Media and Information Literacy Exam
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All 3rd Qtr Lessons
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Communication
the act or process of using words, sounds, signs, or behaviors to express or exchange information or to express your ideas, thoughts, feelings, etc., to someone else
the exchange of information and the
expression of feeling that can result in
understanding
Non-Verbal Communication
Basic Type of Communication
Signs
Symbols
Colors
Gestures
body language
facial expressions
Verbal Communication
Basic Type of Communication
Oral
Written
Sender → Medium → Receiver → Message → Feedback
What are the Elements of the Communication Process?
Lasswell’s Transmission model of Communication(1984)
a one-way, linear process in which a sender encodes a message and transmits it through a channel to a receiver who decodes it

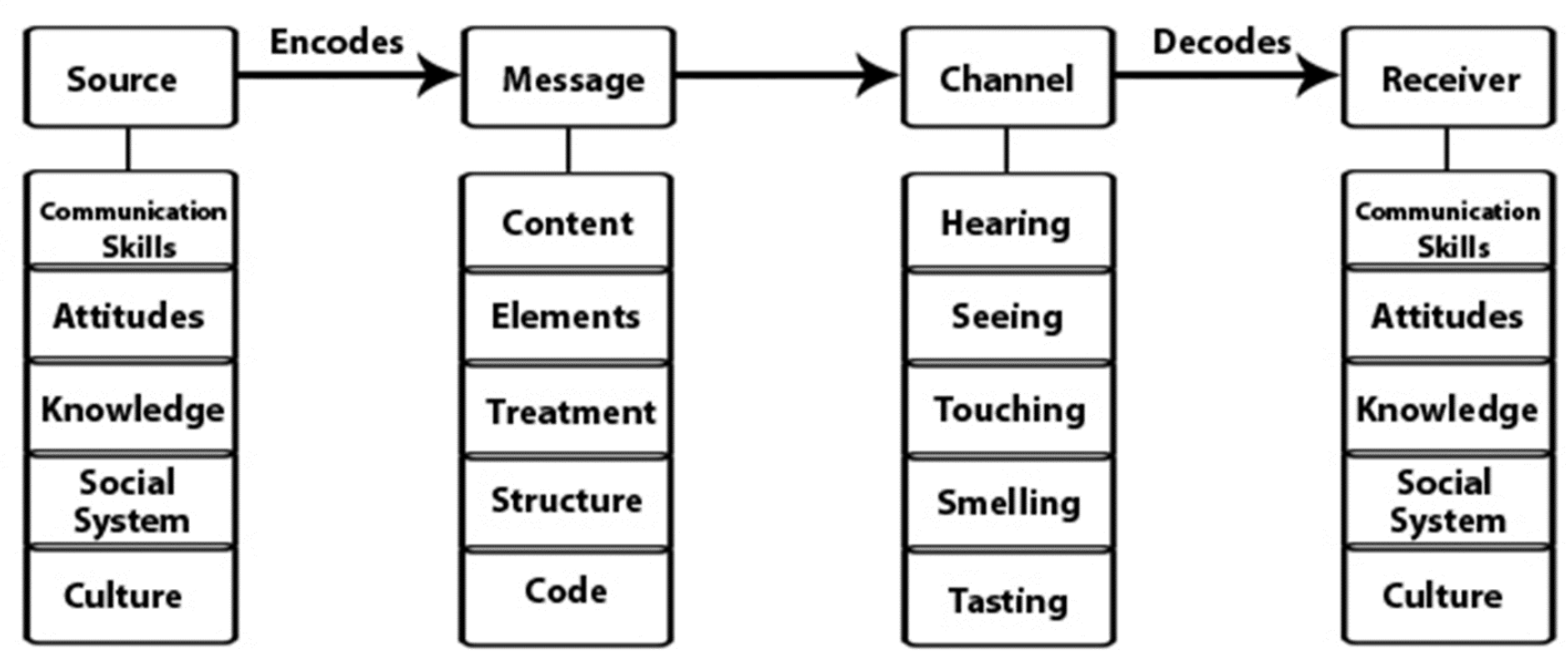
Berlo’s SMCR Model of Communication(1960)
describes the different components that form the basic process of communication.
Because this communication tool also emphasises the coding and decoding of the message, it can be used for more efficient communication.
Literacy
the ability to understand, interpret, create, communicate, and compute, using printed and written materials associated with varying contexts
can also mean that a person is knowledgable or well versed about a specific subject
Accuracy
Criteria for a Reliable Source
verification of the information against the information found
Authority
Criteria for a Reliable Source
trustworthiness of the source (author, institution)
Coverage
Criteria for a Reliable Source
examination of the content and how it fits your information needs
Media
the physical objects used to communicate with, or the mass communication through physical objects such as radio, television, computer, film, and the like.
A broad term encompassing various channels and tools used to communicate, inform, and entertain.
Plays a major role in modern-day society.
Refers to the content itself, the platforms through which it is delivered, or the broader media industry as a whole.
Media Literacy
the ability to access, analyze, evaluate, and create media in a variety of forms.
It aims to empower citizens by providing them with the competencies necessary to engage with traditional and new technologies.
Information
a broad term that covers processed data, knowledge derived from study, experience, instruction, signals, or symbols.
Information Literacy
the ability to recognize when information is needed, and to locate, evaluate, and effectively communicate information in its various forms.
Technology Literacy
the ability of an individual to use technological tools responsibly, appropriately, and effectively.
Using these tools, an individual can access, manage, integrate, evaluate, create, and communicate information.
Media and Information Literacy
the essential skill that allows individuals to engage with media and other information providers effectively.
Develops critical thinking and lifelong learning skills to help us socialize and become active citizens.
Tribal Age
Evolution of Media
During this age, the primary mode of communication is oral communication.
people were required to listen so they wouldn't get left out. Sense of hearing or Auditory sense was the most dominant sense.
Because they did not have a language yet, no alphabet or way of writing, people were forced to stick to their tribes to survive.
Equality of information was practiced at this age. What one member knows should be known by everyone else.
Age of Literacy
Evolution of Media
The Alphabet was introduced to the people. They discovered how to read and to write.
People utilized their sense of sight. Unlike the Tribal age, wherein they mainly used their sense of hearing, this time they used their eyes to recognize symbols, signs and words.
Private communication was developed as well. Since they already knew how to read and write, information can be transferred privately already.
Print Age
Evolution of Media
During this age, the Gutenberg Press, a printing press made by Johannes Gutenberg, was developed. It made the dissemination of information easier as so many more copies of texts reached the masses.
Books, newspapers, and other print media were created with the help of this printing press.
Aside from the printing press, other machineries were also created, and this was the start of the industrial age as well.
Industrial Age(1700s-1930s)
Evolution of Media
People used the power of steam, developed machine tools, established iron production, and the manufacturing of various products(including books through the printing press)
Electronic Age(1930s - 1980s)
Evolution of Media
The invention of the transistor ushered in this age
People harnessed the power of transistors that led to the transistor radio, electronic circuits, and the early computers
In this age, long-distance communication became more efficient
Information Age(1900s to 2000s)
Evolution of Media
At this age, the internet paved the way for faster communication and the creation of the social network
People advanced the use of microelectronics with the invention of personal computers, mobile devices, and wearable technology.
Moreover, voice, image, sound, and data are digitalized
Channel
Roles and Functions of Media in a Democratic Society
provides opportunities for people to communicate, share ideas, speculate, tell stories and give information
Watchdog
Roles and Functions of Media in a Democratic Society
exposes corrupt practices of the government and the private sector.
Creating a space wherein governance is challenged or scrutinized by the governed.
It also guarantees free and fair elections
Resource Center
Roles and Functions of Media in a Democratic Society
Act as a gateway of information for the society’s
consumption.
Also, it becomes a keeper of memories of the community, a preserver of heritage, and source of academic knowledge.
Advocate
Roles and Functions of Media in a Democratic Society
through its diverse sources or formats, it
bridges the gap of digital divide.
Pre-colonial Period
History of Media in the Philippines
During this time, Filipinos disseminated public information through a town crier which they call ‘umalohokan.’ This person shouts the news from one town to another.
Ancient Filipinos had their own system of writing called ‘baybayin and kavi.‘ They wrote their scripts on the leaves using the bark from trees.
Spanish Period
History of Media in the Philippines
Two of the biggest contributions of this period to the Filipinos are Print media and Christianity.
This is why the first ever book published in the Philippines is Doctrina Christiana which is about Christian Doctrines.
There were several firsts during this period, like:
Aviso Al Publico - first Spanish Sheet of Information,
Del Superior Gobierno - first regular newspaper, and
La Esperanza - first daily newspaper.
Diario de Manila - a nationalistic leaflet used by the Katipuneros, who have been in the business for 50 years.
Aside from Print media, Cinema was introduced during this period in 1897.
Petierra, introduced motion pictures to Filipinos and from then it was developed until Antonio Ramos, a soldier, opened a movie house in Manila for the public.
American Period
History of Media in the Philippines
In this period, newspapers published by American journalists were introduced, such as The Manila Times and Manila Daily Bulletin.
During this period, nationalistic newspapers emerged again like The Philippine Herald, which was organized by Manuel L. Quezon. El Nuevo Dia was founded by Sergio Osmena.
The first radio station in the Philippines was introduced during this period as well. It was KZKZ which was run by American Soldier Henry Herman.
Japanese Period
History of Media in the Philippines
Come World War II, the ________ conquerors disbanded all publications in the Philippines except those used by the ________ Government such as Manila Tribune, Taliba, and La Vanguardia.
Despite this, underground papers still made rounds in the country. After the war, the Philippine Press was considered the “freest in Asia."
Martial Law Period
History of Media in the Philippines
During this period, few newspapers operated such as Daily Express, Bulletin Today, and the Times Journal.
The media during this time was fully censored
Post Martial Law Period
History of Media in the Philippines
After Martial Law, censorship was lifted and freedom of expression, speech and the press were reinstituted because of the People Power Revolution.
The Internet was first made available through the help of Benjie Tan at a PLDT network in Makati. Since then, different innovations have been created because of this.
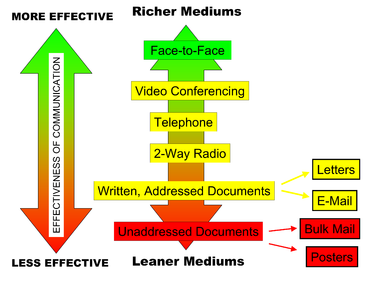
Media Richness Theory/Information Richness Theory
Introduced by Richard Daft and Robert Lengel in 1980s
suggests that different communication channels have different levels of richness, or the ability to convey information effectively
is the amount of social presence the type of
media channel has
ability to handle multiple information cues simultaneously
ability to facilitate rapid feedback
ability to establish a personal feedback
ability to use natural language, and
ability to express emotions
According to the Media Richness Theory, Richness is determined by what five qualities?
Identifying/Recognizing information needs
Determining sources of information
CIting or searching for information
Analyzing and evaluating the quality of information
Organizing, storing or archiving information
Using information in an ethical, efficient and effective way
Creating and communication new knowledge
What are the Stages/Elements of Information Literacy?
Data
refers to unstructured facts and figures that create the least impact on the receiver.
They are just there existing because we do not put a great deal of effort into processing them.
Information
processed data.
Out of all the things that you see, a certain set of details will get your attention and you shall find time to understand it.
These details will be processed, assuming that it is something that you are interested in.
The data then becomes ___________
Knowledge
refers to human understanding, based on experience, learning, and thinking.
When the information you acquire plants a seed in your memory, enabling you to understand it thoroughly, as well as interpret and apply it, then the information becomes _________
Primary Source
Type of Information Sources
an original, uninterpreted, first-hand material of information.
if you are narrating what you have experienced directly.
include artifacts, documents, recordings, autobiographies, personal letters, photos, diaries, and manuscripts.
Secondary Source
Type of Information Sources
provides information obtained from a primary source.
Since the information has been transferred already, this might undergo interpretation and editing based on how it was understood.
References such as books, articles, magazines, and newspapers are considered this kind of source
Tertiary Source
Type of Information Sources
a collection of both primary and secondary sources.
Indigenous Sources
Type of Information Sources
A material is indigenous when it exists naturally in a particular region or environment.
When we refer to someone as indigenous, it connotes that the person belongs to an ethnic tribe that has preserved and still practices the culture and tradition of their ancestors.
General Reference Section
Sections of a Library
This section houses a collection of extensive general reference materials, which are intended to be consulted for a particular question or query, rather than read thoroughly.
Circulation Section
Sections of a Library
This section houses and circulates the major library collection covering the different areas of the discipline.
users can go directly to the shelf and choose the books they would like to browse or use.
All books in this section may be borrowed for overnight use.
Periodical Section
Sections of a Library
This section houses journals, magazines, newspapers, and other serial literature.
professional journals are grouped according to subject.
Current issues are displayed on the display shelves.
Filipiniana Section
Sections of a Library
consists of publications about the Philippines, in all its aspects—cultural, political, social, religious, economic, and others regardless of author and imprints.
The collection covers a range of reading materials designed to meet the instructional and research needs of library users.
The Search Engine
Other sources of information
It is a program capable of searching documents on the web using specific keywords.
It displays a list of websites when keywords are entered in the search field
Internet
Other sources of information
it is our go-to place for information as it is easy to use.
also helps us filter the information we are looking for.
shows the most relevant information and distinguishes what is least relevant.
Indigenous media
Other sources of information
a form of media created, produced, and conceptualized by indigenous people.
They serve as vehicles for communication.
Information coming from them might not be available on the internet and online yet.
“edu“
“gov”
“org“
Useful URL Information
Stands for an educational institution
Represents Government Agencies
Pertains to an organization
Intellectual Property
Ethical Use of Information
Inventions, literary and artistic works, designs and symbols, and names and images used in commerce are governed by IP.
Through the IP, a person is credited as the rightful and original owner of his work.
Copyright
Intellectual Property
protects the owner of his exclusive legal rights for the use and distribution of an original work.
can expire
This is an exclusive right of an IP owner to sell, reproduce, or distribute a material that they created.
is automatically given to an IP owner upon conception of their work.
Trademark
Intellectual Property
If copyright protects literary works, the _________ on the other hand protects identities.
It could be a slogan, logo, or name/brand that identifies a company or organization.
require registration
Once that has been filed and approved, no other party can use it.
Patent
Intellectual Property
awarded by the government to industrial processes and inventions.
It also gives the creator an exclusive right to use, sell, or manufacture IPs.
Citation
Ethical Use of Information
used to inform the readers that certain texts or ideas on his work came from another source.
Public Domain
Ethical Use of Information
Once the duration of the copyright ceases, the work becomes available for ______ ______.
Fair Use
Ethical Use of Information
refers to the limitation and the exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work.
not an infringement of copyright
The purpose and character of the use, including whether such use is commercial or is for non-profit educational purposes;
The nature of the copyrighted work;
The amount and substantiality of the portion used with the copyrighted work as a whole; and
The effect of the use upon the potential market for or value of the copyrighted work
What are the factors to determine fair use?
Plagiarism
Information Deceit
Using someone else's work and ideas,
whether deliberately or not.
by virtue, is tantamount to stealing one's idea.
Fabrication
Information Deceit
it is the production of data or result and reporting them as true and correct.
Example of this is when a researcher answers the survey themselves, instead of looking for respondents to do it for the sake of producing data.
Falsification
Information Deceit
manipulation or modification of data to meet a certain result.
Digital Divide
the gap between digitally adept individuals and non-digitally adept ones.
Flaming
Harassment
Cyberstalking
Denigration
Masquerade
Outing and Trickery
Exclusion
What are the forms of Cyberbullying?
Print Media
Type of Media
oldest form of media
Used for entertainment, advertisements, and
as a source of information.
refers to paper publications such as books, newspapers, magazines, journals, newsletters, and other materials that are physically printed on paper.
Broadcast Media
Type of Media
consists of programs produced by television networks and radio stations.
RADIO, TELEVISION, and FILM are three forms of this media.
New Media(Internet)
Type of Media
digital media that are interactive and incorporate
two-way communication products and services that provide information or entertainment using computers or the internet, and not by traditional methods such as television and newspapers
Examples of this media: Webpage, Hypertext, Instant Messaging, E-mail, Distance Eduction, E-Book, Social Media, Forums, Podcasts
Mass Media
reaches large number of people in short time
Media Effects
intended or unintended consequences of what the mass media does (McQuail, 2010)
Third-party Theory
Media Effects
individuals will perceive media messages to have greater effects on other people than on themselves
Example: seeing an advert for a car, when you're not in the market for a new car
Reciprocal Effect
Media Effects
When a person or event gets media attention, it
influences the way the person acts or the way the
event functions.
Media coverage often increases self-consciousness, which affects our actions.
Boomerang Effect
Media Effects
refers to media-induced change that is counter to the desired change
Cultivation Theory(George Gerbner)
Media Effects
states that media exposure, specifically to television, shapes our social reality by giving us
a distorted view of the amount of violence and risk in the world
Agenda-setting Theory(Lippmann/McCombs and Shaw)
Media Effects
process whereby the mass media determine what we think and worry about public reacts not to actual events but to the pictures in our head, created by media
Propaganda Model of Media Control(Herman & Chomsky)
Media Effects
The model tries to understand how the population is manipulated, and how the social, economic, and political attitudes are fashioned in the minds of people through propaganda.
Propaganda
ideas or statements that are often false or exaggerated and that are spread to help a cause, a political leader, a government, etc.
Activate strong emotions
Simplify information and ideas
Respond to audience needs and values
Attack opponents
What are the 4 propaganda techniques?
Accuracy
Reliability
Authority and Credibility
Purpose and Intended Audience
Currency & Timeliness
Relevance
What are the factors to consider in Evaluating Information?
Genre
comes from the French word meaning 'type' or 'class‘
can be recognized by its common set of distinguishing features (codes and
conventions)
Codes
are systems of signs, which create meaning
Technical Codes
Types of Code
ways in which equipment is used to tell the story
These kinds of code in media include, Camerawork, Editing, Audio and Lighting
Camerawork
Kind of Technical Code
refers to how the camera is operated, positioned and moved for specific effects.
Aspects of this include:
Positioning
Movement
Framing
Exposure
Lens choice
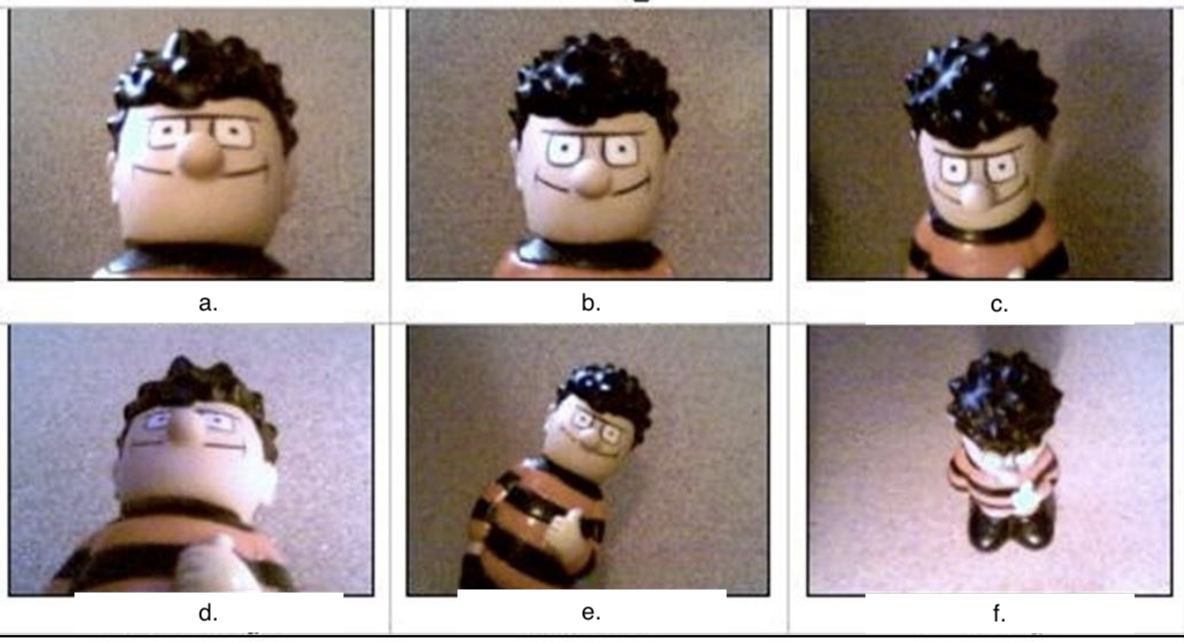
a. Extreme Wide/Long Shot
b. Wide/Long Shots
c. Medium Shot
d. Medium Close-up
e. Close-up
f. Extreme Close-up
Camera Techniques
Give the Basic Camera Shots
a. The subject appears to be far from the camera. Usually used outdoors, often to establish the setting of the following action.
b. Shot in which the subject is seen in its entirety (head to toe), and much of its surroundings are visible.
c. Shot in which the subject and the surroundings are given equal importance. Used to direct the viewer attention to a part of something or to show facial expressions in detail.
d. Subject fills most of the frame, though not as much as in a close-up. Used to direct the viewer's attention to a part of something or to show facial expressions in detail.
e. Used to direct viewers’ attention to texture or a detail or, probably most often, the expressions on a person’s face.
f. If the subject is someone’s face, only part of it is visible.

Two shot
Cut away
Over the Shoulder
Point of View: gives a view like what that creature would see
Selective Focus
Arc Shot
Dutch Angle: the vertical and horizontal lines of the film’s frame is slanted. It used to suggest disorientation
Camera Techniques
Give the Advance Camera Shots
a. Low Angle:
b. Eye-level
c. High Angle
d. Worm’s eye
e. Canted
f. Bird’s eye
Camera Techniques
Give the Camera Shot Angles
a. View of the subject as seen from below eye level. This makes the character look strong, powerful, intimidating, etc.
b. Approximates the angle at which we usually meet and interact with people. Usually used in basic editing and continuation of scenes when there is no need for emphasis.
c. View of the subject from above, created by positioning the camera above the subject. This makes the character look weak and vulnerable.
f. The camera is directly above the subject. This shot is the POV of God. Which may imply that the witness is not related to the scene.

Zoom(in and out)
Camera Techniques
Changing the camera lens’ focal length to give the illusion of moving the camera closer or further from the subject.
Tilt
Camera Techniques
Rotating the camera to the left or right in vertical movement
Pedestal
Camera Techniques
Moving the camera upward or downwards
Pan
Camera Techniques
Rotating the camera to the left or right in horizontal movement.
Track
Camera Techniques
Moving the camera from side to side of a subject.
Editing
Kind of Technical Code
is the process of choosing, manipulating and arranging images and sound.
Is generally done for four different reasons:
Graphic edits
Rhythmic edits
Spacial edits
Temporal edits
Audio
Kind of Technical Code
is the expressive or naturalistic use of sound.
can be diegetic(heard by both audience and characters) or non diegetic(purely for the audience’s benefit)
Three aspects of _____ are:
Dialogue
Sound effects
Music
Lighting
Kind of Technical Code
Is the manipulation of natural or artificial light to selectively highlight specific elements of the scene
Its elements include:
Quality
Direction
Source
Color
Symbolic Codes
Types of Code
show what is beneath the surface of what we see (objects, setting, body language, clothing, color, etc. )
These kinds of codes in media include setting, mise en scene, acting, and colour.
Setting
Kind of Symbolic Codes
the time and place of the narrative
the whole story or just a specific scene
can be as big as the outback or space, or as small as a specific room
can even be created atmosphere or frame of mind
Mise en scene
Kind of Symbolic Codes
‘everything within the frame’
all the objects within a frame of the media product and how they have been arranged
An analysis of ____ ___ includes
Set Design
Costume
Props
Staging and Composition
Acting
Kind of Symbolic Codes
Actors portray characters in media products and contribute to character development, creating tension or advancing the narrative.
The actor portrays a character through:
Facial expression
Body Language
Vocal qualities
Movement
Body contact
Colour
Kind of Symbolic Codes
has highly cultural and strong connotations.
When studying the use of ______ in a
media product the different aspects to
be looking at are:
Dominant ______
Contrasting foils
______ symbolism
Written Code
Types of Code
formal written language used in a media product
can be used to advance a narrative, and communicate information about a character or issues and themes in the media product.
printed language (text within the frame and how it is presented)
spoken language (dialogue and song lyrics)
Conventions
accepted ways of using media codes.
are closely connected to the audience expectations of a media product.
Form Conventions
Type of Conventions
certain ways we expect types of media’s codes to be arranged