Midterm #2 Babu
1/102
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
composition of a nucleotide
phosphate, sugar, nitrogenous base
Hershey and Chase
DNA is a chemical component for herdity
Watson and Crick
come up with Chargaff base properties
Chargaff Base Pairs Rules
DNA has equal amount of As/Ts and Gs/Cs
Rosalind Franklyn
calculates diffraction patterns.
Expert in areas of constructive and deconstructive diffration patterns
Radioactive interferance
Maurice Wilkisons
Works w Rosalyn Franklin on diffraction patterns. Unable to calculate back to structure of DNA molecule from that.
Direction of DNA reading
top 5’ to 3’
bottom 3’ to 5’
chromosomes
where is most of the DNA in the nucleus stored
genes
functional units of sequences of chromosomes
Explain the General DNA transfer
DNA encodes information. Kept safely in the vault
Small sectional copies are made: RNA
RNA exits to the cytoplasm (rough neighborhood)
RNA translates material to make amino acids (proteins)
Breifly distinguish Transcription and Translation
Transcription changes the nucleic acid language like a dielect of a language (British vs American English)
Translation completley changes the language to make proteins
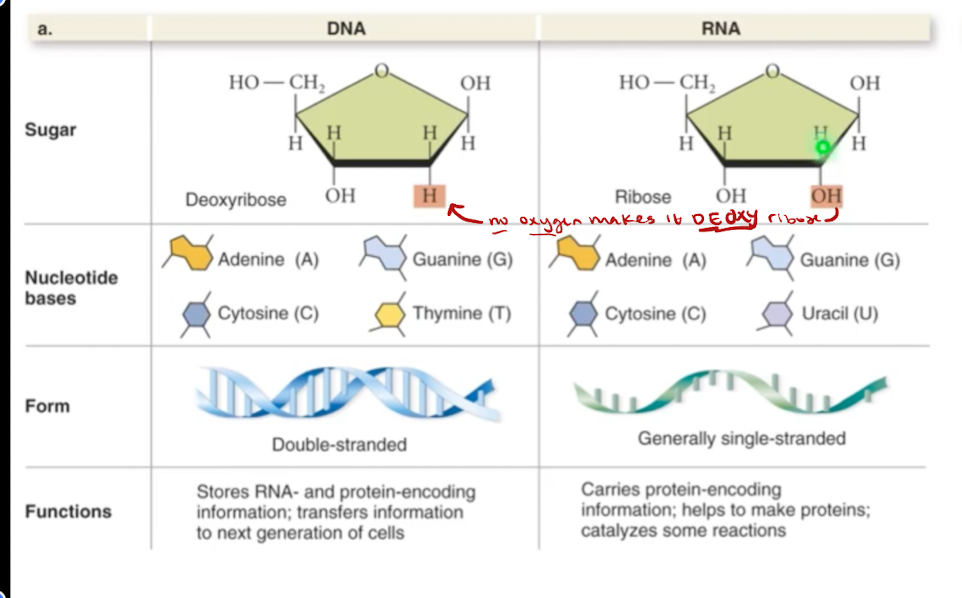
Differences between DNA vs RNA
DNA —> RNA
A → U
C → G
G → C
T → A
RNA → RNA
A→ U
C → C
G → C
U → A
Why would RNA be less stable than DNA?
The extra oxygen it carries increases polarity and therfore its attraction.
Transcription (general)
RNA polymerase(RNA enzyme) makes a copy of one gene from DNA template as hnRNA molecule
3 stages: Initiation, Elongation, Termination
hnRNA
heterogenous Nuclear RNA.
Unprocessed mRNA.
encompasses various types and sizes of RNA
First phase of RNA
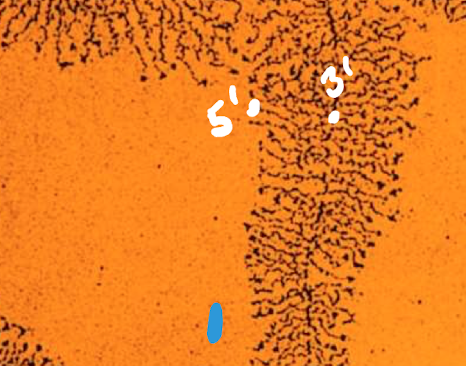
3’ in RNA
The growing end of RNA
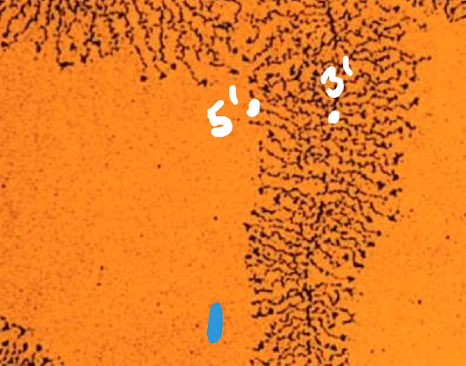
5’ in RNA
The hanging off bit in RNA
What direction are nucleotides made
3’ to 5’
What direction is RNA made from a DNA strand?
Opposite the nucleotide (DNA)
5’ to 3’: RNA would be 3’ to 5’
Bottom DNA 3’ to 5: RNA would be 5’ to 3’
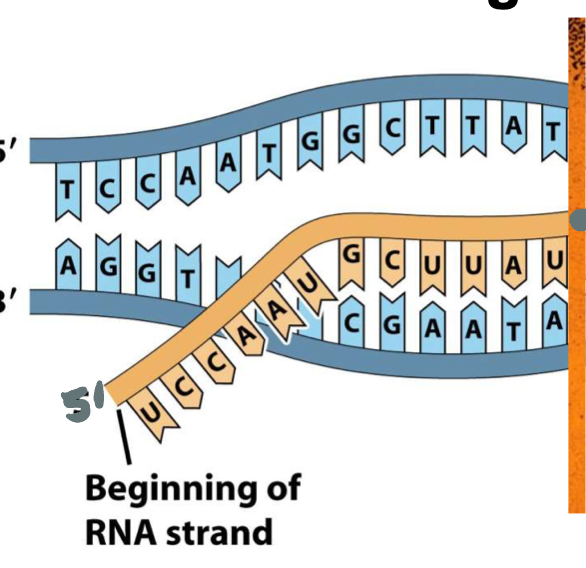
3 stages of transcription
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Initiation (transcription)
Stage 1 of transcription.
RNA polym. binds to promoter and opens DNA helix
RNA synth begins.
Comes and reads the 3’ to 5’ strand.
→Makes 5’ to 3’ RNA
Promoter
Upstream of the gene in DNA. Where RNA bind to initiate transcription of that gene
Elongation (transcription)
Stage 2 of Transcription
DNA threaded through RNA polym. (like a zipper)
RNA strand gets longer, thanks to the addition of new nucleotides.
Termination (transcription)
Stage 3 of Transcription
RNA polym. reaches a bump in terminator region and falls off
Now it is hnRNA
Polycistrone RNA
a mRNA that encodes several proteins and is characteristic of many bacterial and chloroplast mRNAs
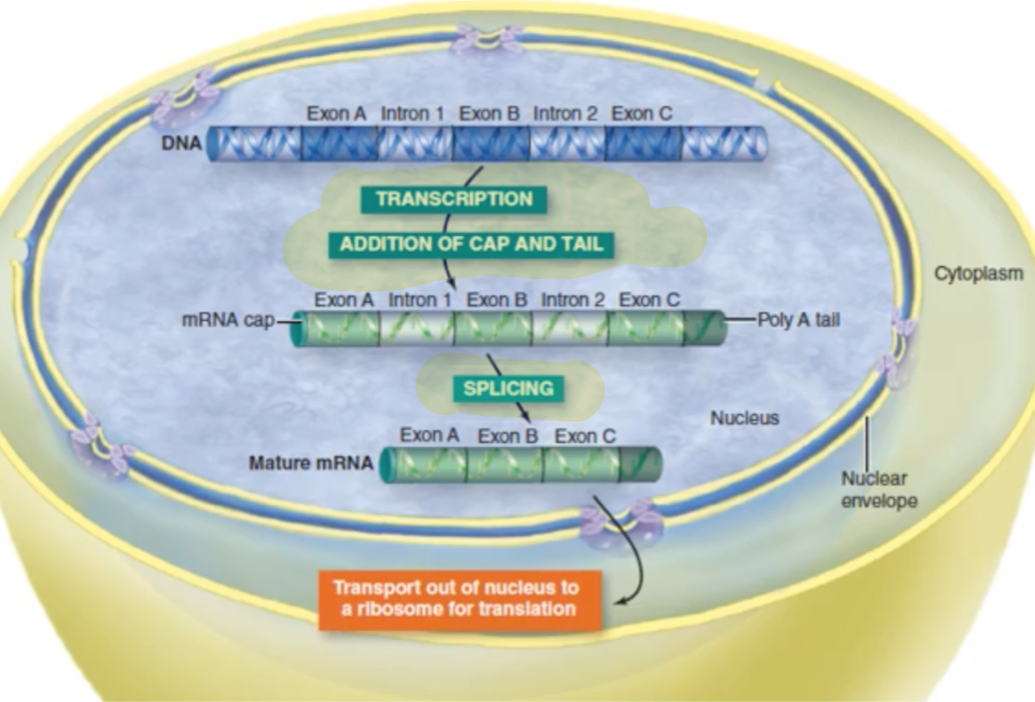
What happens in RNA Processing
After transcription
mRNA created from hnRNA so it can be fully functional (mature)
Caps and tails are added
Introns removed in splicing and exons stitched in
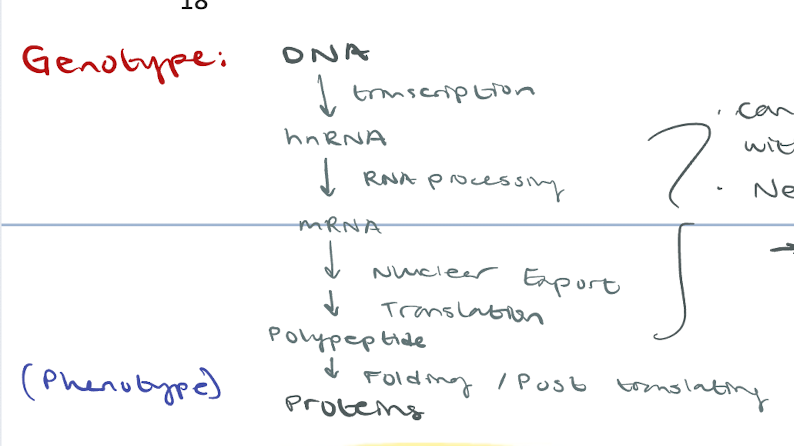
Intron
non coded nucleotide
transcripted but not translated
removed in RNA processing
Vital in genes, non vital in RNA
Exon
Complete info for protein
Stitched in in RNA processing
Splicing: what occurs and when?
Occurs during RNA processing
Introns removed
Exons stitched in
What is the value in RNA processing?
Another level of regulating gene exporting —> increased chance of cell survival
Only in eukaryotic cells
maybe this explains the diverse organisms from eukaryotes
When does RNA leave the nucleus?
After transcription and RNA processing
Translation (general)
RNA going from Nucleic Acid —> Amino Acid (TRANSLATNG the language)
rRNA and tRNA
4 stages:
Initiation
Elongation
Translocation
Termination
mRNA
contains instructions for cells to make proteins
made after rna processing once introns out and exons in
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA: Major Component of ribosomes (organelles that make proteins)
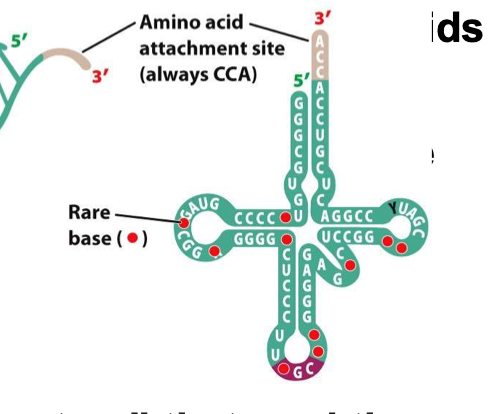
tRNA
Transfer RNA: “interpreters”
Read mRNA code
Insert amino acids to growing proteins
Looks like a 4 leaf clover
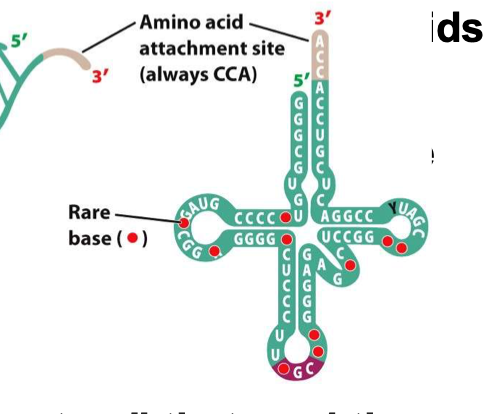
Codons in tRNA
Hydrogen bonds between pairs
64 total. 61 have AA, 3 are stop
4 leaf clover characteristic
Genetic code
64 possible (-3 stop)
Degenerate (code stops mattering as you move down)
start codon
AUG
stop codon
UAA
UAG
UGA
What exactly is being translated in Translation?
Ribosomes export mRNA (nucleus→ cytoplasm) and translate it
Nucleic Acid code in mRNA is translated into amino acids to synthesis polyptides (small part of a protein)
mRNA Nucleic acid language translated by ribosomes to Amino Acid langauge
Initiation (Translation)
Ribosome binds mRNA and tRNA
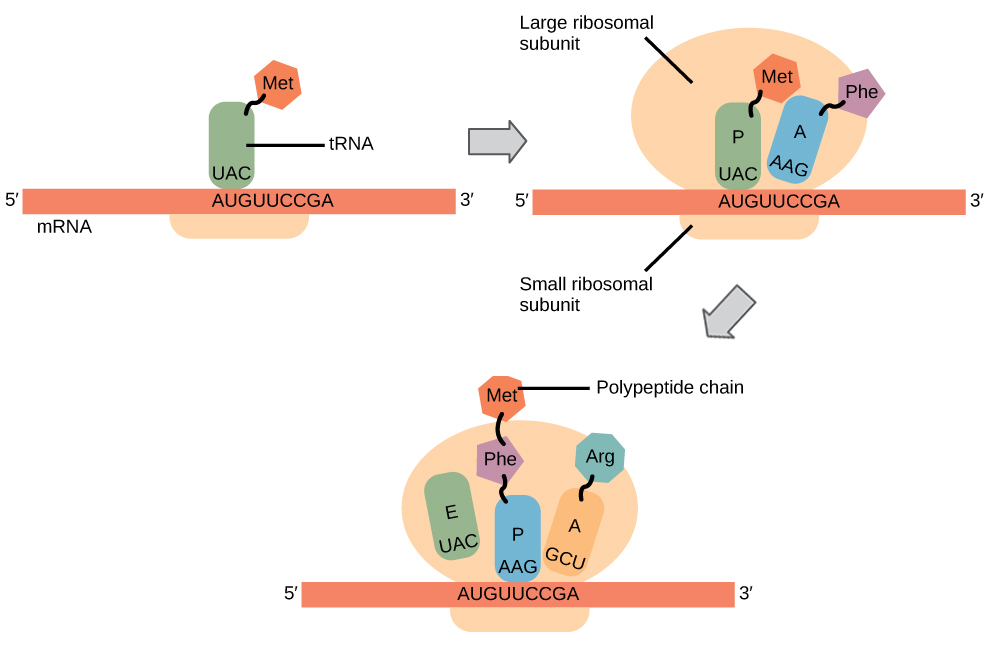
Elongation (translation)
ribosomes catalyze (efficiently form bonds) between AA in A and P site
ribosome continues to translate each codon
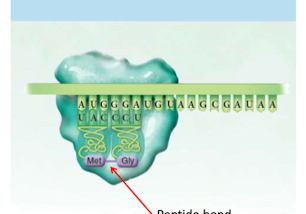
Translocation (Translation)
ribosomes move over one codone and leet other ribosomes in
RNA= freeway
Ribosomes= cars on freeway
Steps 2/3 (Elongation and Translocation) repeated over and over
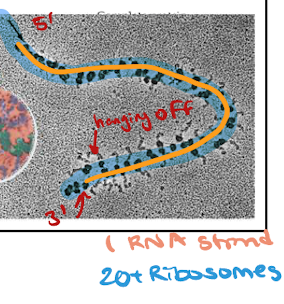
Which steps repeat over and over in translation?
Steps 2/3 (Elongation and Translocation) repeated over and over
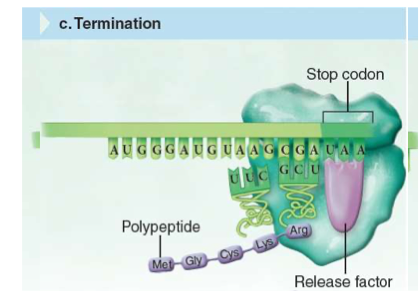
Termination (translation)
Stop codone reached
Release factor binds the ribosomes
Complex falls off
Gene expression and things that affect it
the process by which the information encoded in a gene is turned into a function
DNA availability and nuclear export
Nuclear Export in gene expression
How long RNA stays in cytoplasm affects hoe a gene is expressed.
Short RNAs go quicker and faster (quantity), while long tailed RNAs last for a longer time and make more protein (quality)
Mutation
Change to a DNA
Can alter polypeptide folding causing genetic disorders
alzheimers and cystic fibrosis
Substitution, insertion, deletion
Frameshift Mutation
Change reading frame of DNA through insertion or deletion
Destroys the gene
prion disease
protein refolding disease that has evolved to avoid cell’s defense against them
proteins refold and change 3d shape
either makes a dead or rogue protein
mad cow disease
What requires cell division
growth and development, reproduction
Gamete
A sex cell. One is contributed by each parent in sexual reproduction
Zygote
Fertilized egg cell that results from a male and female gamete
Sexual Reproduction: what part in meiosis and what part in mitosis.
Mieosis: Each parent contributing a gamete (fertillization) to create a zygote
Mitosis: Each cell cloning itself over and over to produce an offspring
Meiosis
Creates a unique gamete
Mitosis
Regenerates/clones cells
Apooptosis
Targets weak or decayed cells for cel death.
Programmed cell death
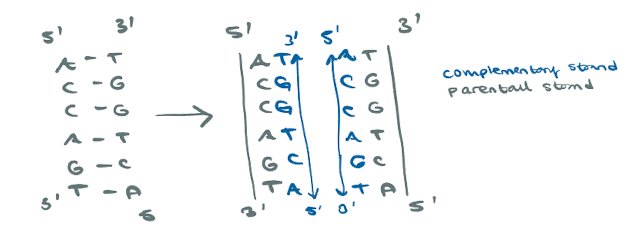
DNA is ________________ replicated, which is:
semi-conservatively:
replication of one parental strand to give its complementary strand, AND the replication of the other parental strand to give its complementary strand
genome
all chromosomes/genes of an organism
Ligase
used in DNA replication to weld DNA shut
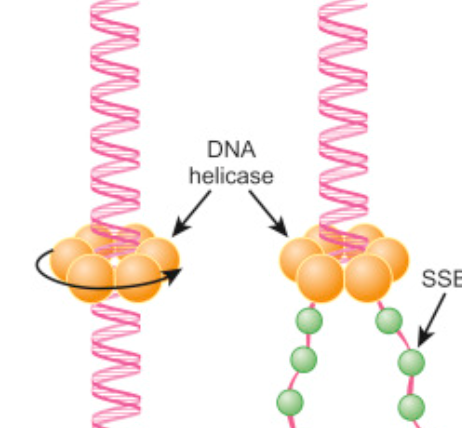
Helicase
Unwinds DNA at origin of replication
DNA polymerase
builds new DNA (5’→3’) off of each template strand
What material checks their work with proofreading?
DNA polymerase
If the polymerase detects that a wrong (incorrectly paired) nucleotide has been added, it will remove and replace the nucleotide right away, before continuing with DNA synthesis .
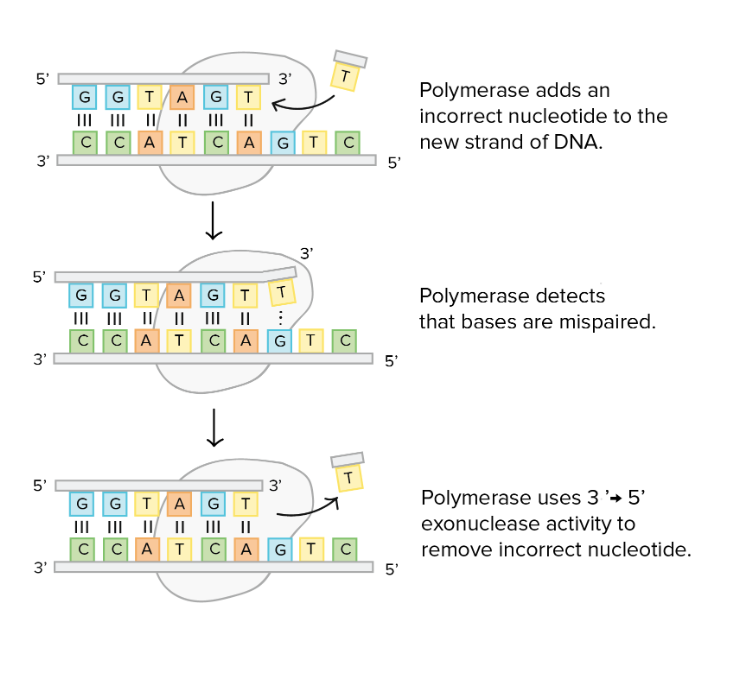
Proof reading
An Error repair mechanism conducted by DNA polymerase
only 1/billion nucleotides is wrong
mutations due occur
worst ones are mutations to proofreading
Error repair mechanisms
DNA repair after DNA replication and proofreading. Any mistake after this is a mutation
Binary Fission and details of the process
the process of asexual reproduction
DNA replication
Separate chromosomes
Move to opposite side of cell and stick to membrane
Cell membrane split into two
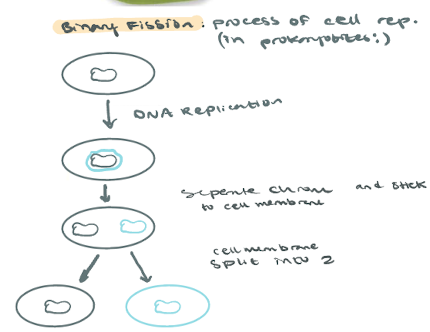
The only reproduction process in prokaryotes
Binary fission (Mitosis)
Supercoiling
The most condense state of DNA
How 6 ft of DNA is packed into each nuclei
Chromatin wound into very tight fibers of nucleosomes
Chromosome
threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus
Chromosome Composition
Chromatin
Chromatin makeup
DNA and histone proteins (binding and shaping agent for DNA)
Eukaryotes require
much more effort for cell reproduction
homogeneous (vs identical)
Very similar but same variation (vs completely the same)
homogeneous pair
same gene , different flavors of same gene
each have the same genes in the same order, but there may be variation between them, resulting in different alleles
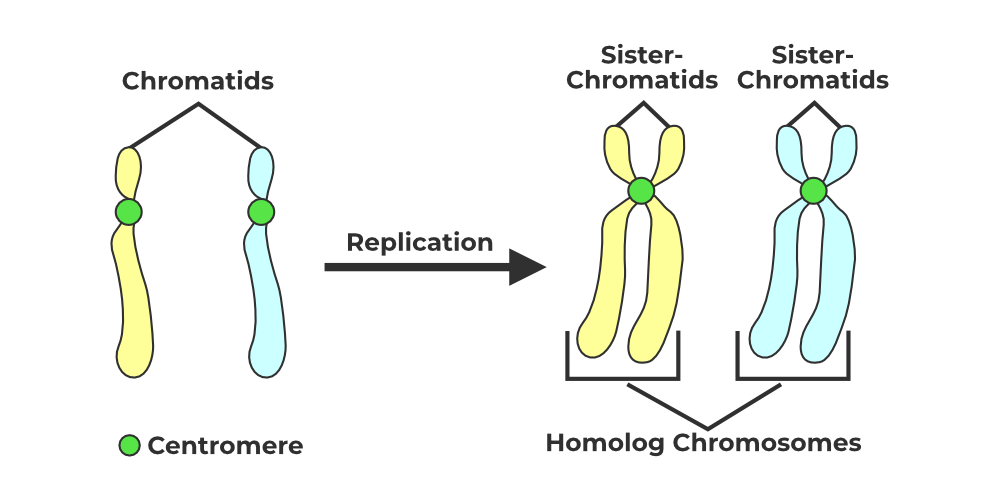
Chromatid
chromosome at most compact state (really just a compact chromosome)
one of the two identical halves of a chromosome that has been replicated in preparation for cell division
sister chromatids
2 chromatid identical copies of a chromosomes that is joined with it’s other chromatid at the centromere
Habloid
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes.

Diploid
The presence of two complete sets of chromosomes in an organism’s cells
Each parent contributes a chromosome to each pair
Know: Cells that rest in G0
Never divide
Know: Longest part of the cell cycle
Interphase
G1
RNA, proteins, and other molecules are made
Gap 1
S
DNA is replicated
Synthesis
G2
Preparing for cell division
T/F: All cells cycle
False, some stay in G1 or permanently in G0 and never divide
Mitosis (simple, as in part of the cell cycle)
division of chromosomes
Cytokinesis
division of cytoplasm; splitting into 2 cells
Stages of the M phase (in cell reproduction)
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Prophase
PROtects the DNA with supercoiling: chroms condense into 2 chromatids
chromosomes move to opp sides of nucleus
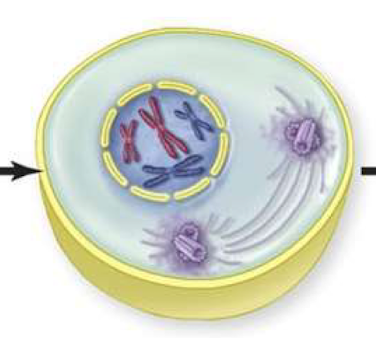
Prometaphase (Late prophase)
nucleus breaks down
spindle fibers attach
Metaphase
chromosomes with spindle fibers attached move to the metaphase plate (midline, spindle equator…)
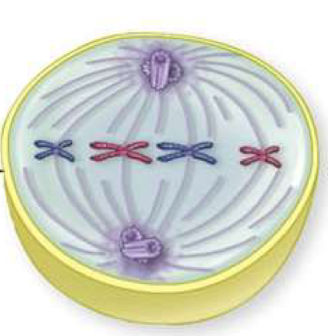
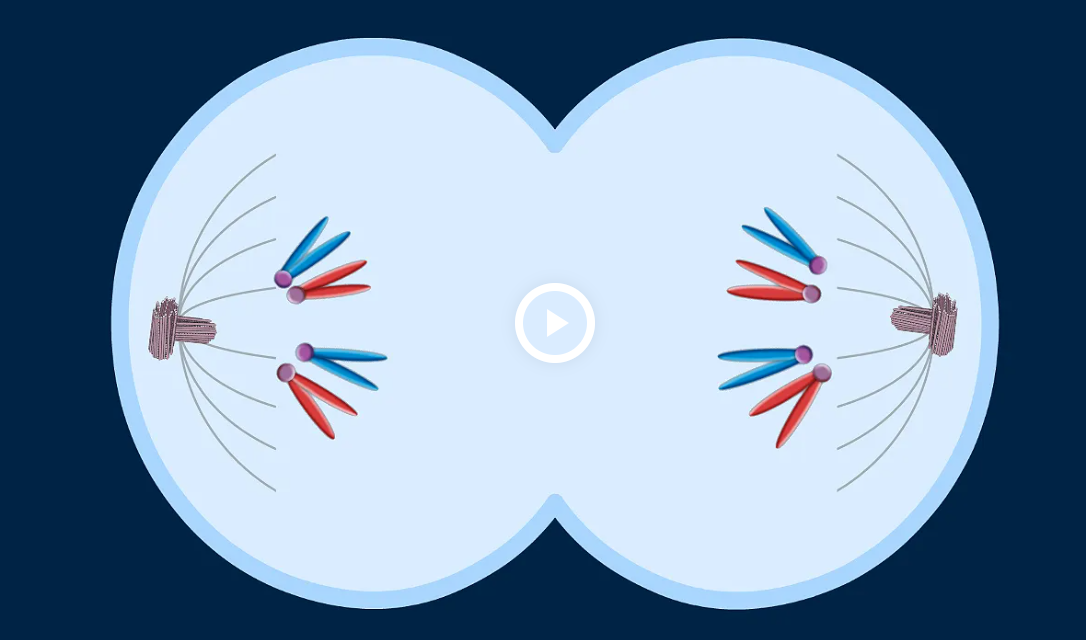
Anaphase
Centromere divide to convert each sister chromatid into a chromosome
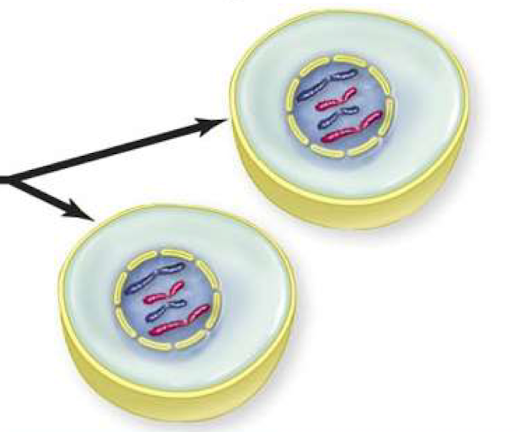
Telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms and DNA decondenses
The cells produced in mitosis are _____, and in mieosis are ______
Diploid (2n)
23 pairs, 46 total
Habloid (n)
each gamete has 0 pairs, 23 total
What happens in fertilization?
Mieosis. Gametes fuse.
each gamete has 0 pairs, 23 total (n)
Together become 23 pairs, 26 total (2n)
What goes down in Mieosis 1
ONE Diploid cell (2n) undergoes replication
Chromosomes not replicated, but split
TWO habloid cells (2xn) are yeilded
½ as many chrom. per cell —> (n)
crossover events occur
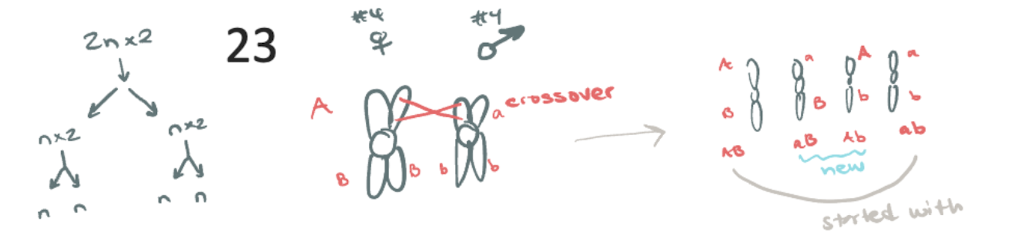
Crossover events also known as
Homologous combination
New genetic material created. These genes affect the same area, but may be different
ex: hair gene crossover yeilds dominate black over recessive blonde
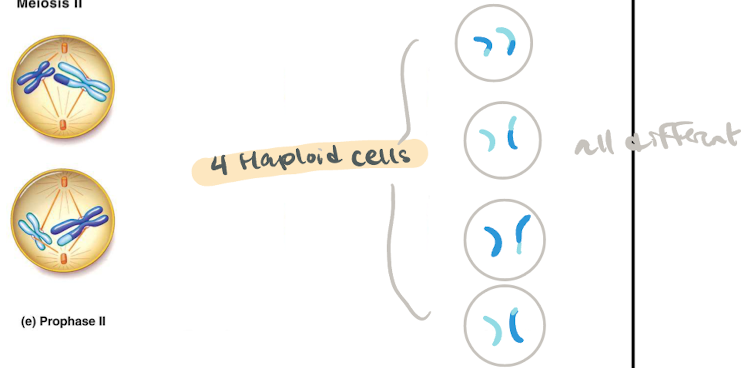
What goes down in Mieosis 2
start with TWO habloid cells (2xn)
produces FOUR habloid cells (4xn)