Greek Art and Archaeology
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Required Info:
what it is (type of object)
date and time period
material, techniques used
location or findspot
size, if relevant
function and/or subject matter
how it is representative of a style, time period, cultural phenomenon
religious, social, or political significance
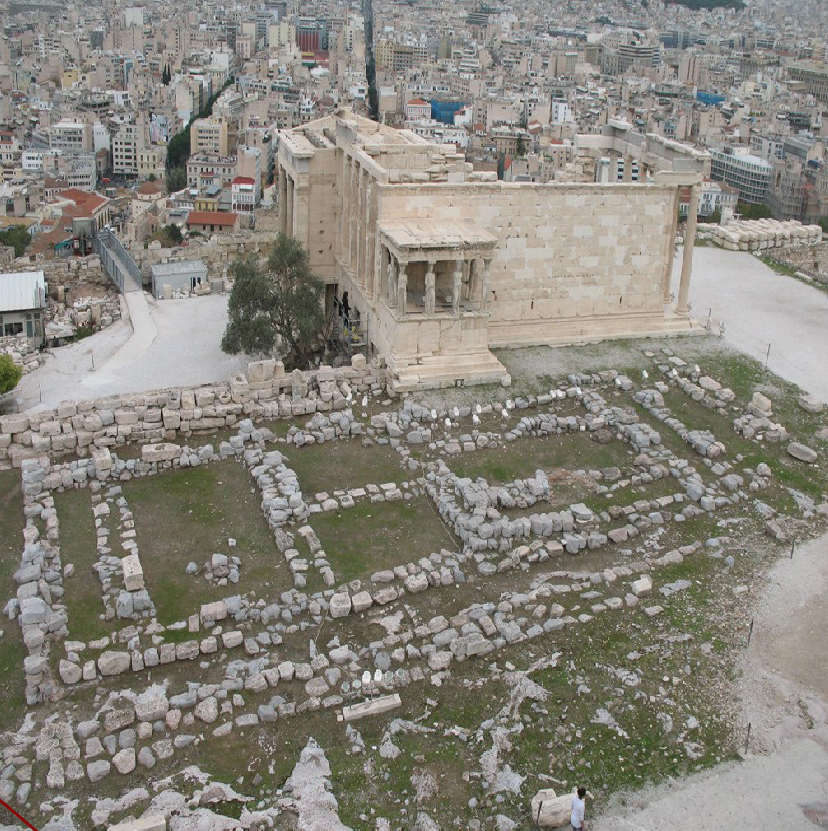

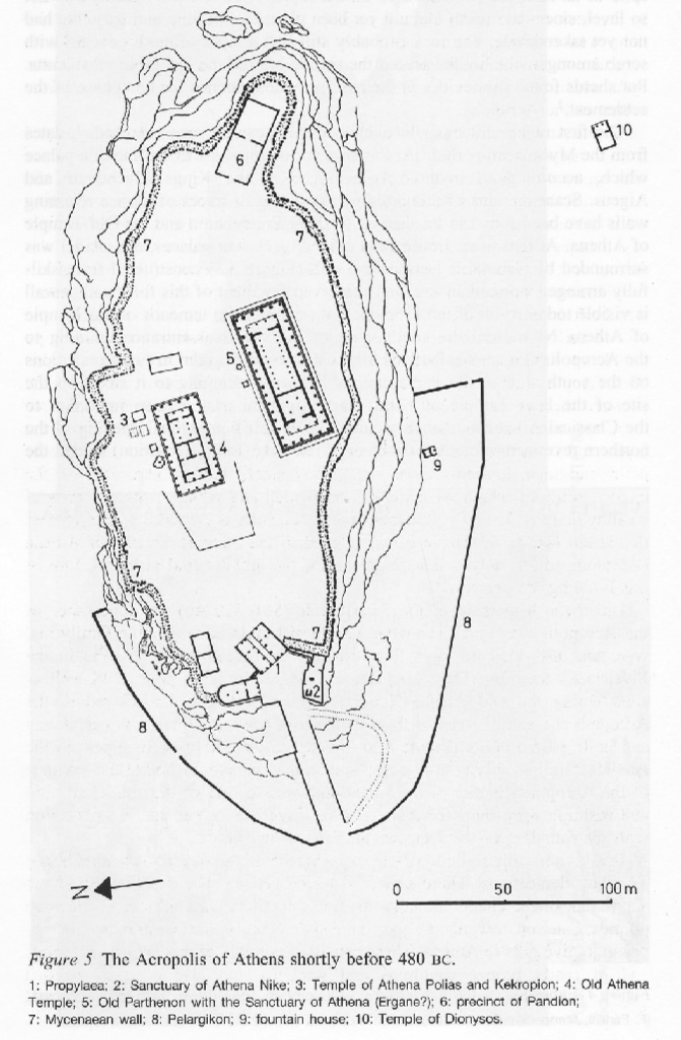
Old Temple of Athena Polias (of the city)
Constructed in 510 BCE
Only the foundations survive (Dorpfeld foundations
Doric temple 6 by 12 columns
Foundations made of limestone, superstructure of limestone, sculpture is marble
Held the Xoanon (cult statue) of Athena
Unusual design: shrines to Hephaistos, Poseidon, Erectheus (mythical king of Athens), Boutes (local hero)
Sculpture made of Parian marble - pristine white marble
shows the Gigantomachy
famous scene shows Athena, upright, striking a giant, while another giant has collapsed to the right
Athena is wearing an aegis - an identifier, made by Zeus to protect her
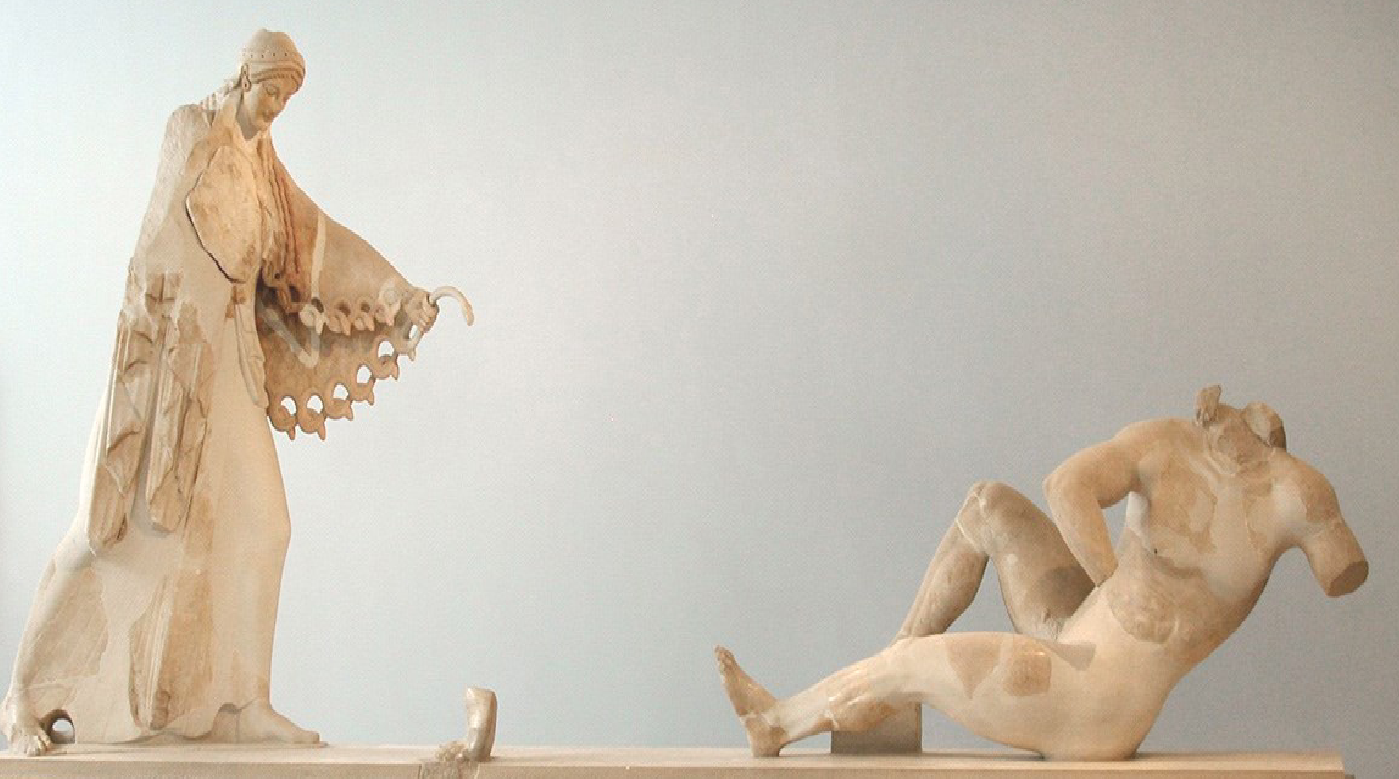

Pediment from the Old Temple of Athena Polias
510 BCE
Parian Marble
Gigantomachy
Shows Athena fighting a giant
note her detailed aegis
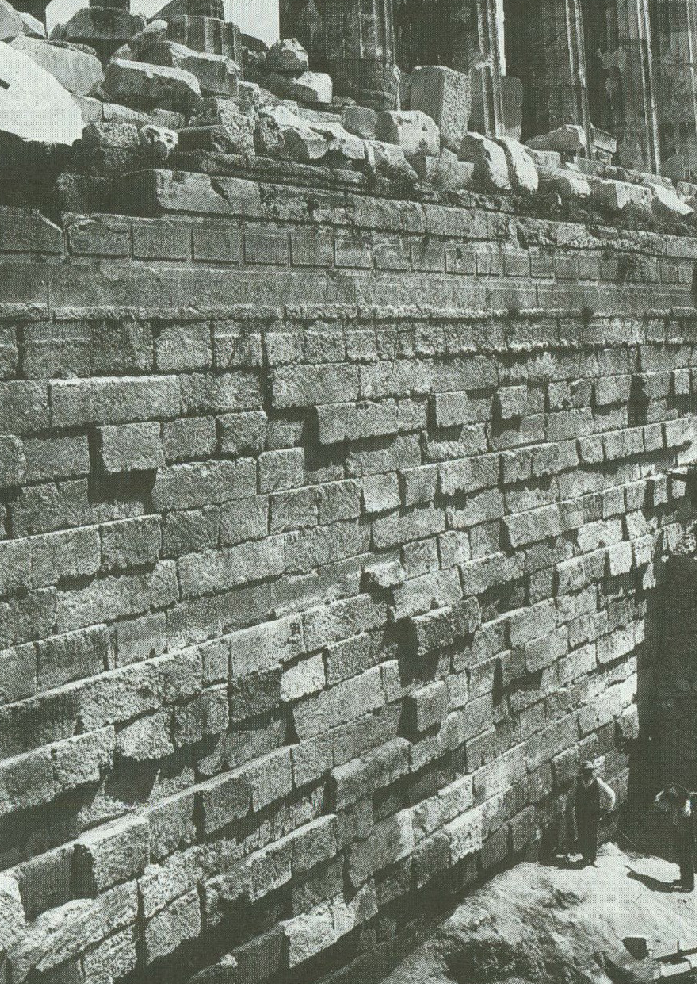

489/488
Base for pre-Parthenon
Around 8,000 limestone blocks used
Huge organisational and engineering feat - each block was 2 tonnes in weight
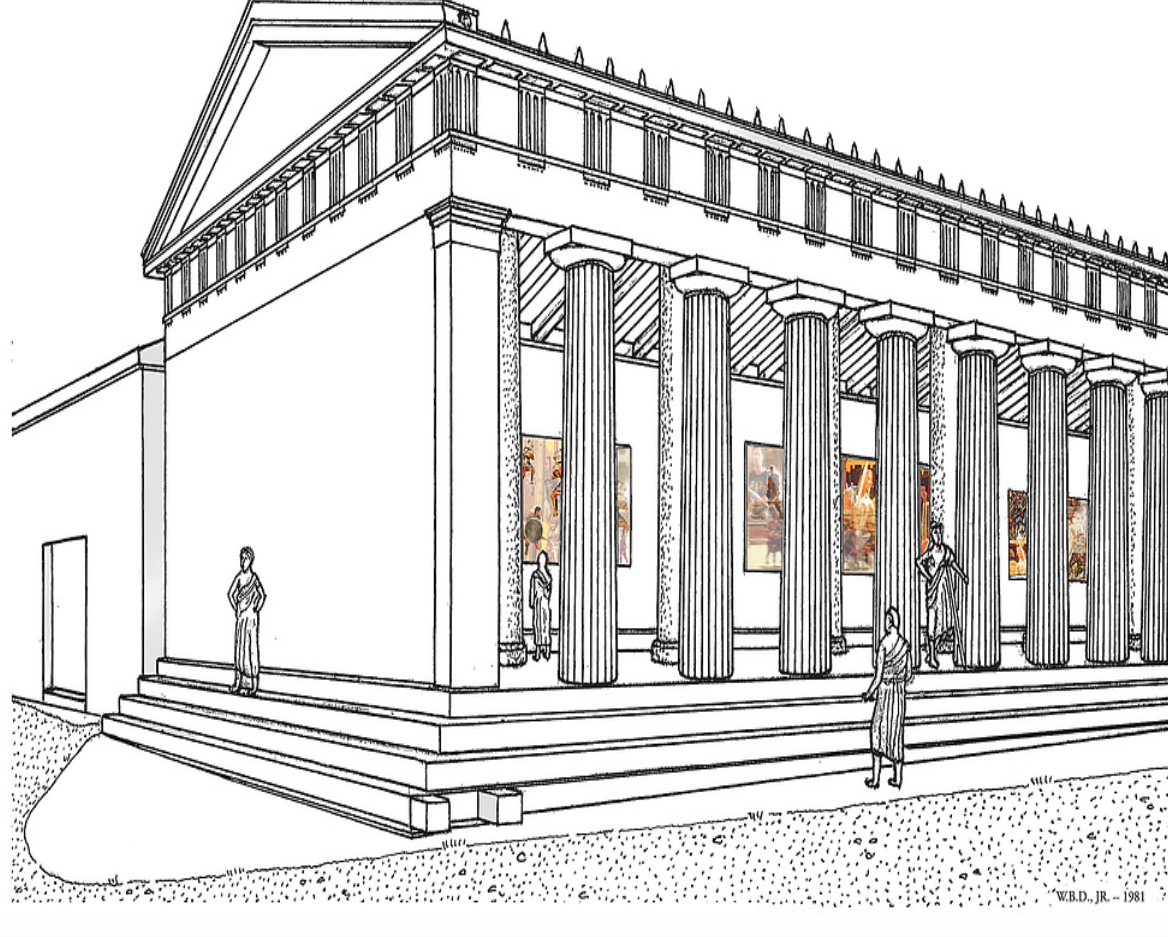
pre-Parthenon
pre-Parthenon:
489/488
Much bigger - much bigger project
also had to build podium
Foundation made of limestone, superstructure pentelic marble (Mt Pentelicus in Attica)
Was the largest temple on mainland Greece at the time
Was a peristyle temple
Had a pronaos (porch), Cella with two lines of support columns, an opisthodomos (back porch), and an adyton
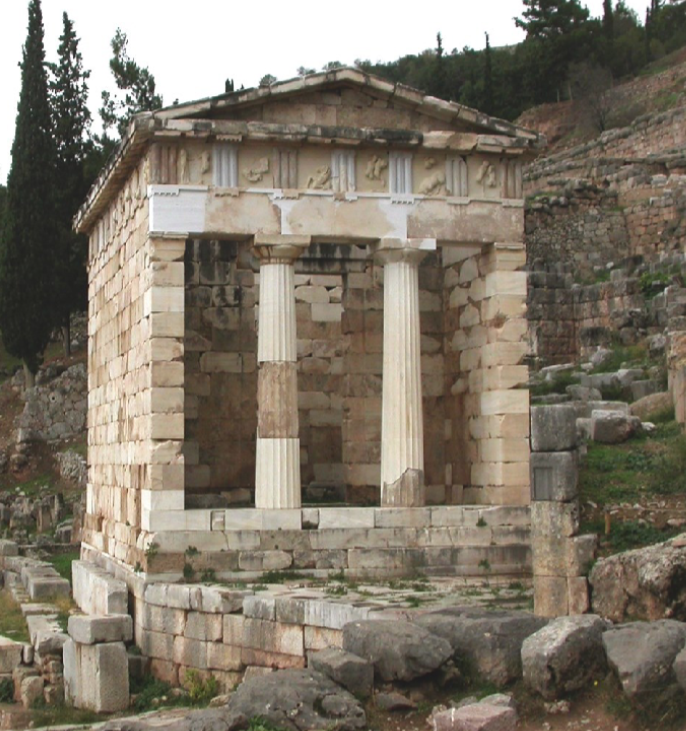

Treasury of Athens at Delphi
c.480 BCE
Made of Parian marble
Inscription with bronze statues of Miltiades crowned victorious by Athena
Human surrounded by deities
Doric style
Decorated with metopes on the labours of Herakles and Theseus on the south side
linking Herakles and Theseus - perhaps a commemoration of the Persian war?
Frieze of metopes and triglyphs

Heracles and the Hind of Ceryneia
c. 480 BCE
From the Treasury of Athens at Delphi
wearing his lion skin - identifier
from the Nemean lion labour
bearded and has short hair (mature
breaking out of the frontal plane of relief
compared to other friezes it is much more 3D
Very energetic pose
Anatomical details - muscles and ribs
at this time there is more experimentation with anatomy and poses - sculptors and painters are breaking away from the stiff, abstracted archaic style
The faces are still in Archaic style with bulbous eyes and archaic smile
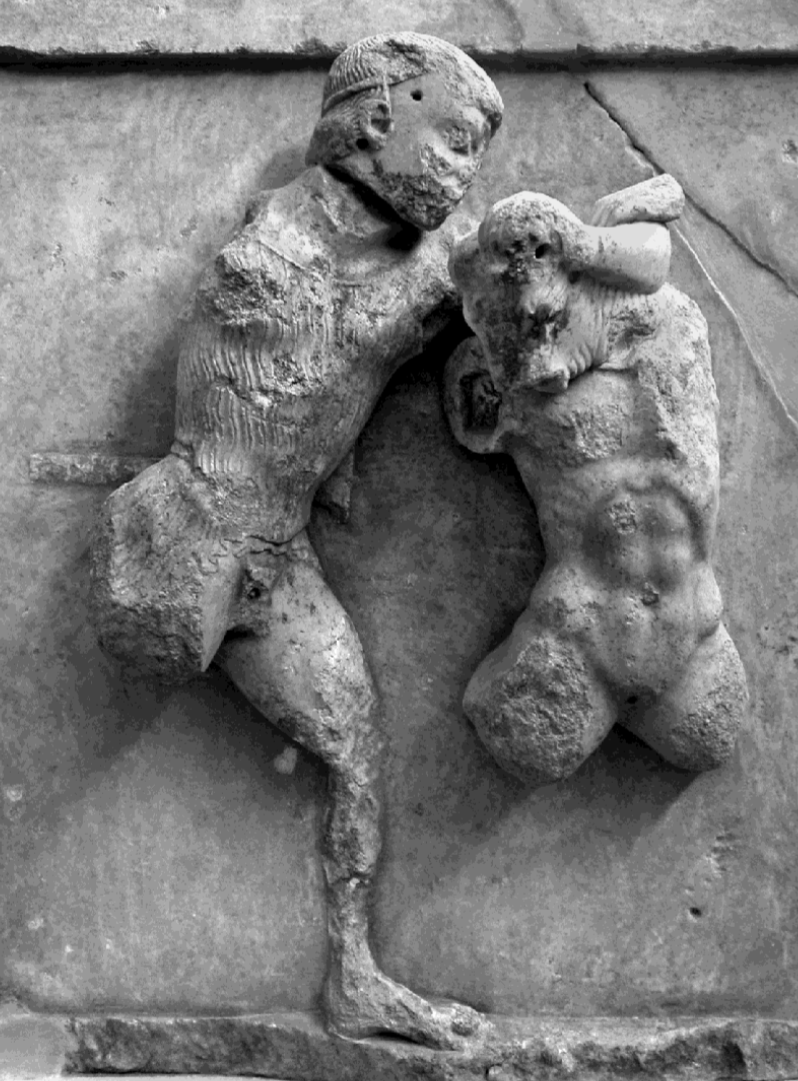

Theseus and the Minotaur
c. 480 BCE
From the Treasury of Athens at Delphi
Athenian hero
depicted on many Athenian buildings
his achievements are placed on the same building as Herakles (a panHellenic hero) - advertises the city to people
this is the first time Theseus and Herakles have been depicted on the same building
Torso of Minotaur softer than those of Heracles
not as abstract and rigid depiction of anatomy
shows that there were different sculptors and different styles used for the friezes
First time Theseus and Heracles appear on the same monument - liken Athenian achievements to the pan-Hellenic hero
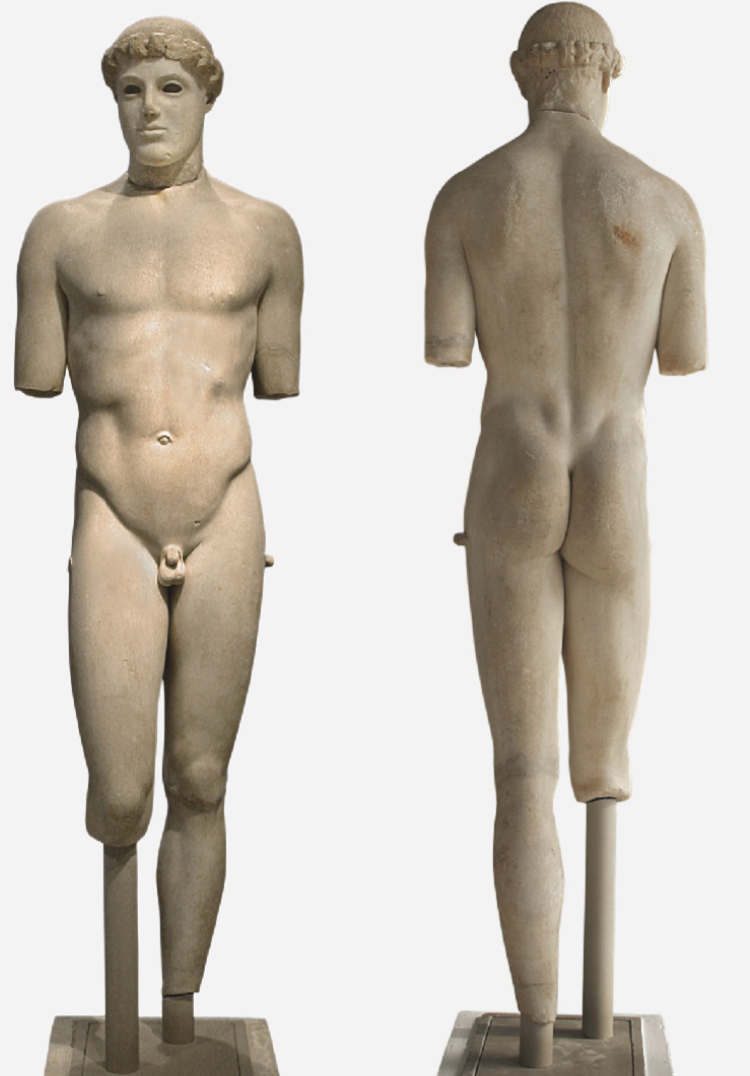

Kritios Boy
480 BCE
A dedication from the Acropolis at Athens - found as part of the debris from the Persian war
c. 1.20m tall - less than life-size
Beardless and long hair that is rolled up - clearly a youth
Right leg is relaxed, back weight baring leg
uneven distribution of weight - contrapposto pose
shoulders and hips line up to the weight baring
His head is also turned slightly
breaking away from the archaic style - now in the early Classical period
There is a very soft rendering of muscles and ribs
Inlaid eyes, no archaic smile (pouty lips)
severe style - very serious expression of the statue
Treatment of abdomen as one organic whole
Shifting away from the Archaic style
Perseschutt: Persian debris
Everything that was buried should be be from 480 BCE or earlier
however there are some later deposits mixed in
The Kritios boy was uncovered from the Perseschutt (Persian debris) so is he archaic or classical?
the Classical period begins in 480 BCE
he looks more Classical than Archaic - he looks later
Kritios boy made by the same sculptor as the second commission of tyrannicides so they may be contemporary c. 477 BCE
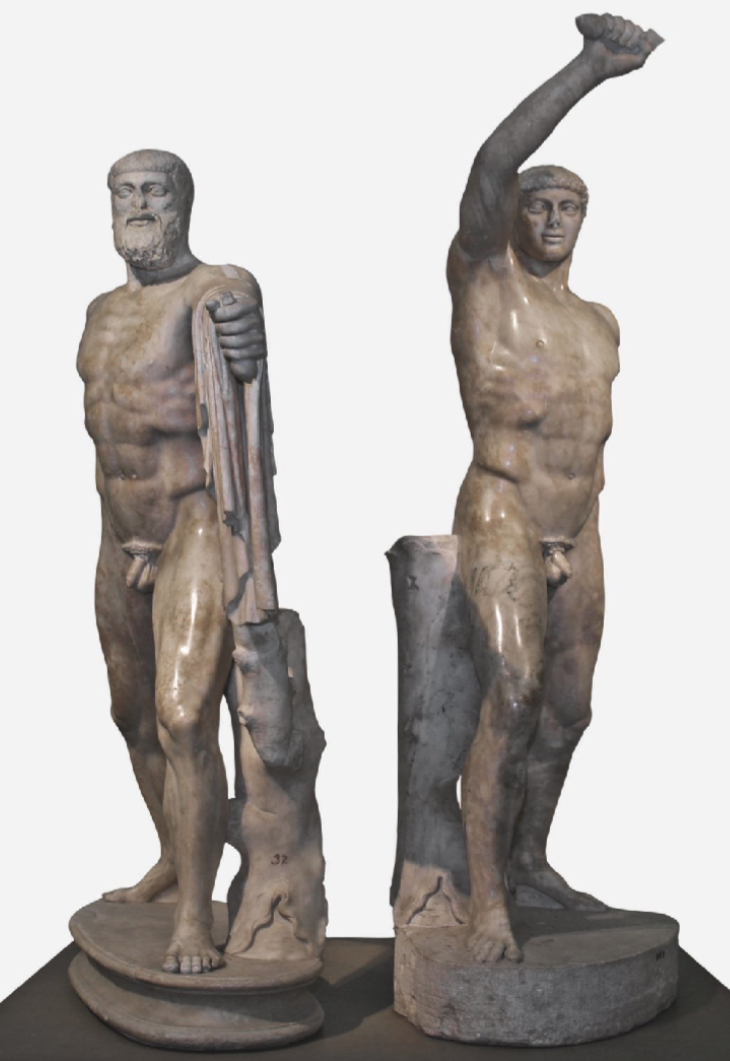

The Tyrannicides
Original statues erected in 509 BCE, replacement statues erected in c. 477 BCE
The Tyrannicides: sculptural group placed in the Agora - centre of the city
Harmodios and Aristogeiton (lovers)
real people - very unusual to erect statues of real people in a civic space like the Agora
Assassination of Hipparchus (brother of Hippias)
they originally intended to kill both Hipparchus and Hippias
they planned the assassination because Hipparchus flirted with Harmodios, who was already eromenos (young lover) of Aristogeiton, so when A. was informed of this he became angry and plotted an assassination of Hipparchus and Hippias
they only killed Hipparchus and didn’t manage to kill his brother
seen as responsible for beginning the events that led to the democratic reforms of Cleisthenes
they were given special honours, hence the sculptures being placed in the Agora
poses were dynamic - adopted by later sculptors
lunging position shows that the experiments with movement and anatomy were becoming more common with art at this point
the original statues were taken to Persia in 480 BCE
there were then replacements made by Kritias and Nesiotis ca. 477 CBE
Roman copy that survives today is of this one
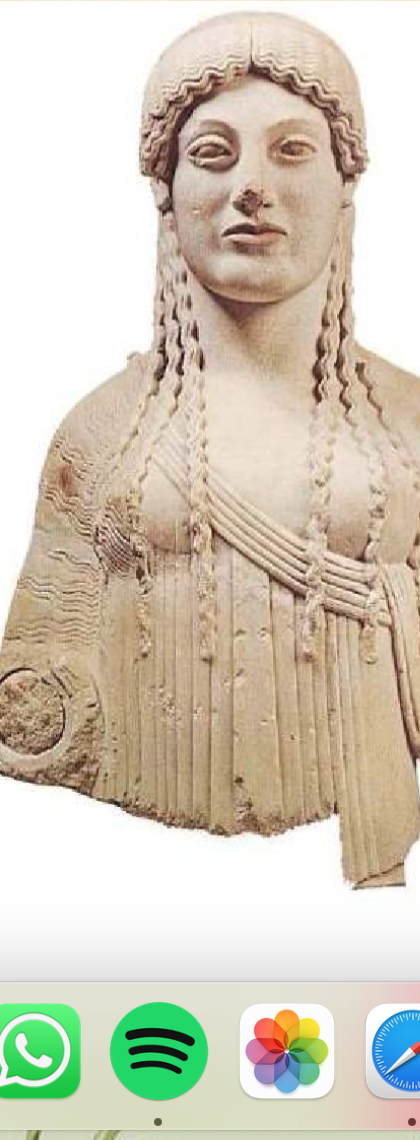

Euthydikos kore
490-480 BCE
Found on the Athenian Akropolis
Severe style
Pouty lips
Still very much like the Athenian kore with her hairstyle
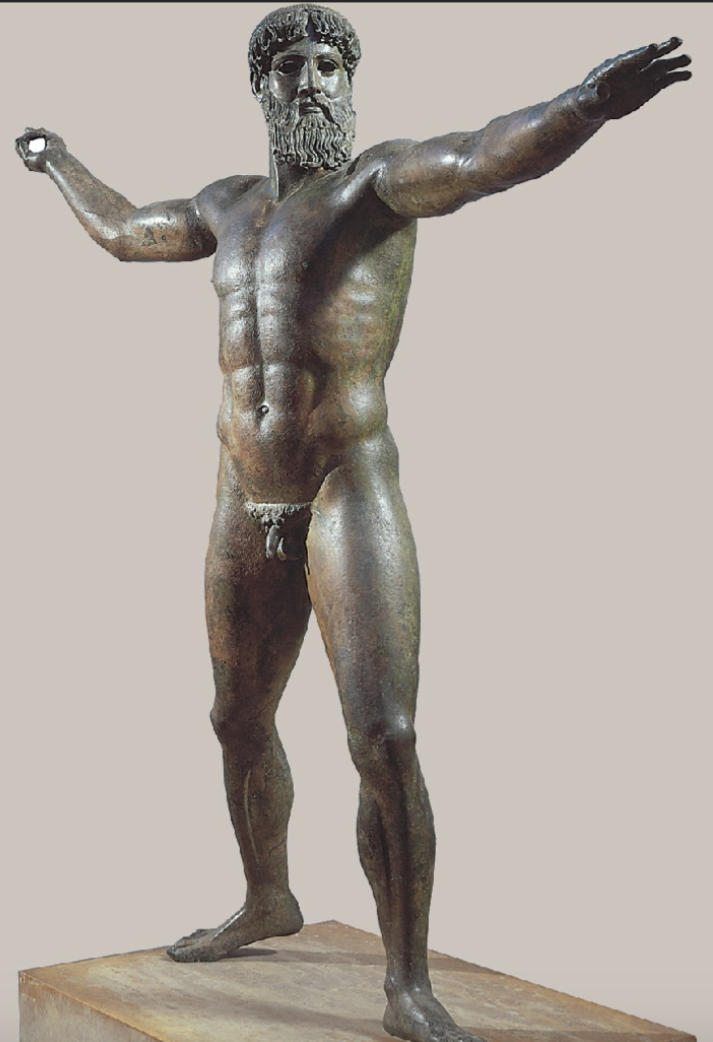

Artemision God
ca. 460-450 BCE
Over life size - 2m high
Preserved as it was in a shipwreck
Zeus? Poseidon?
holding something with his right hand, about to strike
could be a thunderbolt or a trident
most common interpretation is that this is Zeus as there are other examples of smaller sculptures of Zeus which look similar
Hollow cast bronze
Eyes, lips and nipples would have been made of copper, eyebrows out of silver
Disengaged with the viewer - Classical period sculpture was often not focused on engaging with the viewer
body twisted and head is looking towards the direction of movement, not the viewer
Early Classical style - severe, pouty lips
Would have been made in sections, with multiple pieces joined together, called the lost wax technique
clay model covered with bees wax, the covered the wax with clay again and inserted bronze tubes to support the cavity
the clay was then fired, the wax would melt and then there would be a cavity created
liquid bronze was then poured into this cavity, left to solidify and then the outer layer of clay was broken away
cold work could then be done - fine details could be carved into the bronze e.g. fine hair
the statue was then polished and the sections were bonded together
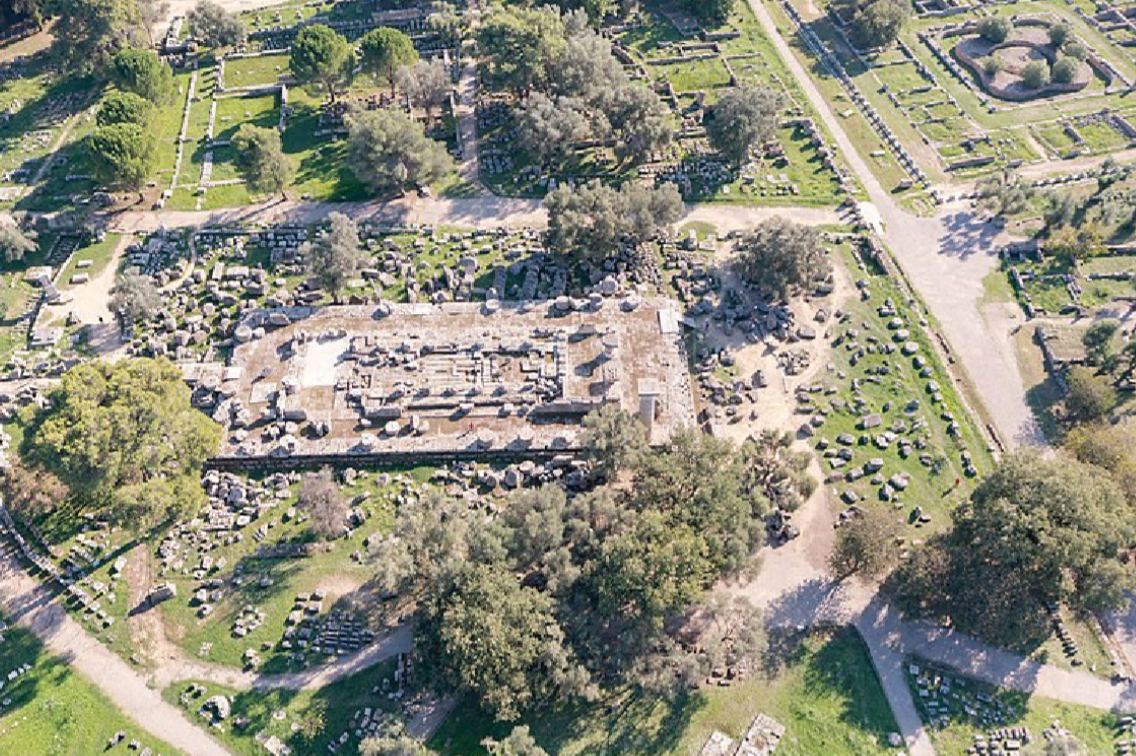

Temple of Zeus at Olympia:
470-465 BCE
limestone with Parian marble roof and sculptures
Parian marble (from the island of Paros) transported to Olympia
Doric Peripteral: 6 by 13 columns
an enormous temple - largest in Greece at the time
early Classical style temple
architect was Libon of Elis - built from the spoils of war between Elis and Pisa
On the East pediment is depicted the myth of Pelops and Oinomaos. Quiet
scene, before the disasterOn the West Pediment there is the myth of the Lapiths fighting the Centaurs.
Dynamic, violent scene. Feautres Perithoos and Theseusthe metopes depict the Labours of Herakles
mythology of the foundation of the games
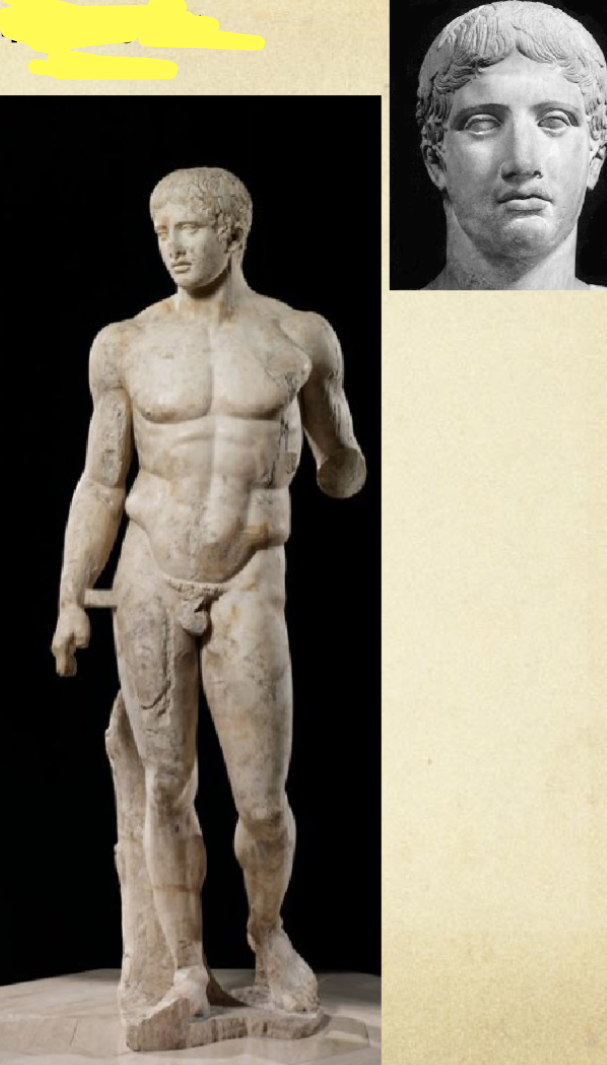

Doryphoros (spear-bearer) by Polykleitos,
450-440 BCE
Made of marble
Roman copy (150-120 BCE) of a Greek original which would likely have been bronze
we have two different Roman copies that look different
2.12m - over life size (6ft 11)
has struts (supports) which are prevalent in Roman copies, not so much in Greek sculpture
semi-engaged pose - one leg engaged, the other relaxed (contrapposto - )
contrapposto - opposite limbs are engaged (the engaged leg is on the same side as the relaxed arm, the relaxed leg is on the same side as the arm holding a spear)
chiastic pose (X = Greek letter khi)
posture movement effects all parts of the body
the pose is mid-movement
realsim in anatomy is integrated with the ideal
intellectualisation of art (artists intentions of what makes an ideal image
Polykleitos wrote a treatise: canon of ideal proportions, symmetry and ratio, but we don’t know if his views reflected the wider canon in Greece
other opinions don’t survive
some scholars think this statue is meant to exemplify the canon
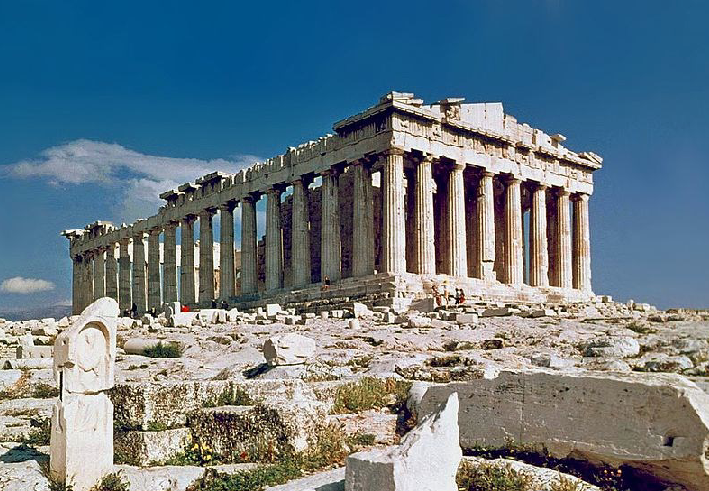

The Parthenon
447-432 BCE
Made of Pentelic marble
Architects: Kallikrates and Iktinos
Sculpture: Phidias workshop
Doric Temple
but has Ionic elements: continuous frieze and some ionic columns
Metopes:
Trojan War
Amazonomachy
Gigantomachy
Centaruomachy
highlight reference to the Persian war
Stylistic difference between the sculpture of the metopes, some look more archaic, the anatomy is less realistic
Pediments:
East: Birth of Athena
West: Poseidon vs Athena for patron of Athens
Ionic frieze
Panathenaic procession?
handing over of the peplos
depicts the 12 gods - sitting down, larger than the mortals
Cult statue of Athena Parthenos (virgin
over 12 metres high
chryselephantine
made by Pheidias
No straight lines on the Parthenon - architectural refinements
Panathenaic Frieze on Parthenon
447-432
Made of Pentelic marble
Ionic frieze
Depicts the 12 Olympian gods
they are sitting down which allows them to be taller than the mortals
above the entrance to the temple - important positioning
Shows the passing over of the peplos??
symbolic moment in the Panathenaic festival
peplos for the traditional cult statue of Athena in the Erechtheion
Shows a scene of riders
very uniform
overlapping to show depth
horses are smaller than proportionally they should be
horses are excited, humans are calm - animalistic and cannot control emotions
However there are elements depicted that are not thought to be part of the procession e.g. horsemen

The Temple of Athena Nike
438-424
Made of Pentelic marble
Ionic order
Ionic frieze, continuous
Greeks fighting Greeks x2 - shows signs of 4th century sculptural developments
Greeks fighting Persians
Divine Assembly - group of gods
Pediments:
Gigantomachy and Amazonomachy
Positioned on a bastion on the Acropolis, to the right of the Propylaea
One room structure

The Propylaea
437-432
Doric columns on the front and back, Ionic on the inside
Made of Pentelic marble and Eleusinian limestone
Gateway to the Acropolis
Assymetrical
Never finished due to the Peloponnesian war
Had a dining room and picture gallery
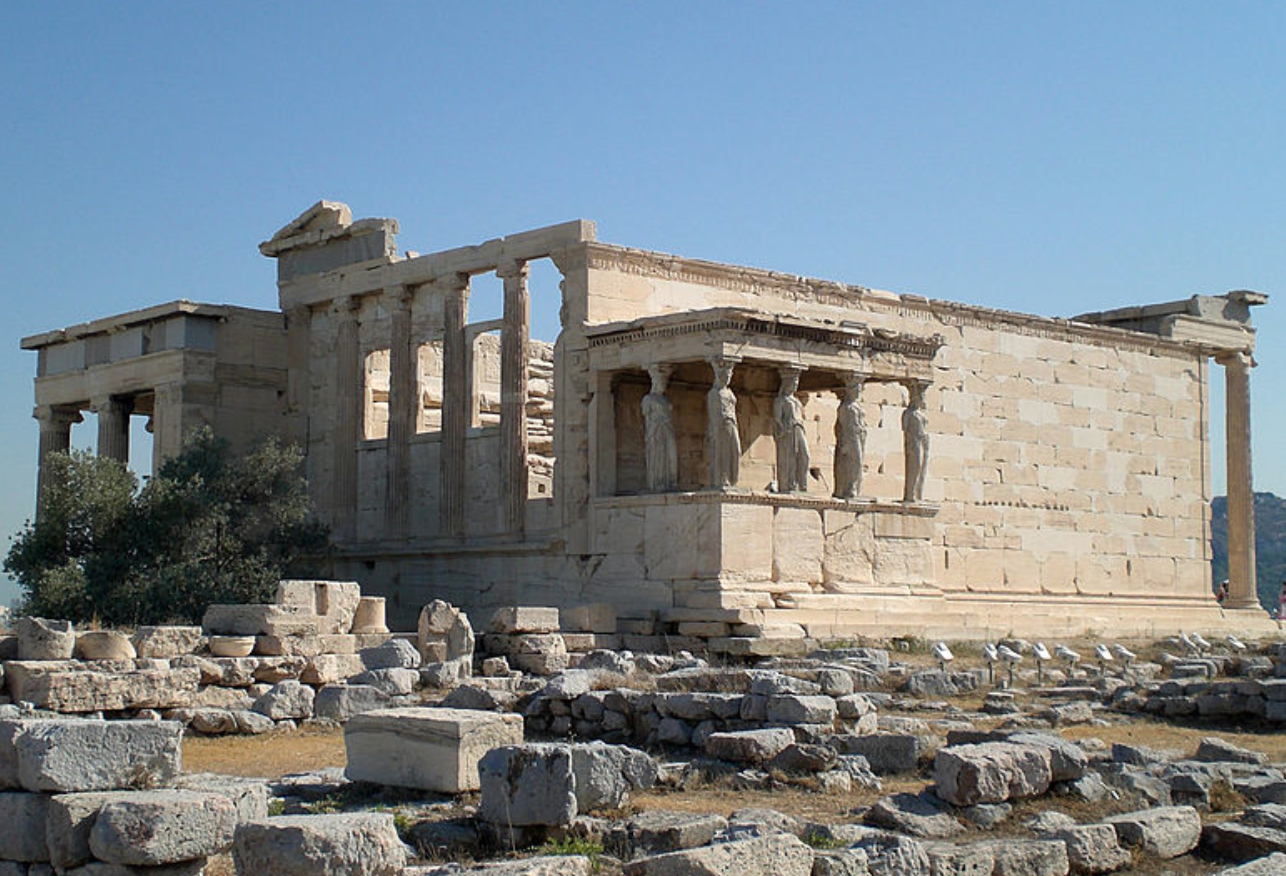

The Erechtheion
421-406
Made of Pentelic marble and Eleusenian limestone
Has a caryatid porch
Ionic style building, Ionic frieze
Unique temple, irregular plan
different levels allow worship of different deities and heroes
Temple housed symbols related to the cults of:
Athena Polias (Athena of the City)
Poseidon - trident marks and water
Hephaistus (altar)
Poseidon-Erechtheus (Erechthonius)
Hero Butes (Athenian Hero)
Tomb of Kekrops
supposedly located under the caryatid porch
wasn’t found
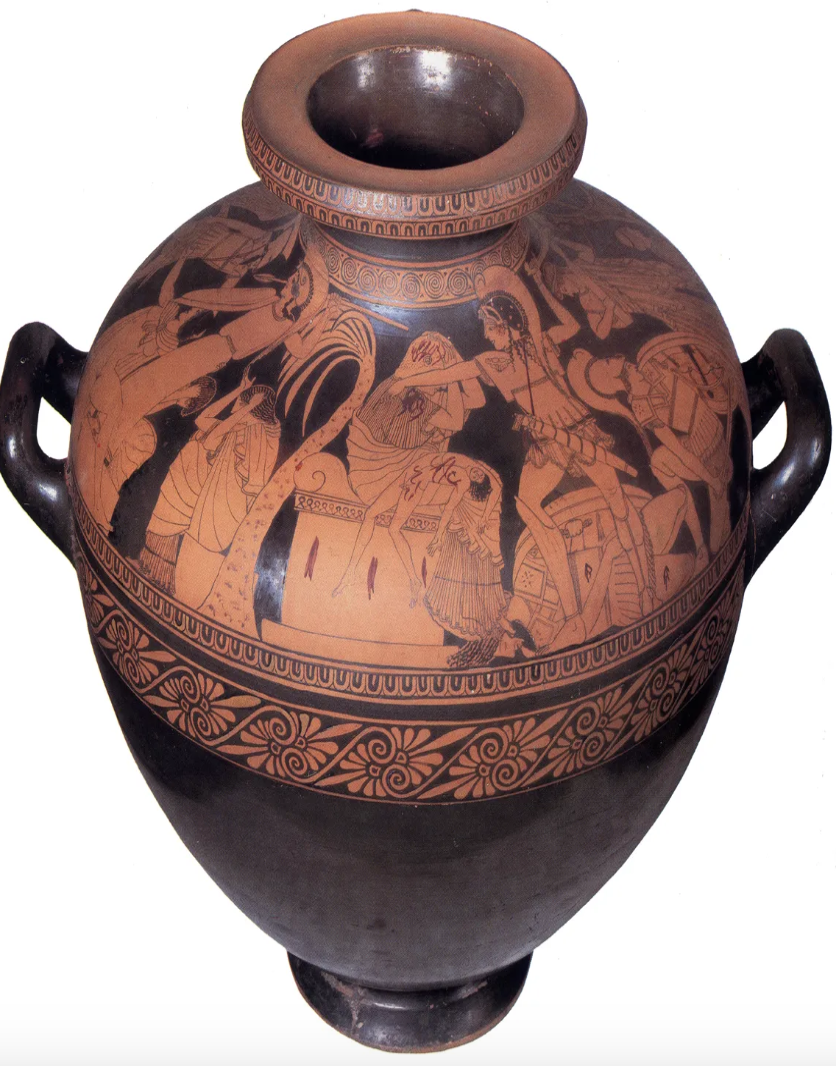

The Vivenzio Hydria
c. 480 BCE
Kleophrades painter
around 30 cm tall
Red figure technique
cinerary urn found in Nola, Italy
composition is confined to the shoulder, none on the body
quite crowded not symmetrical
it has a continuous band of action around the vessel (Sack of Troy)
Priam (King of Troy) is seated on an altar - as if he’s a sacrificial victim
Greek Neoptolomos is attacking Priam
Astyanax (grandson of Priam, son of Hector) is dead, on the lap of Priam
Aged Priam - he is not fighting back
emotional scenes - vulnerability
also shows Kassandra about to be raped
we see an attacks on civilians - war at its worst
women being raped, the elderly and young children escaping or being attacked
also shows a cult statue of Athena in an archaic style (smiling)
a variety of poses
Anatomy, especially Kassandra is more naturalistic in keeping with the developments of sculpture (Kritios boy)
eyes in profile - not frontal
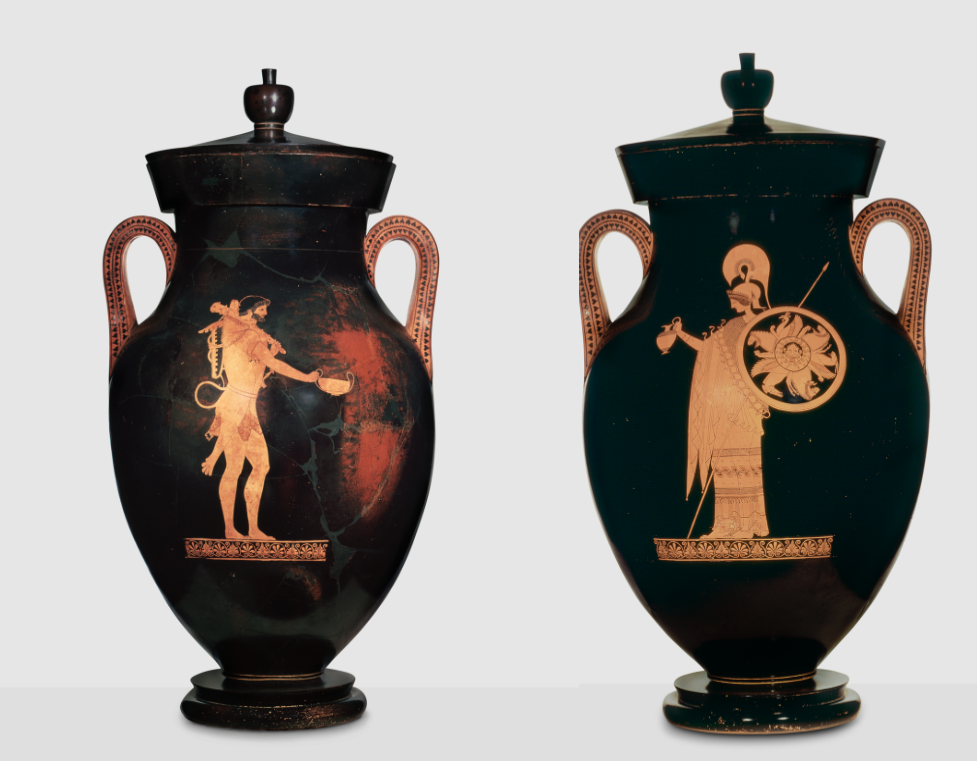

Attic Red figure amphora (with lid)
Berlin Painter
ca. 500-480 BCE
c. 60 cm tall
Red figure technique
Typical single figure composition
Uses the amphora shape to put one figure on each side
Ground line sometimes - figures sometimes stand on platforms so that they aren’t floating (but sometimes doesn’t)
Spotlight effect of figure against a dark background
Early Classical (Severe style)
heavy chin, gravity and monumentality
Depicts Heracles with a kantharos (type of cup) and Athena with an oinochoe (wine pourer)
some link between the two figures?
Athena giving wine to Heracles? - but no myth associated with it
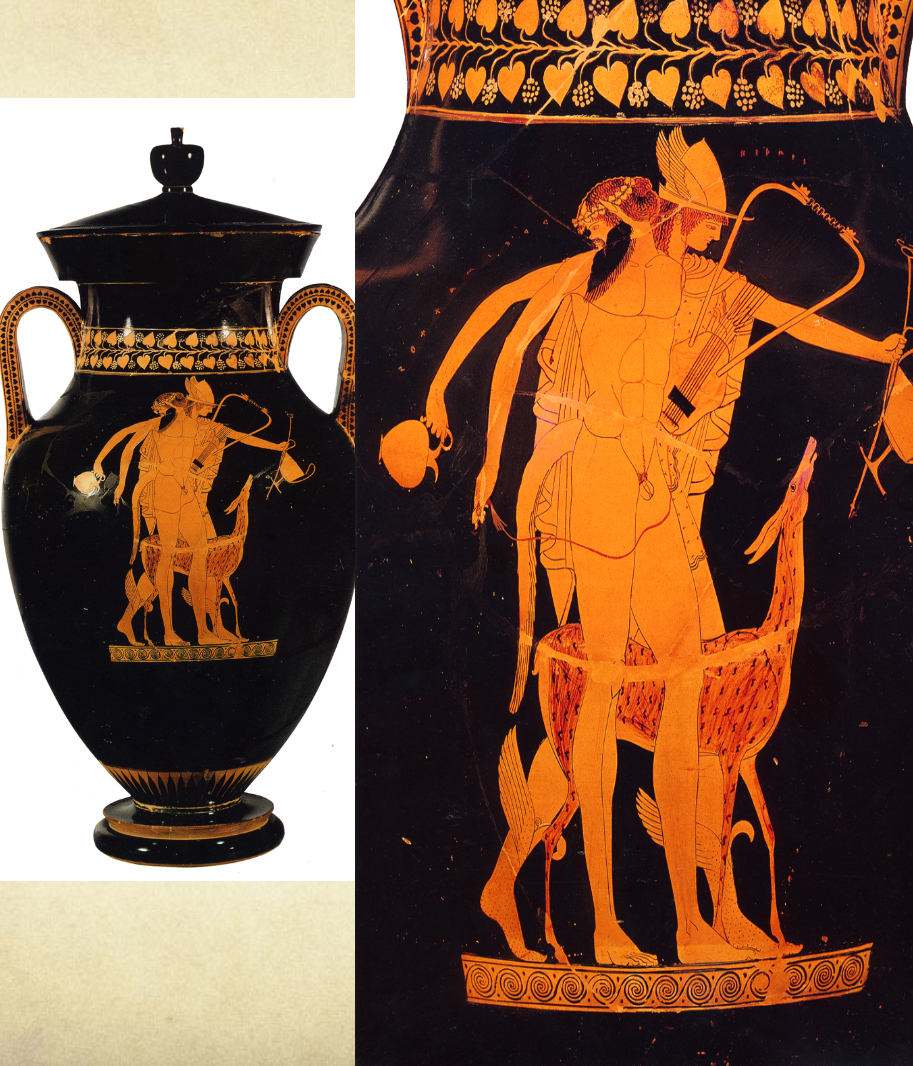

Red figure Amphora
ca. 490 BCE
Berlin Painter
Around 80cm tall
Red figure technique
Three figures (unusual) - overlapping each other
Depicts:
Hermes (name labelled using dipinto) holding a kantharos and a vessel to hold fluids
a deer painted with a darker slip
Satyr Oreimachos - follower of Dionysus with plektron and lyre
Compact figures with radiating limbs
Spotlight effect on black background

Attic red-figure kylix
Byrgos painter
ca. 490 BCE
Tondo (interior of cup)
Symposium
Youth with female (hetaira)
the man is vomiting and the prostitute is helping him by holding his head
warning to drinker - shows what will happen if you drink too much
Dots in drapery (feature of the Brygos painter
5th century increase of compositions with non-narrative scenes even with mythological figures
Everyday scenes increase in 5th century BCE
Stoa Poikile in the Agora
A painted stoa built around 460 BCE
Housed many paintings - gives it its name
Painted by Polygnotos, Mikon, Panaios
Pausanias describes the paintings in four panels
Amazonomachy, Sack of Troy - mythological
Battle of Oenoe 460 BCE, Battle of Marathon 490 BCE - historical events
Historical events placed at the same level as mythological events - they are seen as equally important
juxtaposition of contemporary events likened to mythological events
Pausanias and Pliny give descriptions of wall painting compositions e.g. Painted Stoa in Athens and Lesche of the Cnidias at Delphi
No overlap of figures
Interested in creating illusion of depth and space
figures arraned in 2-3 rows without getting smaller
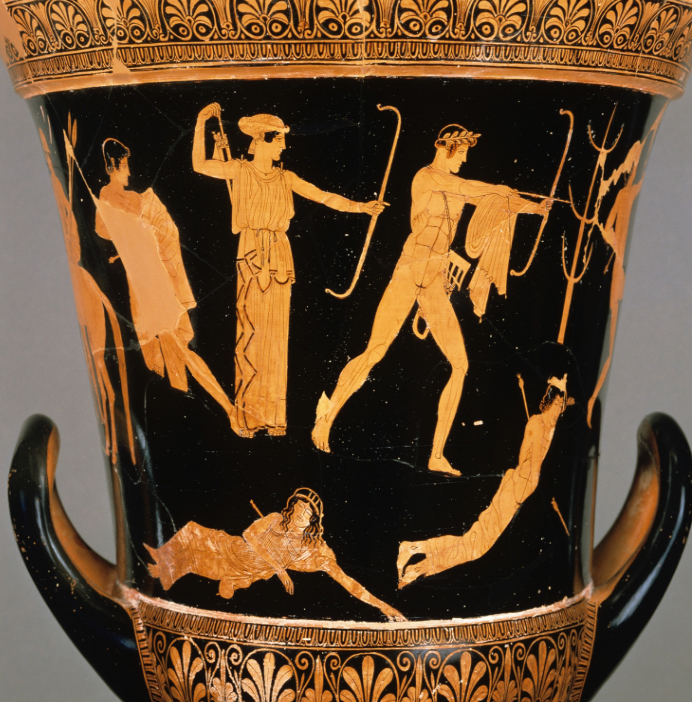

Red-figure calyx- krater by the Niobid Painter (name vase),
ca. 460-450 BC
Space figures distributed in space on wavy
groundlines in various poses.depth: No reduction of figures who would
be further awayinfluence from wall-painting
Apollo and Artemis killing Niobe’s children
Heracles and Athena; uncertain subject; figures relaxed
Three-quarter views; foreshortening; no stiff Archaic drapery

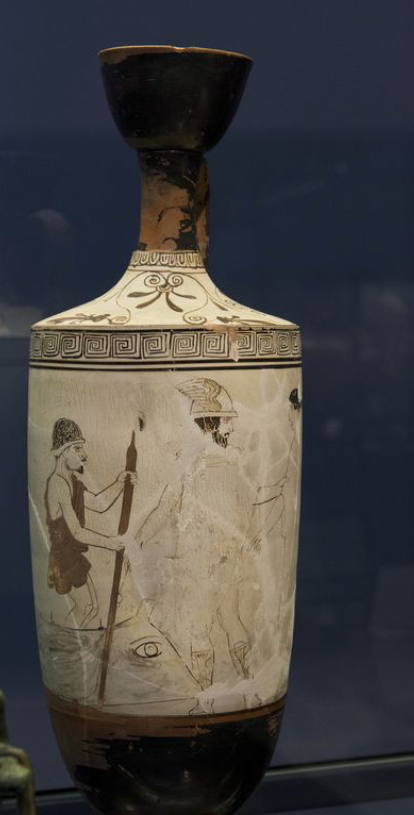
Visit to the grave
Bosanquet Painter, Attic
ca. 440 BC
White-ground lekythos
Chlamys and spear: hunter? Perhaps the deceased
Shallow basket: Kaneon or Kaniskion
Relationship between the dead and the family
Tomb seems extravagant but these were banned
Represents daily life - becoming more popular

White Ground Lekythos Iconography: Mythology
450
Thanatos painter
Hermes as Psychopompos (Leader of the Souls)
Hermes leads the soul
Charon (the Ferryman) in exomis (workman garment
Mythological scenes that deal with death

White Ground Lekythos Iconography: Domestic Scenes - Warrior Bids Farewell House interior
Achilles Painter,
440 BCE
Woman on klismos
Relaxed pose
Man: Going to war? Farewell
Style
• Foreshortening
• Contrapposto
•Transparent drapery

Hegeso Stele, Attica
c. 400 BC
Pentelic marble
Found in the Kerameikos
1.5m high
Servant girl (smaller)
standing in a relaxed pose on the right, wearing a tunic, slippers, hair in a sakkos
holds open box on the knees of a mature woman seated in profile.
Woman (Hegeso) wears a himation (veiled over head) and a chiton.
raises right hand holding a jewel (presumably)
legs rest on a stool-she sits on a klismos (chair)
painted details
fine drapery
elite woman
influence from Parthenon programme
Architectural features
Placed in Kerameikos in family group of graves
Inscription: ‘Hegeso, daughter of Proxenos’
Quiet and contemplative scene: typical of late 5th and 4th BC
Meant to draw attention, its location in the Kerameikos - many travellers pass it
Compare to lekythos
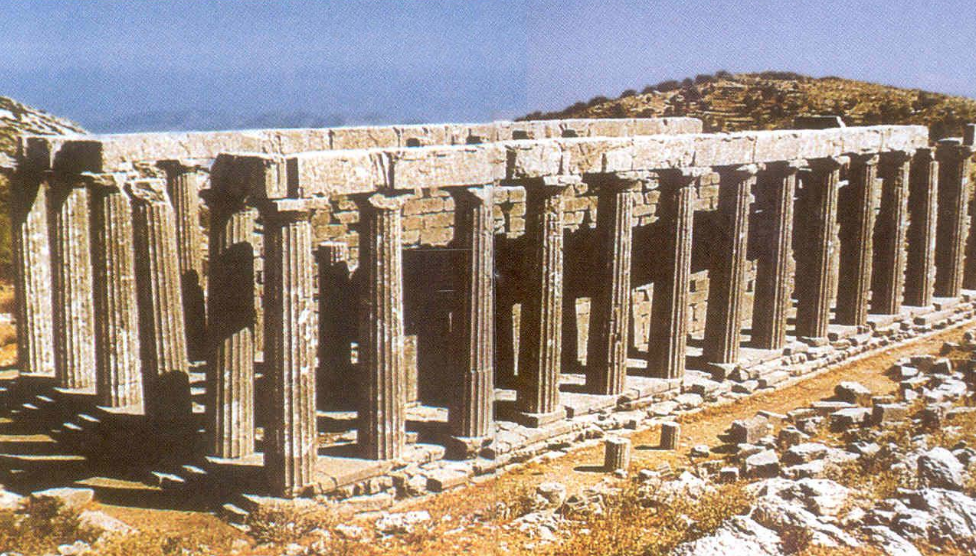

Temple of Apollo at Bassae
c. 400 BCE
Doric peripteral
but has some Ionic elements and one Corinthian column
Dedicated to Apollo Epikourios (helper)
Grey limestone
Architect: iktinos (Parthenon architect)
North-south orientation; north entrance rather than usual east entrance bc the geography dictates it
38.25m long x 14.5m wide
Ionic columns in the cella are actually spur walls meaning the columns are connected to the wall, styled like Ionic columns
In the middle there is one Corinthian column (first evidence in greek arch)
Corinthian column base is more elaborately molded
Another entrance on the east side opposite statue of Apollo- by then associated with sun
Adyton with side door on the east: sun and orientation towards statue of Apollo
So there is a deliberate effect with light where sun shines through entrance and shines on Apollo
Sunken area in the middle of the room
Interior Ionic frieze within the cella:
Amazonomachy- dynamic poses, figures with flowing capes filling the background
Centauromachy- gestures of distress from naked woman rape victim, big hand- another woman kneeling down holding onto a small figure in archaising style because she’s a statue of a goddess- provincial style?
Another Amazonomachy scene- drapery filling the space
figures fill up space right from the top to the bottom
scene shows Achilles about to kill Penthesilea (queen of amazons).
clingy drapery and dynamic movements typical of period
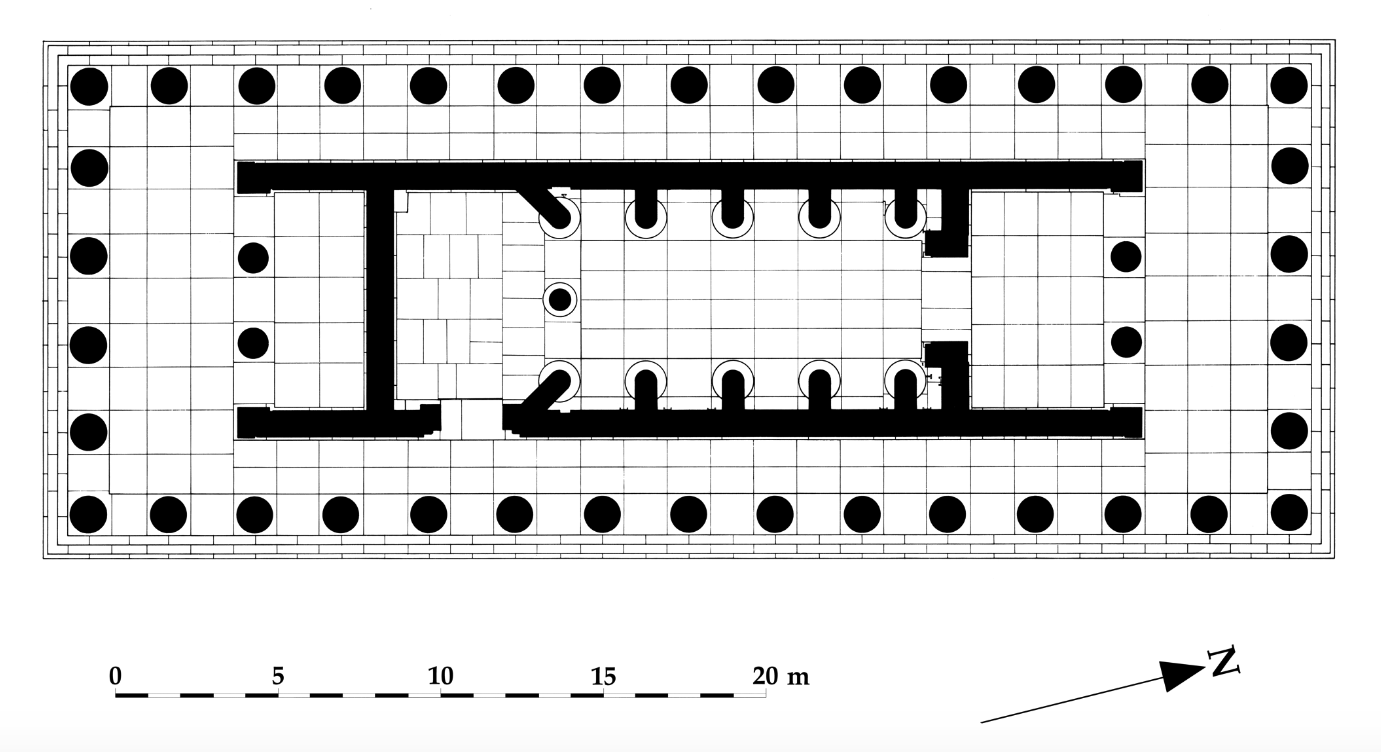
Aerial plan of temple of Apollo at Bassae
c. 400 BCE
Doric peripheral temple
interior colonade is Ionic
singular column is Corinthian
The columns are actually stud walls not columns
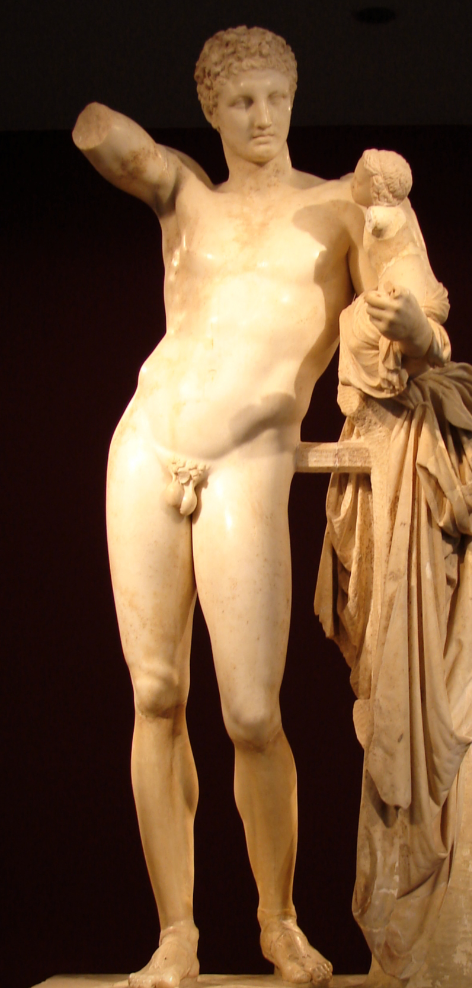

Hermes and baby Dionysus
340 BCE
By Praxiteles
Parian marble
Over life size
Found at temple of Hera at Olympia
Mortal activity- yet gods
Original, found in the Temple of Hera, Olympia
Hermes looks at baby- holds a bunch of grapes teasing Dionysus who reaches out to them
But slender proportions, long legs, small head and s-curve (push up of hips creates an imbalance)
Soft modelling of surface
Realistic heavy drapery
Original or copy?
Sandals, tree-trunk, highly polished marble (more roman) points to a late date but drapery is greek.
Stance influenced by Polykleitos 5th century sculpture
We have pausanius who mentions it being at the temple of hera but maybe he was seeing the original and we are not
Struts e.g. tree trunk is a bit more rare.
Face is very praxitelian - deep set eyes with dreamy quality
smaller mouth than 5th century and nice cupids bow
soft face
treatment of hair- quite full with nice curves
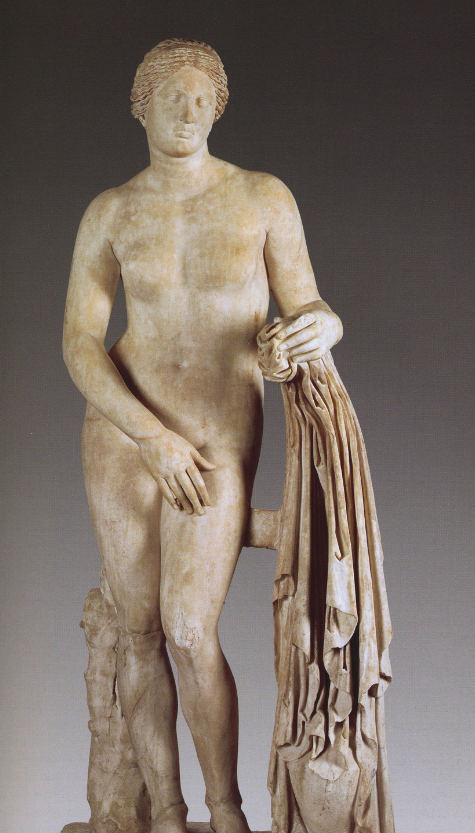

Aphrodite of Knidos
c. 350 BCE
By Praxiteles
Roman copy of Greek original
marble but unknown original material
Over life size
2.15m
Pliny told us:
she should be seen from all sides
height of female beauty
S-curve of body
Soft facial features, slightly parted lips.
Praxitelaisn facial features; arms preoccupied
Parts gilded or painted
Modelling soft and tender
First large female sculpture nude - only wears an armlet
What does the gesture do? Cover up her genitals (bathing)
Who is she looking at? The viewer? Why is she covering up? Sculpture responds to presence of viewer
Fervour that the statue created at the time
Her face and hairstyle became in fashion for sculopture afterwards
Hair- parting with crimped curls, band
Deep-set eyes, small cupids bow small mouth, soft treatment of face

Apoxyomenos (the scraper) ,
c. 330 BCE
By Lysippus
court sculptor of Alexander the Great
Roman copy of Greek original
copy over 2m high
marble but unknown what the original was made of
copy found in Rome
Nude athelete who completed exercise
Strigil - scraping with olive oil to clean away dirt
Stance: contrapposto but relax leg to the side limbs/legs extending to the side and frontal
Slim body, flat cheekbones, compact
Arm stretched with other one in right angle
Out-turned foot, bent knee
Relaxed vs. active sides
Frontality broken to movement in 3 dimensions
Idealised face but looking more real
Staring into distance
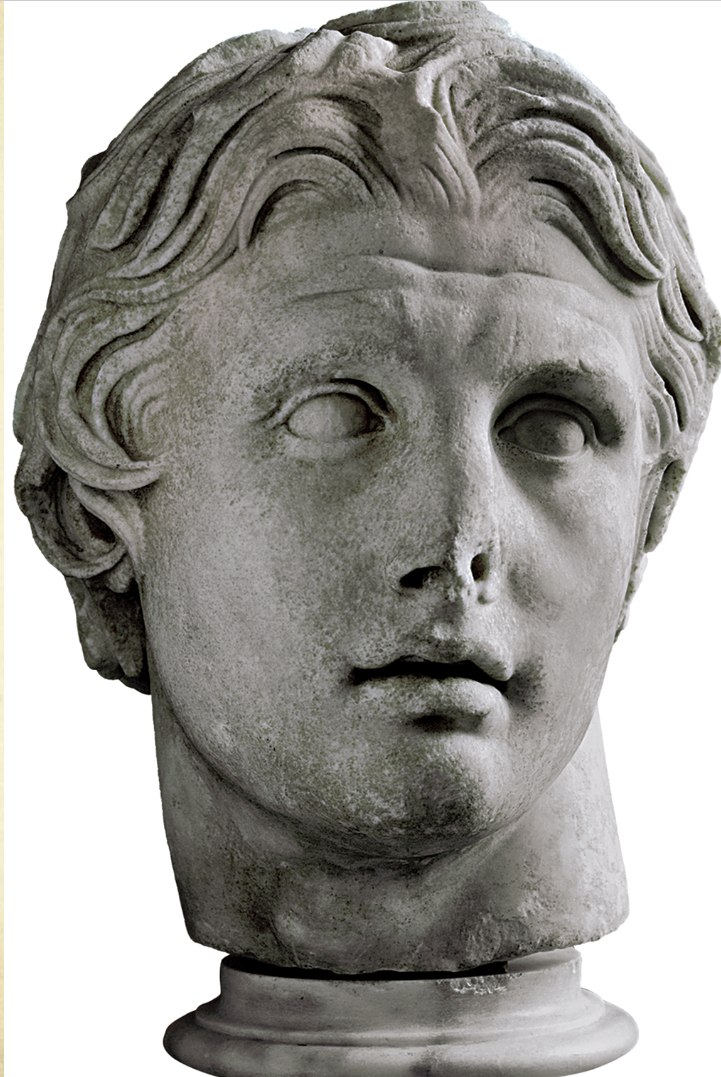

Head of Alexander from Pergamon
c. 200 BC
Found in the lower Agora in Pergamon (western Turkey)
Marble
Pergamene style hair, rounded eyes
No Lysippean portait of Alexander survives
The types however are seen in Hellenistic and Roman statues of Alexander.
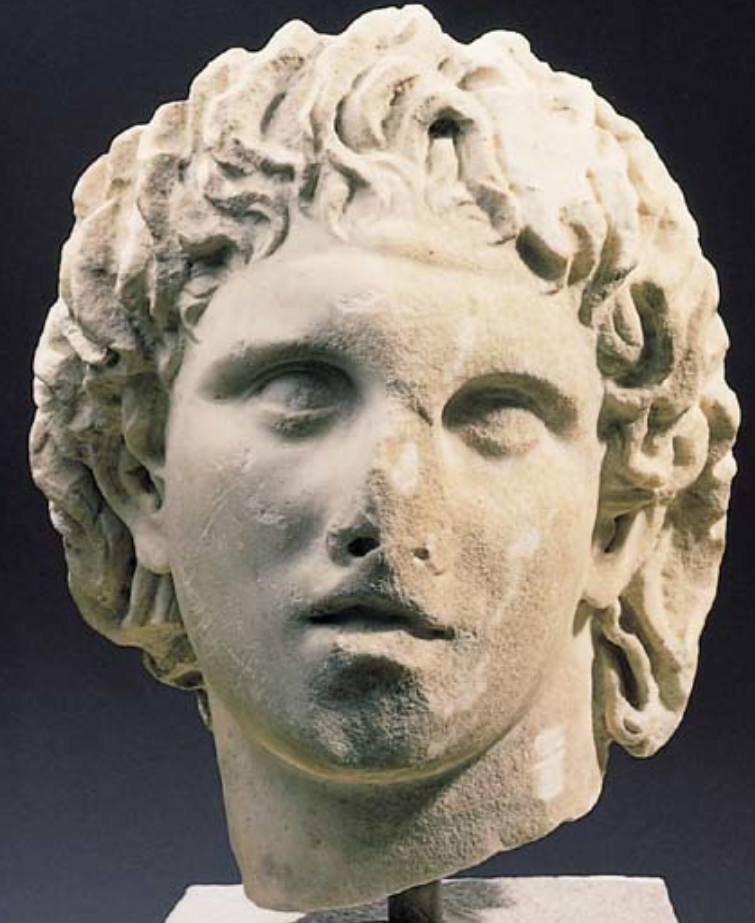

Head of Alexander from Pella
c. 200 BCE
Found in Pella
Marble
Hellenistic, but possibly a copy of a Lysippus portrait
Youthful, no beard
Slightly furrowed forehead
Long mane of hair - lion like
in the middle goes up - an anastole (cowlick)
Tilt of the head and eyes to the left, deep set eyes, mouth slightly open
Breathless quality, turns for attention
A charismatic military leader
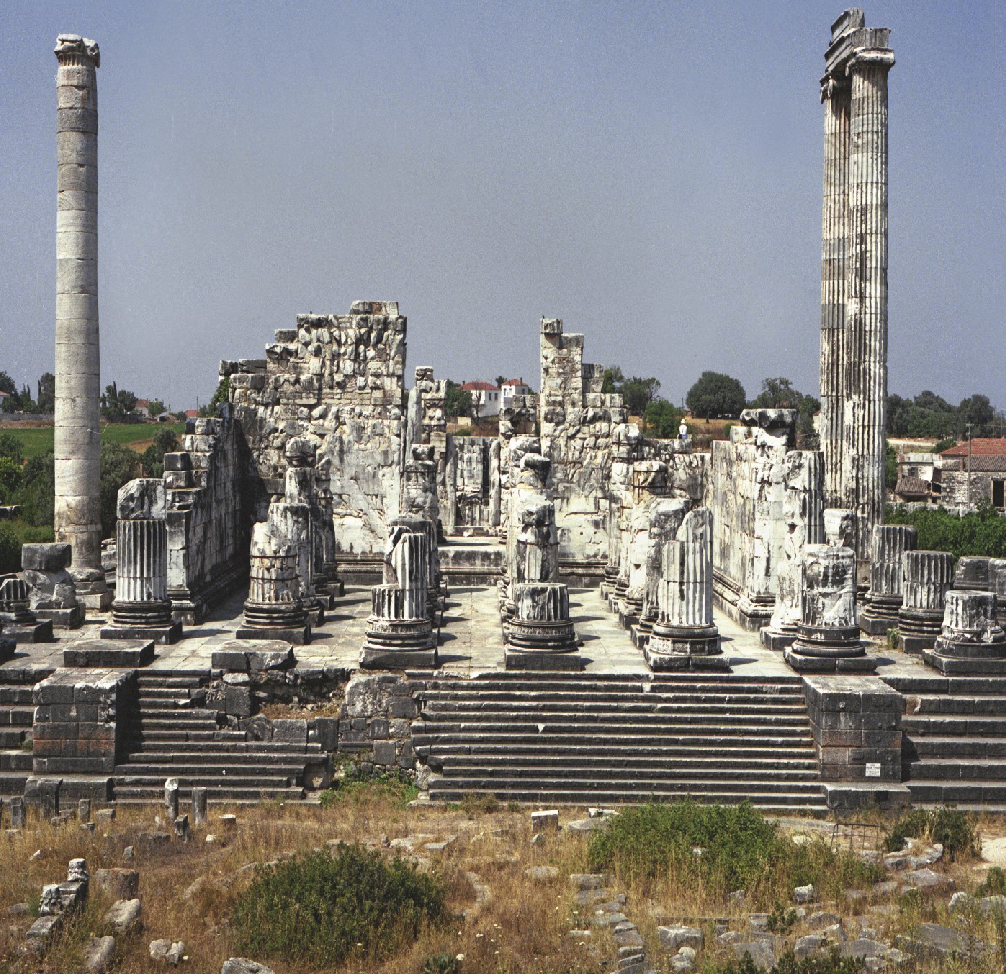

Temple of Apollo at Didyma in Ionia
c. 330 BCE
Marble
Columns nearly 20m high - very tall
Ionic building
height and levels used in this temple to create a different experience for those entering
Housed an oracle of Apollo
Architects:
Daphnes of Miletus
Paionios of Ephesus
Eastern facade - entrance
large staircase leading to stylobate with Ionic columns
Two peristyles - dipteral building
The pronaos contains 12 columns
there is no opisthodomos
The columns have a roof over - it would have created a lot of darkness
there was a forest of columns which would have been fairly dark
an interesting experience for those visiting the temple
Then there was an open air courtyard
Viewers’ experience: depth and height of structure - makes you feel small
very different experience to other temples
Architects’ sketches have survived on interior walls
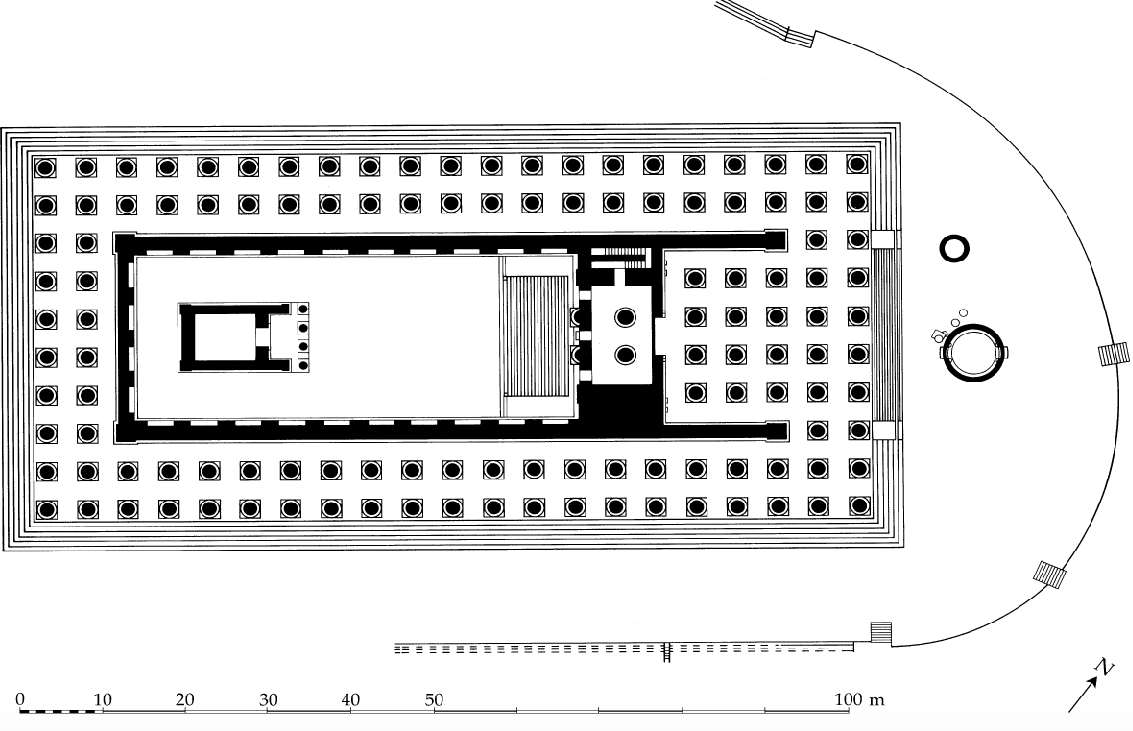
Plan of Didyma
c. 330 BCE
Marble
Huge amount of columns is clear from the image
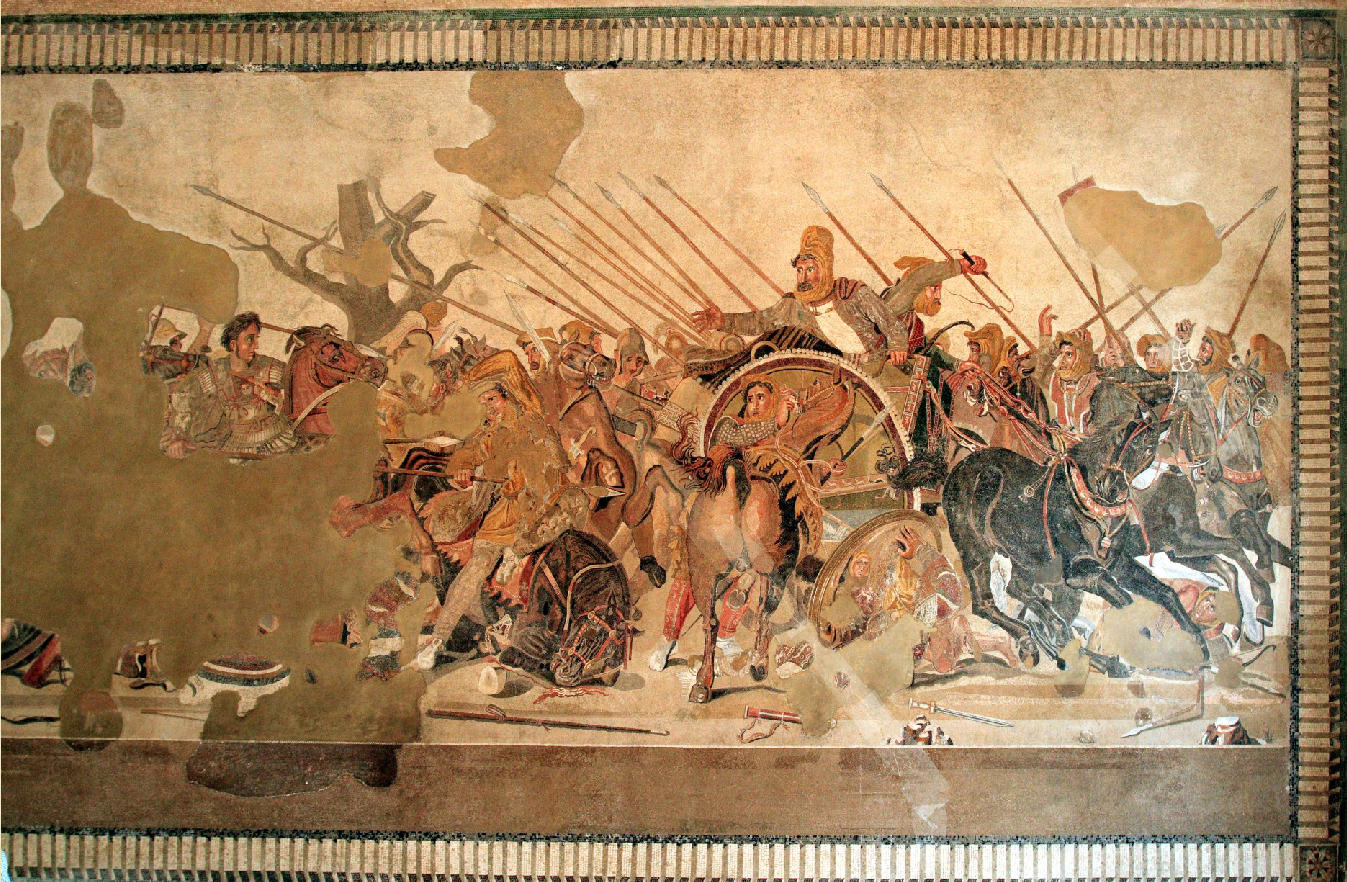

The Alexander Mosaic
100 BCE
From House of the Faun at Pompeii (floor mosaic)
c. 5m x 3m
1.5 million tesserae
Pliny the Elder mentions the painting by Philoxenos of Eretria ca. 330-320 BCE
Depicts Battle of Issus
Interest in fortune and fate
Action and arrested action
Alexander has a medusa on his breastplate
Incredibly detailed, volume added by shading
We can use this to infer about Hellenistic wall painting
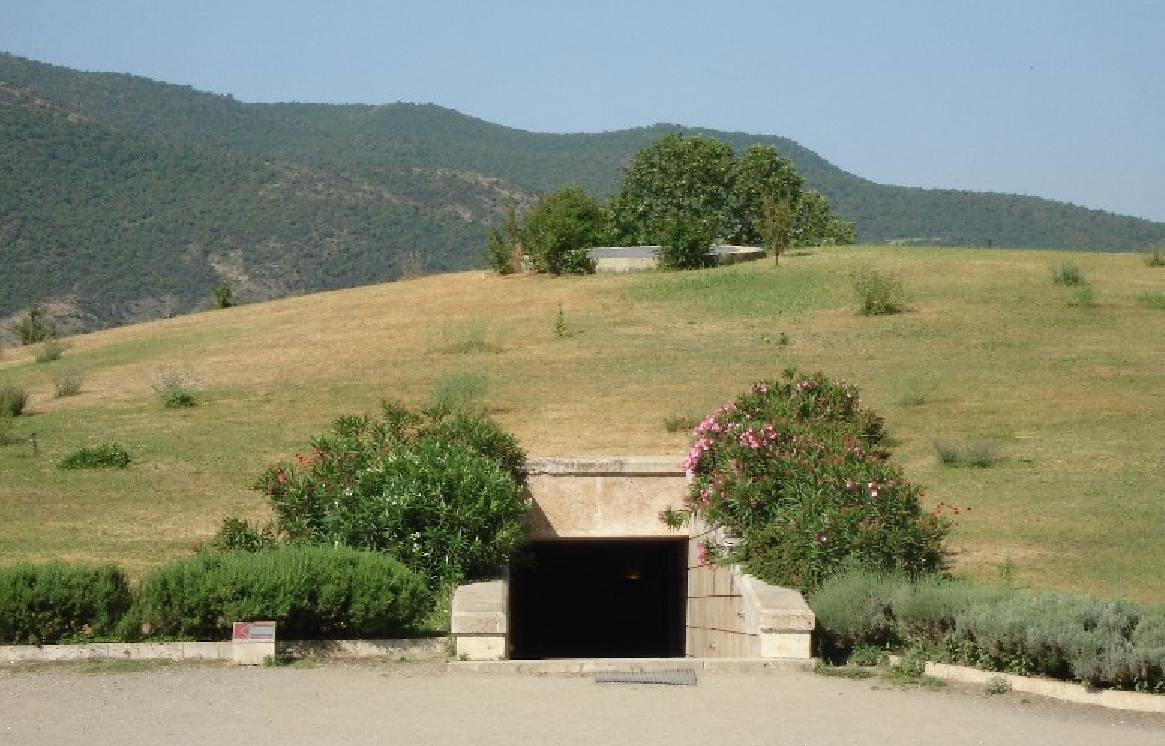

Ancient capital of Macedon: Aigai (modern Vergina)
Most famous for the built chamber tombs of the fourth century and Hellenistic period
Found at Vergina, Pella and elsewhere
Façade with lintel and painting
Type favoured by royalty and regional chiefs
Great Tumulus at Vergina (3 tombs)
Tomb I (of Persephone) and Tomb II
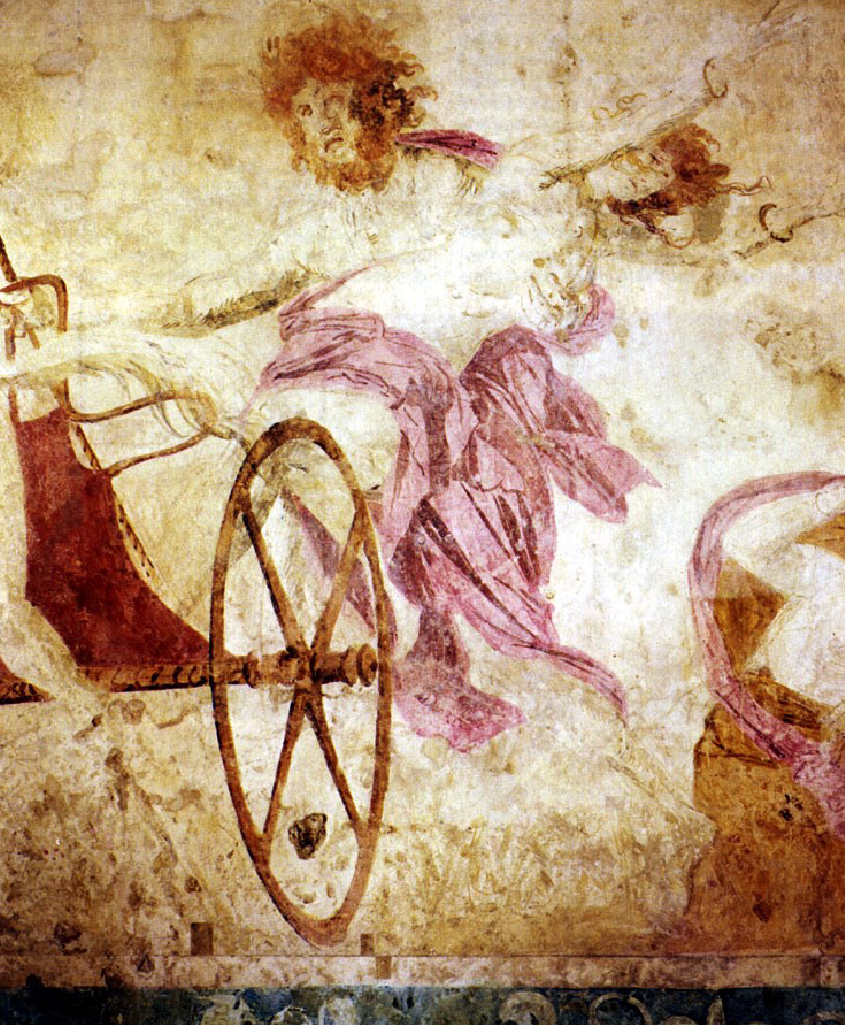

Tomb I - Tomb of Persephone
c. 340 BCE
Painting shows Hades abducting Persephone
also Demeter and 3 fates
Forshortening for chariot wheel achieved by shading
Faces show high drama
Body movement - high drama
Impressionistic brush strokes
Tombs were for elite families
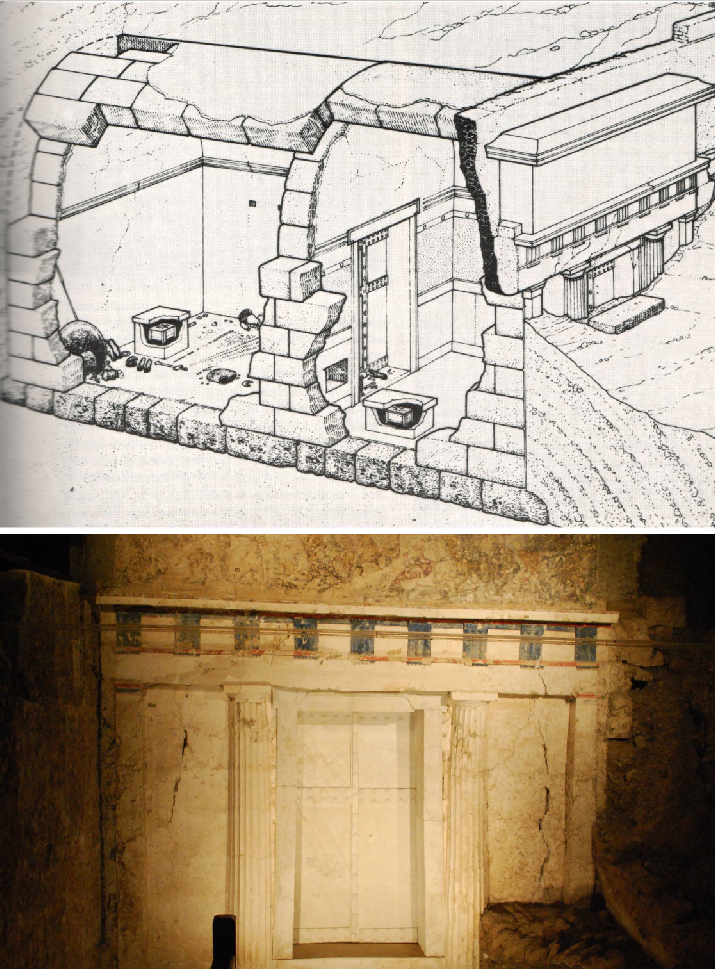
Tomb II
Mid to late 4th century
No interior paintings
There is an Ionic frieze on the facade - hunting scene
Man and woman buried inside
possibly Philip II
Illusion of palace architecture - columns and metopes carved into the tomb walls
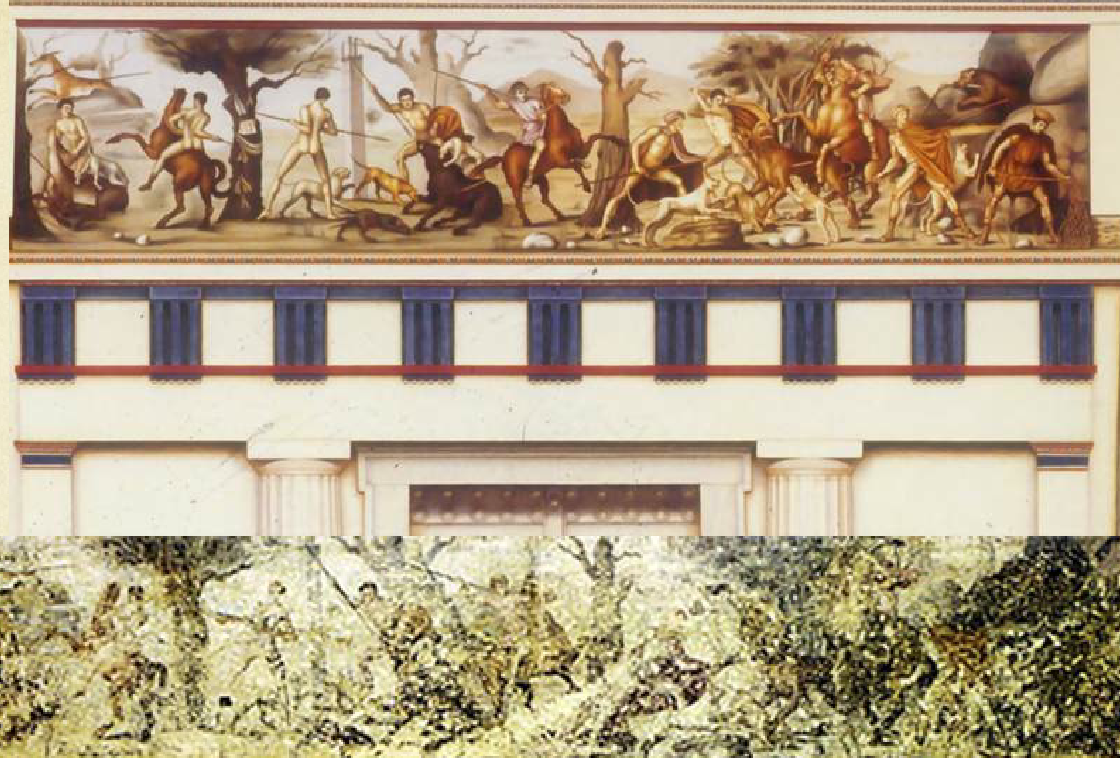

Tomb II Ionic Frieze
Mid to late 4th century
Painted on plaster
Men hunting naked and clothed, on horseback and on foot
Macedonian hat
One figure wears a purple garment - royalty
Many animals, including lions, boars, bears and deer
lions don’t seem to have lived until this point so might be a mythological scene/imaginary hunt
Heroic nudity
Scene of an ideal hunt, not realistic scene

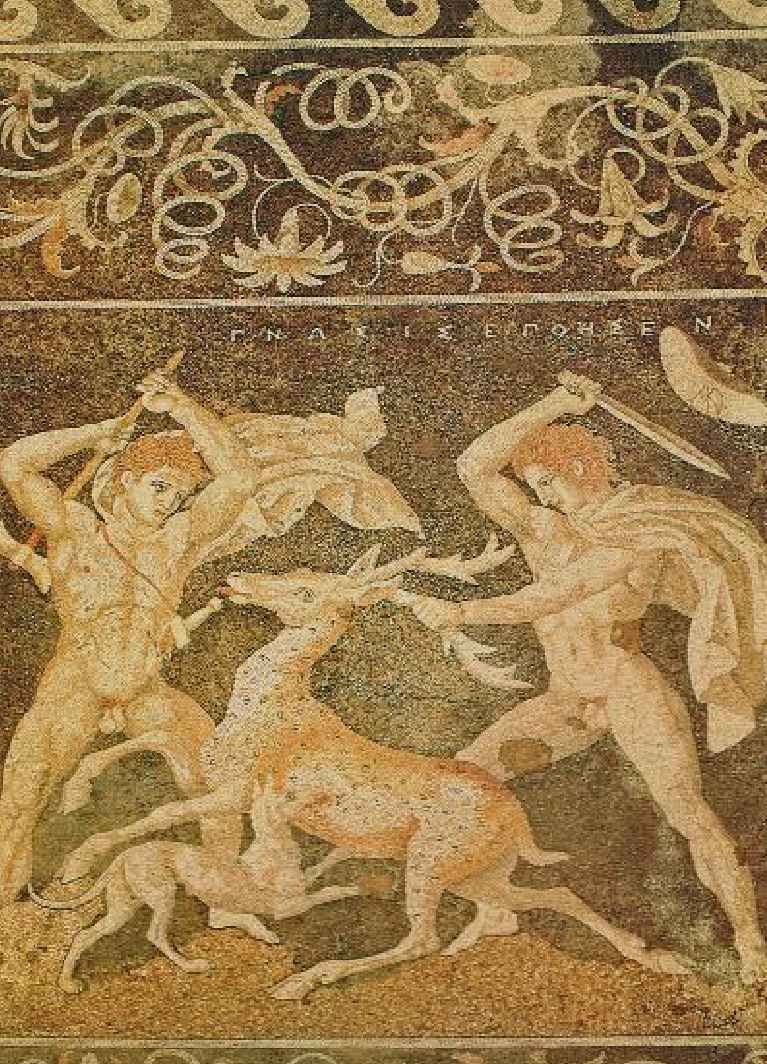
Mosaic of Olynthos
First half of 4th century
Pebble mosaic
pre tesserae
Two toned
Bellophron and Chimera - mythological scene
Abstract designs around it

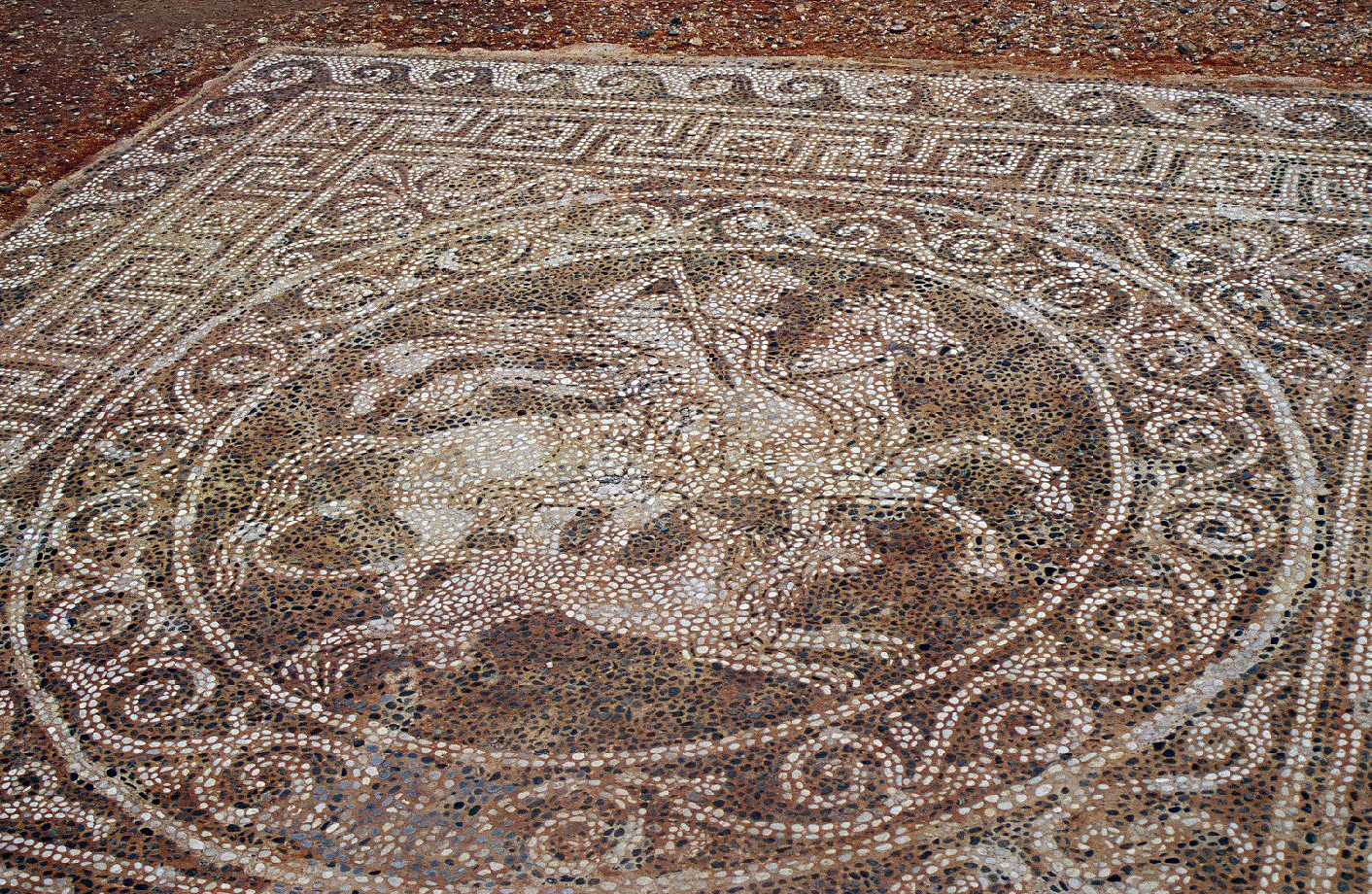
Pebble Mosaic from Pella (capital of Macedon), Macedonia,
Later 4th century
From Pella, Macedonia
Designed by Gnosis (name added at the top)
Wave pattern (like at Olynthos)
Floral designs
There is much more detail
Light figures against a dark background (like at Olynthos)
Figures more advanced, musculature achieved by shading
Pebbles more closely packed, more colours used
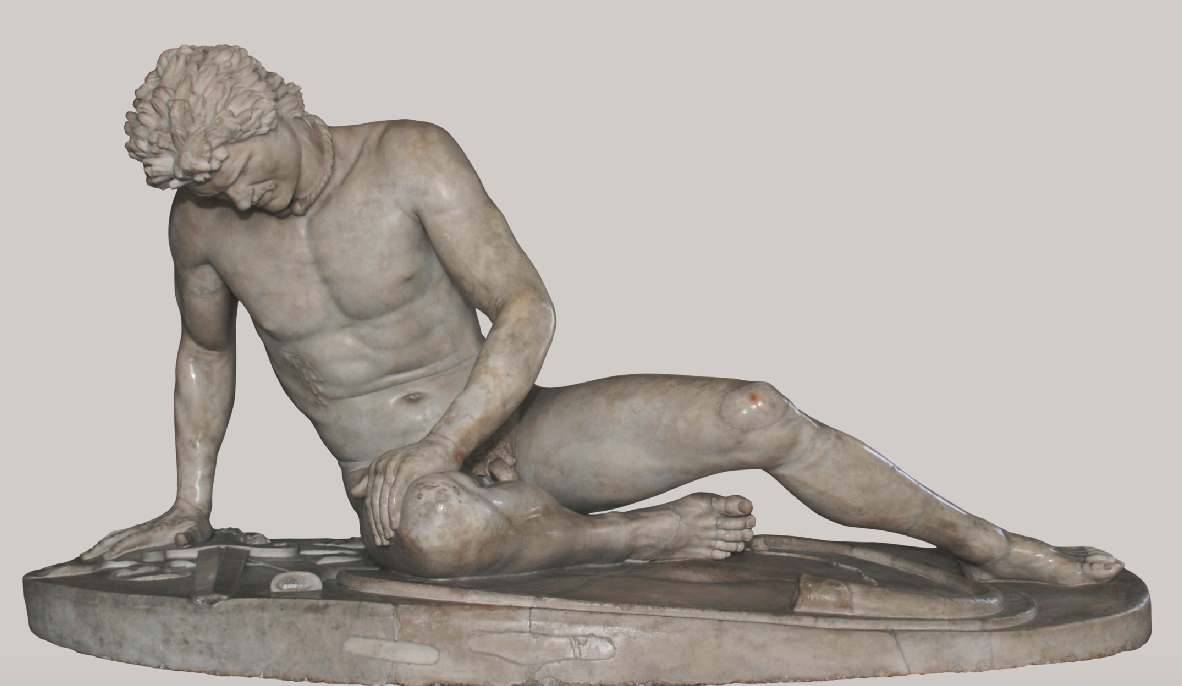

Dying Gaul
ca 220 BCE
A copy of a Hellenistic original in marble
original thought to have been bronze
95 cm height, 1.85 length
Clearly a foreigner as he has a moustache and is wearing a torque (a necklace associated with the Gauls and Celts)
Hair rendered in thick textured strands
they used lime water to style thier hair
He is in a state of quiet agony
anguish in the face
wrinkles
bulges of brows
his lips are closed and he is quiet
He is about to die
sad depiction of a foreign opponent
Nude: heroic and vulnerable
Slow twist of figure to be seen from more than one angle
Style known as Hellenistic baroque
later 3rd century BCE and esp. 2nd BCE
emotion and drama
interested in textures, very detailed
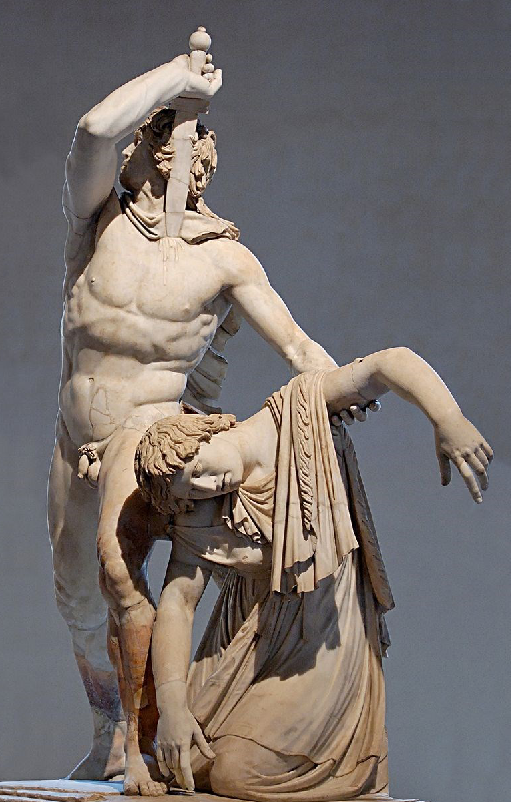

Ludovisi Gaul and His Wife
ca 220 BCE
Epigonos
Hellenistic Baroque style
Roman copies of bronze original
He seems to be killing himself and his wife is dead
possible that he killed her because he didn’t want her to be taken captive
but no evidence that he killed her so we don’t know who did and why she is dead
Focus on the dignity of the opponent
makes the Romans look better - they defeated such a great opponent
Dramatic twisting of the body
made to be viewed from multiple angles
Interested in different textures especially hair and textiles
huge attention to detail - fabric curves around the contours of the body
He is not showing much emotion
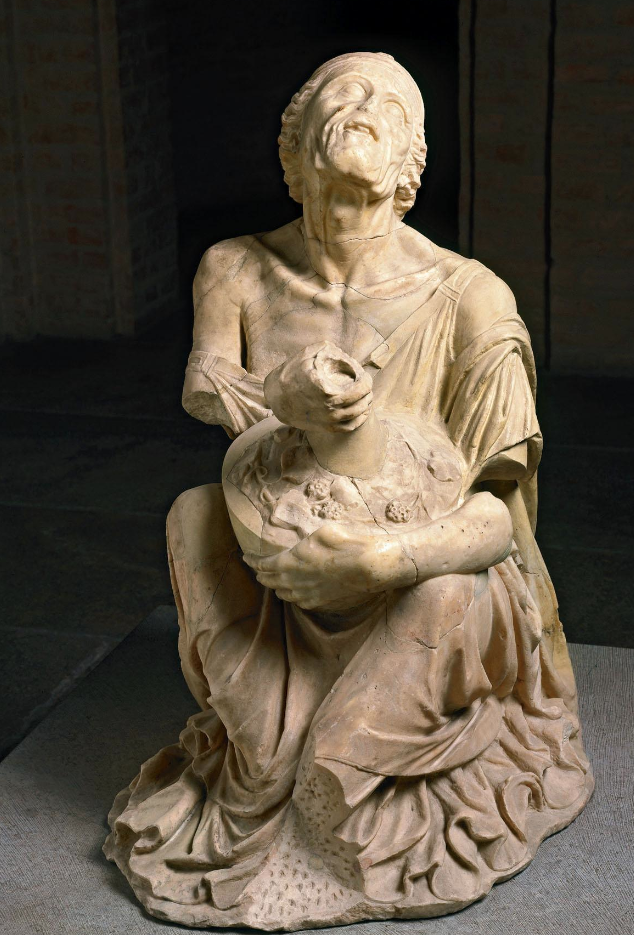

Old Drunken Woman
Roman copy of Greek original
Late 3rd century BCE
Around 90cm high - smaller than life-size
Holding ivy wreathed wine jar
Jar is called a lagynos used in Dionysiac Festivals
Ptolemaic kingdom
Votive offering for Dionysus? Showing a participant of the festival?
Is she drunk?
her mouth is slightly parted - laughing, shouting?
Realism:
aging body, exposed bony shoulder
vanished sexual attraction
usually showing a shoulder would be attractive but this is not the case here
wrinkles on face
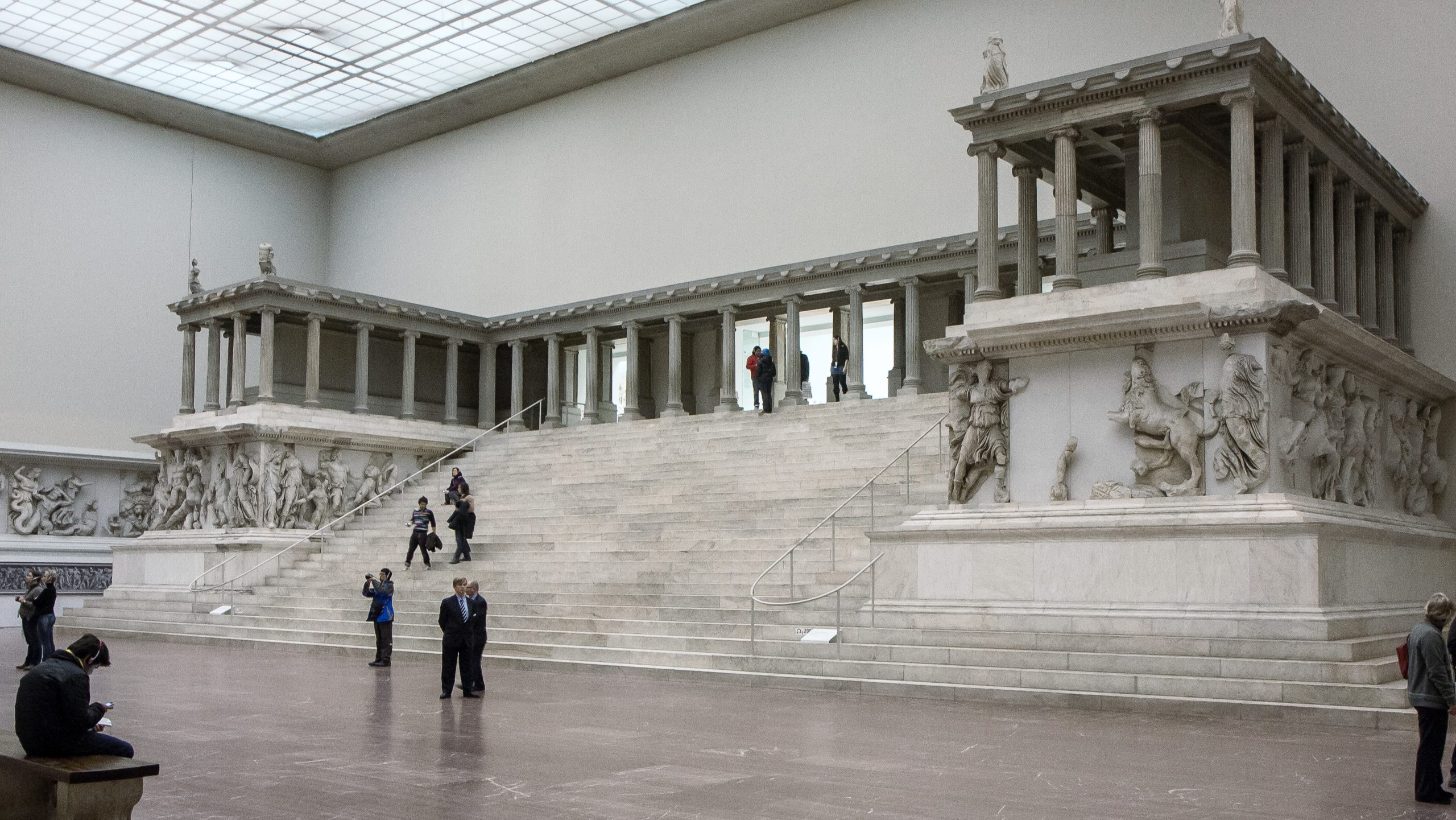

Altar of Pergamon
c. 160 BCE
Ionic style building
Made of marble
Dedicated to Zeus and Athena
Has a monumental staircase that leads the visitor up to the altar
Contains a large sacrificial altar in an open air courtyard in the centre
Decorated with an Ionic frieze of the Gigantomachy - incredibly detailed
figures are anatomically accurate
the figures have armpit hair, finger nails etc
Chiaroscuro - balance of light and dark
Lots of interlocking poses
A masterpiece at the height of the Hellenistic period
The gods are victorious
sense of order being triumphant over chaos
Gods vs Giants - gods are clearly winning
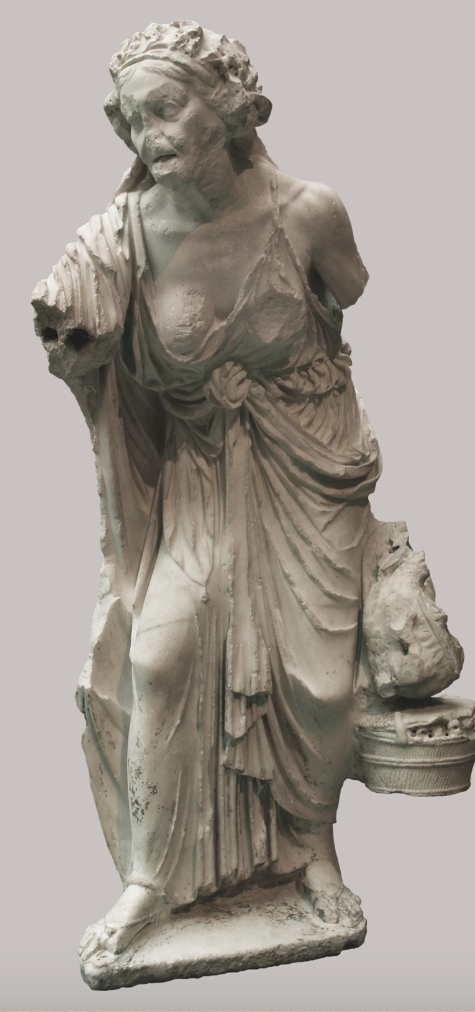

‘Old Market Woman’
Roman copy of a Greek original
Late 2nd century BCE
Around 1.50m high
Old woman: wrinkled face, sagging skin, thin
rib cage , stooped over carrying a basket full of objects
Coming from or bringing to market
Exemplies interest in new subjects:
shows elderly person
works in labour not a position of high society
concentration of effects of aging on the body - toothless
more focus on realism
Unexpected: wearing a wreath of grape leaves, wearing a fine dress held by metal fasteners (not wearing rags)
was she celebrating the City Dionysia?
was it a votive for Dionysus?
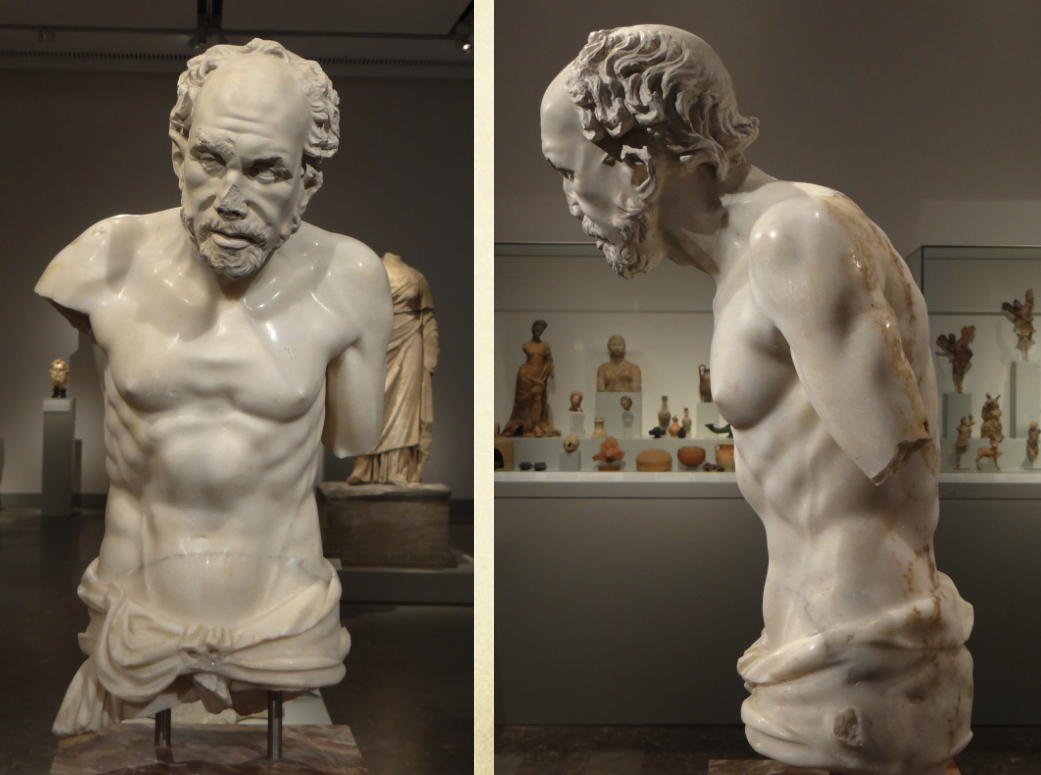

Old Man
From Aphrodisias in modern western Turkey
Aphrodisias is a centre for sculpture
200 BCE
Life size figure
Made of marble
Showing body in a realistic way - no more idealism, sculptors are now interested in depicting realistic bodies
Again shows the way that the body ages realistically
It is leaning forward towards the viewer - confronting them with the inevitability of aging
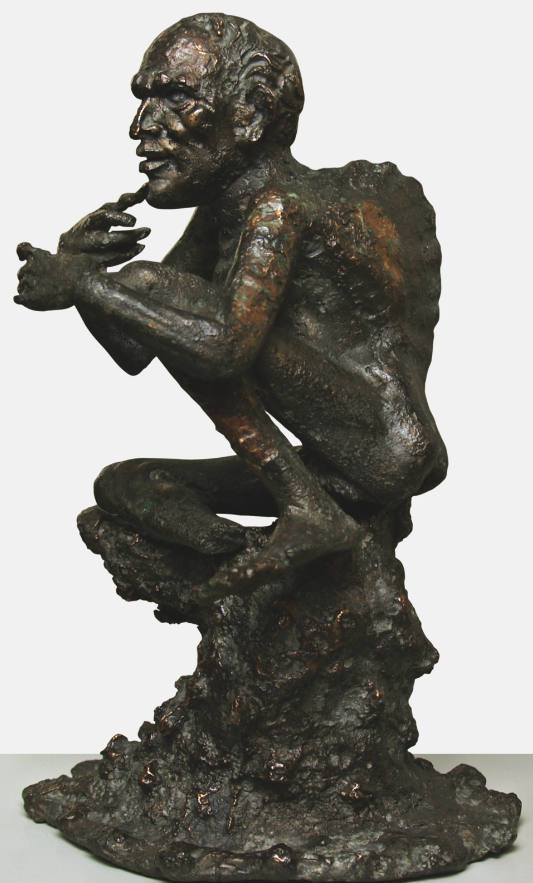

Small Bronze Figurine (Berlin)
Hunchbacked
Bodily proportions: head too large for the body
Where are these images made?
Alexandria? Large sculpting industry
Objects/painting showing interest in disease or mental disability
Purpose:
medical examples
magical amulets? apotropaic function? (e.g. Medusa)
satire? humour?
expensive materials
perhaps unlikely to have been used for teaching
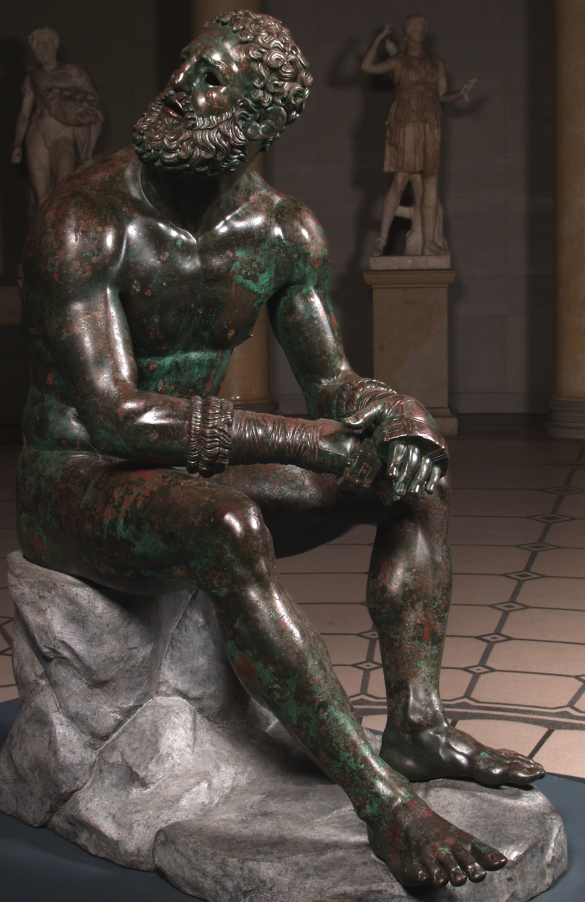

Terme Boxer
c. Late 2nd century BCE
c. 1.80m
Bronze Greek original
Wearing his boxing gloves and has cauliflower ears
Athletes known from 6th century BCE
not a new subject but shown in a different way
Aging face
not an idealised athlete which we had before
Copper effect - lips and nipples in copper
Sharp twisting of face and torso
seems to be responding to something
possibly resting after a match
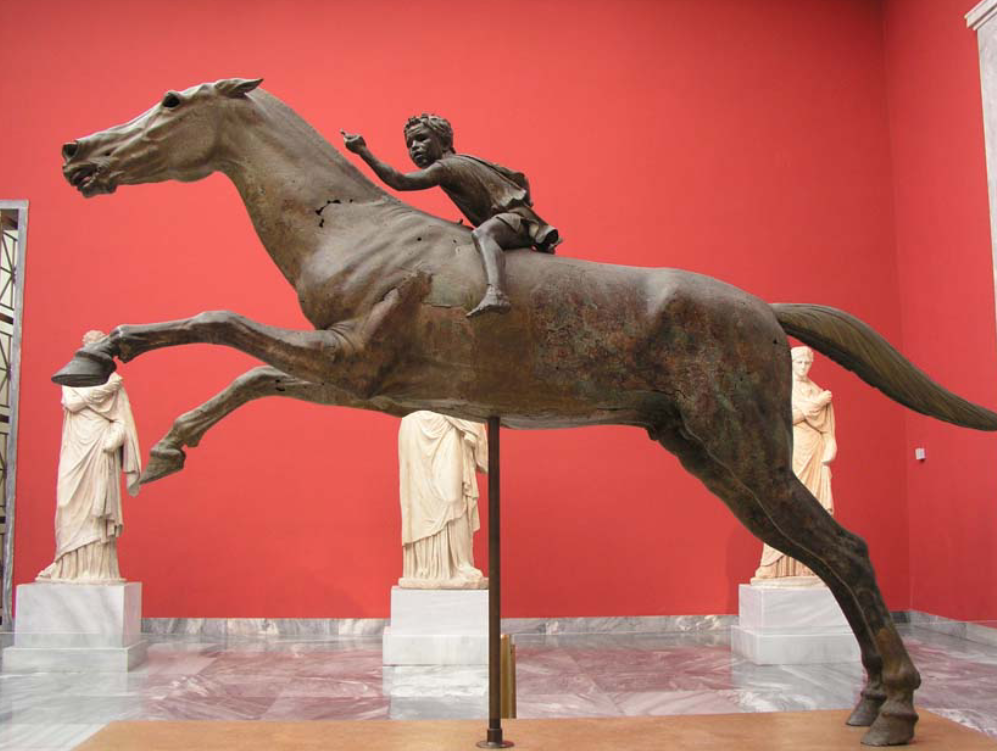

Horse and Jockey from Artemisium
Original Greek bronze
Late 2nd century BCE
Found in a shipwreck
often the case when Greek originals are preserved
Could be an athletic victory monument for a horse race
the patron of the horse who won the race would often erect and display sculptures in Greek sanctuaries to celebrate their success
Jockey: 80cm height
boy of African origin?
Hellenistic interest in depicting other peoples e.g. the Gauls
Belong together with the horse?
the two pieces were put together, they weren’t made together
were they made to be together - the boy does seem small in comparison to the size of the horse
Energetic motion of the animal - leaping into the air
this is fairly unique - most other horses in sculpture before this appear stationary
there is huge detail in the horses anatomy
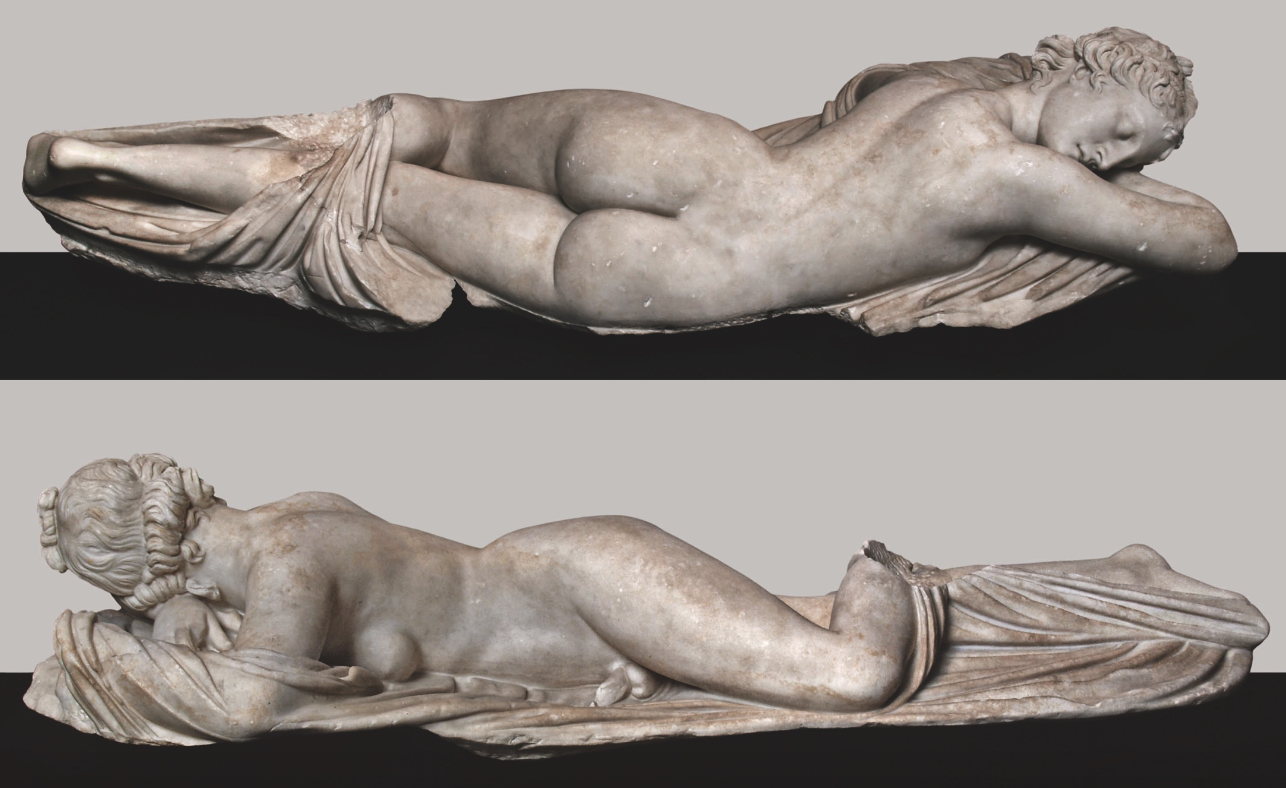

Sleeping Hermaphrodite
Unusual to see sleeping sculpture before this
Roman copy of Greek original from the 2nd century BCE
1.5m length
Sleeping figures usually shown in vase painting
New sculpted form in the Hellenistic period
Aim to direct/stir viewers’ experience
Defies expectations of viewer
Viewer observes but the figure doesn’t engage with the viewer - they are asleep
Passive form
The figure is asleep
There are multiple Roman copies
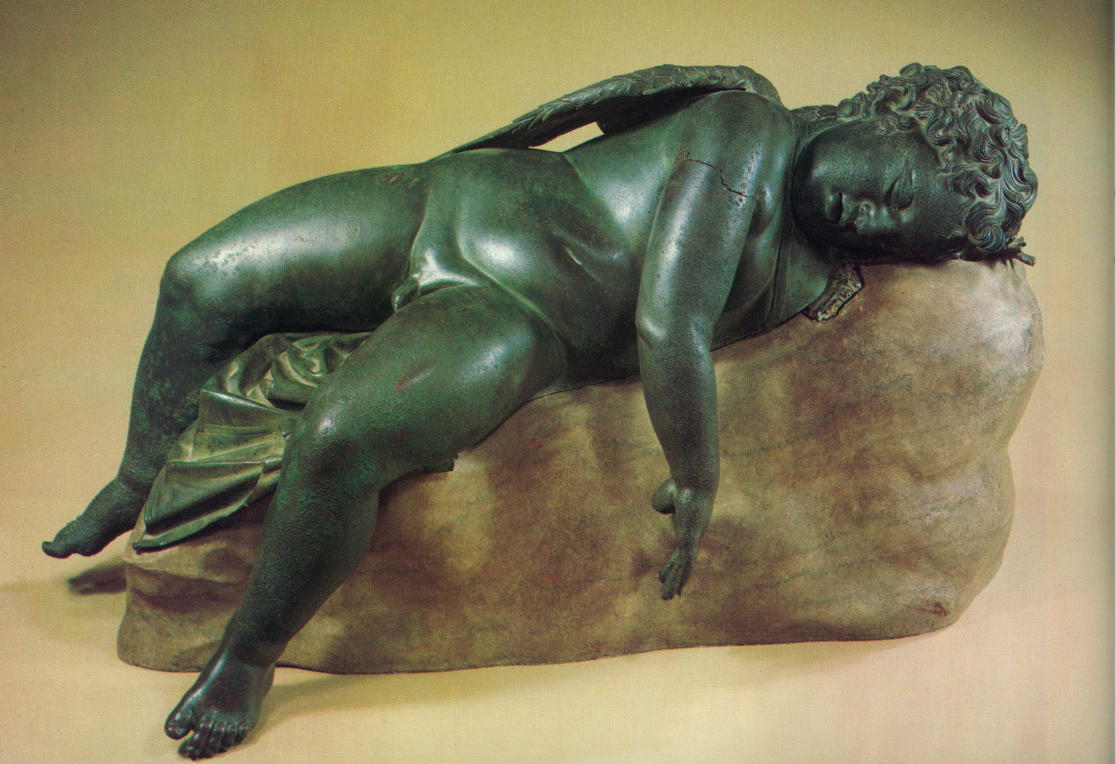

Sleeping Eros
Bronze Greek original
150-100 BCE
80 cm long
Child-like sleep
Wings in back; stone is a modern addition
Original find spot unknown
Eros creating trouble
but asleep so can’t cause trouble
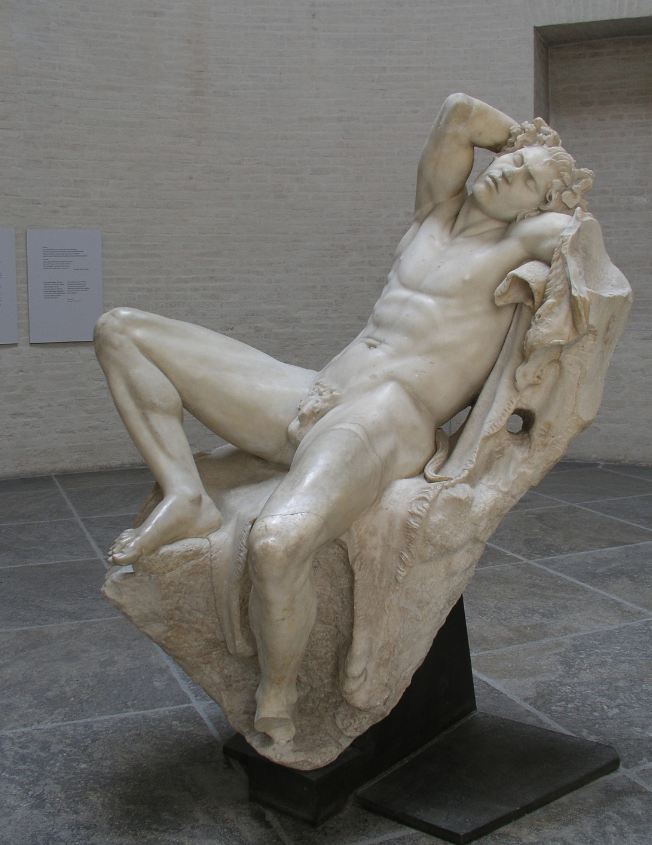

Barberini Faun (Satyr)
c.200 BCE
Greek original
2.15m height
Follower of Dionysus but live in woods
trouble makers, but asleep so can’t cause trouble
Asleep
Made of marble
Idealised male
Uneasy sleep?
he is frowning
Grape leaves in his hair and has a tail
Animal skin on rocky surface
Dormant figure at sleep
Viewer looks but is not observed
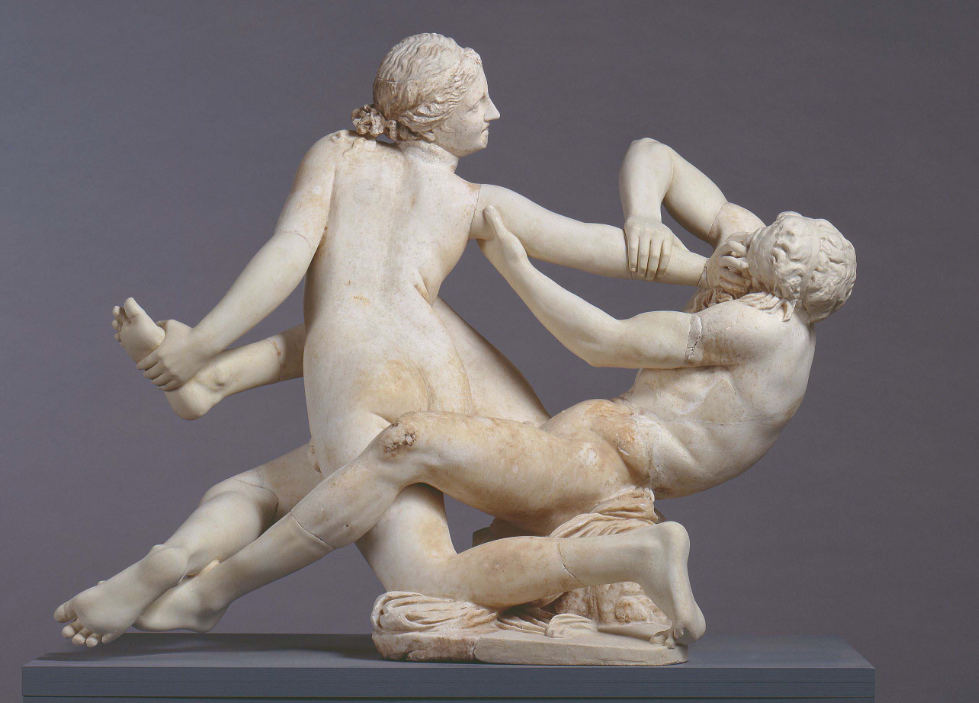

Dionysiac Realm
This is a Roman copy, the original from the 2nd century BCE
Marble
Semi-erotic in nature
Satyr struggling with hermaphrodite
Struggling or playful?
Intertwined groups
sculptors enjoy showing intertwined groups
Sculptural show off in 3D
Light subjects
Variety of points of view to look at sculpture at all sides
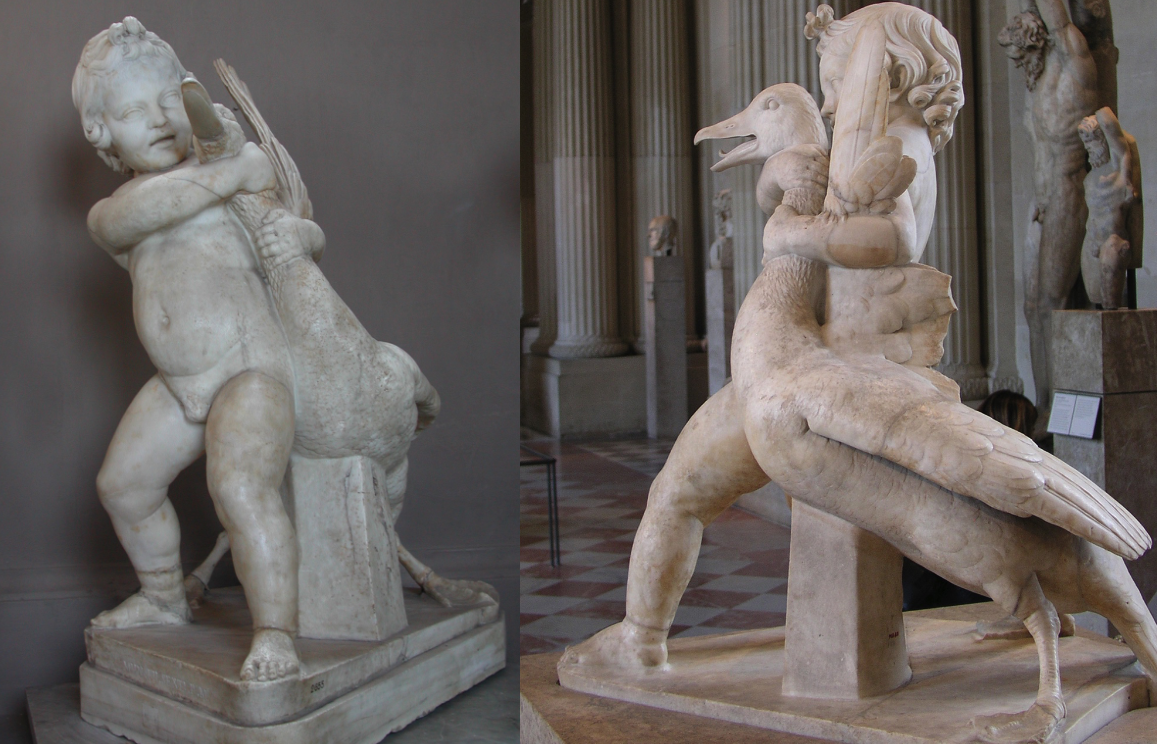

Boy strangling Goose
Original from 150 BCE; Roman copy
Babies and children become popular subject matters
interest in children starts in the 4th century e.g. Hermes and Dionysus by Praxiteles
Behaving like children - cuddling the goose but the goose is trying to get away
Sculptor: Boethus of Chalcedon
Over 40 Roman copies survive - various poses
incredibly popular statue
Multidimensional composition
An ordinary scene