Microbiology Mastering Ch. 24
1/126
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Tori, a 24-year-old graduate student, had been suffering from a respiratory infection for over a week. She went to the student health center, where the physician prescribed her a broad-spectrum antibiotic. By the end of her round of antibiotics, Tori was no longer suffering from respiratory complications, but she had noticed an increase in itchiness in her genital region. Within a few days, the itchiness was getting worse and was accompanied by a vaginal discharge that had a cheesy consistency and foul odor. Tori returned to the student health center to discuss her condition with the physician. A sample of her discharge was taken and sent to the laboratory for microscopy and plating.
Part A: Based on the lab results, which organism is most likely causing Tori’s new symptoms?
Trichomonas vaginalis |
Candida albicans |
Gardnerella vaginalis |
Sporothrix schenckii |
Candida albicans
*Diagnosis of a yeast infection usually involves patient history, observation of yeast cells via microscopy, and growth of a culture on Sabouraud dextrose agar. Differentiation between yeasts and bacteria is reliant on biochemical characteristics. Differentiation between yeasts and molds is reliant on spore type and function.
Part B: Which of the following best explains why Tori developed a new series of symptoms?
The antibiotics that treated Tori’s primary respiratory infection also removed some of her normal bacterial flora, resulting in an overgrowth of other organisms. |
Tori contracted a sexually transmitted infection that was not related to the primary respiratory infection. |
Tori’s immune system was compromised because of her respiratory infection, and this resulted in a yeast infection. |
The initial antibiotics were not successful in clearing the respiratory infection, so the organism disseminated to the genitourinary tract. |
The antibiotics that treated Tori’s primary respiratory infection also removed some of her normal bacterial flora, resulting in an overgrowth of other organisms.
*Tori had undergone treatment with a broad-spectrum antibiotic for her respiratory infection. Antibiotic treatment most likely affected the normal flora in the vagina, resulting in a preferential decrease in bacterial numbers. Yeasts are normal flora in the vagina, but with fewer bacteria present to antagonize their growth, the yeast cells were allowed to flourish beyond their normal levels. The increased numbers of yeast cells led to Tori’s new symptoms. She had developed a yeast infection as a secondary infection to her primary respiratory infection. A secondary infection is defined as an infection caused by an opportunistic microbe after a primary infection has weakened the host’s defenses. Yeast infections are common secondary infections after antibiotic treatment for a primary bacterial infection.
Part C: Which of the following could Tori’s physician choose as a treatment for her yeast infection?
an antiviral medication, such as acyclovir |
an oral narrow-spectrum antibiotic, such as penicillin G |
a topical over-the-counter ointment, such as clotrimazole or miconazole |
a single oral dose of fluconazole |
-a topical over-the-counter ointment, such as clotrimazole or miconazole
-a single oral dose of fluconazole
*Treatment of a yeast infection includes the application of topical ointments and the use of oral antifungal agents. Nonprescription antifungal creams are among the most commonly purchased over-the-counter medications in the United States.
Part D: Which of the following infections are also caused by C. albicans?
genital warts |
fulminating disease |
syphilis |
oral thrush |
-fulminating disease
-oral thrush
*Candida albicans is also the causative agent of oral thrush and fulminating disease. Infants are prone to thrush because they come in contact with the yeast as part of mom’s normal flora when nursing. Fulminating disease, which most often afflicts immunosuppressed individuals, results when the yeast enters the bloodstream and travels throughout the entire body, resulting in a systemic infection. Individuals suffering from AIDS are susceptible to this type of infection.
Part E: Which of the following statements best describes why the treatment for Tori’s fungal infection may result in side effects to her own cells?
Fungal cells and human host cells both have cell walls made of cellulose. |
Fungal cells and human host cells both have flagella for movement. |
Fungal cells and human cells both reproduce via budding. |
Fungal cells and human cells have a nucleus, multiple organelles, and 80S ribosomes for protein synthesis. |
Fungal cells and human cells have a nucleus, multiple organelles, and 80S ribosomes for protein synthesis.
*One of the key similarities between a fungus and its human host is that both are eukaryotic. This makes it difficult to develop antifungal drugs, because therapeutic agents that target certain properties of the fungus (e.g., ergosterol in the membrane, DNA replication, protein synthesis) also have the potential to target the host cells. One of the keys to antimicrobial therapy is selective toxicity, which means that the agent will hinder/kill the pathogen without doing much damage to the host. The more similar the agent is to its host, the harder it is to achieve selective toxicity.
Part F:
Blastoconidia and chlamydoconidia are male and female mating structures used for reproduction in yeasts, whereas bacterial endospores are asexual reproductive structures. |
Blastoconidia and chlamydoconidia are produced only by yeasts in extreme conditions, whereas bacterial endospores are asexual reproductive structures. |
Blastoconidia and chlamydoconidia are spore structures produced by budding in yeasts, whereas bacterial endospores are produced by bacteria under extreme conditions. |
Blastoconidida and chlamydoconidia are identical to endospores. |
Blastoconidia and chlamydoconidia are spore structures produced by budding in yeasts, whereas bacterial endospores are produced by bacteria under extreme conditions.
*Blastoconidia and chlamydoconidia are asexual spores used for reproduction. Blastoconidia and chlamydoconidia produce cells that are identical to the parent cells, whereas sexual spores produce offspring that have characteristics of both parents. Endospores are produced by bacteria during harsh conditions.
Part G: How do pseudohyphae in yeasts differ from vegetative hyphae in filamentous fungi?
Yeasts use pseudohyphae for obtaining nutrients, whereas filamentous fungi use their vegetative hyphae to invade host tissues. |
Yeasts use pseudohyphae to invade host tissue, whereas filamentous fungi use their vegetative hyphae for obtaining nutrients. |
Yeasts use pseudohyphae as a means of sexual reproduction, whereas parasitic fungi use their hyphae to invade host tissue. |
Yeasts use pseudohyphae as a means of obtaining nutrients, whereas filamentous fungi use vegetative hyphae as a means of reproduction. |
Yeasts use pseudohyphae to invade host tissue, whereas filamentous fungi use their vegetative hyphae for obtaining nutrients.
*Yeasts use the pseudohyphae as a virulence factor to better penetrate the host’s tissues and also to evade phagocytosis. Filamentous fungi use their vegetative hyphae as a means to absorb nutrients from their environment. In optimal conditions, the vegetative hyphae will grow into a substrate to obtain food and will then support the growth of aerial hyphae, which project above the surface of the medium. These aerial hyphae are responsible for producing the reproductive spores of the fungus.
Part A: In which part of the body would candidiasis present as curd-like?
vagina |
folds of skin |
toe nails |
in the mouth |
vagina
*The vagina will present with a curd-like discharge.
Part B: What percent of people harbor Candida naturally in their body without showing any signs or symptoms?
less than 1% |
40-80% |
100% |
5-10% |
40-80%
*More than half of the population has Candida living within their body cavities asymptomatically.
Part C: Which structure is characteristic of Candida?
pseudohyphae |
cell wall of chitin |
filamentous hyphae |
yeast buds |
pseudohyphae
*The formation of pseudohyphae from clusters of budding yeasts is indicative of Candida.
Part D: In which population might we observe a higher incidence of thrush?
pregnant women |
the elderly |
the sexually active |
college-age students |
the elderly
*As we age, our immune system usually becomes less effective and leaves us prone to opportunistic infections such as candidiasis.
Part E: Which of the following habits might best prevent infection with Candida?
Change wet diapers often. |
Use condoms during sexual intercourse. |
Take vitamin C supplements. |
Irrigation of the vaginal cavity daily with a douching agent. |
Change wet diapers often.
*Wet clothing next to the body for prolonged periods will aid in the growth of Candida
Part F: hich of the following medications is typically used for superficial candidiasis in AIDS patients?
acyclovir |
amphotericin B |
fluconazole |
ampicillin |
fluconazole
*Fluconazole is an antifungal used to treat AIDS patients in which topical antifungals are not successful.
Part A: Which condition is associated with bacterial infection of the bladder?
urethritis |
bacteremia |
cystitis |
pyelonephritis |
cystitis
*A cyst describes a hollow organ filled with fluid, as is the bladder.
Part B: Some strains of E. coli have __________ allowing them to bind and then enter into epithelial cells of the urethra.
cilia |
fimbriae |
flagella |
gram-negative cell wall |
fimbriae
*The fimbriae allow for attachment and entry into host cells.
Part C: What is the primary source of infection for UTIs?
Fecal contamination |
Dehydration |
Contaminated drinking water |
Sexual intercourse |
Fecal contamination
*E. coli is the primary cause of UTIs and is commonly found in feces.
Part D: Which demographic is most likely to develop a urinary tract infection?
Dehydrated persons |
Diabetics |
Men with enlarged prostates |
Females |
females
*Women and girls are more prone to a urinary tract infection due to the close proximity of the source of infection and the portal of entry.
Part E: What might a clinician expect to observe in the urinalysis of a patient with a UTI?
Leukocytes |
Dark urine |
Epithelial cells |
Crystals |
Leukocytes
*Leukocytes are a clear indication that an infection is present in the urinary system.
Part F: Which of the following measures would be most effective in preventing a UTI?
The use of a catheter |
Daily use of topical antifungals |
Drink cranberry juice |
Wiping front to back after defecation |
Wiping front to back after defecation
*Wiping front to back will prevent the introduction of E. coli to the urethra.
A Very Sick Man A 25-year-old homosexual man was admitted to the hospital with oral candidiasis (thrush), diarrhea, unexplained weight loss, herpes lesions, and pneumonia. Cultures of pulmonary fluid revealed the presence of Pneumocystis jirovecii. The man admitted to frequently paying for sex.
Part A: Given the man’s symptoms and described history, what diagnosis could be made?
Chances are this patient is suffering due to the diarrhea and weight loss, which have led to a state of immunosuppression allowing the other infections to set in. |
The oral thrush and diarrhea have led to the patient being immunocompromised and allowed for the additional infections. |
Chances are this patient is HIV positive and is now severely immunocompromised due to AIDS. |
Immunosuppression has allowed for multiple infections, all of which may be explained by the patient’s sexual activity. |
Chances are this patient is HIV positive and is now severely immunocompromised due to AIDS.
*The symptoms and number of concurrent infections lead to the conclusion that this patient has developed AIDS.
Part B: According to the patient’s history, how did this man most likely acquire the infection?
by ingestion of contaminated food or water |
through unprotected sex with a prostitute |
by exposure to someone with pneumonia |
It is impossible to tell. |
through unprotected sex with a prostitute
*The patient’s history of paying for sex with male prostitutes means that if he has had unprotected sex his chances of acquiring HIV are statistically higher than those of any other groups.
Part C: If this man is HIV positive, what changes to the man’s immune system allowed the opportunistic infections of Candida (thrush) and Pneumocystis (pneumonia) to arise?
The virus has lowered his blood monocyte count to the point that his immune system is compromised. |
The virus has lowered his CD8 T cell count to the point that his immune system is compromised. |
The virus has lowered his CD4 T cell count to the point that his immune system is compromised. |
The virus has lowered his T cell count to the point that his immune system is compromised. |
The virus has lowered his CD4 T cell count to the point that his immune system is compromised.
*The lowering of the CD4 T cells to or below a count of 200 is the threshold for AIDS.
Part D: What laboratory tests should be performed to confirm the patient’s status and current diagnosis in this case?
A CD4 T cell count to determine AIDS status should suffice. |
An antibody test to determine if the patient has seroconverted for HIV and a PCR test should be performed to determine the type of herpesvirus that is infecting the patient. |
A serum antibody test to determine if the patient has seroconverted for HIV and a CD4 T cell count to determine AIDS status should be performed. |
An antibody test to determine if the patient has seroconverted for HIV should suffice. |
A serum antibody test to determine if the patient has seroconverted for HIV and a CD4 T cell count to determine AIDS status should be performed.
*Determining HIV status will help in determining the cause of immunosuppression since there are other diseases and cancers that may suppress the immune system.
Part E: What treatments should be prescribed for this patient?
antimicrobial medications for the opportunistic infections and antiretroviral therapy to try to control the HIV infection |
supportive therapies to minimize any discomfort |
antibiotics for the infections, as well as supportive therapy |
antiretroviral therapy for the HIV infections and allowing the patient’s immune system to clear the opportunistic infections |
antimicrobial medications for the opportunistic infections and antiretroviral therapy to try to control the HIV infection
*Medications should be prescribed to alleviate the opportunistic infections before they overwhelm what is left of the patient’s immune system while also trying to limit the spread of HIV through the remaining T cells by starting the HIV drug cocktail.
A Sick Mother-to-Be Preparing for delivery, an obstetrician notices genital sores and severe swelling of the labia on a pregnant 24-year-old female. Upon questioning the woman, the doctor discovers that she previously had swollen and painful lymph nodes near her groin but did not seek treatment because she assumed it was related to the pregnancy.
Part A: What type of microbe could be causing an infection with just these symptoms?
viral |
protozoan |
bacterial |
fungal |
bacterial
*Some bacterial STDs would fit the symptoms listed as long as they are not associated with a characteristic discharge, which was not seen in this patient.
Part B: What microbial agent would be associated with the symptoms seen in this mother-to-be?
Treponema pallidum |
Haemophilus ducreyi |
human herpesvirus 1 |
Chlamydia trachomatis |
Chlamydia trachomatis
*Infection by Chlamydia trachomatis has a characteristic small lesion that may not be noticed on the labia and it will result in swelling of the draining lymph nodes.
Part C: What risk is there, if any, to the unborn child during passage through the birth canal?
neonatal herpes meningitis |
chancres |
trachoma |
no evident risk |
trachoma
*Trachoma is the infection of the cells lining the eye socket by C. trachomatis that may lead to tissue damage and blindness in the newborn.
Part D: If there is not enough time between determination of an STD in the pregnant mother and time of delivery, after birth the doctor may choose to prophylactically treat the infant for infections. What would the treatment be?
an oral dose of acyclovir |
delivery by caesarian section |
erythromycin cream initially placed in the newborn’s eyes |
surgical correction of eyelid deformities |
erythromycin cream initially placed in the newborn’s eyes
*The cream followed by two weeks of oral erythromycin should limit the chances of an infection in the newborn
Part E: If left untreated in the mother, all of the following may result from the continued STD infection EXCEPT __________.
a scarred conjunctiva |
proctitis |
gummas |
arthritis |
gummas
*Gummas are associated with tertiary syphilis.
A Painful Problem
A 20-year-old male reports to his physician that he has experienced painful urination, as though he were urinating molten metal. He has also noticed a pus-like discharge from his penis.
The man reports having been sexually active with two or three women in the previous six months. Because his partners reported being “absolutely sure” that they carried no sexually transmitted diseases, the patient had not used a condom.
Part A: What disease does this patient have? What is the common name for this disease?
genital herpes; “crabs” |
gonorrhea; “the clap” |
chlamydia; “red eye” |
syphilis; “tabes” |
gonorrhea; “the clap”
*This is the typical history and presentation of a male patient with gonorrhea, commonly known as “the clap”
Part B: How is this disease transmitted?
This disease is most commonly transmitted by unprotected sex. |
This disease is spread through contaminated swimming pool water. |
This disease is spread by aerosol transmission on a windy day. |
This is a disease transmitted by eating contaminated hamburger. |
This disease is most commonly transmitted by unprotected sex.
*infections of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, gonorrhea, are spread by direct person-to-person contact only.
Part C: Based on the recommendations in this textbook, which antibiotic would be the treatment of choice for this disease?
erythromycin |
trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole |
doxycycline |
cephalosporin |
cephalosporin
*Cephalosporin is the antibiotic recommended in this textbook.
Part D: Virulence factors associated with this organism include all of the following, EXCEPT __________.
capsule |
endotoxin |
flagella |
fimbriae |
flagella
*Neisseria gonorrhoeae does not have flagella
Part E: Why did the man’s sexual partners believe they were not infected with a STD?
His partners had been drinking beer and felt they were invincible, but not very coherent. |
Clinical signs and symptoms in females are often not detectable, especially early in the infection. |
Females develop signs of blindness and cataracts. |
The female partners were on birth control pills and thought they were protected against STDs. |
Clinical signs and symptoms in females are often not detectable, especially early in the infection.
*Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), ectopic pregnancy, and infertility occur later in the course of the disease.
What would you expect to happen to the vaginal microbiota of a patient with a defect in estrogen production?
The vagina would become axenic. |
Growth of opportunistic pathogens would increase. |
Growth of normal microbiota would increase. |
Growth of opportunistic pathogens would decrease. |
Growth of opportunistic pathogens would increase.
Which structure connects the kidney to the urinary bladder?
ureter |
loop of Henle |
renal medulla |
urethra |
ureter
How do vaginal microbiota slow/prevent reproduction of Trichomonas vaginalis?
normal microbiota are unable to prevent/slow growth of this organism |
production of a biofilm that prevents attachment |
fermentation of sugars |
production of antibiotics |
fermentation of sugars
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the normal microbiota of the urinary and reproductive systems?
Lactobacilli are primarily responsible for creating the acidic pH in the vagina. |
The male urethra contains more normal microbiota than the female urethra. |
The relative proportions of different species of normal microbiota in the vagina will be different at different times of the menstrual cycle. |
Prepubescent girls are more likely to get vaginal infections than teenagers. |
The male urethra contains more normal microbiota than the female urethra.
Part A: What is the term used for microbiota that normally do not cause disease but that might cause disease when the balance of microbiota is disrupted by use of antimicrobial drugs?
True pathogens |
Opportunistic pathogens |
Transient pathogens |
Commensal pathogens |
opportunistic pathogens
*Opportunistic pathogens do not normally cause disease but can do so when the balance of microbiota is disrupted.
Part B: Which type of antibody produced by a mother can protect her unborn baby?
IgA |
IgD |
IgG |
IgM |
IgG
*IgG antibodies are the only antibodies that can traverse the placenta to protect an unborn baby.
Part C: What structure do spirochetes use for motility?
Fimbriae |
Peritrichous flagella |
Cilia |
Axial filament |
Axial filament
*Spirochetes use their axial filaments for motility.
The sperm is stored in
testes. |
ductus deferens. |
prostate. |
epididymis. |
scrotum. |
epididymis.
The bacterium responsible for maintaining the acidic pH in the reproductive tract is
Bacteroides |
Lactobacillus |
Staphylococcus |
Fusobacterium |
Streptococcus |
Lactobacillus
The normal microbiota of the vagina help maintain a vaginal pH of around 7.5. T / F?
FALSE
Males have a single opening for the urinary and the reproductive tract. T / F?
TRUE
Except the urethra, the rest of the urinary tract is axenic. T / F?
TRUE
The ________ connects the kidney to the bladder.
fallopian tube |
collecting duct |
renal capsule |
urethra |
ureter |
ureter
The normal pH of the vagina is
pH 4.5. |
pH 7. |
pH 6. |
pH 6.5. |
pH 8. |
pH 4.5.
The prostate produces
hormones. |
urine. |
semen. |
sperm. |
antimicrobials. |
semen
Which of the following would you expect to increase the likelihood of cystitis?
being a male |
treatment with long-term antibiotics |
insertion of a urinary catheter |
consuming more than 4 liters of fluid daily |
insertion of a urinary catheter
What makes the pathogenesis of leptospirosis different from that of most other bacterial UTIs?
It does not originate from fecal contamination. |
It has a high mortality. |
It does not cause fever. |
The organism is nonmotile. |
It does not originate from fecal contamination
When certain strains of group A Streptococcus infect an individual, sometimes antibody-antigen complexes accumulate in the kidneys. This disease is called __________.
cystitis |
glomerulonephritis |
leptospirosis |
pyelonephritis |
glomerulonephritis
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of UTIs?
UTIs are more common in men than in women. |
Dysuria is the most common symptom of a UTI. |
The presence of flagella and fimbriae make it easier for bacteria to cause a UTI. |
Enteric bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, are the most common cause of UTIs. |
UTIs are more common in men than in women.
Which of these pathogens CANNOT be transmitted congenitally or from mother to baby during childbirth?
Leptospira interrogans |
Chlamydia trachomatis |
Treponema pallidum |
human herpesvirus 2 |
Leptospira interrogans
What disease is caused by Gardnerella vaginalis?
Urethritis |
Vaginal yeast infections |
Vaginosis |
Toxic shock syndrome |
vaginosis
*C. vaginalis causes vaginosis
Which microbe is the most common cause of urinary tract infections?
Mycoplasma hominis |
Escherichia coli |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
Staphylococcus aureus |
Escherichia coli
*E. coli causes most urinary tract infections.
Why do scientists use an antibody test to reveal the presence of Leptospira interrogans in a sample?
L. interrogans is too small to be visible with a light microscope. |
L. interrogans is secreted only in very small numbers. |
It is hard to see the pink-colored L. interrogans bacteria in a blood sample. |
L. interrogans does not stain well with the Gram stain. |
L. interrogans does not stain well with the Gram stain.
*L. interrogans does not stain well with the Gram stain, which is normally used to detect bacteria in samples.
Why is Leptospira interrogans highly motile?
It has cilia. |
It has two axial filaments. |
It has peritrichous flagella. |
It has a tuft of flagella. |
It has two axial filaments
*The spirochete L. interrogans is highly motile because of its two axial filaments, one at each end.
What is cystitis?
Inflammation of the kidneys |
Inflammation of the prostate |
Inflammation of the urethra |
Inflammation of the bladder |
Inflammation of the bladder
*Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder.
The bacterium, most commonly linked to urinary tract infections is
Staphylococcus |
Proteus |
Pseudomonas |
Klebsiella |
Escherichia coli |
Escherichia coli
Which of the following bacterium is zoonotic, and uses cuts and scrapes on the skin to enter the host, but ends up causing an infection in the kidneys?
Salmonella |
Escherichia coli |
Proteus |
Pseudomonas |
Leptospira interrogans |
Leptospira interrogans
During the spring calving season, a ranch hand begins to run a fever and feel nauseous and achy. After he develops a headache and vomiting, he goes to a clinic. A microscopic exam of a urine sample reveals long thin microbes that move very rapidly in a corkscrewing pattern. The man may have contracted
glomerulonephritis. |
staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome. |
lymphogranuloma venereum. |
trichomoniasis. |
leptospirosis. |
leptospirosis.
Mental confusion is often the only sign of a urinary tract infection in elderly patients. T/F?
TRUE
When bacteria invade the kidney, the result can be
pyelonephritis. |
ectopic. |
bacteriosis. |
prostatitis. |
cystitis. |
pyelonephritis.
The disorder ________ is a complication of systemic infections with Streptococcus in which antigen-antibody complexes form in the blood and get trapped in the kidneys.
pyelonephritis |
glomerulonephritis |
leptospirosis |
urethritis |
cystitis |
glomerulonephritis
Which of the following is commonly the source of leptospirosis?
infected animal feces |
humans infected with leptospirosis |
infected animal urine |
infected animal bites |
infected human urine |
infected animal urine
Which organism causes toxic shock syndrome?
Candida albicans |
Streptococcus pyogenes |
Staphylococcus aureus |
Mycoplasma hominis |
Staphylococcus aureus
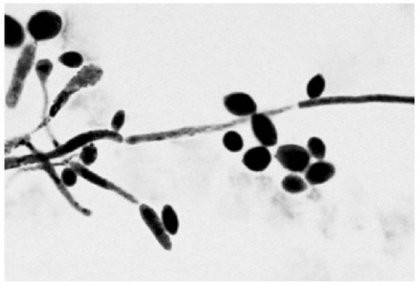
The presence of the specimen shown in the figure in a vaginal discharge is evidence of infection with
Chlamydia trachomatis. |
Candida albicans. |
Treponema palladium. |
Trichomonas vaginalis. |
Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
Candida albicans.
How does TSST-1 exotoxin lead to toxic shock?
It causes red blood cell lysis. |
It kills epithelial cells of mucous membranes. |
It binds to receptors on T cells and activates them. |
It damages the endothelial cells of capillaries. |
It is a pyrogen, causing fever. |
It binds to receptors on T cells and activates them.
The majority of cases of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome are diagnosed in
menstruating women. |
nasal surgery patients. |
anyone with a Staphylococcus aureus infection. |
uncircumcised males. |
newly delivered mothers. |
menstruating women
Presence of clue cells is diagnostic of
urinary tract infection |
gonorrhea |
primary syphilis |
trichomoniasis |
bacterial vaginosis |
bacterial vaginosis
Why does taking antibacterial medications put women at risk for candidiasis?
Antibacterial agents can alter metabolism, creating conditions that favor the growth of Candida albicans. |
Antibacterial agents deplete the normal bacterial microbiota, resulting in a change of pH. |
Antibacterial agents serve as growth stimulants for Candida albicans. |
Bacteria killed by antibacterial agents provide nutrients for Candida albicans. |
Depletion of the bacterial microbiota results in higher carbon dioxide levels (which favor the growth of Candida albicans). |
Antibacterial agents deplete the normal bacterial microbiota, resulting in a change of pH.
Which of the following statements is CORRECT regarding the incidence of STDs?
Bacterial STDs are declining worldwide as a result of the ready availability of antibiotics. |
Viral STDs in the U.S. are considered epidemic. |
The incidence of most STDs could be reduced by vaccination. |
The incidence of STDs is known with a high degree of accuracy. |
Viruses transmitted by sexual contact are not widespread. |
Viral STDs in the U.S. are considered epidemic.
A Case of Genital Sores A 20-year-old sexually active college student reports to his campus clinic complaining of genital sores. The ulcers are soft, painful, and pus-filled. Upon questioning, the student reveals his current girlfriend is an Asian exchange student. The campus lab initially has difficulty identifying the causative agent, but finally is able to isolate a Gram-negative coccobacillus on blood agar.
Part A: What disease has this patient contracted?
syphilis |
chancroids |
chlamydia |
gonorrhea |
chancroids
*Chancroids are soft, painful genital ulcers. The base of a soft chancre is yellowish gray in color and bleeds easily when scraped.
Part B: What is the causative agent for this sexually transmitted disease?
Chlamydia trachomatis |
human herpesviruses |
Haemophilus ducreyi |
Treponema pallidum |
Haemophilus ducreyi
*Haemophilus ducreyi is a small, Gram-negative coccobacillus bacterium requiring heme and NAD+, which can be derived from blood, for growth.
Part C: How is this disease transmitted?
via an insect bite at site of the open sore |
by ingestion of bacterially contaminated food |
by contact with objects that are contaminated with semen or vaginal secretions |
by direct contact with an open sore during sexual activity |
by direct contact with an open sore during sexual activity
*H. ducreyi is an obligate parasite that colonizes humans, and it would require direct contact such as sexual activity for transmission.
Part D: In what areas of the world is this infection most prevalent?
South America |
Russia |
Europe |
Africa and Asia |
Africa and Asia
*H. ducreyi is prevalent in Africa and Asia.
Part E: What would be the best treatment options?
cauterization |
metronidazole |
acyclovir |
erythromycin |
erythromycin
*Effective antimicrobial drugs are azithromycin, erythromycin, ceftriaxone, and ciprofloxacin.
If a person who is experiencing a genital chancre tests positive on a MHA-TP test, they should be treated with __________.
acylovir |
penicillin G |
metronidazole |
symptom relievers only until the disease runs its course |
penicillin G
Which of the following is NOT true of syphilis?
The bacterium that causes syphilis cannot survive for a long time on surfaces outside the host. |
Some infected individuals experience only the primary stage of the disease. |
Syphilis is diagnosed by observing distinct colonies growing on blood agar plates. |
A rash is a typical sign of secondary syphilis. |
Syphilis is diagnosed by observing distinct colonies growing on blood agar plates.
What would be the effect of a mutation that inactivates Neisseria gonorrhoeae's genes for fimbriae?
increased ability to infect |
antibiotic resistance |
decreased ability to infect |
increased immune recognition |
decreased ability to infect
What is the most common sexually transmitted bacterium?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
Treponema pallidum |
Staphylococcus aureus |
Chlamydia trachomatis |
Chlamydia trachomatis
A college student visits his physician, complaining of painful urination and a pus-filled discharge from his penis. Examination of that discharge reveals Gram-negative diplococci. What is the likely diagnosis?
gonorrhea |
syphilis |
genital warts |
trichomoniasis |
gonorrhea
Part A: A patient has syphilitic gummas; which stage of syphilis does she have?
latent |
tertiary |
secondary |
primary |
tertiary
*Gummas form as a result of severe inflammation during tertiary syphilis, which can last for years.
Part B: Transmission of the causative agent of syphilis across the placenta often causes birth defects, such as mental retardation and organ malformation, if the woman is in which phase?
primary |
tertiary |
secondary |
latent |
latent
*If transmission occurs while the mother is in latent phase, birth defects often occur.
Part C: Researchers culture Treponema pallidum in
carbohydrate broth tubes. |
blood agar. |
tryptic soy agar. |
cell cultures. |
cell cultures
*Scientists have been able to culture T. pallidum only in cell cultures.
Part D: A patient is diagnosed with primary syphilis, he likely has
latent syphilis. |
sore throat, headache, mild fever, malaise, and a widespread rash. |
gummas. |
a chancre. |
a chancre.
Why are special stains or phase contrast microscopy necessary to observe Treponema pallidum?
T. pallidum is a mycoplasma and thus too small to be seen with a regular light microscope. |
T. pallidum does not take up crystal violet or safranin. |
T. pallidum is too thin to be visible with regular light microscopy. |
T. pallidum is an acid-fast staining bacterium. |
T. pallidum is too thin to be visible with regular light microscopy.
*At 0.1 m in diameter, T. pallidum is too thin to be viewed with a regular light microscope.
Which sexually transmitted pathogen causes lymphogranuloma venereum?
Treponema pallidum |
Candida albicans |
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
Chlamydia trachomatis |
Chlamydia trachomatis
*Chlamydia trachomatis causes lymphogranuloma venereum.
Which life stage of Chlamydia trachomatis attaches to host cells and infects them?
An initial body |
A reticulate body |
An elementary body |
An inclusion body |
An elementary body
*An elementary body attaches to a receptor on the host cell.
If a person has had gonorrhea, what is the best way to prevent the disease from recurring?
Immunization |
Prophylactic (preventive) drugs |
Oral contraceptives |
Abstinence, monogamy, or use of condoms |
Abstinence, monogamy, or use of condoms
*Contracting gonorrhea does not confer long-term specific immunity, so patients can be reinfected; abstinence, monogamy, or using condoms reduces the likelihood of reinfection.
Which phase of syphilis presents with a rash, which may be on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet?
The secondary phase |
The primary phase |
The latent phase |
The tertiary phase |
The secondary phase
*Patients may have a rash during the secondary phase of syphilis.
At what stage of the disease are syphilis patients most contagious?
The latent phase |
The secondary phase |
The tertiary phase |
The primary phase |
The primary phase
*In the early stages of the disease, the spirochetes are more numerous, so patients are most contagious.
Which gonorrhea patients most often lack obvious symptoms?
Men |
The elderly |
Women |
Immunocompromised people |
women
*Among women who are infected, 50% to 80% lack signs or symptoms of gonorrhea.
Which of the following is the most common sexually transmitted pathogen in the United States?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
Human papillomavirus |
Human herpesvirus 2 |
Treponema pallidum |
Human papillomavirus
*Human papillomavirus is the most common sexually transmitted pathogen in the United States.
It is difficult to develop a vaccine against Neisseria gonorrhea due to high variability of its surface antigens. T / F?
TRUE
Chlamydia reproduces in the vesicles within infected cells. T / F?
TRUE
Which of the following contributes to the invasiveness of Treponema pallidum?
fimbriae |
IgA protease |
hyaluronidase |
TSST |
lipooligosaccharide in the cell wall |
hyaluronidase
Which of the following is TRUE about Chlamydia trachomatis?
The bacterium reproduces in the cytoplasm of the infected cells. |
The elementary body is the form of the pathogen that reproduces inside the infected cells. |
The infectious stage is called the reticulate body. |
The bacterium is an intracellular pathogen. |
The bacterium can cross the placenta. |
The bacterium is an intracellular pathogen.
A young adult shows up at a free clinic complaining of painful swellings in the groin. The young woman has a history of occasional casual sex, but denies noticing any genital sores or experiencing painful urination. The young woman is most likely infected with
Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
Treponema pallidum. |
Chlamydia trachomatis. |
Trichomonas vaginalis. |
Mycoplasma hominis. |
Chlamydia trachomatis.