Lecture 2 - Osmosis, Tonicity, and Pressures
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is osmosis?
Flow of water across a semipermeable membrane due to differences in solute concentration (membrane blocks movement of solute)
concentration difference of solutes causes difference in _________ _____________, which will cause osmosis
osmotic pressure
true or false: osmosis is NOT simply diffusion of water; it occurs because of a pressure difference!
true
why will the water be pulled over?
the right side has more solute, thus greater osmotic pressure that will pull water over
- permeable to solvent, not permeable to solute (permeable to water (solvent), not solute)
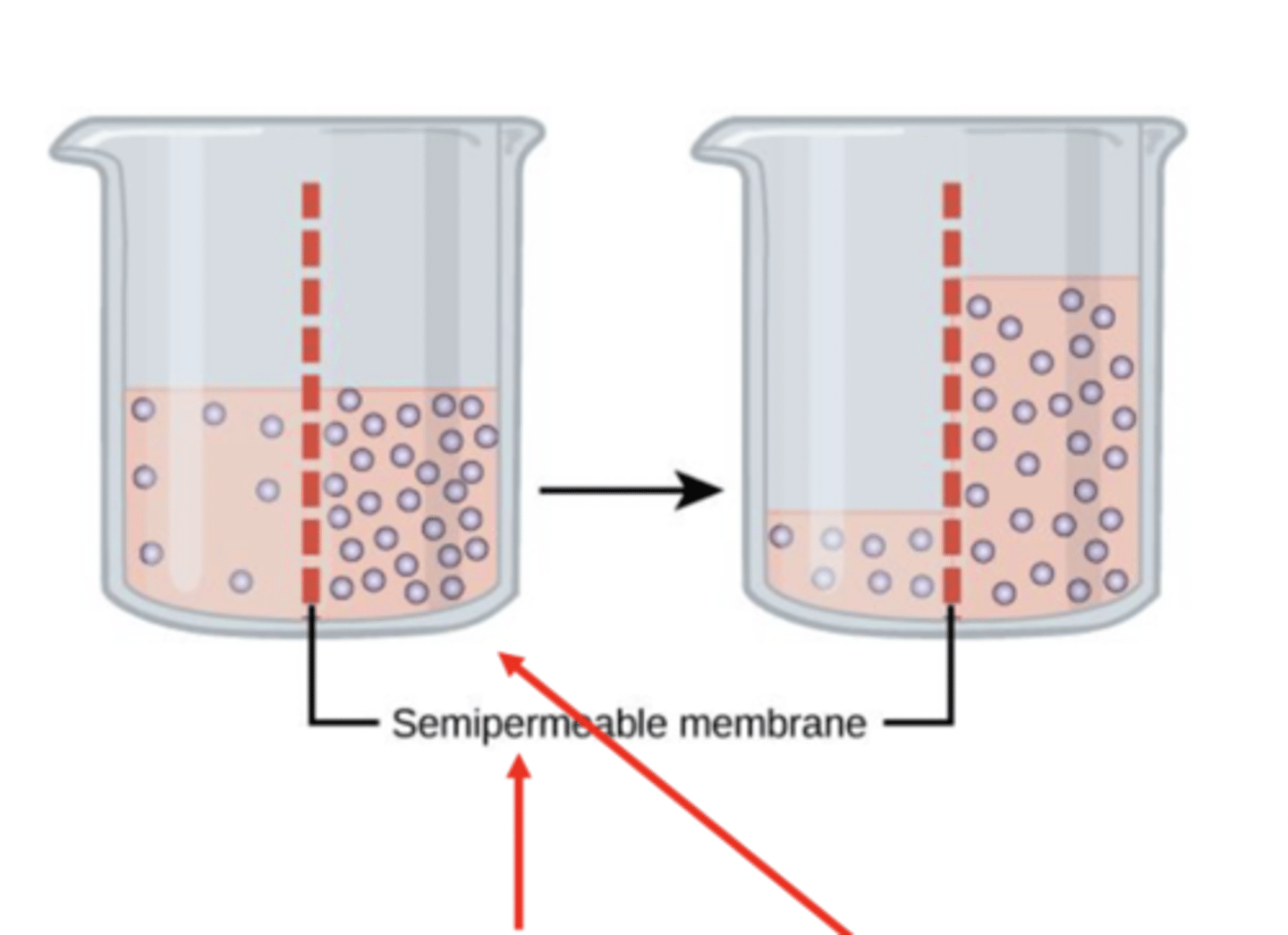
how is osmotic pressure (pulling water) created?
created by a difference in solute concentration across a semipermeable membrane ~ impermeable to certain solutes
- measure of tendency of solution to pull in water (solvent) by osmosis
- also refers to the amount of hydrostatic pressure required to stop osmosis
what is hydrostatic pressure (pushing pressure)
pressure exerted by a stationary fluid at equilibrium which causes water/fluid to move or be pushed
why are osmotic and hydrostatic pressures very important in cells and blood exchange?
allows fluid exchange across capillaries
hydrostatic pressure = fluid pressure usually causes what?
water and some very small solutes to leave blood vessels, which is called dominant pressure
interstitial hydrostatic = exerted by fluids between cells in tissue
blood hydrostatic = exerted by fluid within blood vessels (high dominant)
osmotic
due to solutes
hydrostatic
due to fluid
true or false: hydrostatic pressure opposes osmotic pressure
true;
osmotic tends to pull
hydrostatic tends to push
osmotic pressure (aka colloidal osmotic or oncotic pressure if referring to tissues & cells):
High osmolarity (many solute particles) exerts ________ osmotic pressure to pull water into a space, such as a blood vessel
high;
pulling water in, blood pressure goes up
water leaving blood vessels = edema
true or false: pressures favor filtration out of capillaries and into tissues
true
true or false: osmolarity and osmolality are functionally the same
true
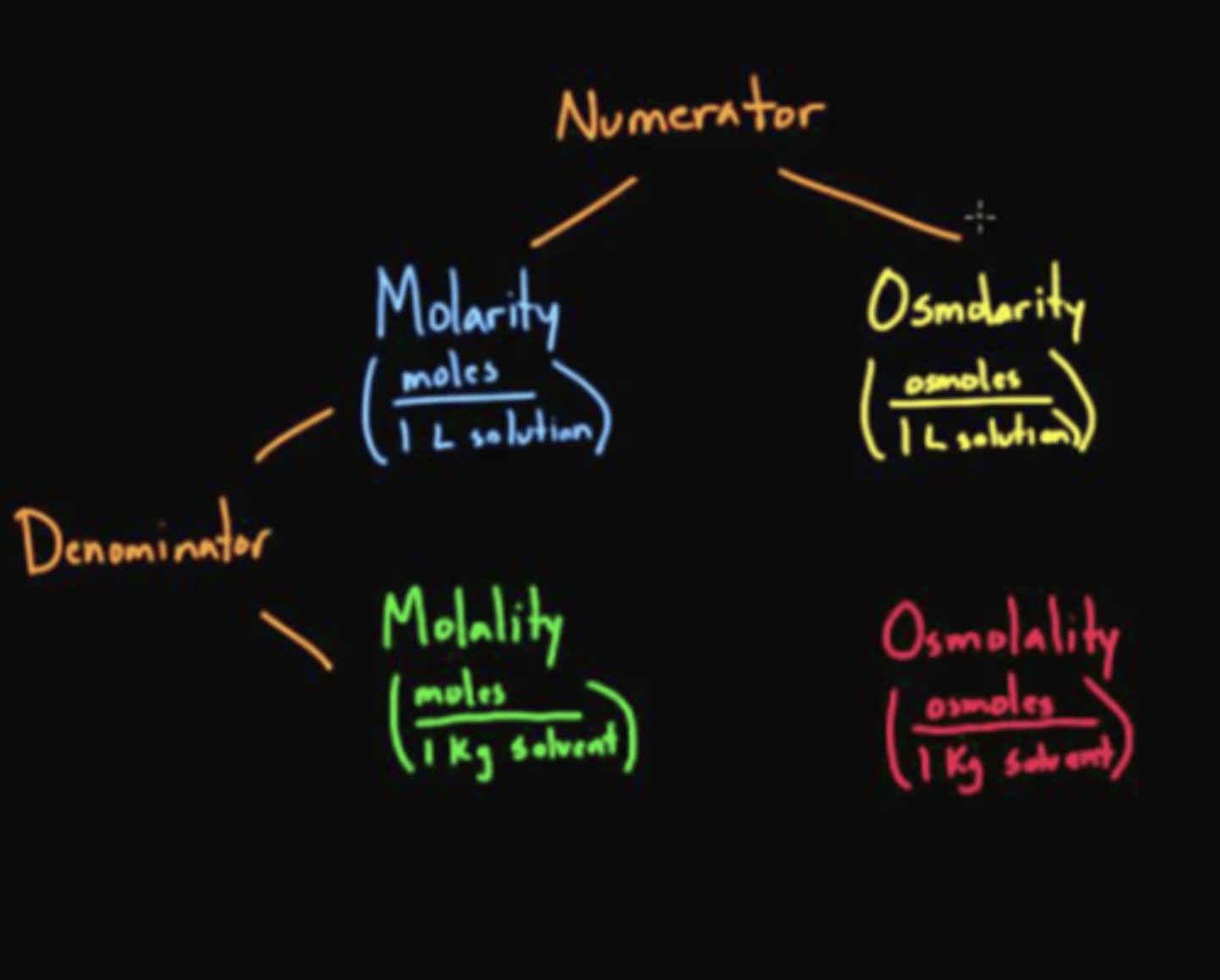
osmolar concentrations express what?
osmotic strength of solutions such as urine, plasma, NaCl
osmolarity is what?
concentration of osmotically active particles per liter of solution (osmotic/L or mOsm/L)
a 1 mol/L NaCl solution would have an osmolarity of what
2 mOsm/L
osmolality is what?
concentration of osmotically active particles expresses as osmoles/kg water
3 types of osmotic balance?
1. isosmotic
2. hyperosmotic
3. hypo-osmotic
isosmotic
solutions of equal solute concentrations
- same osmolarity/equal osmotic pressures
what happens to a normal cell placed in an isosmotic solution?
nothing!
hyperosmotic
refers to a solution with higher concentration of solute
- higher osmolarity compared to another solution
- solution exerts more pressure
what happens to a normal cell placed in a hyperosmotic solution?
- water moves from cell to the solution
- water follows the concentration gradient
- pulls it from the cell = shrivels up
hypo-osmotic
refers to a solution with lower concentration of solute
- lower osmolarity compared to another solution
- solution exerts less pressure
what happens to a normal cell placed in a hypo-osmotic solution?
- solution to the cell
- swells up
what is tonicity?
tissue tone: a measure of the effective osmotic pressure
tonicity = defined by the response of cells or tissue immersed in the solution
a solution is _________________ to cells/tissues if cells/tissues neither swell nor shrink when immersed in solution
- no osmotic pressure difference between cell interior and extracellular solution
isotonic
a solution is _______________ to cells/tissues if cells/tissues swell when immersed in solution
- more solutes inside cell (higher osmolarity) relative to extracellular environment, greater osmotic pressure inside cell
hypotonic
a solution is ________________ to cells/tissues if cells/tissues shrink when immersed in solution
- less solutes inside cell (lower osmolarity) relative to extracellular environment, greater osmotic pressure outside cell
hypertonic
oncotic pressure is also called what?
colloid osmotic pressure
what is oncotic pressure?
form of osmotic pressure specifically exerted by proteins, mostly ALBUMIN, within blood vessels
what does oncotic pressure tend to do?
tends to pull water into blood vessels
oncotic pressure opposes what?
interstitial colloidal osmotic pressure (tissue proteins that want to pull water out of vessels)
a decrease in blood oncotic pressure leads to what?
edema