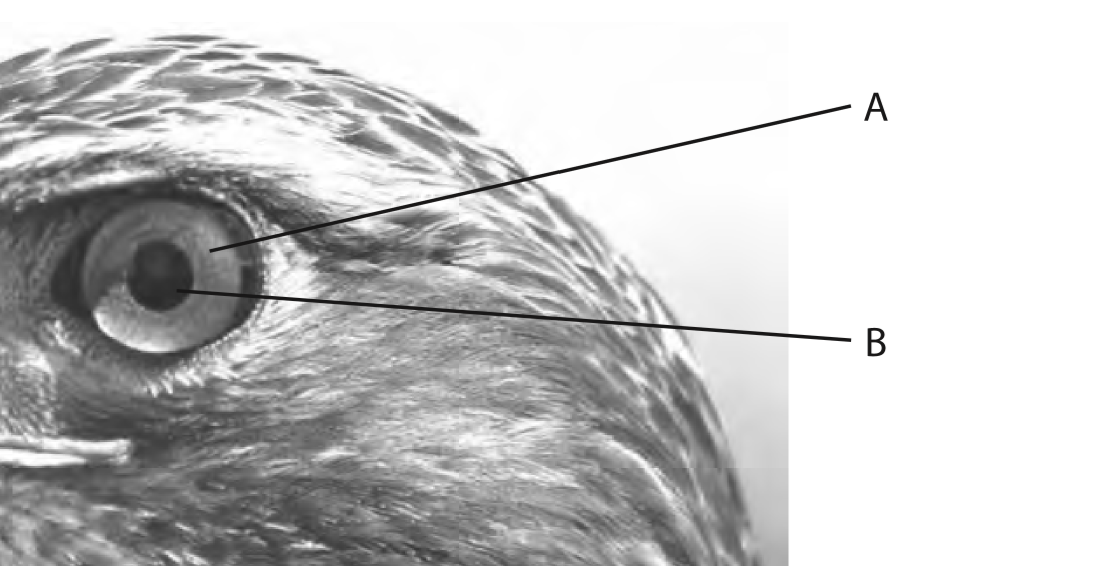
What is B?
iris/cornea
What is mean the term population?
Number/amount/group of organisms of same species
Explain what is meant by the term hormone
Hormones are released from glands
Travel in blood
To target cells/organs
Causing an effect
Suggest why a person might produce hard lumpy faeces
Constipation
Lack of water
Lack of fibre
Why might a person produce watery faeces?
Diarrhoea
Less water absorbed
Food poisoning / infection
Describe how food is moved through the gut
Peristalsis
Contraction
Muscles
Pushed/squeezed
Explain how egestion differs from excretion
Faeces vs urea / excretory product
Undigested food vs metabolic waste product
Anus vs kidney/lung/skin
Not in cells vs in cells
Describe how the kidney machine removes urea from the blood
Diffusion
Along a partially permeable membrane
From high concentration to low concentration
Suggest how concentration of glucose in dialysis solution helps to maintain normal glucose concentration
same conc. in fluid and blood / normal blood conc.
in fluid / correct glucose conc. in fluid / eq;
if high in blood moves out of blood/into fluid;
if low in blood moves into blood/out of fluid;
Describe processes that take place in the kidney but not in the kidney machien
Ultrafiltration
Small molecules go out of blood / large molecules / protein stays in blood
Selective reabsorption of glucose/salts/water/amino acids
Active transport using energy from glucose
Suggest why the transplanted kidney is placed in the lower abdomen instead of in the kidney’s usual location
Nearer to bladder
Easier access
Easy to connect to blood vessels / shorter
What process takes part place at A?
Ultrafiltration
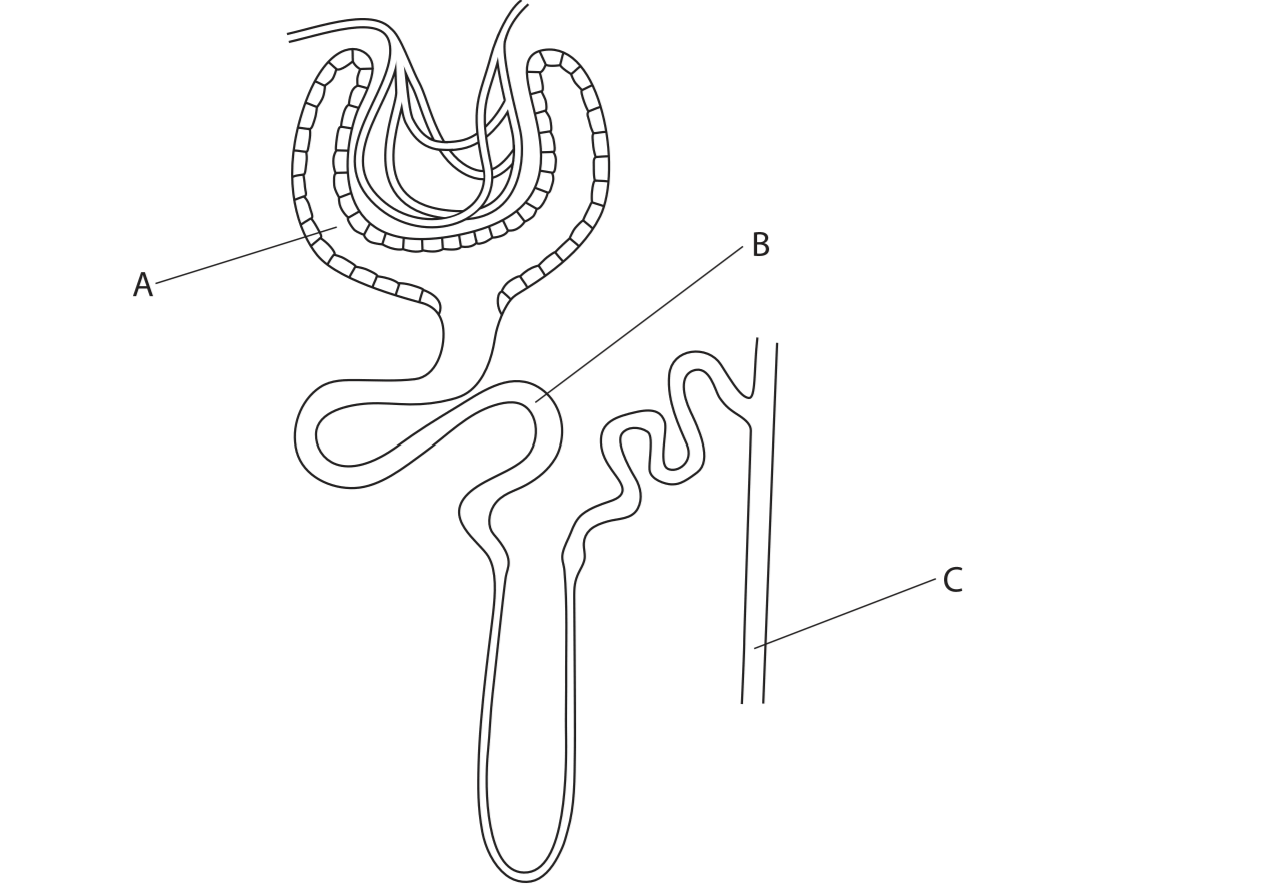
What process takes place at B?
Glucose reabsorption
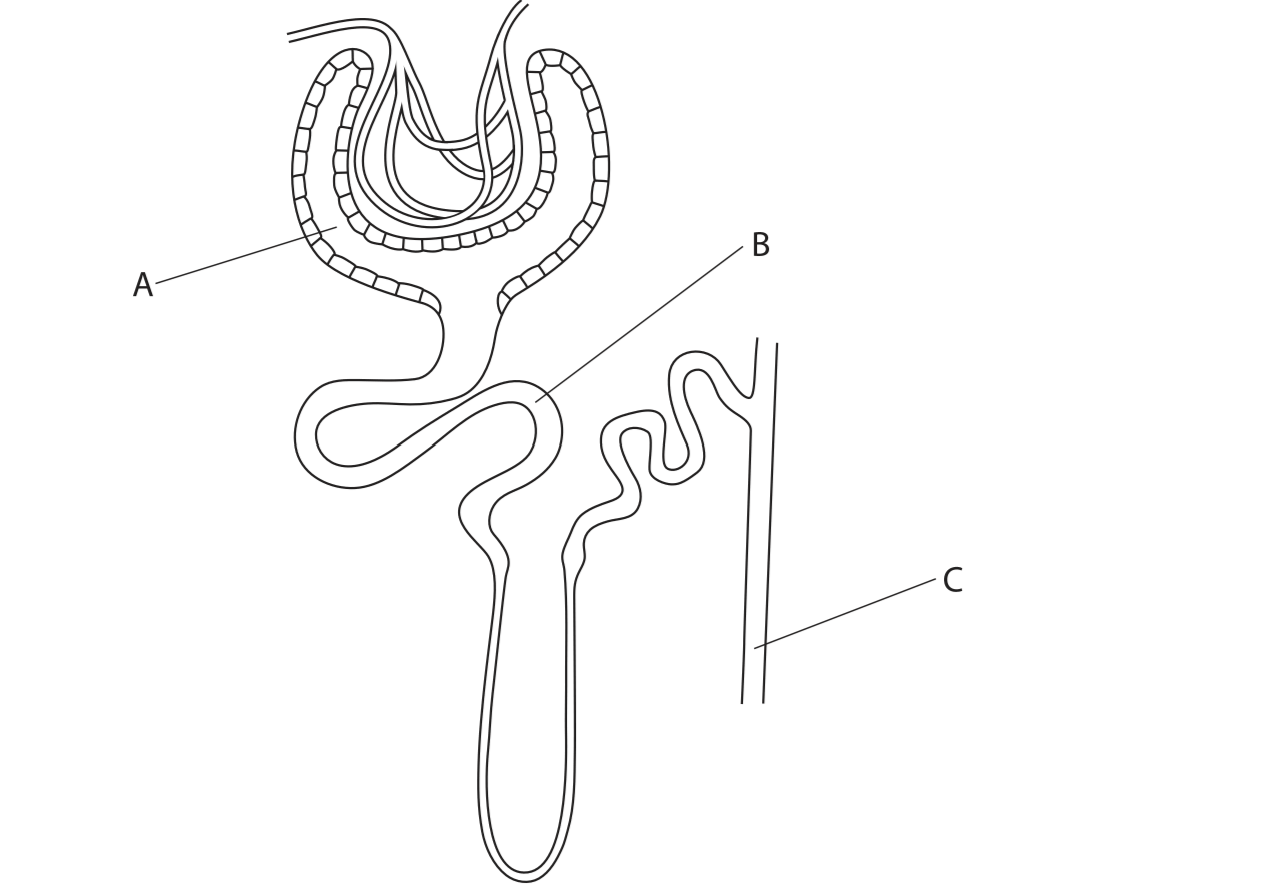
Explain how the structure of the blood vessels entering and leaving the glomerulus help to move glucose into the Bowman’s capsule
Vessel entering is wider
Increased pressure
Allowing ultrafiltration
Describe how glucose is reabsorbed from the nephron back into the blood
Vessel entering is wider
Increased pressure
Allowing ultrafiltration
What is meant by the term gas exchange?
the absorption of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide
Suggest ways in which fish gills are adapted for efficient gas exchange
Large surface area
Thin
Large blood supply of capillaries
Permeable
What is C?
Heart
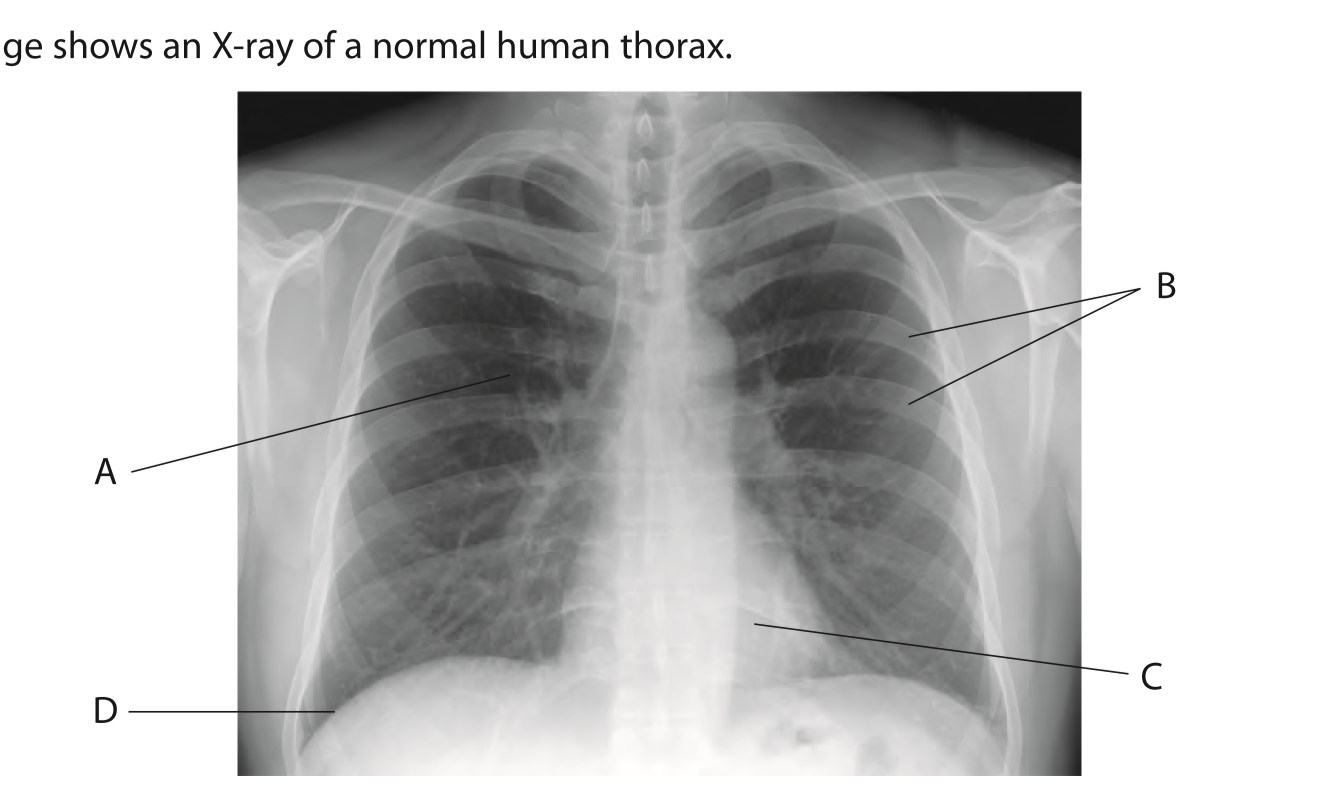
Describe how ribs and diaphragm help a person to breath inn
Diaphragm contracts
And moves down
Ribcage moves up
Increasing the thoraccic volume
Decreasing thoracic pressure
Suggest why people with cystic fibrosis often have lung infections
Bacteria/pathogens can
Reproduce and multiply in the lungs
Remaining there
Suggest why gas exchange is reduced in someone with cystic fibrosis
Less oxygen
Can get to the alveoli
Suggest and explain the effect of emphysema on gas exchange
Less surface area
Slower diffusion / gas exchange
Less oxygen
Explain how coronary heart disease can cause death
Coronary arteries
Blocked
By fat/cholesterol
Forming a clot
Getting less blood to the heart
And therefore oxygen
Causing the muscles
To have less respiration
Causing a build up of lactic acid and an angina
Resultign in heart attack
What is osmoregulation
Maintaining water/salt concentration of body
Where are villi located?
On the small intestine
What is cell X?
Leaf
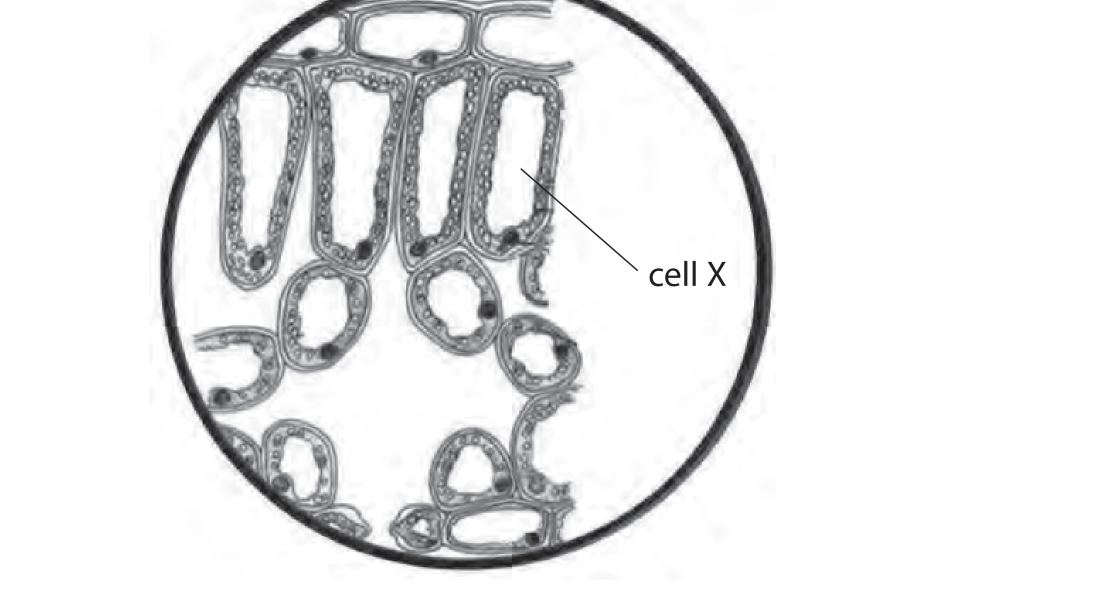
How do palisade mesophyll cells help the leaf in photosynthesis?
Densely packed
With lots of chloroplasts
To take in light
How does the spongy layer help the leaf in photosynthesis
Has air spaces
For diffusion/gas exchange
Xylem
Can transport water
How do the guard cells help the leaf in photosynthesis
Open and close
To let in carbon dioxide
Water lilies float on surface, guard cells found on upper surface of water lilly. Suggest a reason for this adaption
Upper surface exposed to air
Allows carbon dioxide in
Allows transpiration
Suggest why red onion used for viewing cells
Easier to see / no need to stain contrast
Explain how the rate of transpiration is affected by changes in the environment
High humidity decreases rate
Reduced concentration gradient
High wind increases rate
Increased concentration gradient
High temperature increases rate
More kinetic energy
High light increases rate
Stomata open
Explain how this experiment can be used to understand the need for transport systems in larger organisms such as humans
Humans have smaller SA:V ratio
Therefore diffusion
Is too slow
Need to move nutrients
In circulatory system
Explain how the structure of the leaf is adapted for its role as the organ of photosynthesis
large surface area;
thin (leaf);
upper epidermis / cuticle;
transparent / lets light through;
chloroplasts / chlorophyll;
palisade (mesophyll);
close to surface;
absorb light;
spongy (mesophyll);
diffusion;
stomata / guard cells;
carbon dioxide;
xylem;
water; ignore if transpired
Explain how the rate of photosynthesis is affected by changes to abiotic factors throughout the day
Two from:
1. temperature
2. light (intensity)
3. carbon dioxide /
CO2;;
Then:
4. indication of level of
abiotic factor during the day;
5. stated effect on rate of photosynthesis;
Explain how very high temperatures might reduce the growth of plants
1. less photosynthesis;
2. (more) transpiration /
evaporation /loss of water / eq;
3. wilting / loss of turgor /
stomata close /
less mineral ion transport;
4. less carbon dioxide uptake;
5. enzymes denature /
change in shape of active site / eq;name
Name the two parts of a plant cell where most water is found
Cytoplasm
Vacuole
What are nitrate ions used for in plants?
Amino acids
Growth
DNA bases
Chlorophyll
Describe and explain how the structure of the small intestine is adapted for absorbing digested food
long;
2. villi / villus / microvilli;
3. increase surface area / eq;
4. diffusion / active transport / osmosis;
5. capillaries;
6. (blood flow) maintains concentration gradient /
maintains diffusion gradient;
7. thin walls / one cell thick / short distance;
(applies to villi or capillaries)
8. lacteal(s);
Suggest the consequences of having a diet that contains too much fat
Obesity
Blockage of arteries
High blood pressure
Diabetes
Joint damage / arthritis
Gall stones
Suggest the consequences of having a diet that lacks fresh fruit and fibre
lack vitamin C / antioxidant / scurvy /
bleeding gums / eq;
2. constipation / less food movement /
bowel cancer / raised cholesterol /
increase heart disease / eq;
What is meant by the term transpiration
Evaporation of water
At surface of plant
Describe how the structure of a leaf is adapted to absorb carbon dioxide
Large surface area
Thin
Moist
Spongy mesophyll
Stomata
Describe how the bottles can be sterilised
Steam / radiation / high temperature / disinfectant / ethanol / washed in hot water
Explain why breathing rate is higher after exercise
Oxygen is required
For respiration
To provide energy to muscles
And to remove lactic acid
An oxygen debt builds up
And carbon dioxide needs to be removed
Describe how smoking damages the lungs
1. bronchitis;
2. cilia(ted cells) anaesthetised / damaged / eq;
3. bacteria / pathogens / microorganisms;
4. cancer / carcinogens / tumour;
5. tar;
6. emphysema;
7. less surface area / less gas exchange / less diffusion / eq;
8. idea that alveoli digested / damaged / fused /
Suggest how carbon monoxide will increase the risk of producing a smaller baby
1. red blood cells;
2. (oxy)haemoglobin / carboxyhaemoglobin;
3. less oxygen;
4. (less) respiration / metabolism / energy / ATP;
Describe how the structure of a fish differs from that of a human heart
Fewer chambers
Fewer valves
No septum
Chamber walls have similar size
Fewer blood vessels
Explain the differences in the concentrations of gases (fish heart and human heart leaving aorta)
1. less oxygen/deoxygenated in fish heart;
2. more carbon dioxide in fish heart;
3. oxygen used in respiration;
4. carbon dioxide produced by respiration;;
5. blood oxygenated in human lungs;
6. carbon dioxide removed in human lungs;
Explain why the pressure of the blood returning to the fish heart is lower than the pressure of blood returning to the human heart
1. single circulation /
no separate lung circulation /
blood passes through heart once /
blood in fish has to pass through two sets of
capillaries / eq;
2. fish are smaller / fish have smaller heart /
fish heart has thinner walls;
Explain how having more red blood cells is an advantage to athletes who take part in long distance races
more oxygen;
haemoglobin;
muscles;
respiration;
(less) anaerobic respiration;
(less) lactic acid / (less) oxygen debt /(less)
fatigue / (less) cramp;
more energy;
run faster / run longer / run further / less tired /
eq;