Cs 490 test 1
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Interrupt
a mechanism by which other modules (I/O, memory) may interrupt the normal sequencing of the processor. The process checks for an interrupt flag at the end of each fetch-execute cycle to determine if something needs to be dealt with.
difference between a multiprocessor and a multicore system
A multicore computer is a special case of a multiprocessor, in which all of the processors are on a single chip.
Multiprocessing
a mode of operation that provides for the physical computation of processes in parallel, on different CPUs/computing hardware
I/o bound
Process spends more time waiting for i/o instead of computing instructions on alu/cpu
CPU bound
Process spends more time computing instructions than waiting for i/o
Multiprogramming
a mode of operation that provides for the interleaved execution of two or more computer programs by a single processor
Scheduling
Most installations used a hard copy sign up sheet to reserve computer time
kernel
a portion of the operating system that includes the most heavily used portions of software
difference between a monolithic kernel and a microkernel design
Microkernels implement the most important core features in the memory resident portion of the operating system where Monolithic kernels include all possible OS features in the core. Microkernels use memory more efficiently by allowing some operating system features to be managed as if they were normal processes and can be swapped in/out of memory.
Process
Supports goal of an operating system as a resource manager
Comprised of:
a program in execution
Associated data in memory
Process control block (Created and managed by os software)
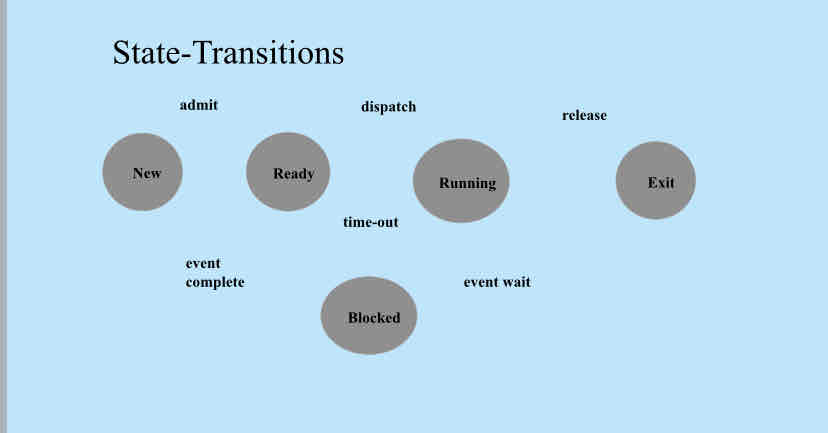
5 state model
1) running - process currently being executed
2) ready - process is ready to execute
3) blocked - process can’t resume execution until some event occurs
4) new - process just created, not yet loaded into memory
5) exit - process is completed and its pcb storage can be reclaimed
7 state model
Adds ready/suspend and blocked/suspend to 5 state model
State transitions
Admit, event complete, dispatch, time out, event wait, release
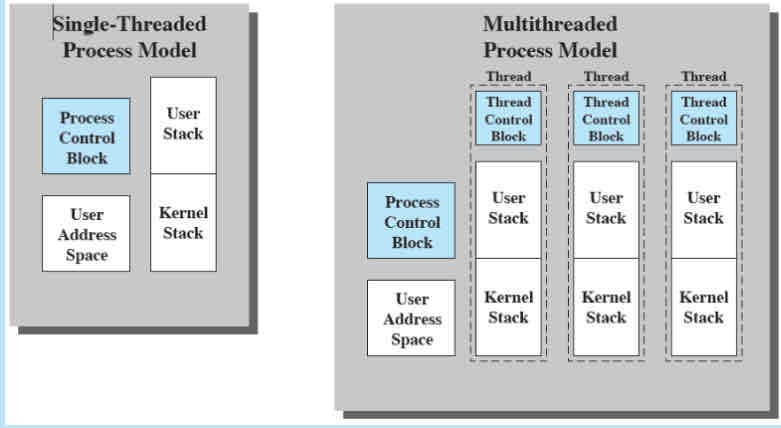
Multithreading
In this process an environment contains a virtual memory address space that holds the process image and protected access to processors, communication, files, and other resources
Single threaded vs multi threaded processes
User level threads
All details of thread management are performed by the application itself via thread libraries
Kernel level threads
The operating system can map many user level threads into some subset of kernel level
Mutual exclusion
a program object that prevents multiple threads from accessing the same shared resource simultaneously
Dekkers algorithm
A solution to mutual exclusion. works to enforce mutual exclusion without locking the processes
Atomic actions
Multiple actions on a memory location completes within a single instruction cycle
Multiple applications
multiprogramming was invented to handle this, and allow processing time to be shared among multiple active applications
Structured applications
modular design sometimes encompasses developing problem solutions built from multiple concurrent processes
Operating system structure
OS services can be developed as a set of concurrent processes
Semaphore
A special variable type with an integer value. Used with shared memory systems, processes can each utilize the shared semaphores
Binary semaphores
Semaphores that start with 1
Counting semaphores
Semaphores that start with >= 1
SemWait
Decrements the value as an atomic action
SemSignal
Semaphore value is incremented
Monitor
Controls the shared data. Provides types of locks using condition variables or condition flags
positives of semaphore
Allows more than one thread to access critical regions. Flexible resource management. Machine independent.
Negatives of semaphores
a primitive tool, and may be scattered throughout the code, requiring programmers to be disciplined at verifying the correctness of the combined operations
Condition variables
Manages synchronization. Cannot be scattered in code
Producer/consumer problem
Common buffer/sync problem. Need to ensure that a producer doesn’t try to add to a full buffer and that a consumer doesn’t try to take from an empty buffer.
Reader/writer problem
A data area is shared among many processes. Some processes only read the data area, (readers) and some only write to the data area (writers)
Conditions that must be satisfied:
•Any number of readers may simultaneously read the file
•Only one writer at a time may write to the file
•If a writer is writing to the file, no reader may read it
variations include reader priority (writers starve)
Deadlock
the permanent blocking of a set of processes that compete for system resources or communicate with each other
Starvation
A process or resource is unable to make progress or access a resource it needs due to allocation of resources to other processes or tasks
4 conditions for deadlock to occur
Mutual exclusion, hold & wait, no preemption, circular wait
Uniprocessor
Only one process can run at a time, and to run another one you’d have to wait until the current one is finished.