Practical 3 wishlists
1/129
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
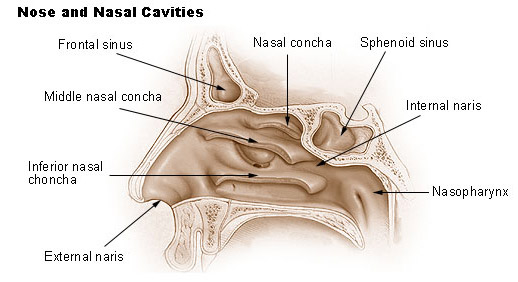
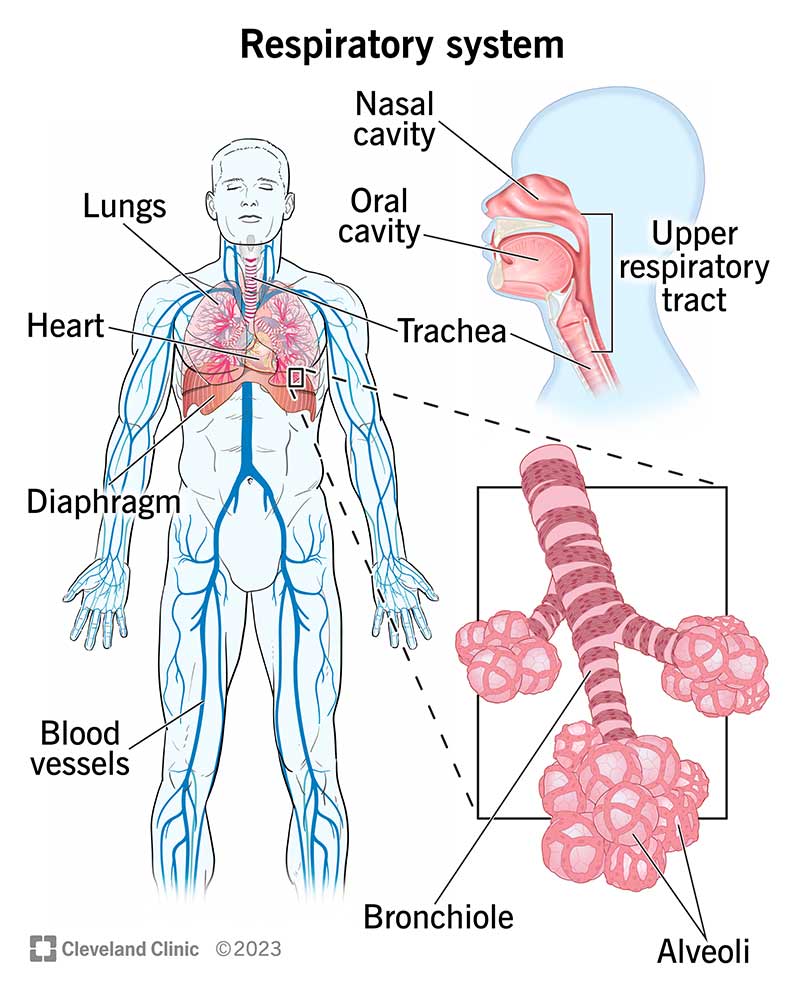
external nares
aka the nostril; the outer opening of the nose that allows air to enter the nasal cavity; starting point of the respiratory tract, where inhaled air is filtered, warmed and moistened before moving deeper into the body
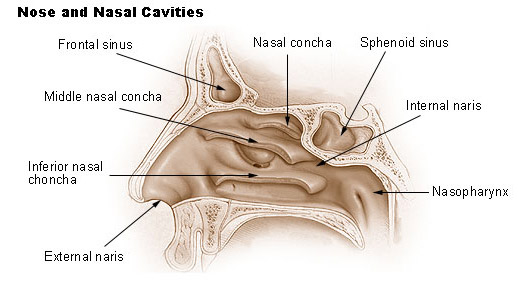
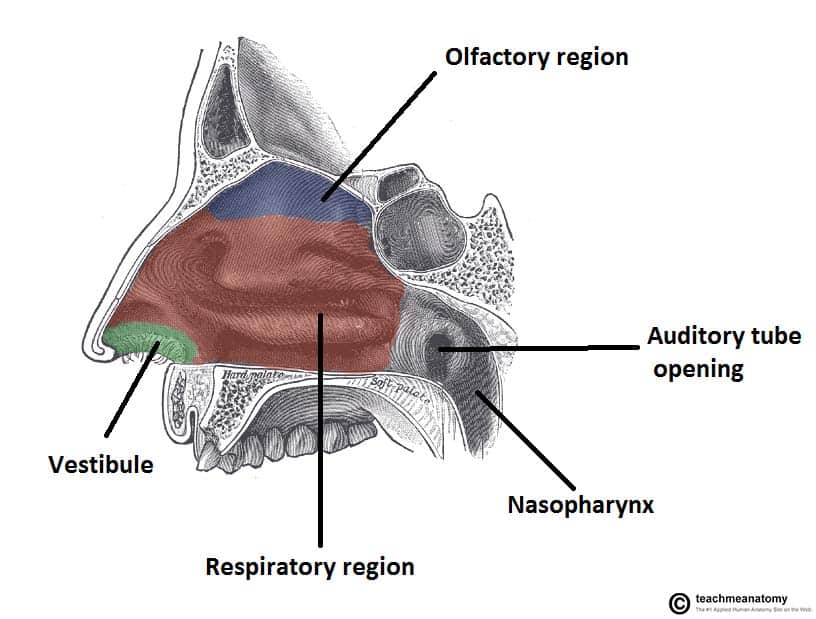
nasal vestibule
the most anterior part of the nasal cavity, located just inside each nostril; lined with skin nd contains coarse hairs that act as a filter to trap dust, dirt and other particles from inhaled air, preventing them from entering the lungs
nasal cavity
the interior space of the nose that extends from the nostrils to the nasopharynx (upper part of the throat)
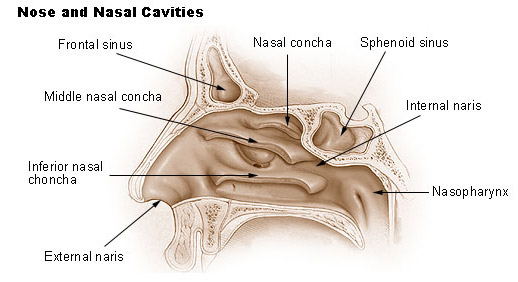
nasal conchae
bony structures located within the nasal cavity; play crucial roles in regulating airflow, warming and humidifying air, and filtering particles
oral cavity
the mouth; the initial part of the digestive system a complex structure that plays essential roles in digestion, speech, and oral health
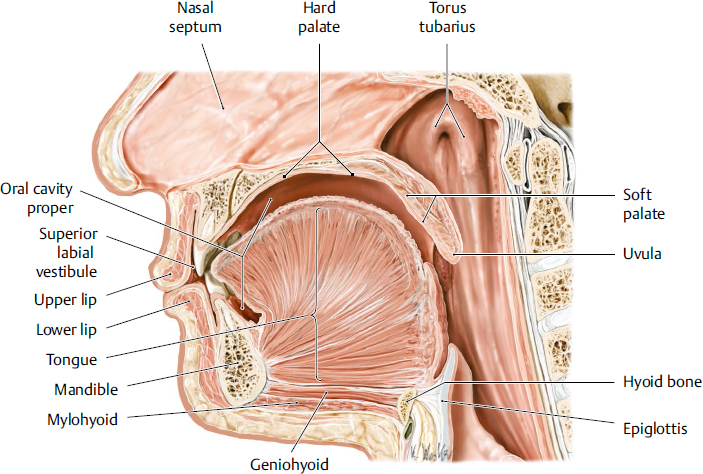
tongue
a muscular organ located in the oral cavity that plays crucial roles in taste, speech and swallowing; innervated by hypoglossal nerve
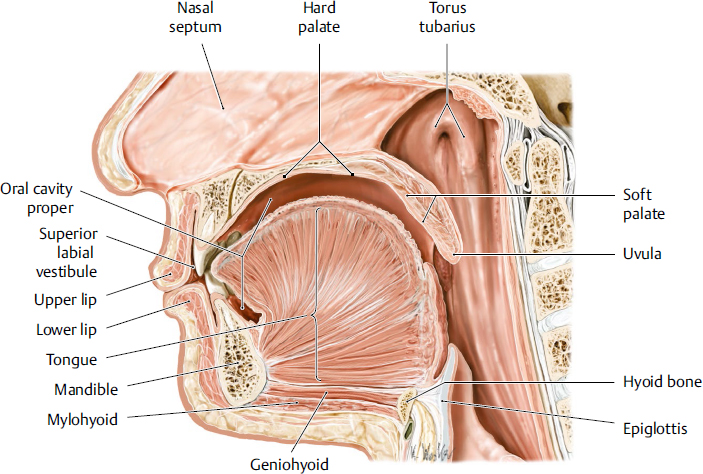
hard palate
the bony roof of the mouth, forming the anterior portion of the palate; located between the upper teeth and the soft palate; composed of part of the maxilla and palatine bones; separates oral cavity from nasal cavity
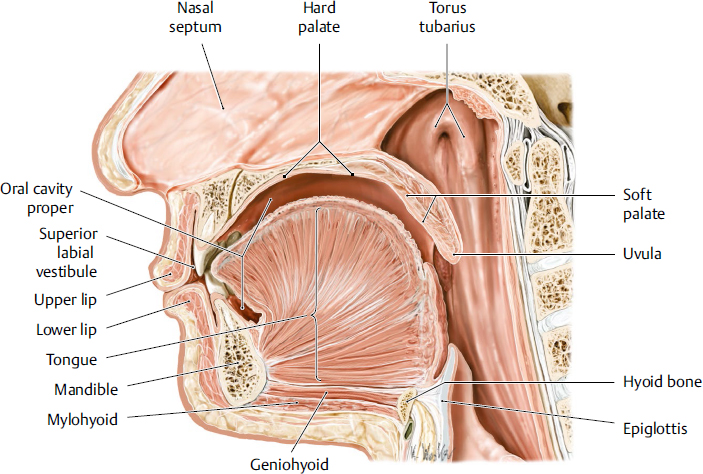
soft palate
the muscular, flexible back part of the roof of the mouth that separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity; primarily functions to aid speech, prevent food from entering the nasal cavity and aiding breathing
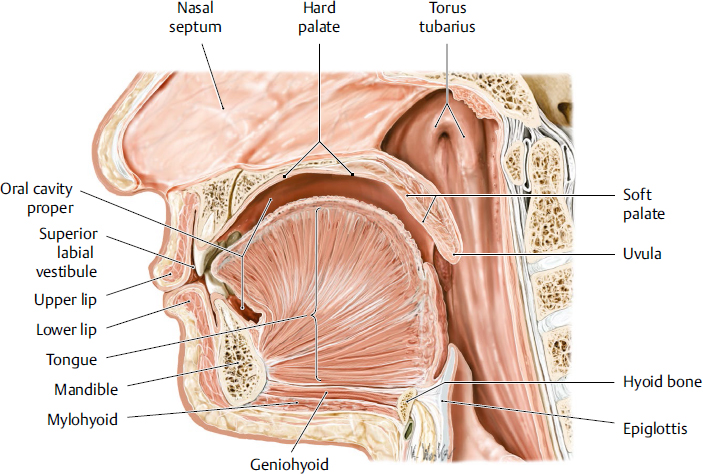
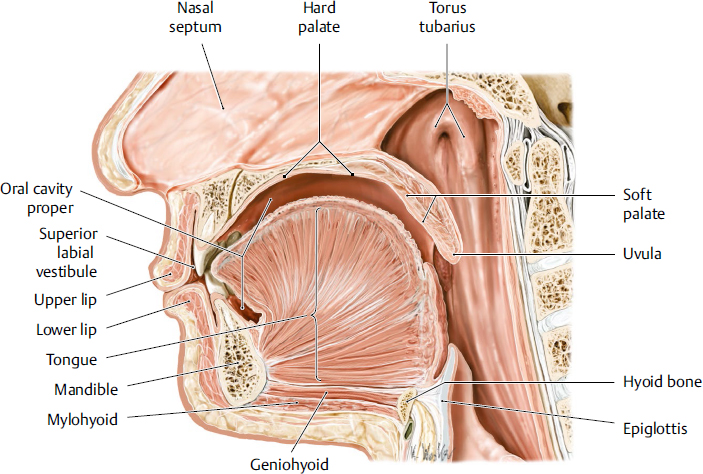
uvula
a fleshy extension at the back of the soft palate which hangs above the throat
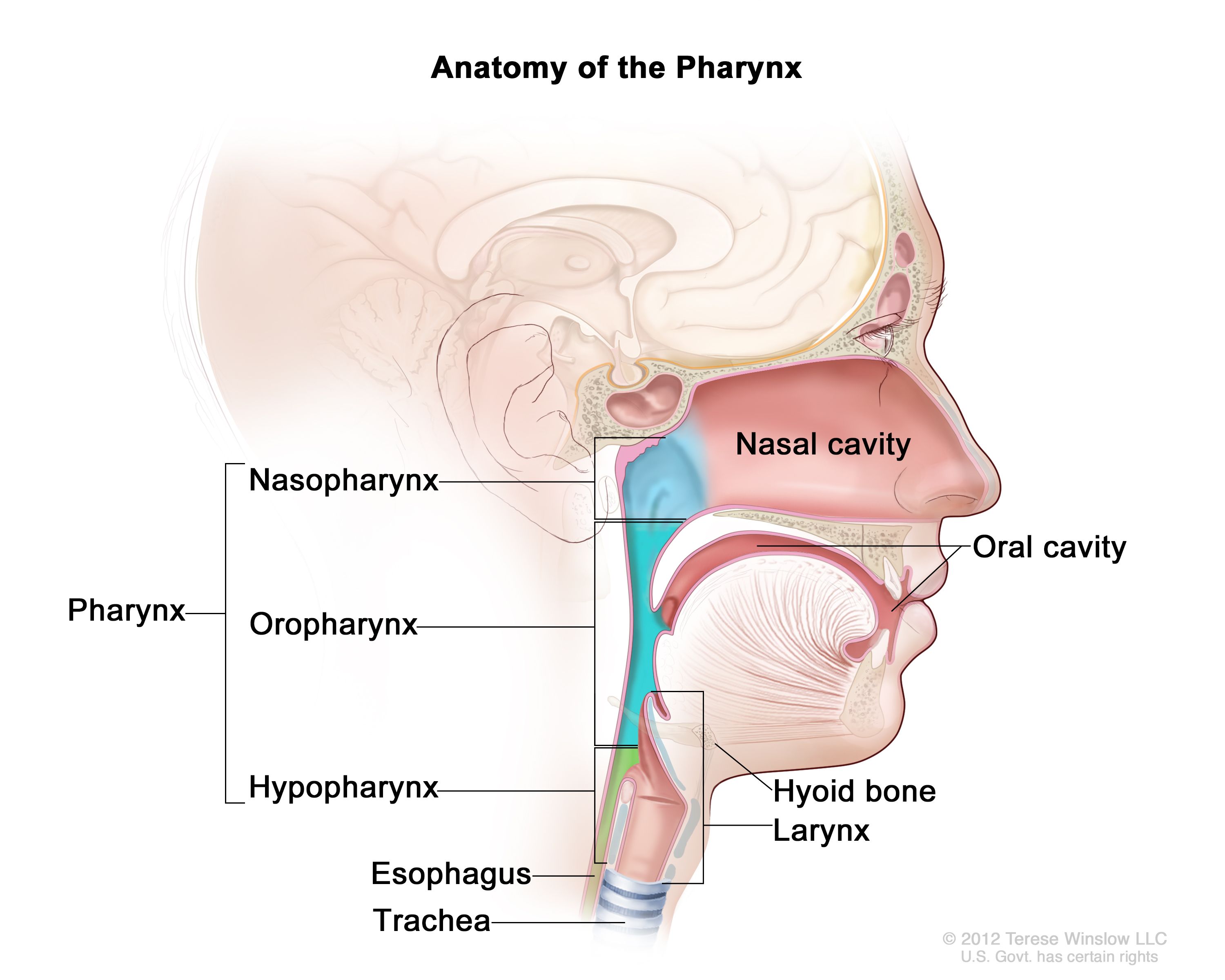
pharynx
the membrane-lined cavity behind the nose and mouth, connecting them to the esophagus; a muscular tube in the middle of the neck that helps you breathe and directs food and liquid into the digestive system
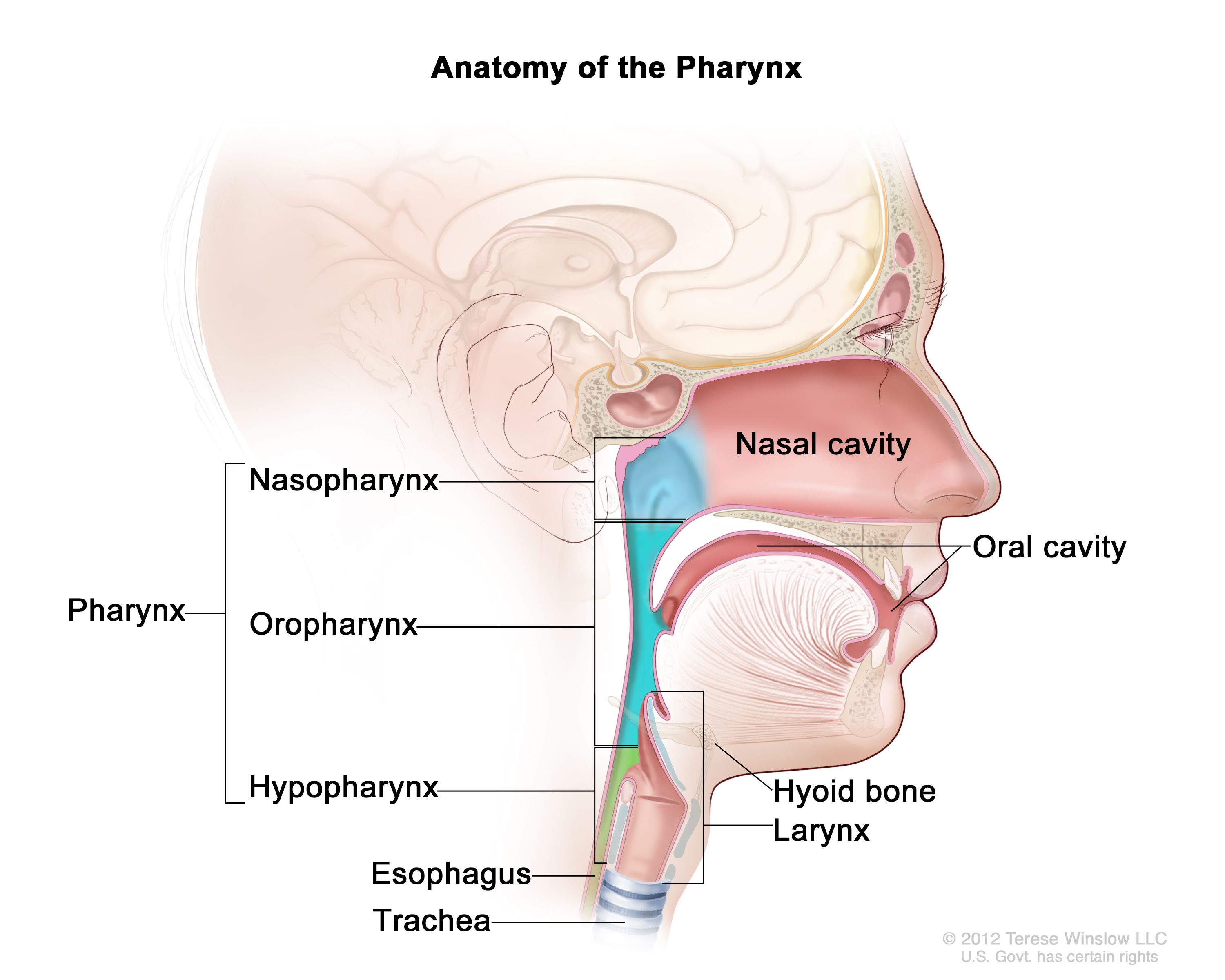
nasopharynx
the upper part of the pharynx; the passageway at the back of the nose and throat that connects the nasal cavity to the mouth and windpipe
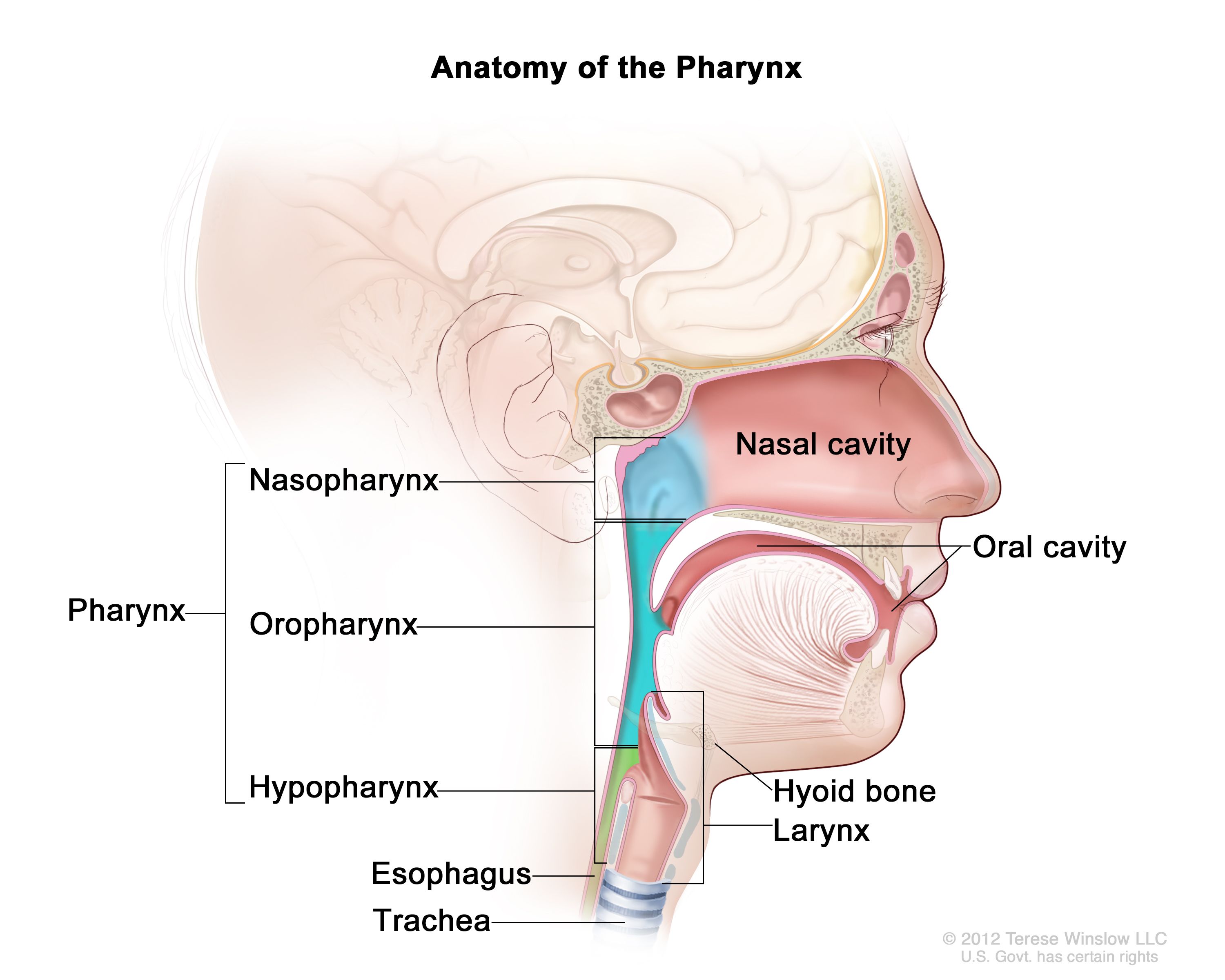
oropharynx
the part of the pharynx that lies between the soft palate and the hyoid bone; middle part of the throat, behind the mouth
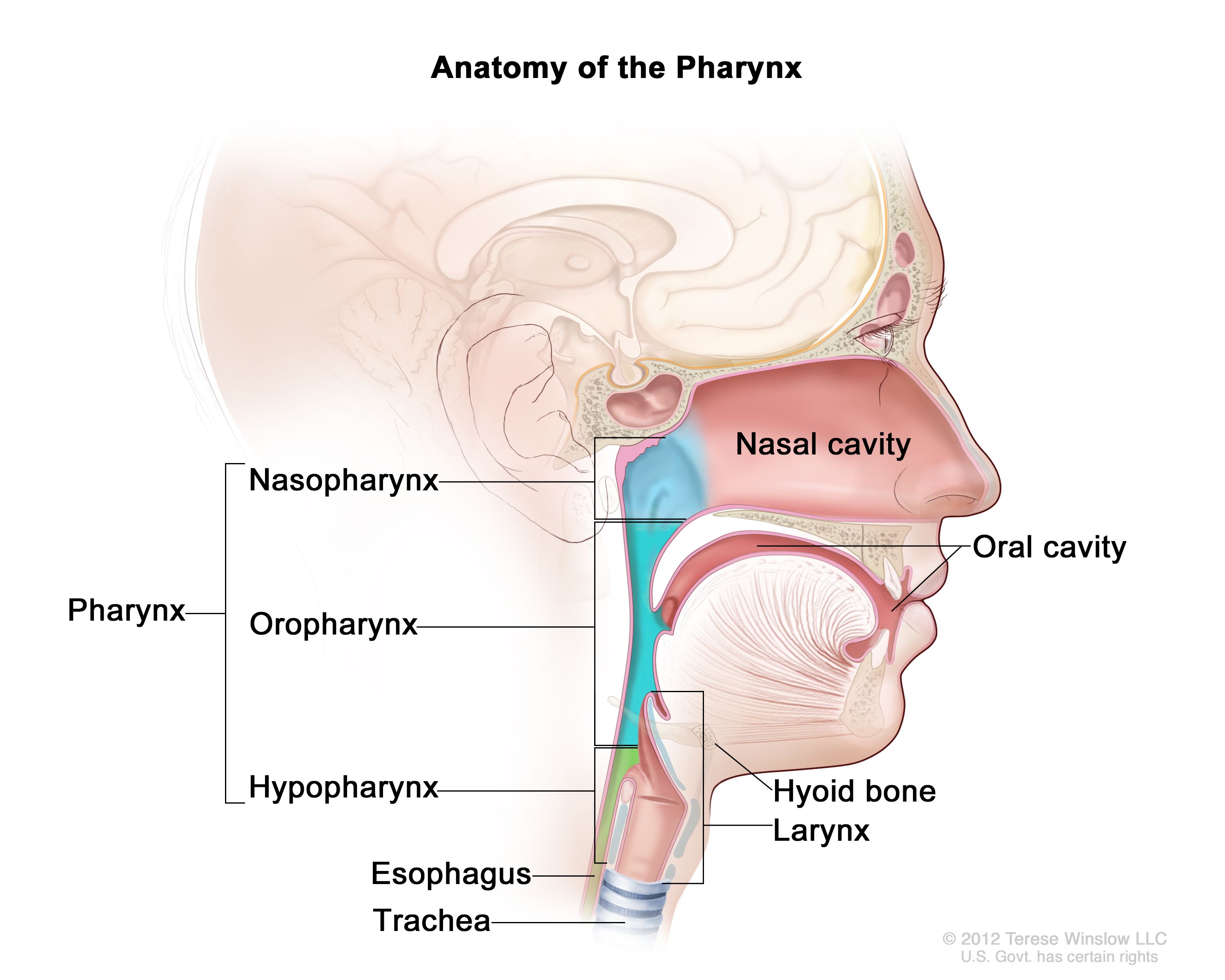
laryngopharynx
the most caudal portion of the pharynx; crucial connection point where food, water and air pass; refers to the point at which the pharynx divides anteriorly into the larynx and posteriorly into the esophagus; also referred to as the hypo pharynx
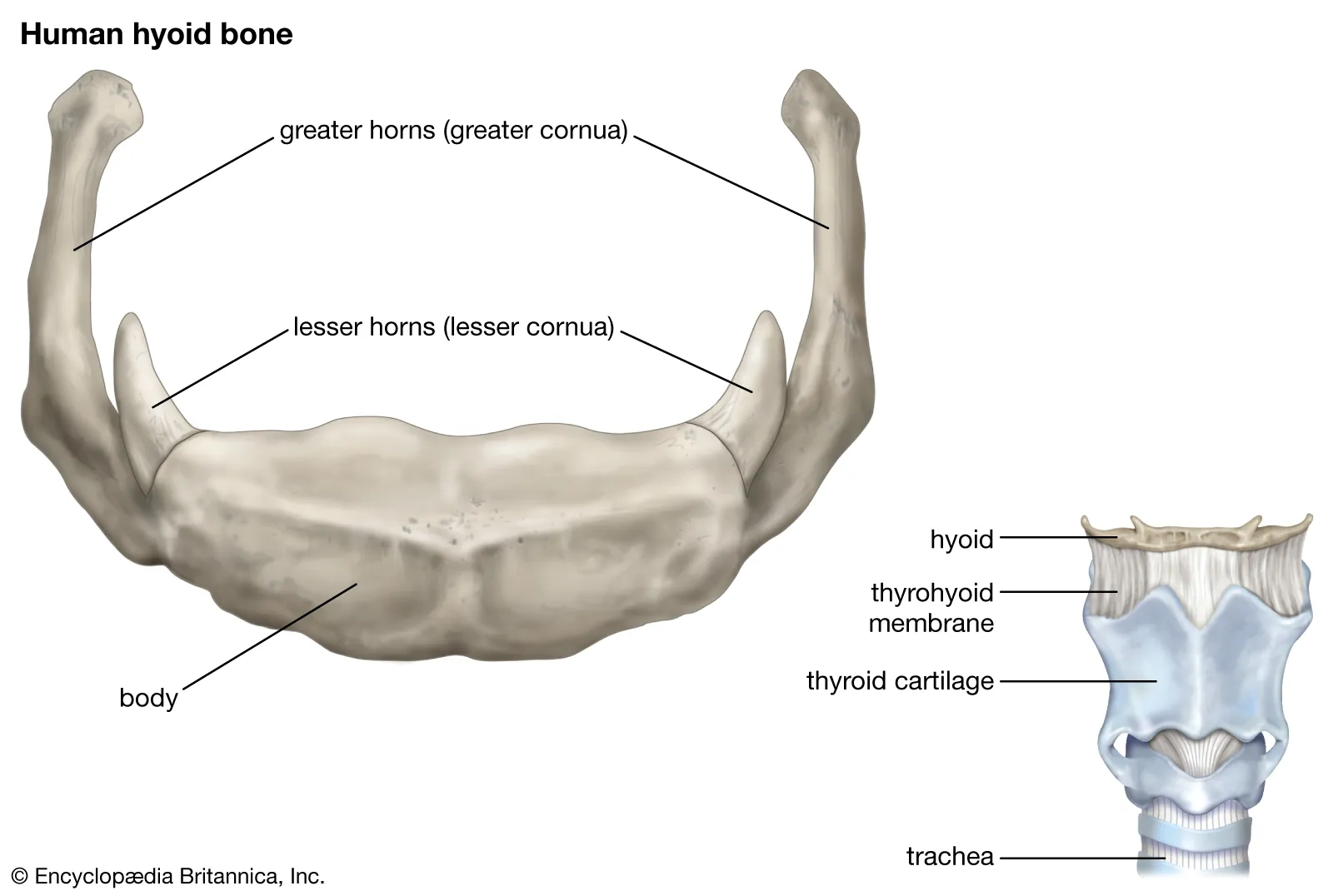
hyoid
a u-shaped bone in the neck located at the base of the mandible and above the larynx; not connected to any other bones — suspended by muscles and ligament and serves as a crucial anchor for muscles involved in speaking, swallowing, breathing and keeping the airway open.
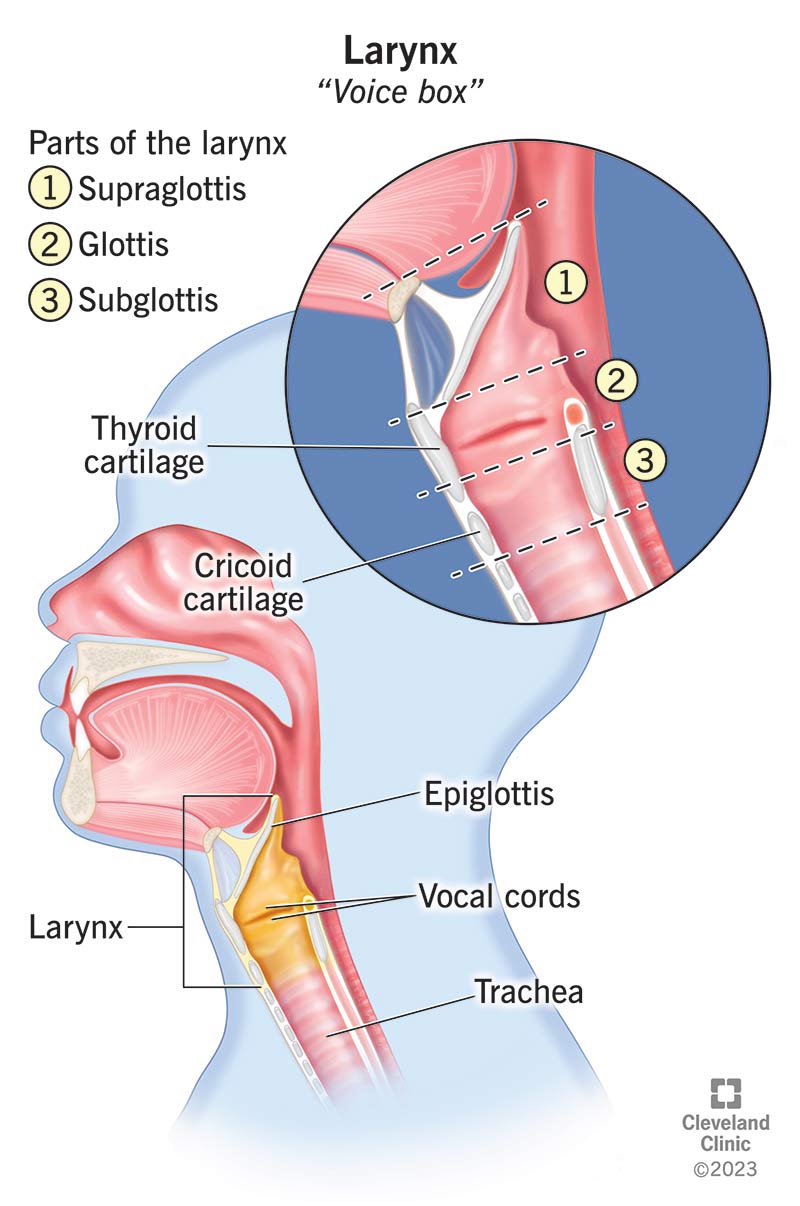
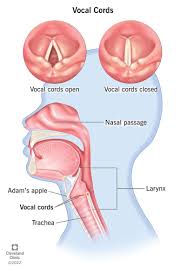
larynx
the hollow muscular organ forming an air passage to the lungs and holding the vocal cords in humans and other mammals; the voice box
vocal folds
two bands of tissue located in the larynx that are essential for producing sound; vibrate as air from the lungs passes between them, creating sound waves that are then modulated by the throat, nose and moth; pitch and tone of a person’s voice are determined by the tension, length and vibration of the vocal folds
epiglottis
a flap of cartilage located at the top of the trachea; plays a crucial role in protecting the airways during swallowing
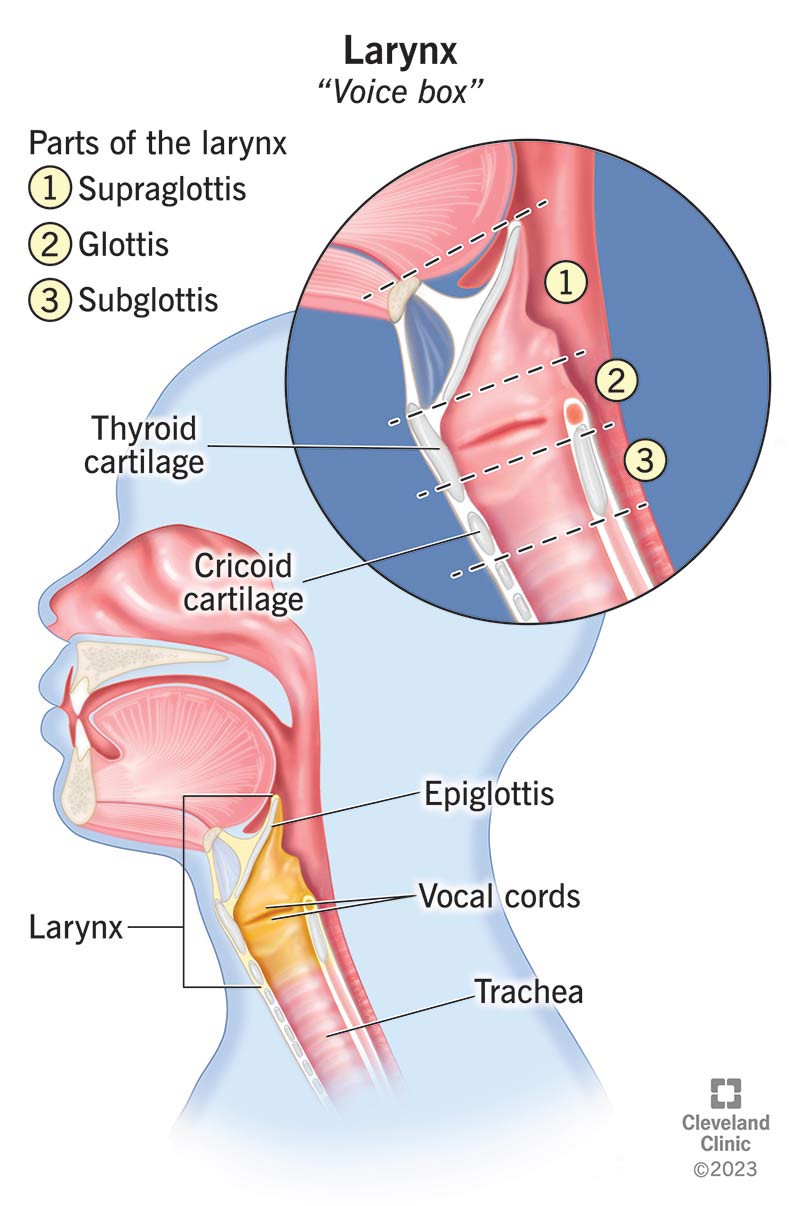
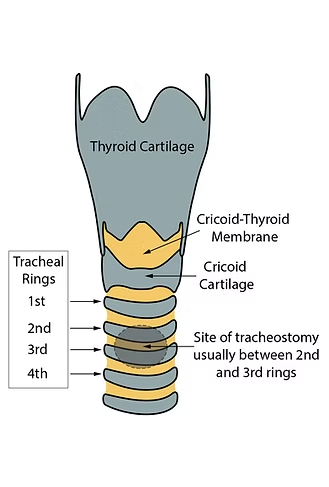
cricoid cartilage
ring-shaped cartilage of the larynx
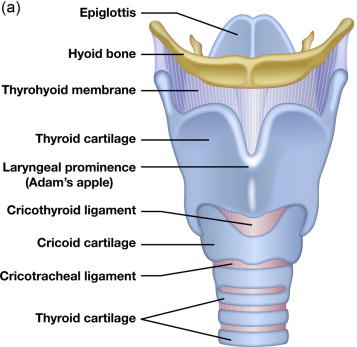
thyroid cartilage
a large cartilage of the larynx; a projection which forms the Adam’s apple in humans
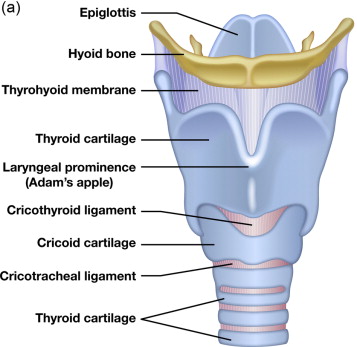
laryngeal prominence
the Adam’s apple; a visible bulge on the front of the neck; formed by the anterior portion of the thyroid cartilage
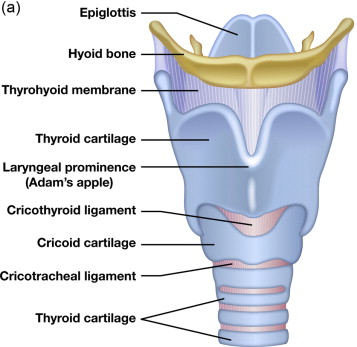
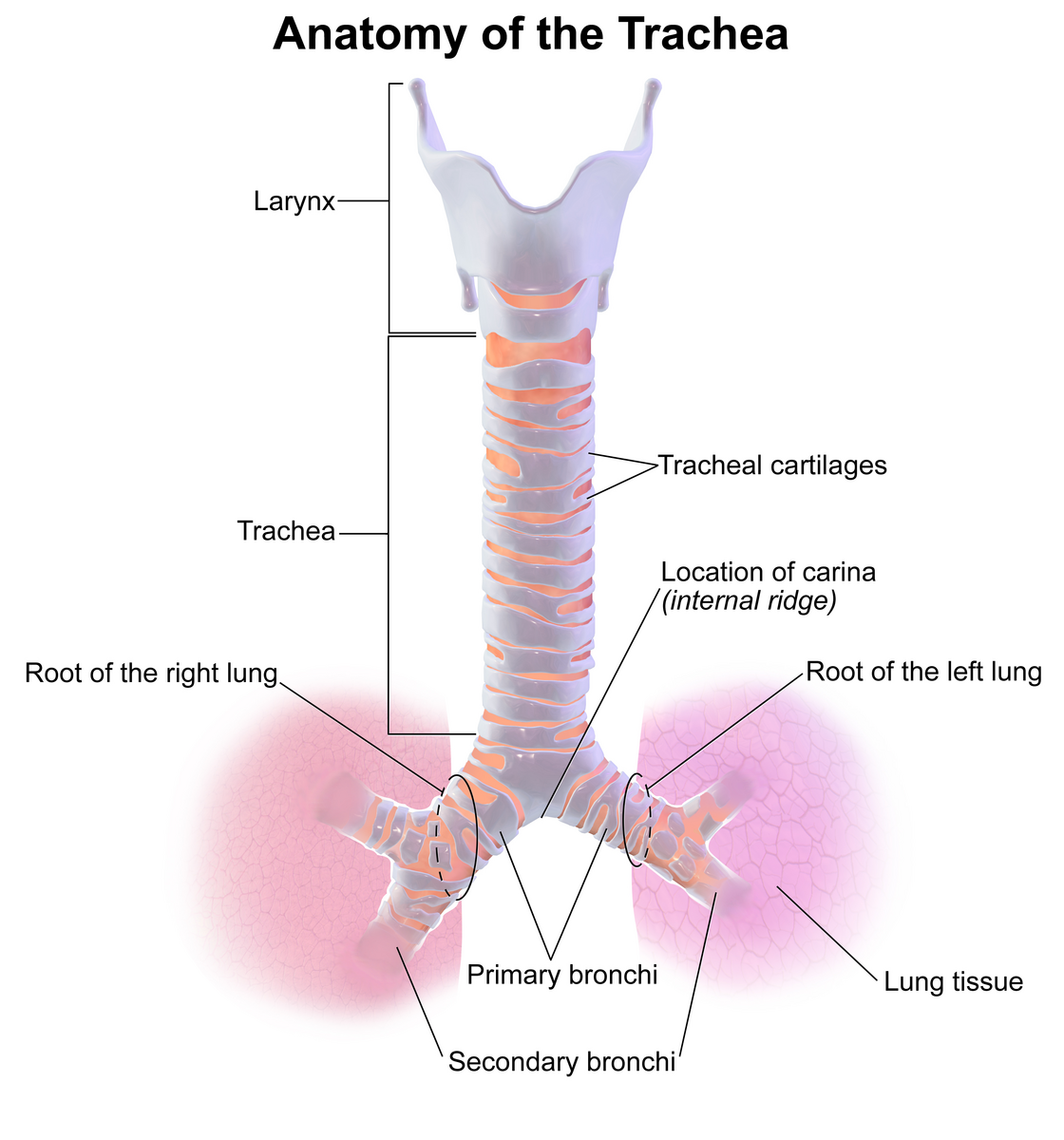
trachea
a large membranous tube reinforced by rings of cartilage; extends from the larynx to the bronchial tubes; conveys air to and from the lungs; also referred to as the windpipe
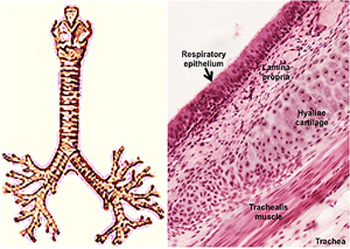
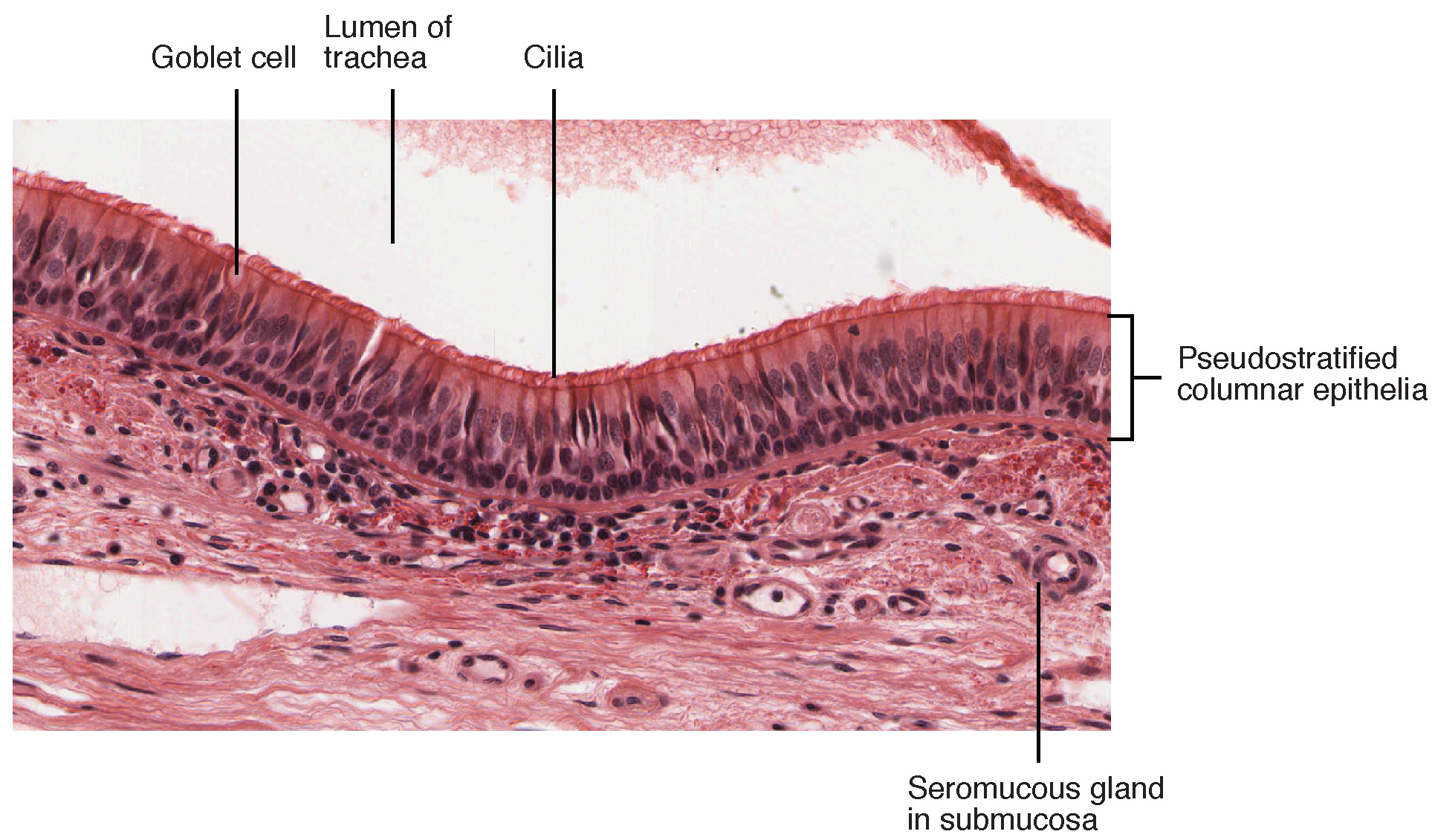
microscopic view of trachea
tracheal rings
cartilage; semicircular, cartilaginous structures that support and maintain the shape of the trachea (airway that connects the larynx to the lungs)
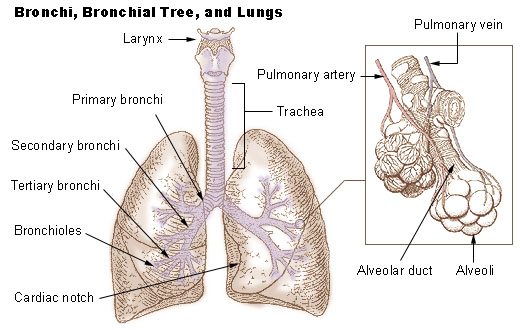
primary bronchi
the first parts of the bronchi; left and right bronchi in the center part of the lungs; widest part of the bronchi and attach to the trachea
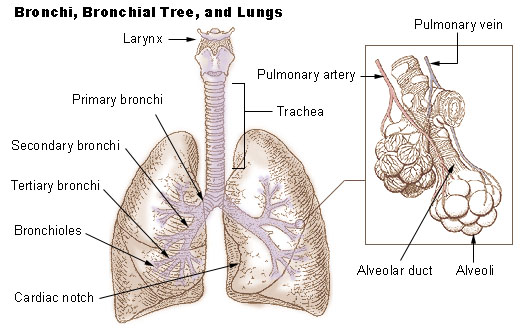
secondary bronchi
second part of the bronchi, near the middle of the lungs; parts of the bronchi that cross into the lobes of the lungs
tertiary bronchi
the third order of branching on the bronchial tree; arise from the second bronchi and divide further into bronchioles
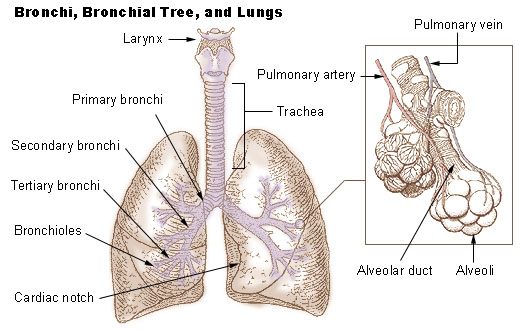
lungs
a pair of cone-shaped organs in the thoracic cavity that are responsible for respiration with the right lung being larger than the left due to the hearts position; receive air through the bronchial tubes
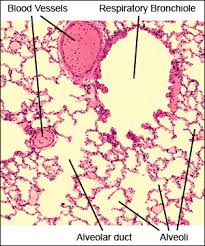
microscopic view of lung tissue
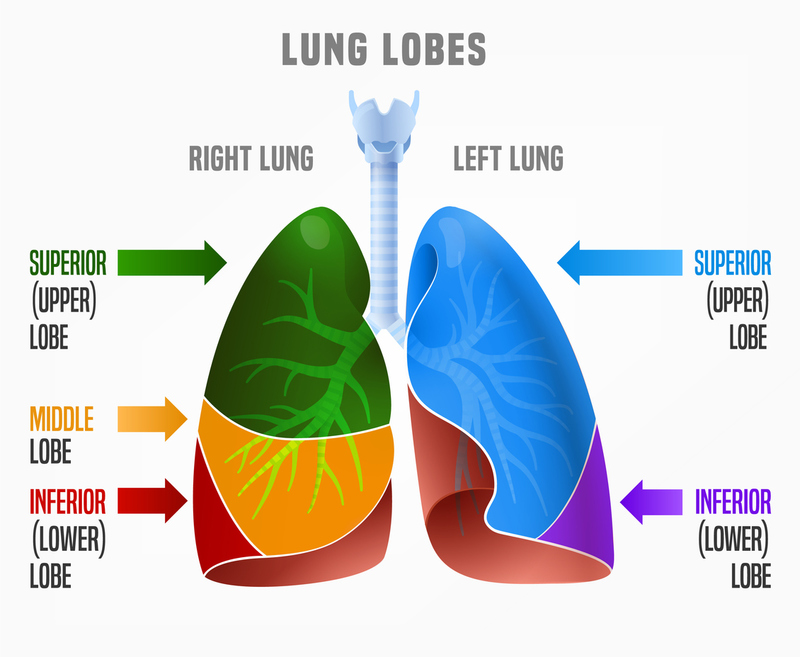
superior right lung lobe
the uppermost lobe of the right lung; situated in the upper portion of the right thoracic cavity, above the horizontal fissure; plays crucial role in gas exchanges it receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary artery and releases CO2 into alveoli, oxygenated blood is then transported through pulmonary veins
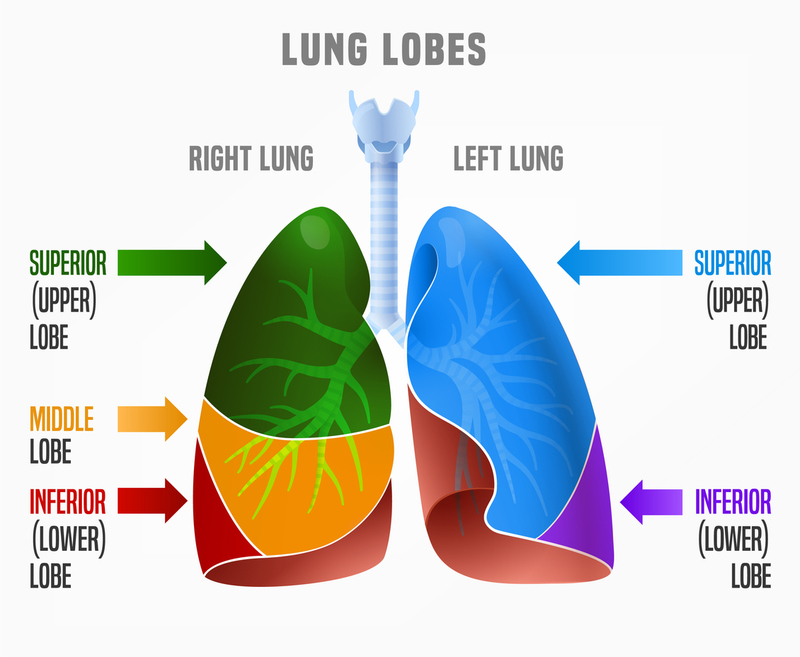
middle right lung lobe
one of three lobes in the right lung; separated from the upper lobe by the horizontal fissure and the inferior lobe by the oblique fissure; participates in gas exchange and ventilation; smallest lobe of the right lung and more prone to infections due to location and structure
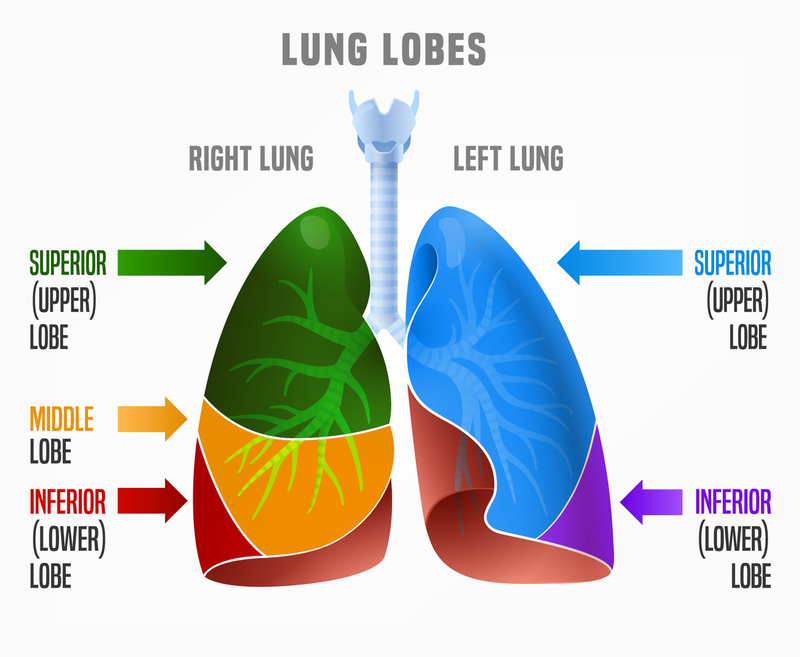
inferior right lung lobe
the bottom lobe of the right lung; separated from the middle lobe by the oblique fissure; posterior surface is in contact with diaphragm, medial surface faces the mediastinum and contains the hilum of the lung
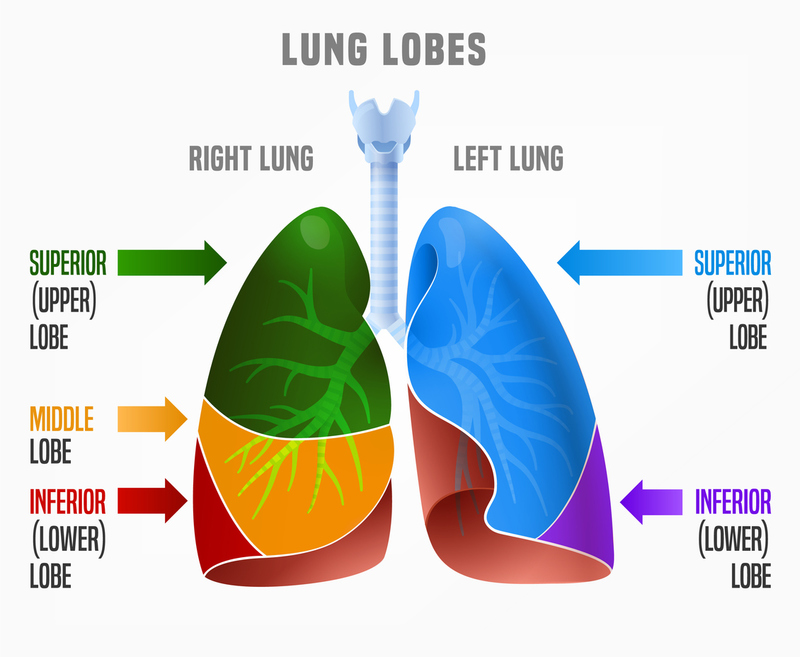
superior left lung lobe
the upper portion of the left lung; located above the oblique fissure which separates it from the inferior lobe; responsible for gas exchange and ventilation
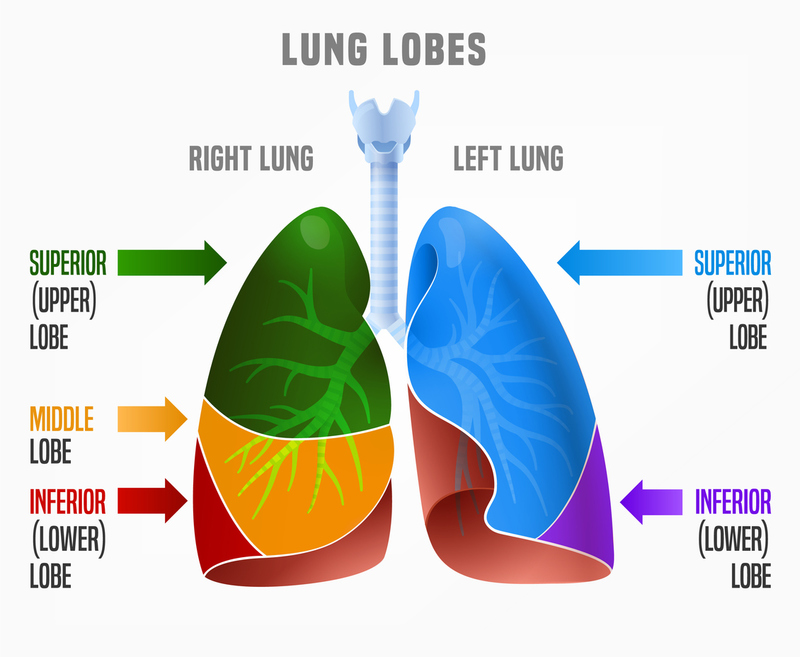
inferior left lung lobe
one of two lobes that makes up the left lobe; separated from the superior lobe by the oblique fissure; plays a crucial role in gas exchange and is a common site for many lung conditions
alveoli
any of the many tiny air sacs of the lungs which allow for rapid gaseous exchange; where the lungs and the blood exchange O2 and CO2

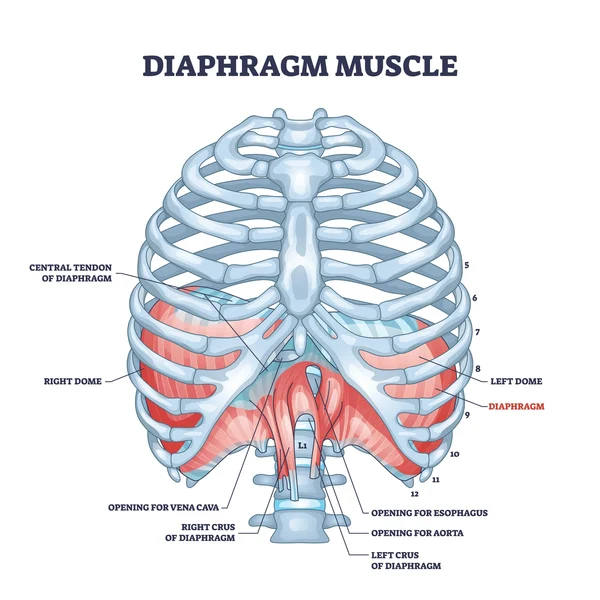
diaphragm
a dome shaped, muscular partition that separates th thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity
obstructive pulmonary disease
a group of chronic lung conditions that cause airflow obstruction, making it difficult to breathe; primary causes are cigarette smoking, air pollution and genetics
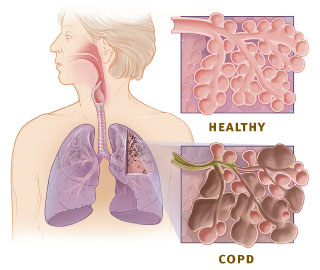
restrictive pulmonary disease
a group of conditions that limit the lungs’ ability to expand and take in air, resulting in decreased lung volumes and impaired gas exchange; can be caused by chest wall abnormalities, obesity, certain medications and other disorders
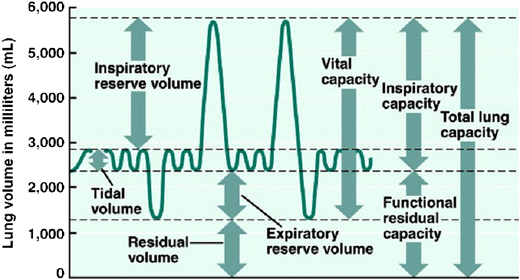
lung parameters
include lung volumes (tidal, inspiratory, expiratory reserve and residual) and lung capacities (inspiratory, functional residual, vital, and total)
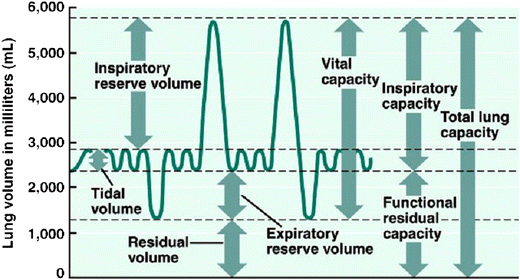
tidal volume
the amount of air that moves into or out of the lungs during a single, normal breath; around 500 ml for an average healthy adult or 1 ml per pound of ideal body weight
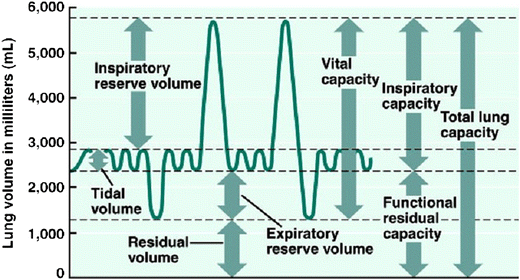
inspiratory reserve volume
the maximum amount of air you can forcibly inhale into your lungs after a normal, resting breath; represents the additional capacity of the lungs beyond the tidal volume and is used to meet higher oxygen demands during exercise
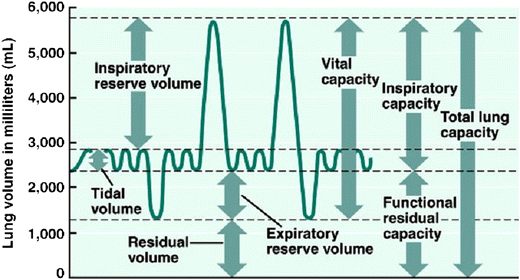
inspiratory capacity
the maximum volume of air a person can inhale after a normal, quiet exhalation; the sum of the tidal volume and the inspiratory reserve volume; important for assessing lung function
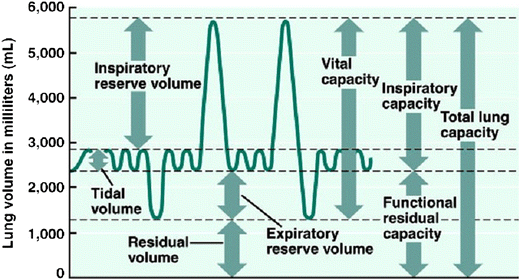
expiratory reserve volume
the maximum amount of air you can forcibly exhale after a normal, quiet exhalation; represents the extra volume of air you can breathe out with maximum effort and is a measure of lung function; average for males is about 1100 mL
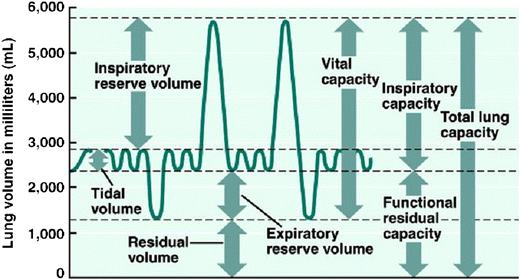
residual volume
the air that remains in the lungs after a maximal, forceful exhalation; essential for keeping alveoli open and preventing lung collapse
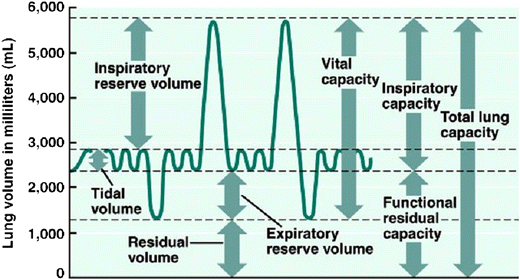
functional residual capacity
the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal expiration; the use of the expiratory reserve volume and the residual volume; represents the point of equilibrium between the outward elastic recoil of the chest wall and the inward elastic recoil of the lungs
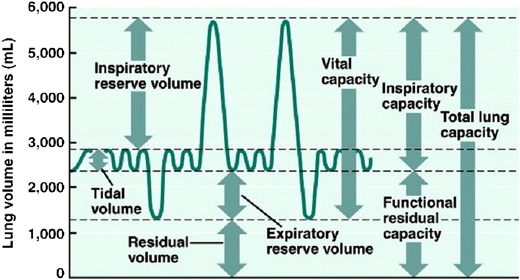
vital capacity
the maximum amount of air that a person can exhale from their lungs after taking a deep breath; equal to the inspiratory reserve volume + tidal volume + expiratory reserve volume
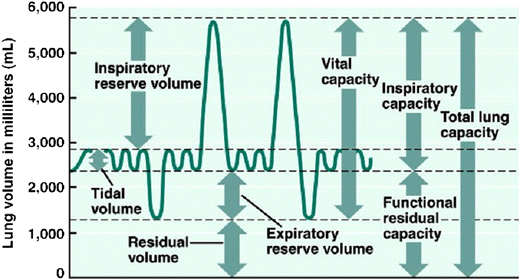
total lung capacity
the maximum amount of air that the lungs can hold after a forceful inhalation; sum of all lung volumes
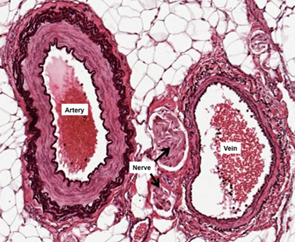
microscopic structure of veins
a three—layered wall called the tunica intimate, tunica media and tunica adventitia, which encloses a central space called the lumen.
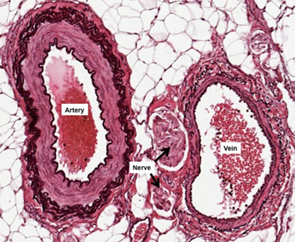
microscopic structure of arteries
consists of three distinct layers — tunica intimacy, tunica media, and tunica adventitia; elastic
veins and arteries of the head and neck
common carotid artery, internal carotid artery, external carotid artery, external jugular vein, internal jugular vein, brachiocephalic artery and vein, subclavian artery and vein, superior vena cava
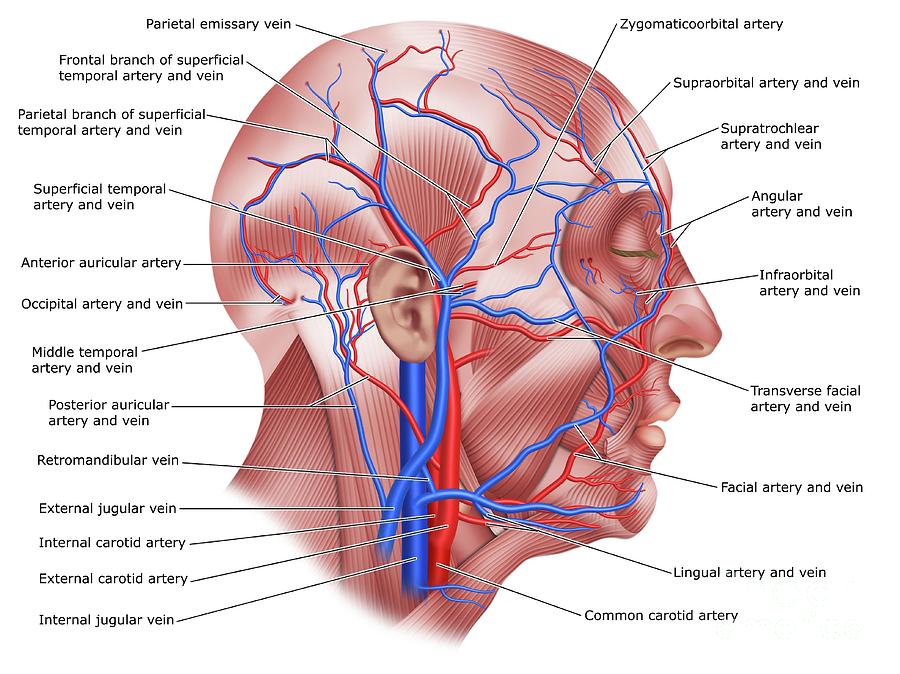
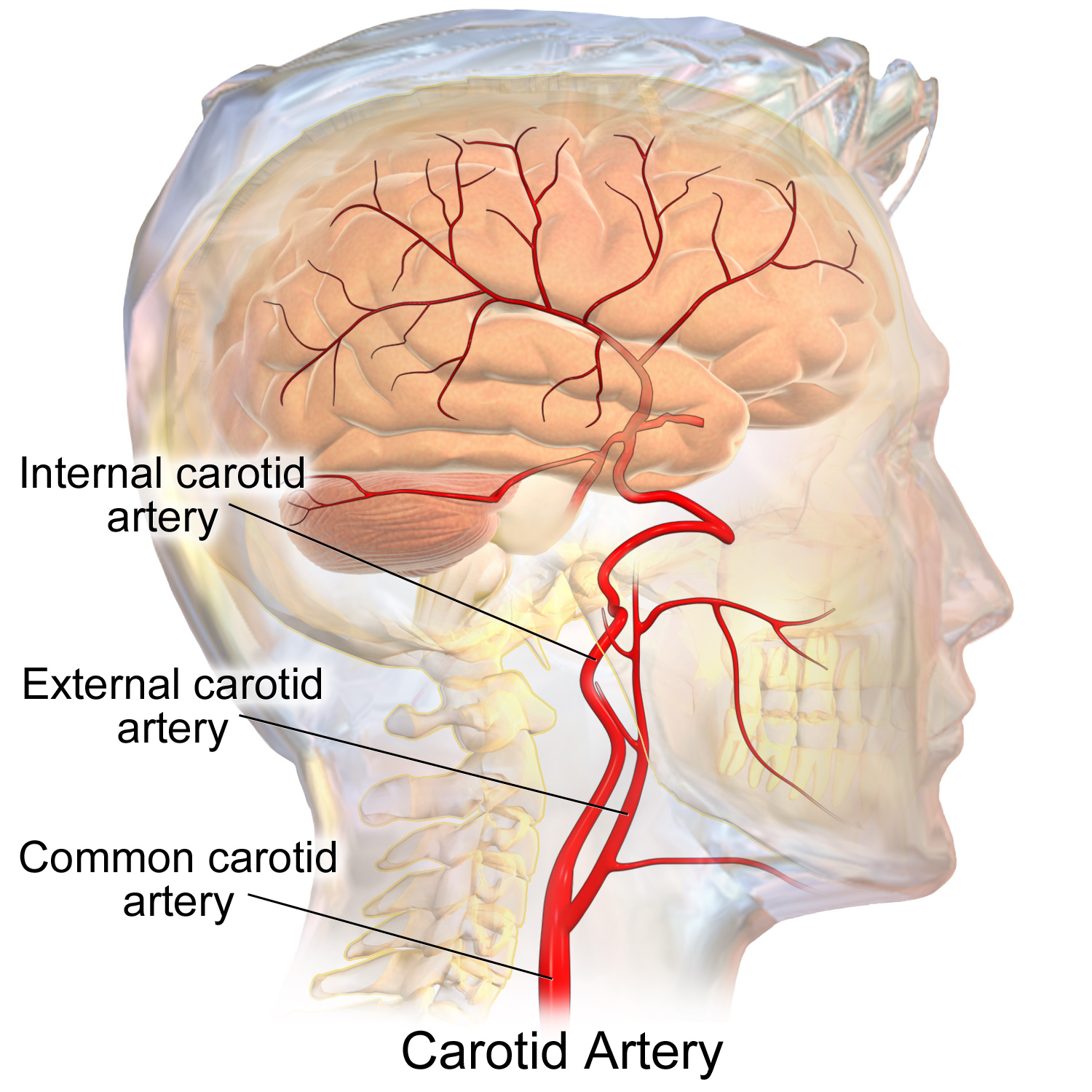
common carotid artery
a large blood vessel in the neck that supplies oxygenated blood to the head and neck.
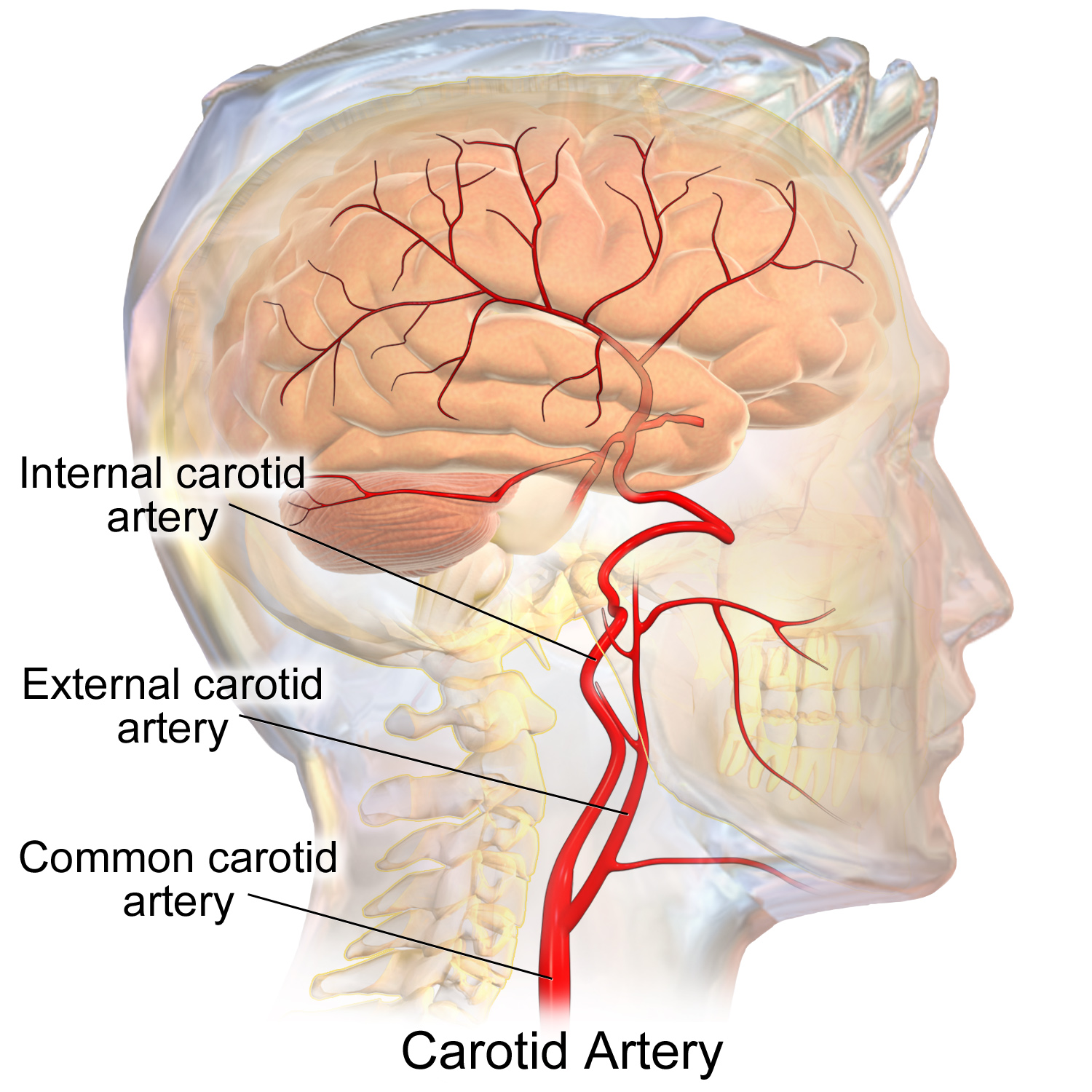
internal carotid artery
a major blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain and other structures in the head and neck; originates from the common carotid artery and then ascends through the carotid canal in the temporal bone and enters the skull; supplies oxygenated blood
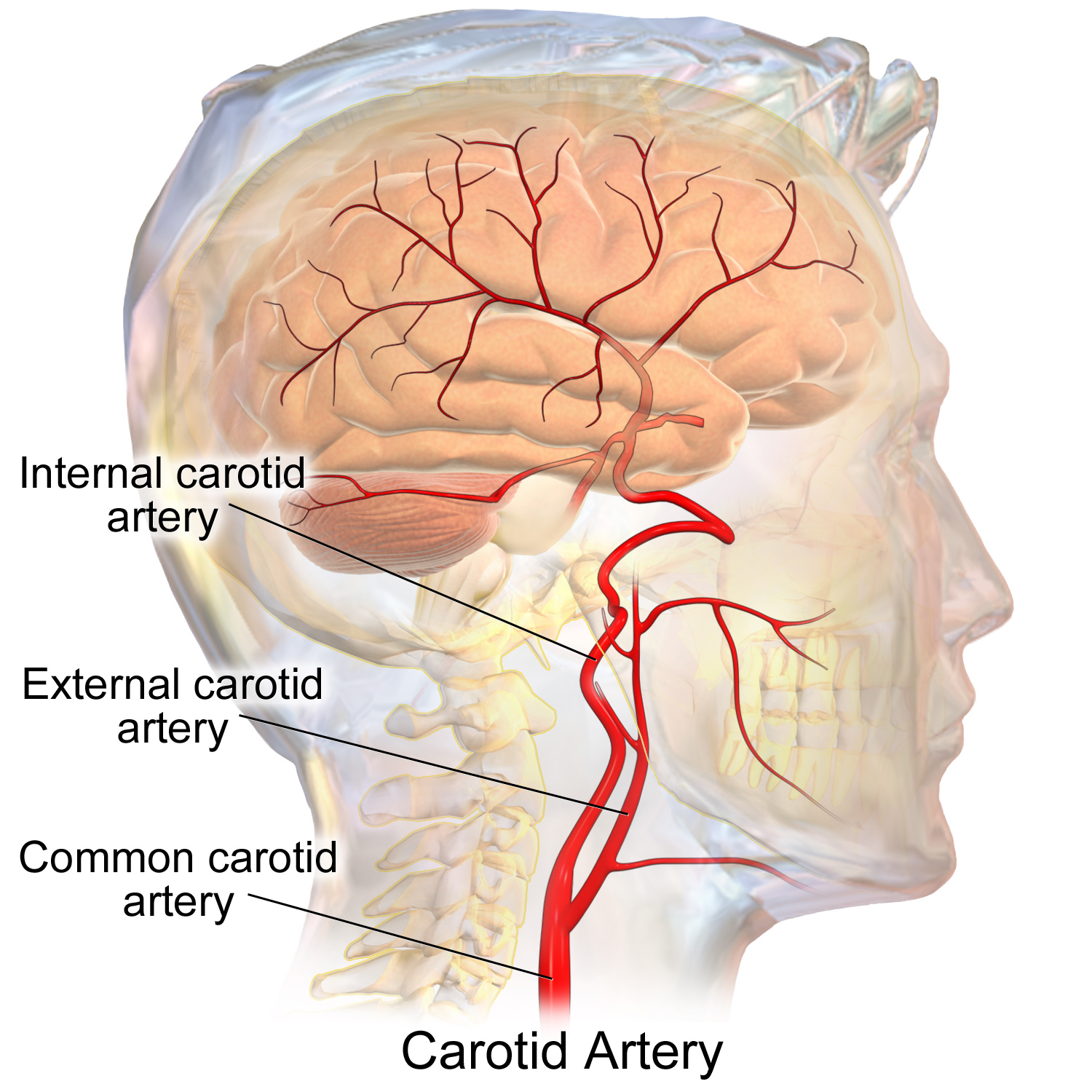
external carotid artery
a major blood vessel in the neck that supplies blood to the face, scalp, and neck; branches from the common carotid artery and has 8 major branches which terminate near the neck of the mandible
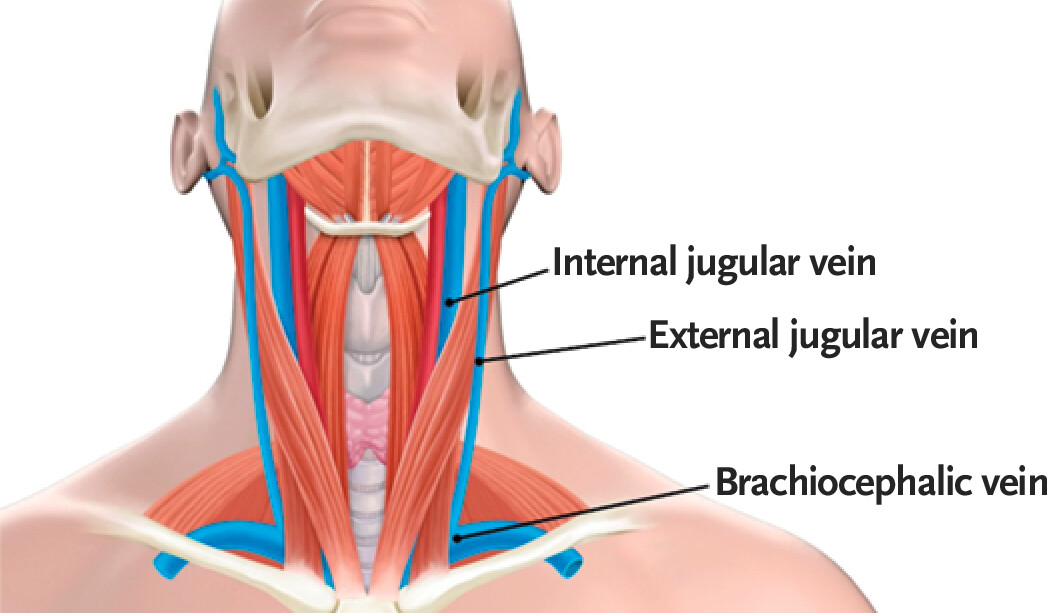
external jugular vein
a superficial vein located in the anterior and lateral neck; plays a crucial role in draining blood from the head, face, and neck regions; originates at the angle of the mandible and then descends vertically along the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
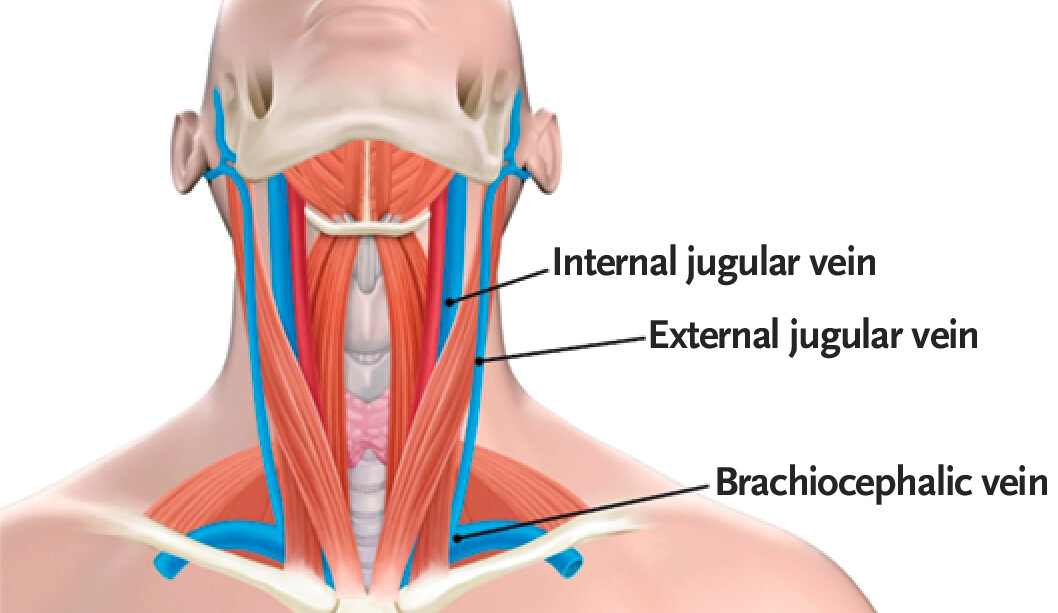
internal jugular vein
a large, deep, vein located in the neck; runs along the lateral border of the common carotid artery and vagus nerve within the carotid sheath, joins with the subclavian vein to form the superior vena cava
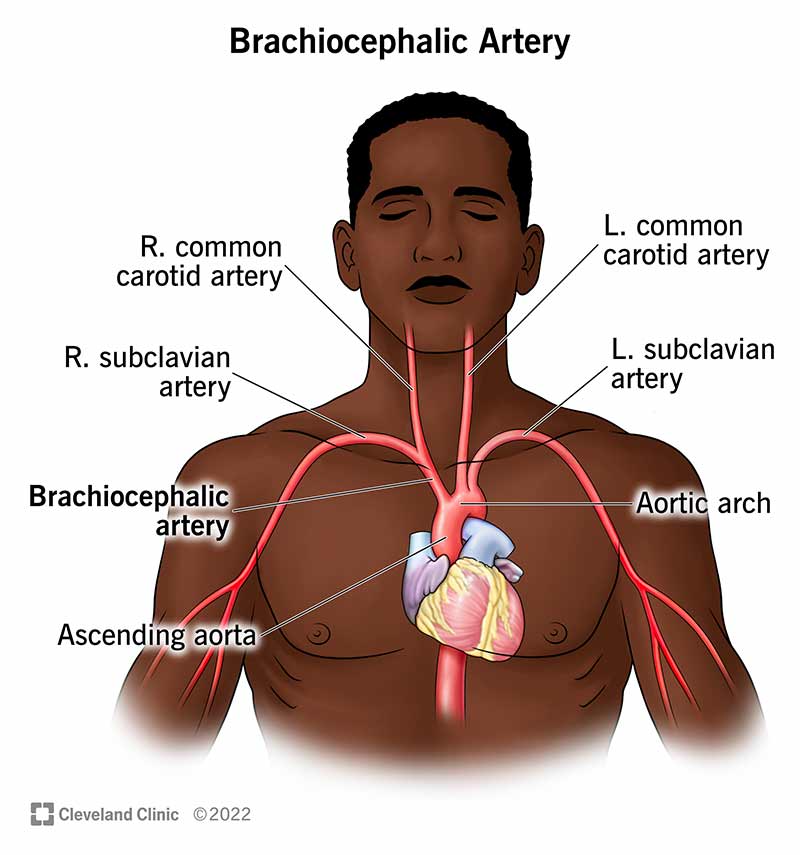
brachiocephalic artery
two large blood vessels that branch off the aortic arch; supply oxygenated blood to the right upper extremity and the right side of the head and neck; both originate from aortic arch and divide into common carotid artery and right subclavian artery
brachiocephalic vein
a large pair of veins in the upper chest that carry deoxygenated blood from the head, neck, and arms back to the heart; formed by the union of the internal jugular vein and subclavian vein with the left and right veins merging to form the superior vena cava
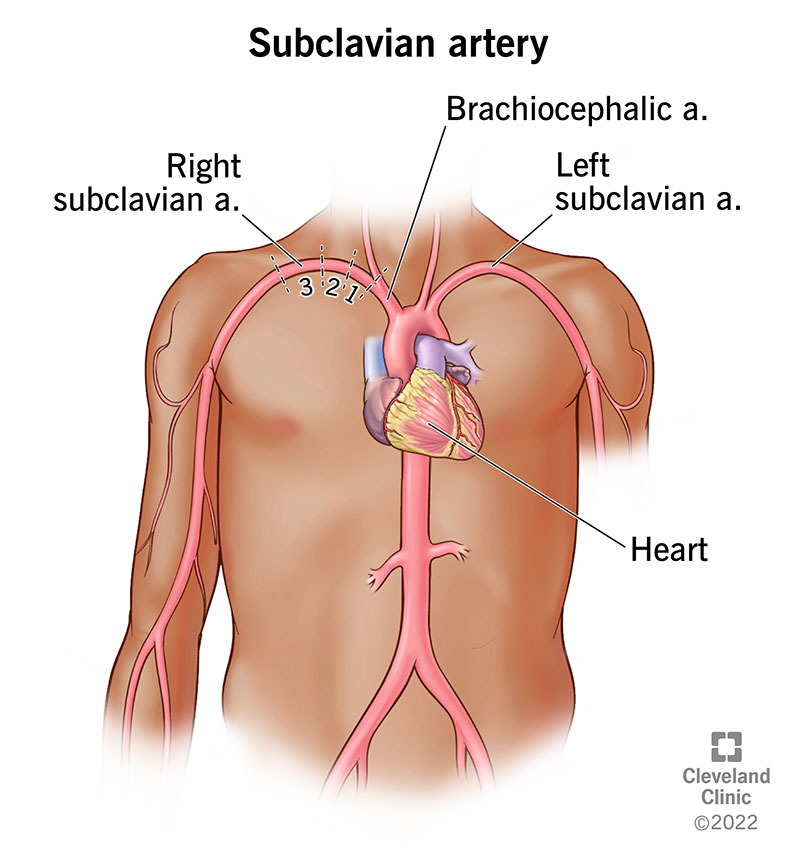
subclavian artery
a large blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the upper extremities, head, and neck; runs along the lower border of the clavicle on both sides of the body; right originates from the brachiocephalic trunk while left originates directly from aortic arch, passes over the first rib and becomes the axillary artery
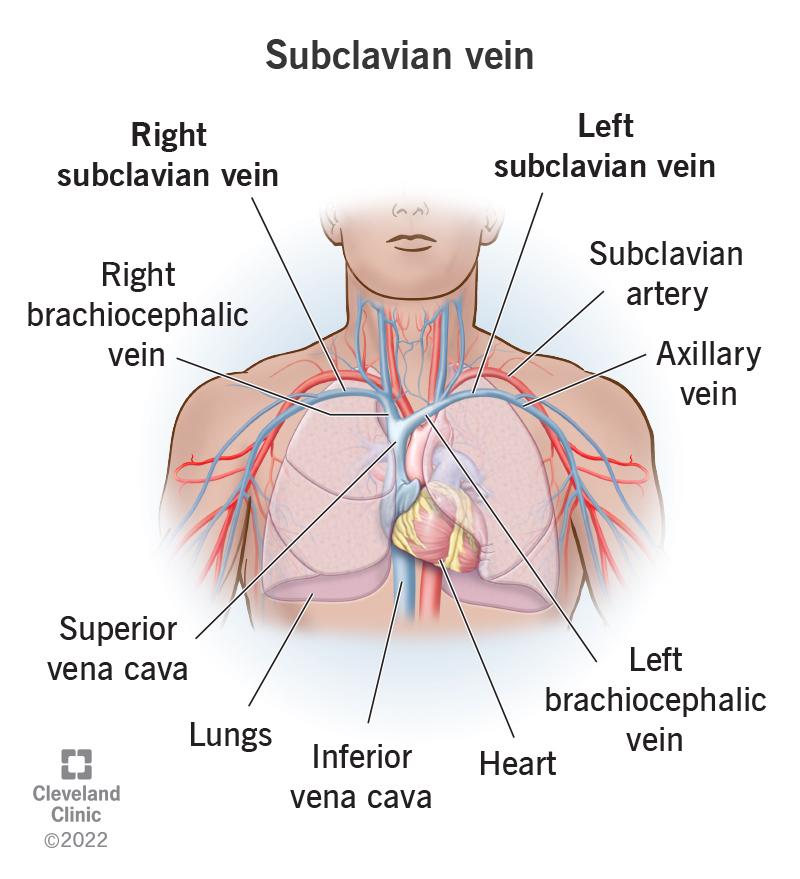
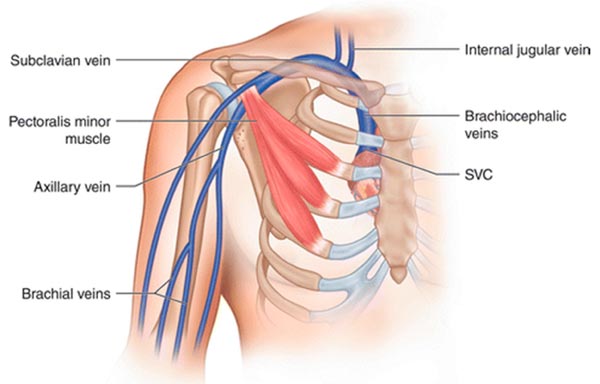
subclavian vein
a large, deep, vein located in the upper chest, just below the clavicle; plays a crucial role in draining blood from the upper extremities back to the heart; originates at the lateral border of the first rib where it continues as axillary vein and runs medially and posterior to the clavicle where it joins with the internal jugular vein at sternoclavicular joint to make the brachiocephalic vein
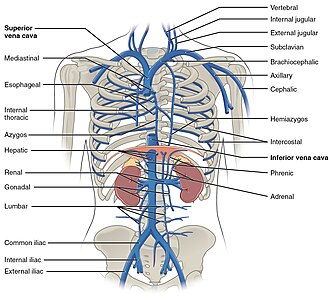
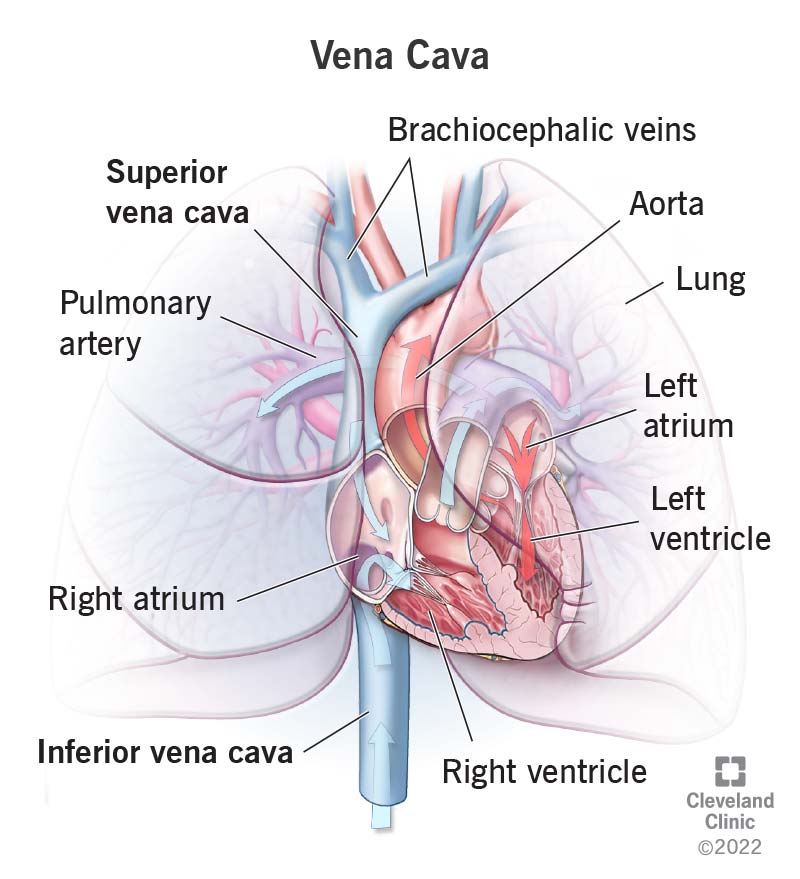
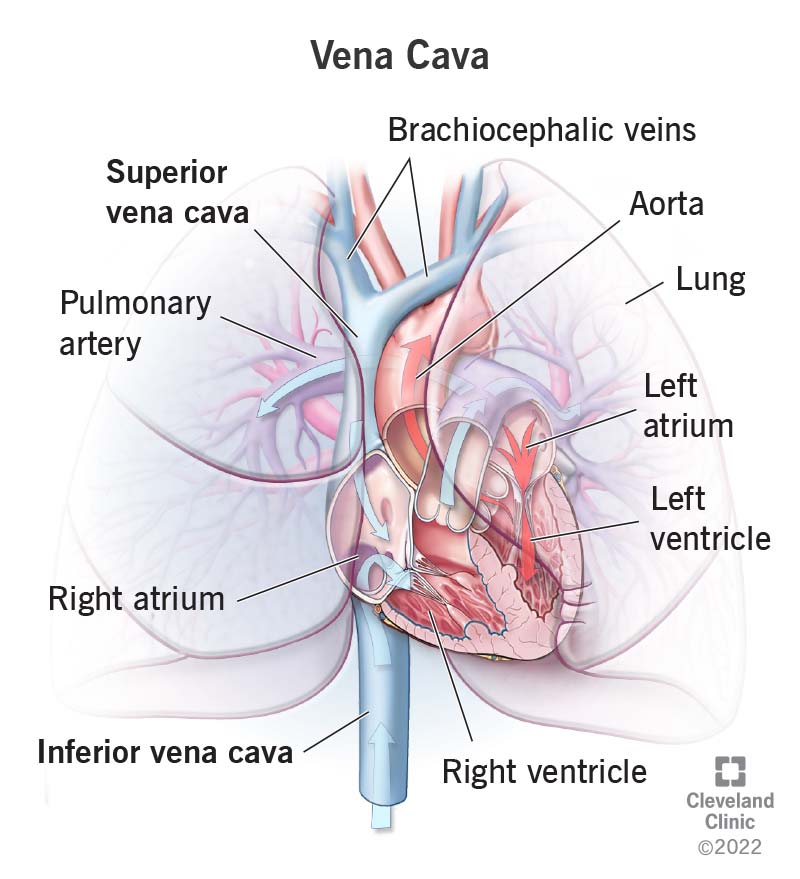
superior vena cava
a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the head, neck, arms, and chest back to the heart, originates at the junction of the two brachiocephalic veins and empties into the right atrium of the heart; plays a crucial role in the CV by returning deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the heart for oxygenation.
veins and arteries of the thoracic and abdominal cavity
inferior vena cava, thoracic aorta, abdominal aorta (Celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, inferior mesenteric artery), hepatic artery and vein, left gastric artery, splenic artery, renal artery and vein
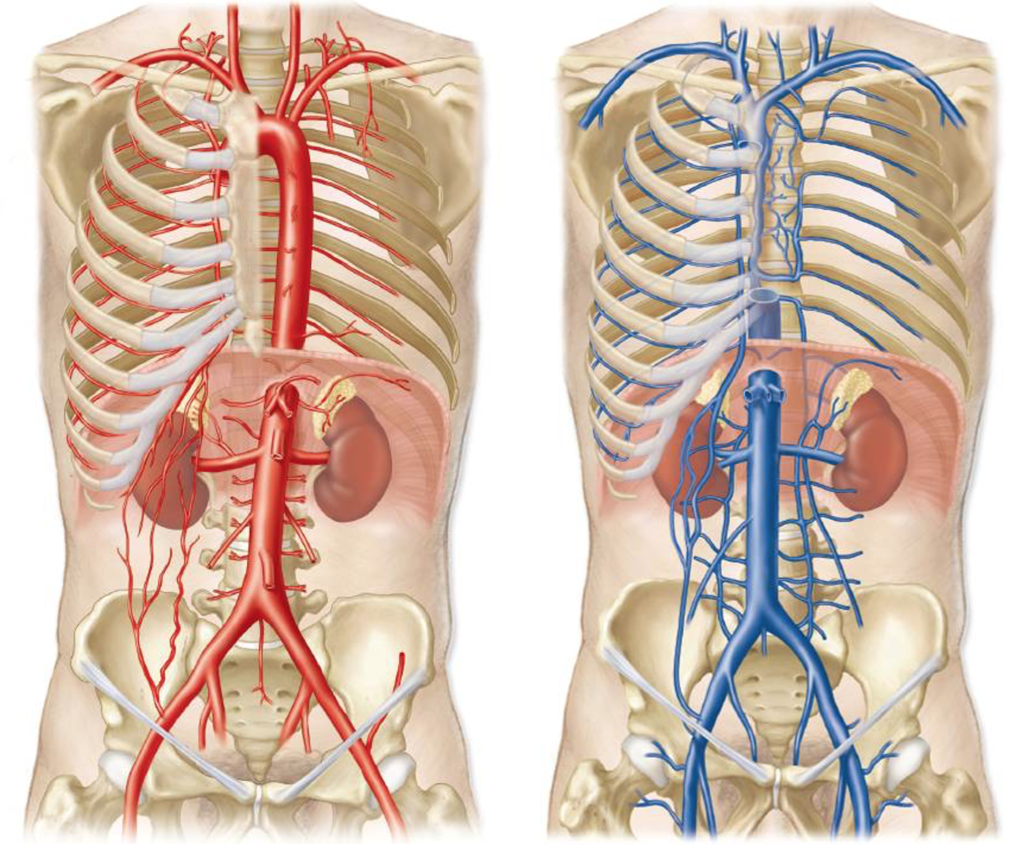
inferior vena cava
a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the right atrium of the heart; located posterior to the right side of the vertebral column in the abdominal, originates at the junction of the right and left common iliac veins; largest vein in the human body and is not equipped with valves.
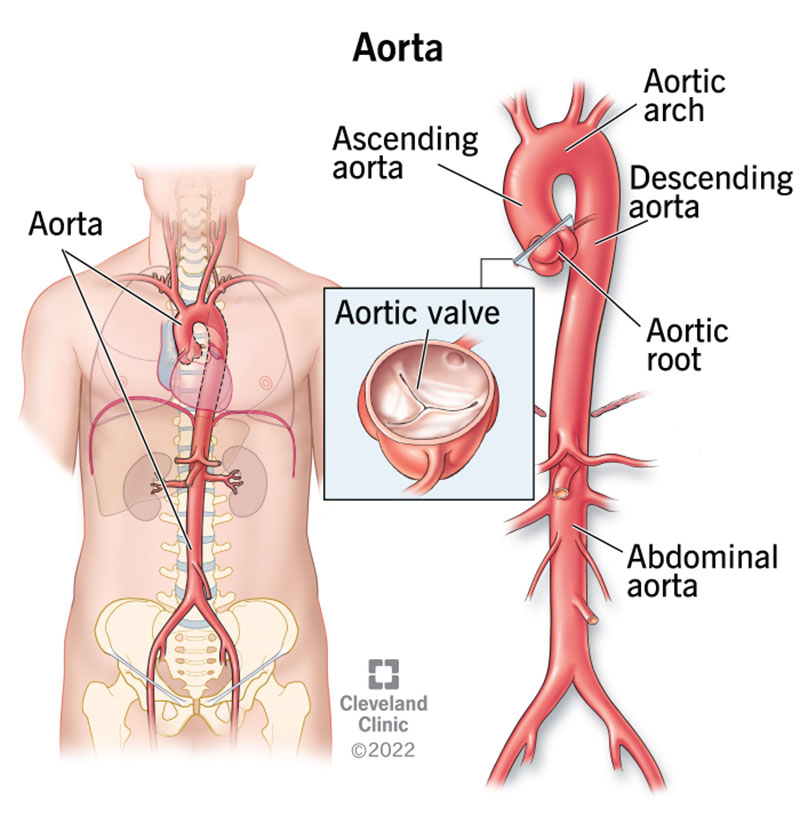
thoracic aorta
the portion of the aorta that extends through the chest cavity; a continuation of the ascending aorta and extends downward from the aortic arch to the diaphragm; divided into the ascending and descending aorta; located behind the heart and passes through the mediastinum; carries oxygenated blood from the hear to the rest of the body; main artery that supplies blood to the organs and tissues of the chest
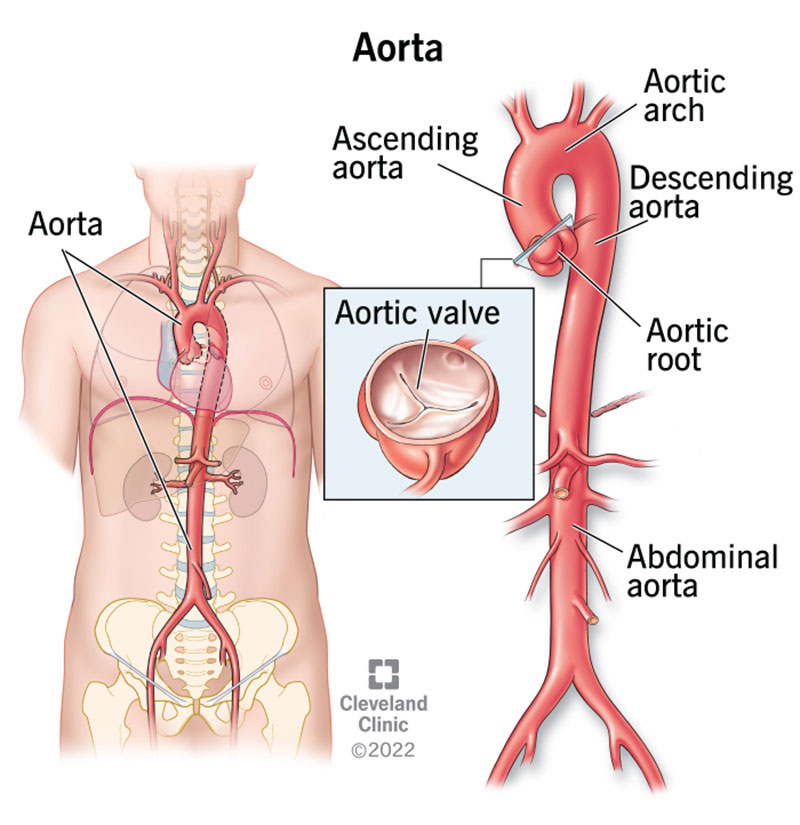
abdominal aorta
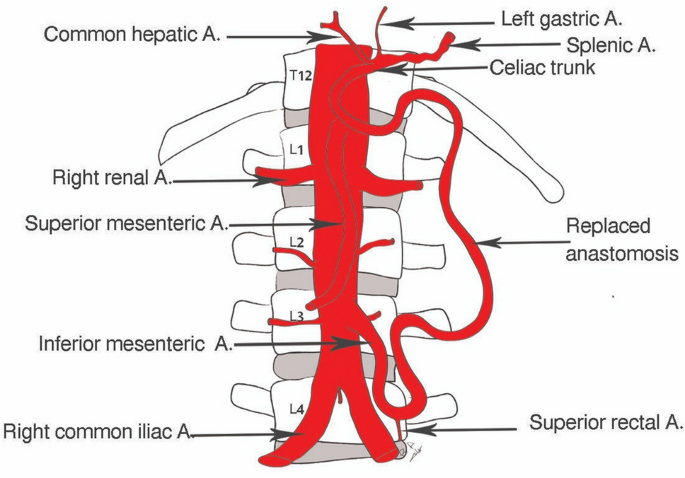
composed of three branches — celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery and inferior mesenteric artery; a continuation of the descending thoracic aorta, located in the abdomen; the largest artery in the boy, carrying oxygenated blood from the heart to the organs and tissues in the lower body; extends from diaphragm to ~L4 vertebrae and then bifurcates into right and left common iliac arteries, lies left of the inferior vena cava.
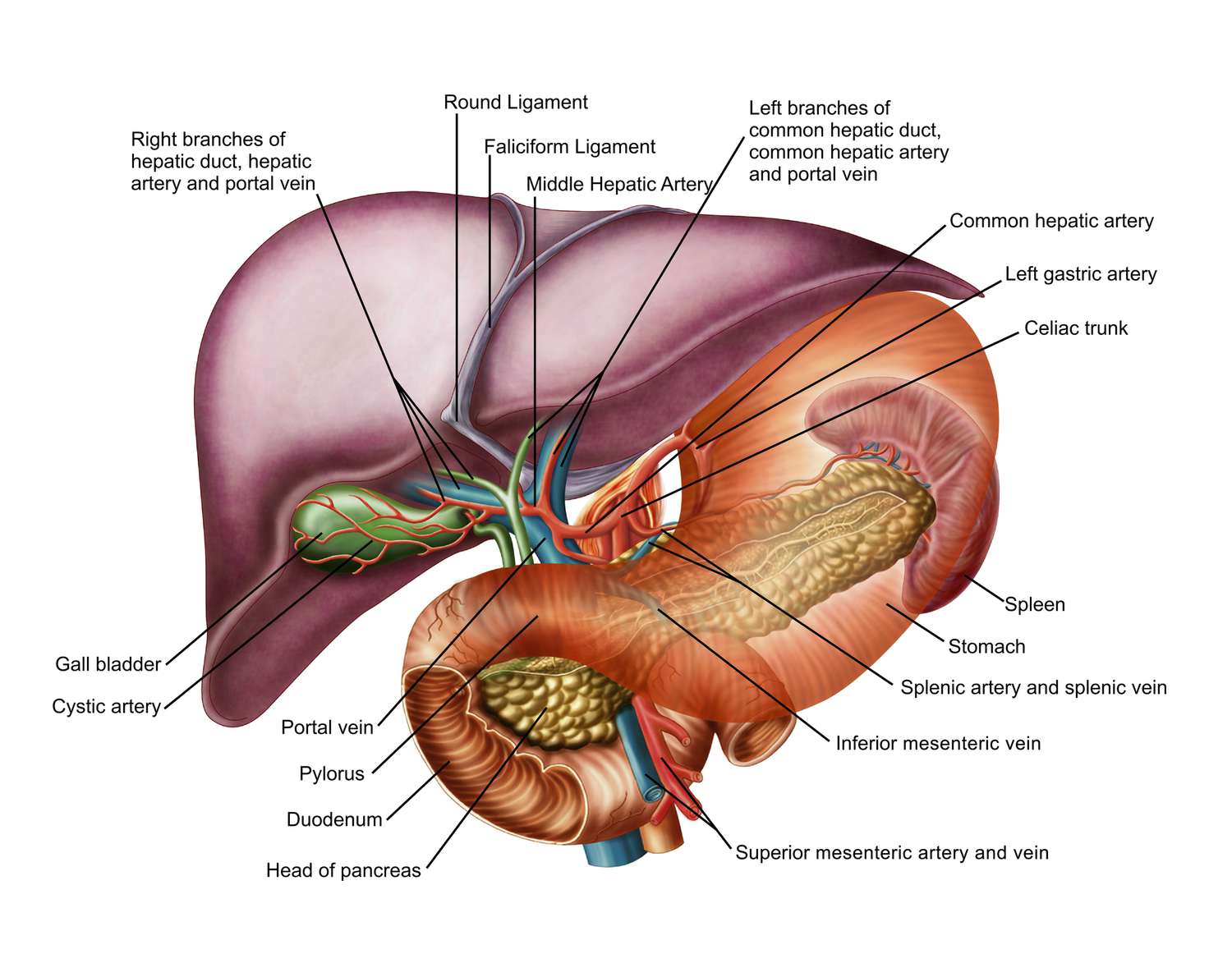
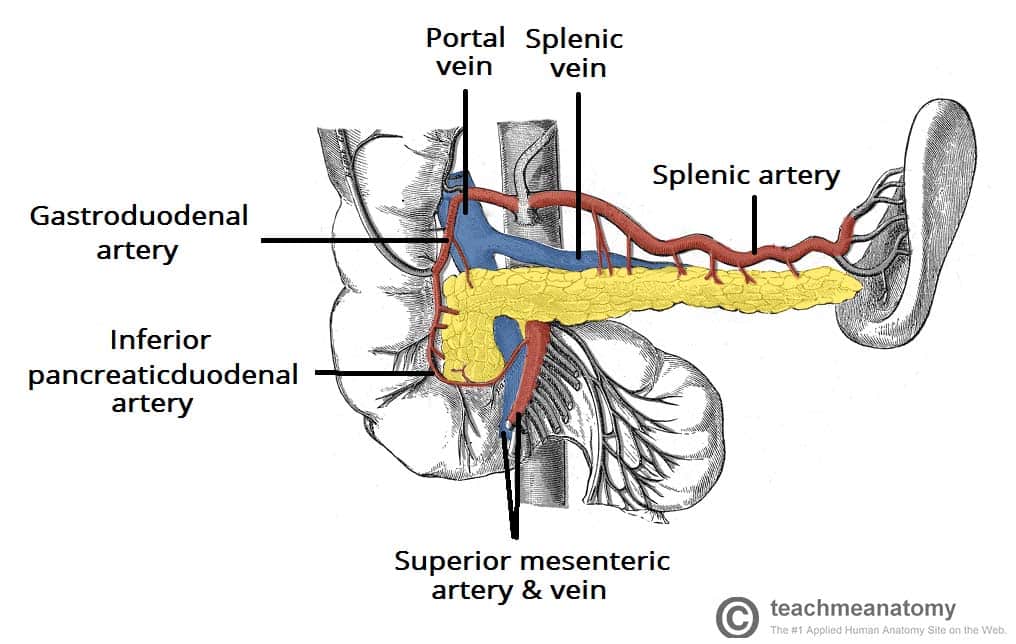
celiac trunk
part of hepatic portal system; a short, major artery that branches off the abdominal aorta and supplies blood to the upper abdominal organs, including the stomach, liver, spleen and pancreas; divides into three branches — left gastric artery, common hepatic artery and splenic artery; carries oxygenated blood to the organs of foregut; originates from abdominal aorta at ~T12/L1
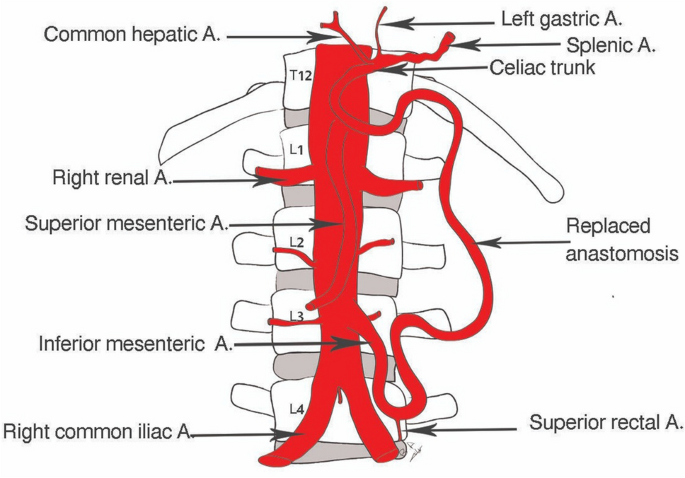
superior mesenteric artery
part of hepatic portal system; a major branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the majority of the small intestine (jejunum & ileum), as well as the ascending and transverse colon; originates from the anterior aspect of the aorta around L1, just inferior to celiac trunk
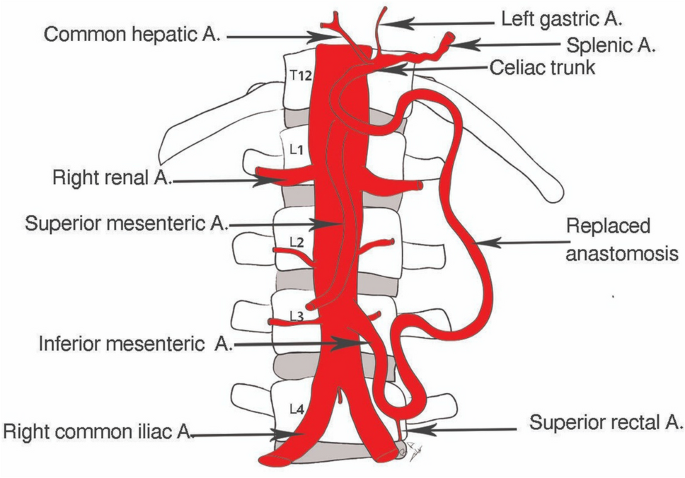
inferior mesenteric artery
a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the distal part of the large intestine (handout); arises from the anterior aspect of the abdominal aorta around L3 and runs inferiorly and to the left, passing behind the duodenum and pancreas
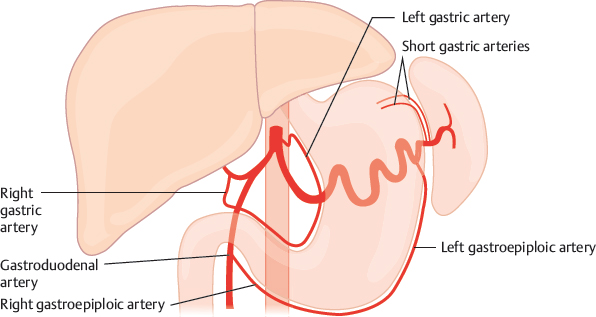
hepatic artery
a major blood vessel that supplies the liver with oxygen and nutrients; originates from the celiac trunk; branches off into proper hepatic artery and gastrodudenal artery; part of the hepatic portal system which carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract to the liver for detoxification and processing.
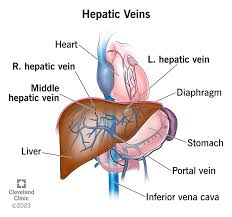
hepatic vein
referred to as hepatic portal vein; a system of blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the liver to the inferior vena cava; broken down into right, middle and left hepatic veins
left gastric artery
arises from the celiac trunk and runs along the superior portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach
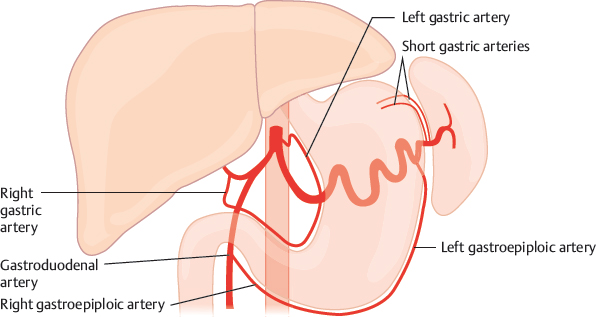
splenic artery
part of hepatic portal system; a major blood vessel that supplies the spleen with oxygenated blood; a branch of the celiac trunk; travels horizontally across the posterior part of the stomach and superior to the pancreas, then follows a tortuous path along the superior border of the pancreas to the spleen
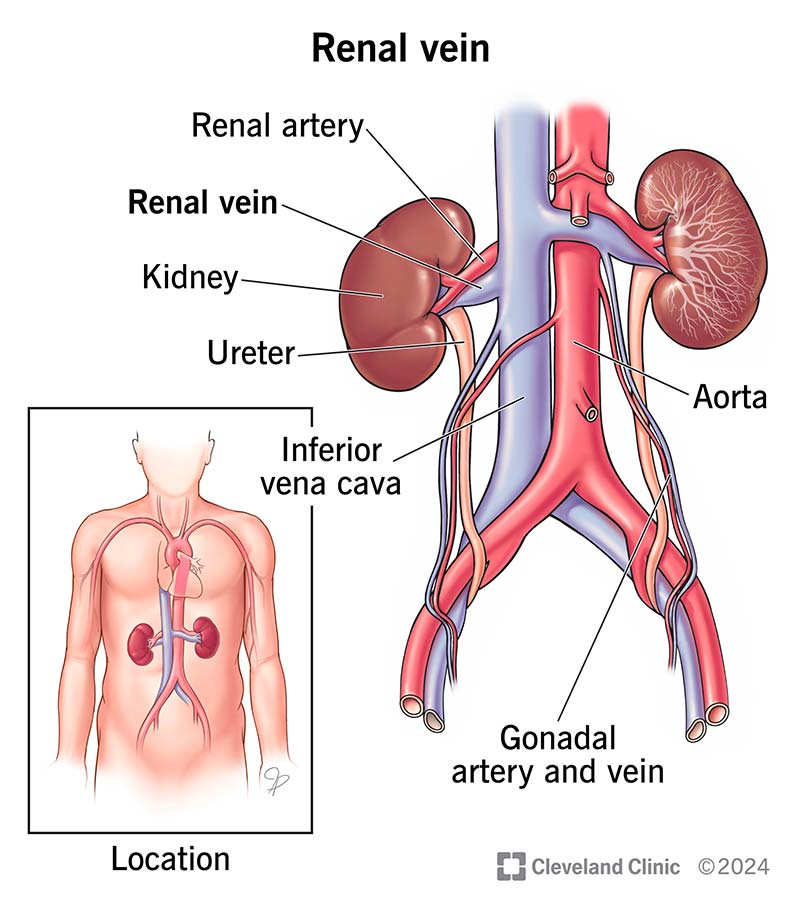
renal artery
two large blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the kidneys; support the kidneys with blood for filtration and excretion of waste products and helps regulate blood pressure and electrolyte balance; originates from the aorta and then divides into posterior and anterior branches upon entering the kidney
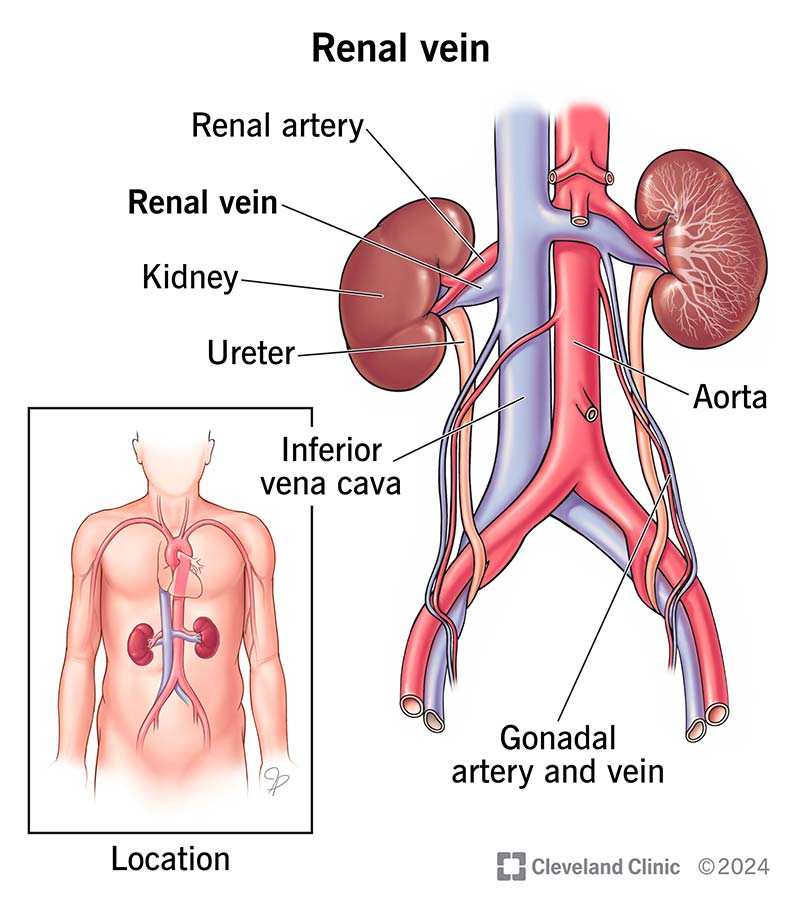
renal vein
large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava; originates in the renal hilum and travels along the lateral border of the kidneys, eventually joining inferior vena cava
veins and arteries of the arms and legs
axillary artery and vein, racial artery and vein, radial artery and vein, ulnar artery and vein superficial palmar artery and vein, common iliac artery and vein, internal iliac artery and vein, external ilic artery and vein, femoral artery and vein
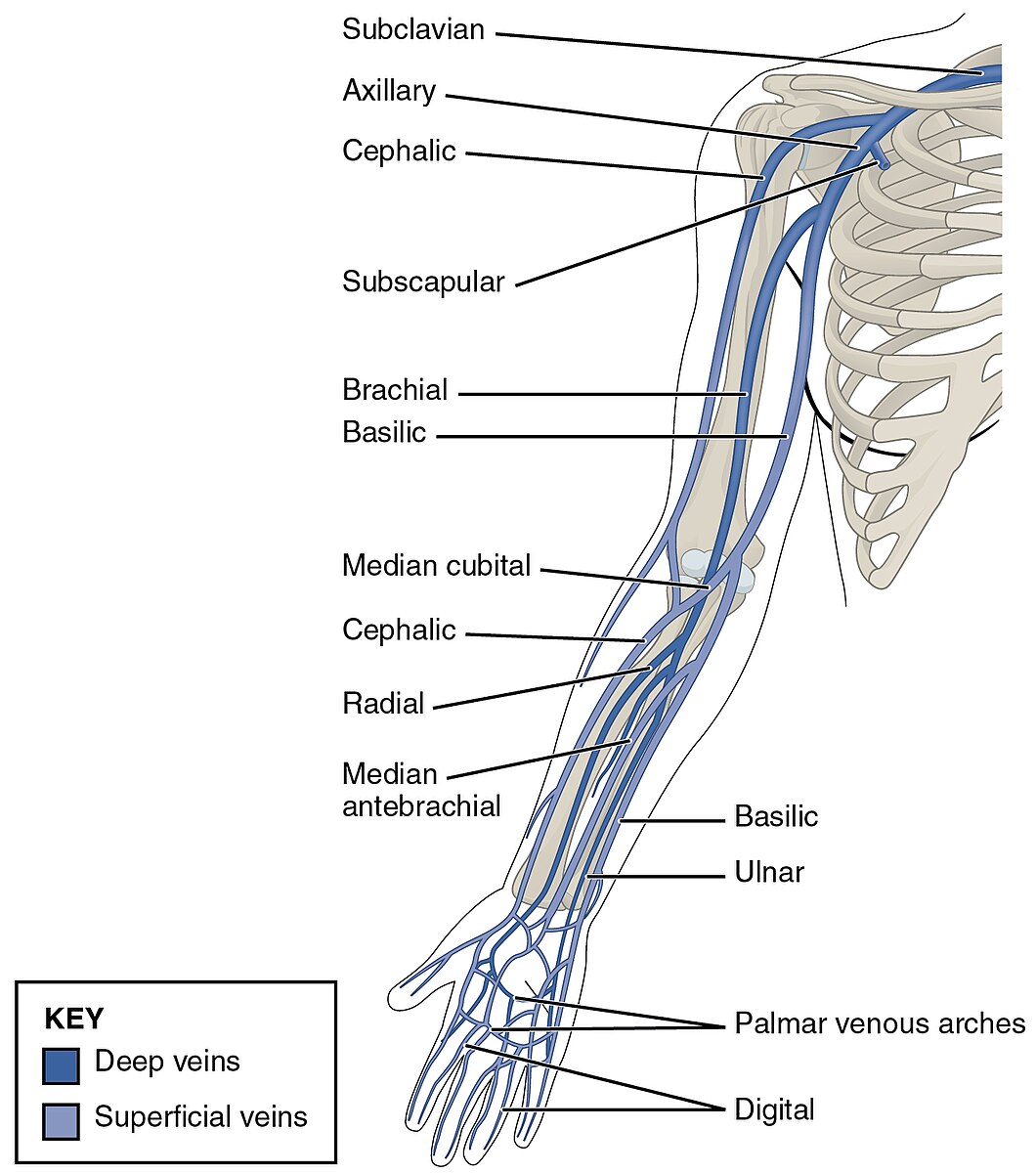
axillary artery
a major blood vessel that supplies the upper extremity; a continuation of the subclavian artery and runs through the axilla before becoming the brachial artery; extends from the lateral border of the first rib to the inferior border of the teres major muscle; supplies blood to muscles, skin, and other tissues of the upper extremity
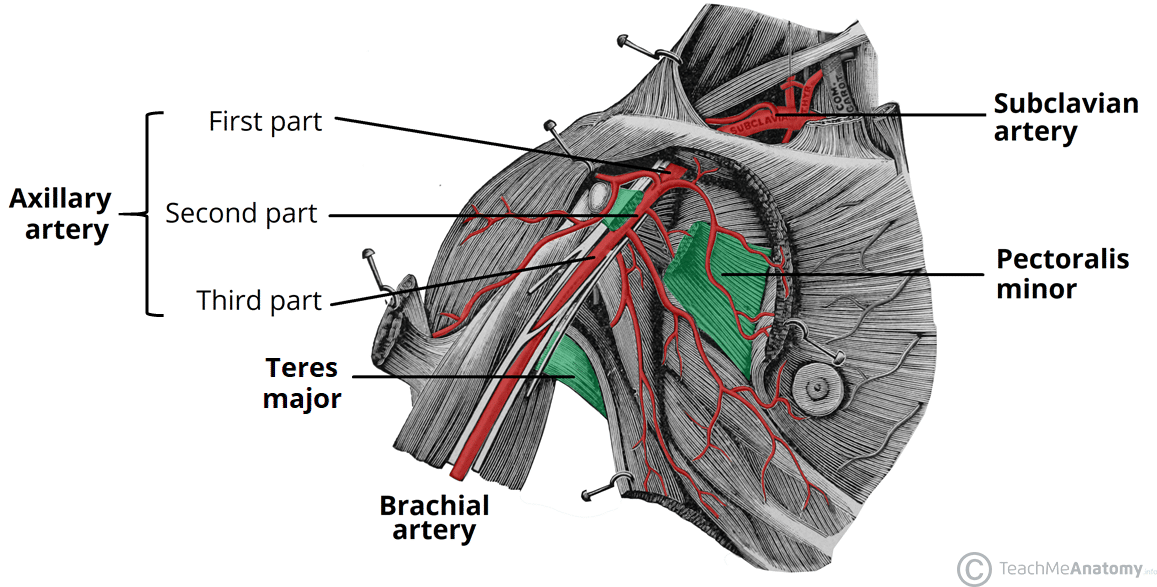
axillary vein
a major vein in the armpit that collects deoxygenated blood from the upper arm and drains into the subclavian vein; begins at the lower border of the teres major tendon and latissimus dorsi muscle
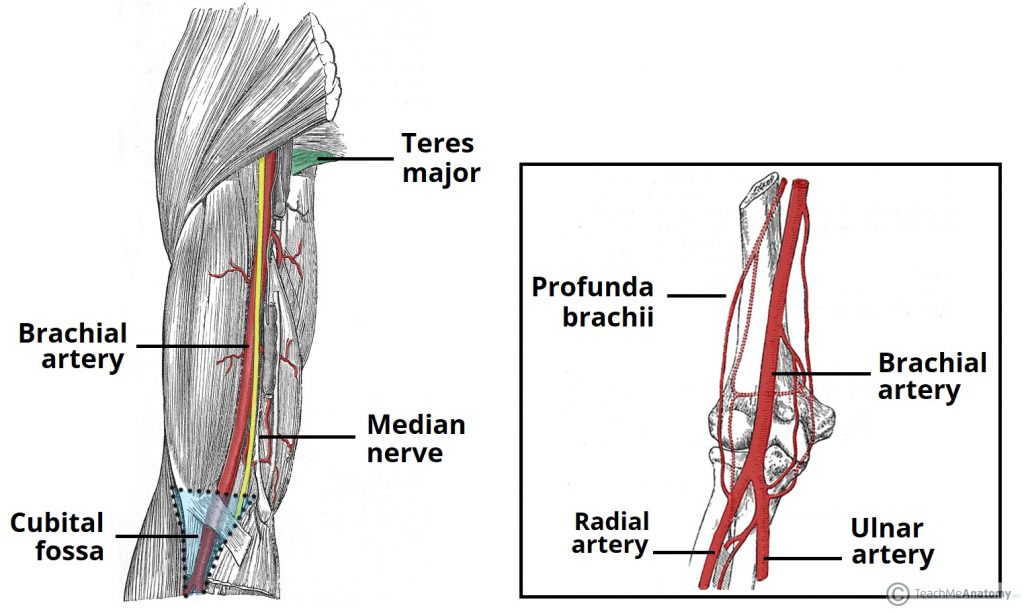
brachial artery
a major blood vessel located in the upper arm; continuation of the axillary artery and supplies blood to the muscles, skin and other tissues of the arm, originates at the lower border of the teres major muscle and runs on the anterior surface of the arm, medial to the biceps brachia muscle and terminates at the cubital fossa
brachial vein
a deep vein that accompanies the brachial artery in the region of the arm; formed by the unification of the ulnar and redial veins at the elbow
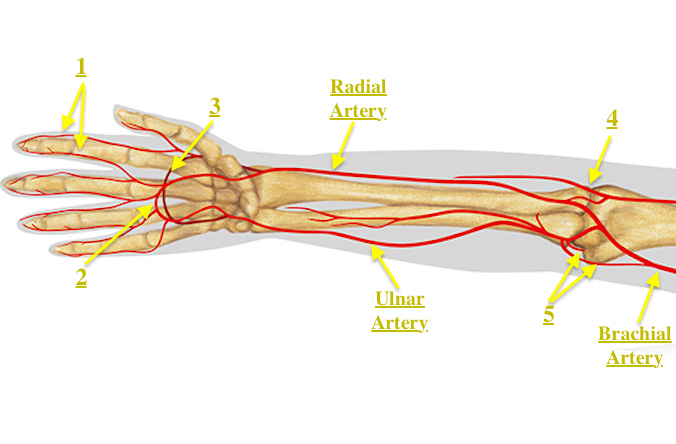
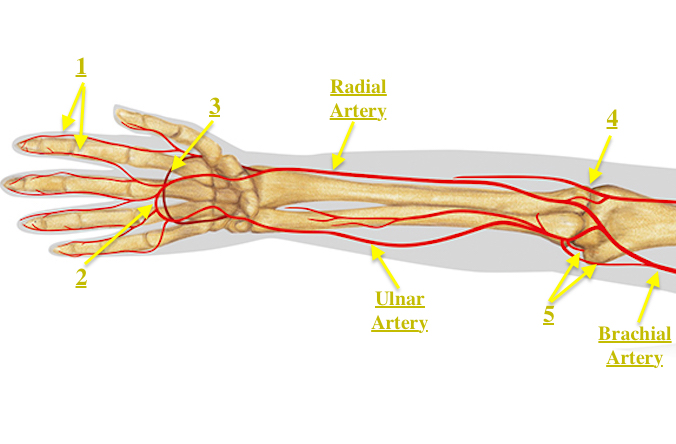
radial artery
located on the lateral side of the forearm, running parallel to the ulnar artery; originates from the brachial artery at the level of the elbow join and extends distally to the wrist; supplies blood to the forearm, wrist, and lateral three fingers (thumb-middle)
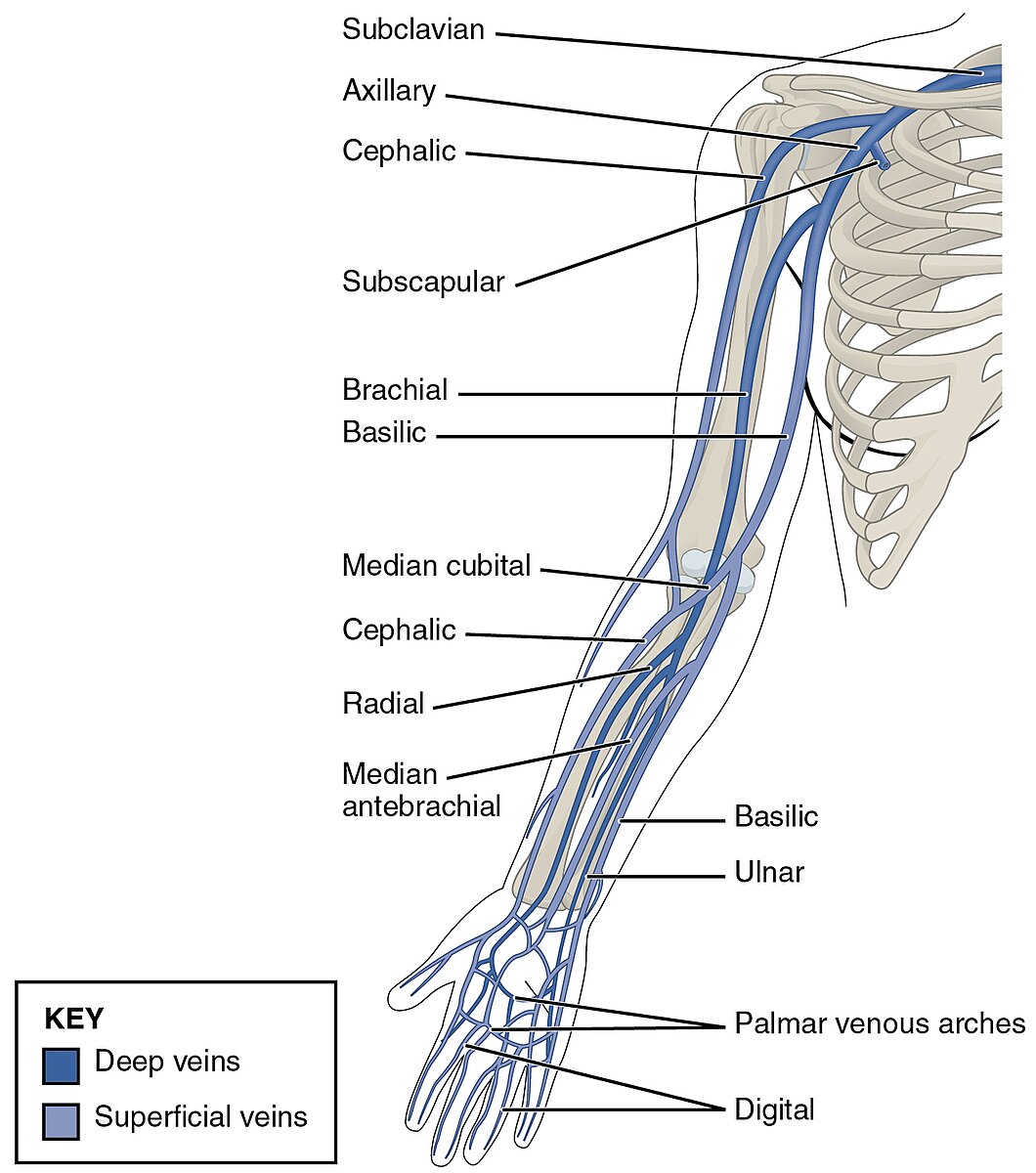
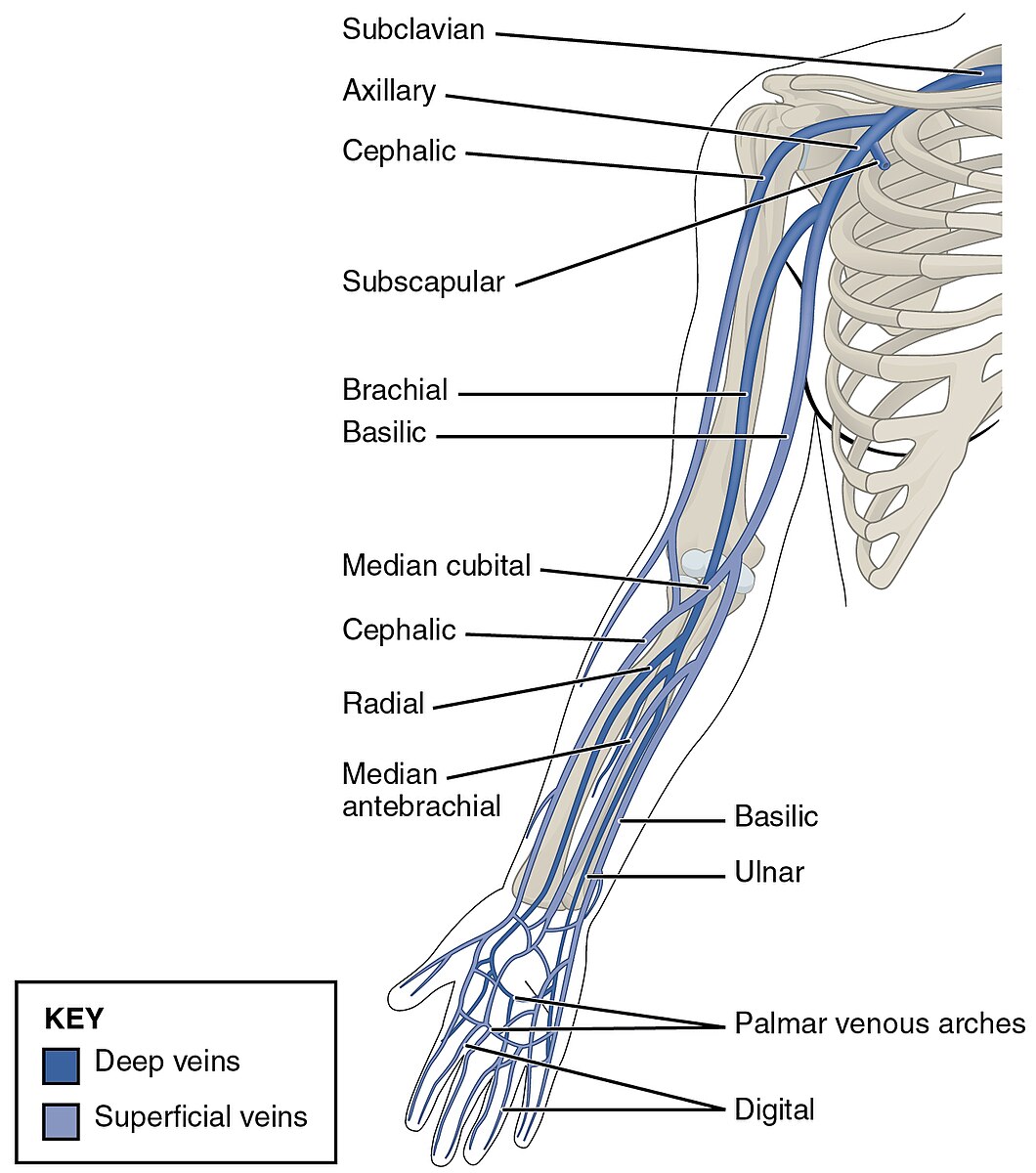
radial vein
a deep vein in the forearm that runs alongside the radial artery; collects venous blood from the deep structures of the hand and the lateral aspect of the forearm; joins with the ulnar vein at the elbow to form the brachial vein
ulnar artery
a major branch of the brachial artery, located in the forearm; runs along the medial side of the forearm and passes through the carpal tunnel at the wrist; supplies blood to the muscles, skin, and bones of the forearm and hand
ulnar vein
deep veins in the forearm that accompany the ulnar artery and unite at the elbow with the radial veins to form the brachial veins
superficial palmar artery
formed predominantly by the ulnar artery with a superficial palmar branch of the radial artery; referred to as the superficial palmar arch
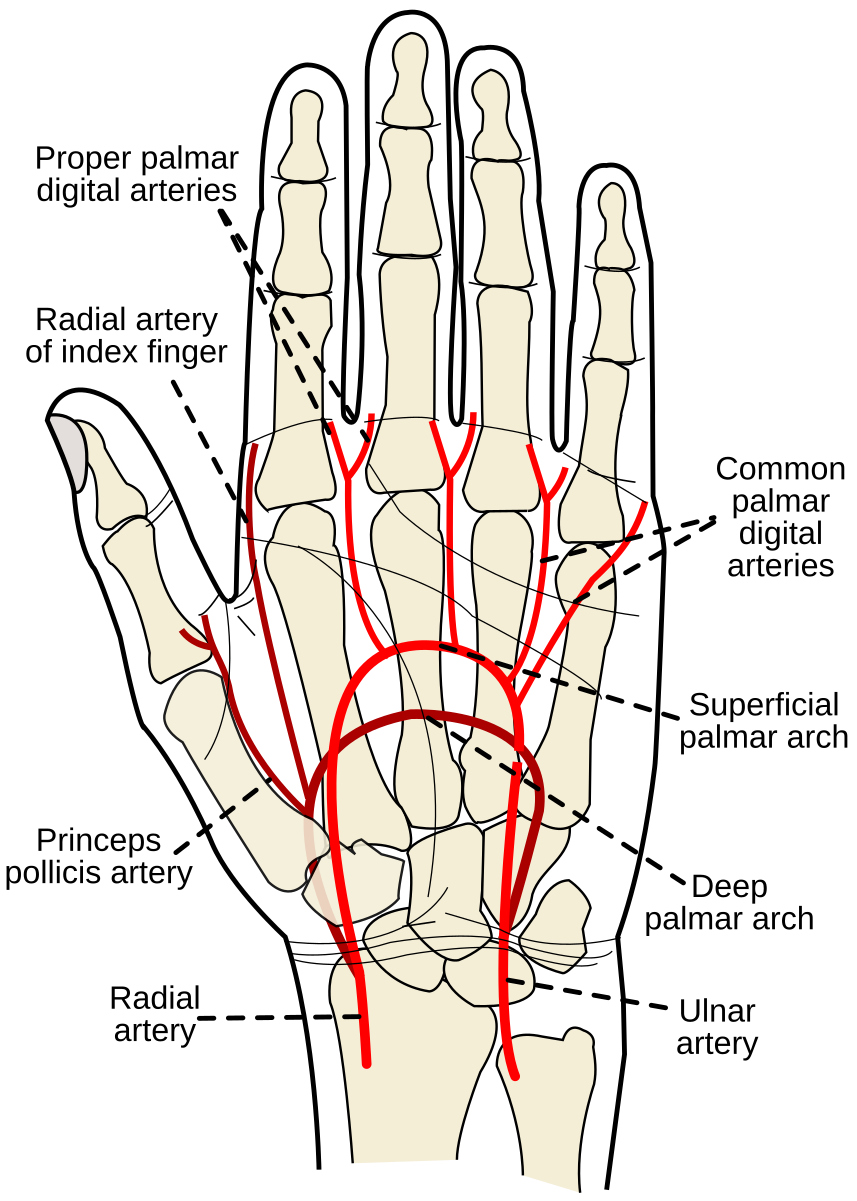
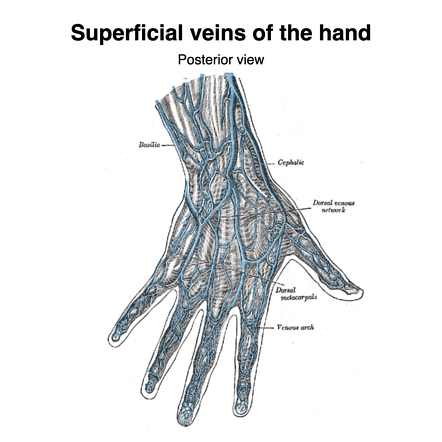
superficial palmar vein
formed by the union of the common palmar digital veins and drains into the median ante brachial vein; shunts blood to the dorsal venous network via intercapitular veins; accompanied y superficial palmar artery/arch; referred to as a venous arch occasionally
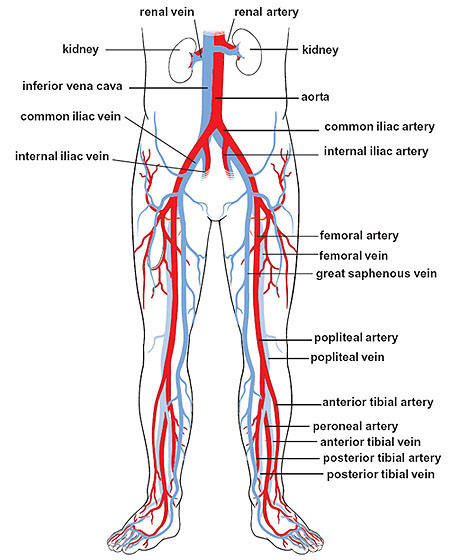
common iliac artery
paired blood vessels located in the pelvis that supply blood to the lower limbs and pelvic organs; arise from the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta at around l4, descend laterally along pelvic brim (anterior to sacroiliac joints) and then bifurcates into internal and external iliac arteries
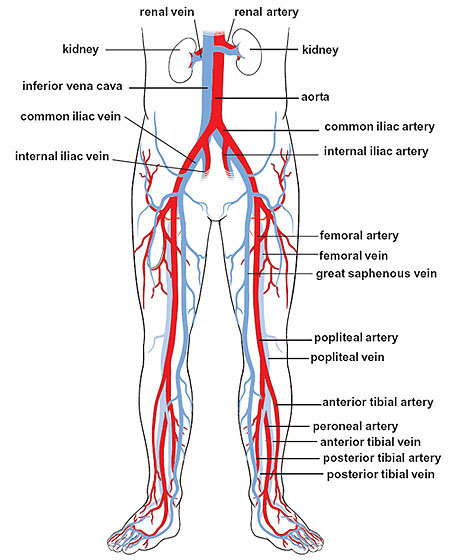
common iliac vein
two large veins that collect deoxygenated blood from the pelvis and lower body and drain into the inferior vena cava; formed by the union of the external and internal iliac veins and located on either side of the spine, joining ~L5 to create the inferior vena cava; no valves — more susceptible to blood clots
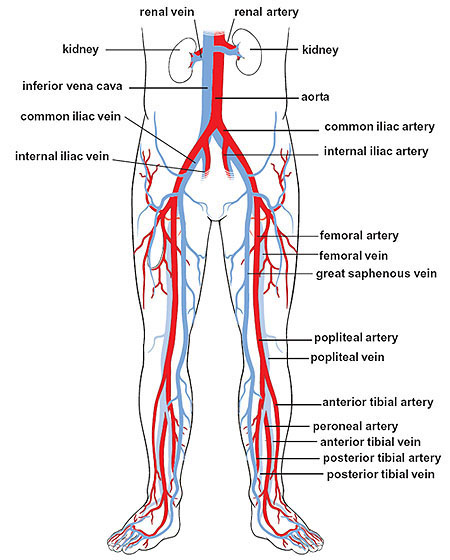
internal iliac artery
a major blood vessel in the pelvis that supplies the pelvic organs, buttocks and lower extremities; arises from the bifurcation of the common iliac artery at the level of L5-S1; descends medially through the pelvis, crossing anterior to the sacrum and posterior to the internal iliac vein
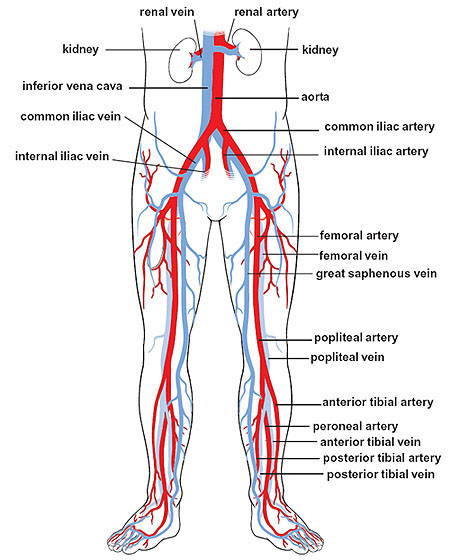
internal iliac vein
a large vein in the pelvis that collects blood from the pelvic organs, gluteal region and perineum; formed by several smaller veins joining together and terminates by merging with the external iliac vein to form the common iliac vein
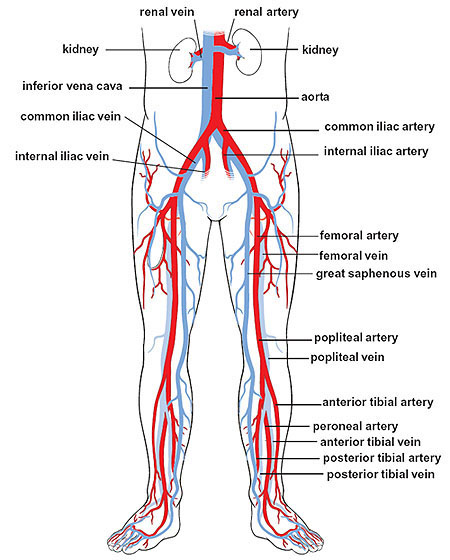
external iliac artery
a major blood vessel in the lower abdomen that supplies blood to the lower limb; originates from the bifurcation of the common iliac artery in the pelvis, runs along the medial border of the psoas major muscle and passes under the inguinal ligament and becomes the femoral artery in the thigh
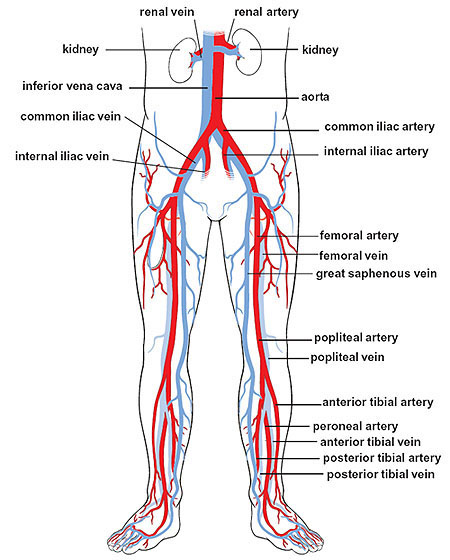
external iliac vein
an upward continuation of the femoral veins in the thighs; starts behind the inguinal ligament and merges with the common iliac vein
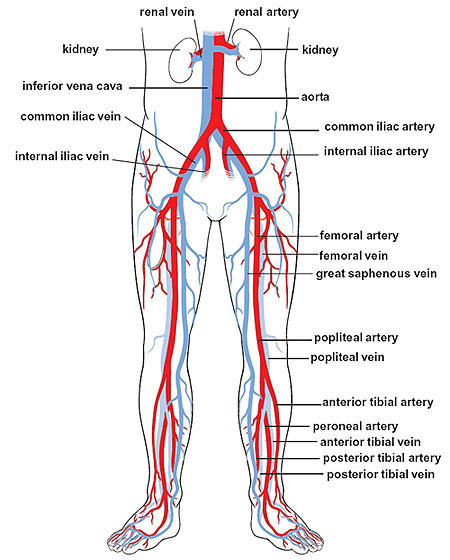
femoral artery
the main artery supplying oxygenated blood to the leg, originating in the groin and running down the thigh; a continuation of the external iliac artery and becomes the popliteal artery once it passes through the adductor hiatus; clinically significant for providing a pulse point
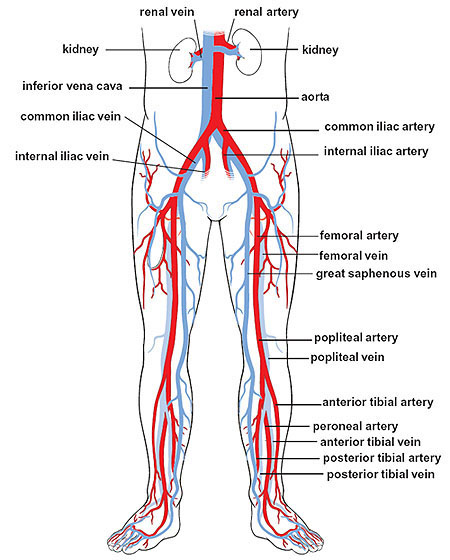
femoral vein
the main deep vein of the thigh, accompanying the superficial and common femoral arteries; forms from the popliteal vein
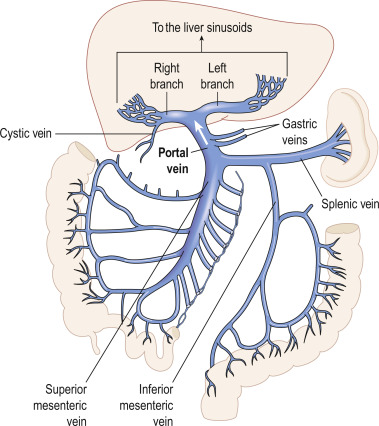
hepatic portal system
celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, splenic artery, gastric artery, hepatic portal vein; a network of veins/arteries that carry blood from the digestive organs to the liver; plays a crucial role in processing nutrients, toxins and other substances absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
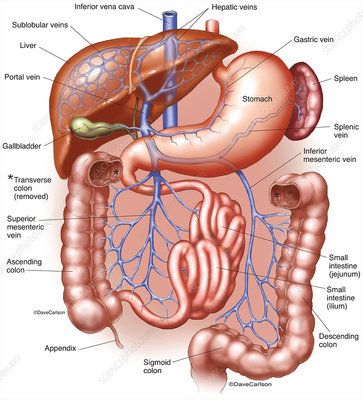
gastric artery
supplies the funds and proximal body of the stomach by branching from the splenic hilum; tends to be broken down into right and left arteries
hepatic portal vein
a vein conveying blood to the liver from the spleen, stomach, pancreas, and intestines; primary function is to carry nutrient rich blood from the digestive organs directly to the liver for processing
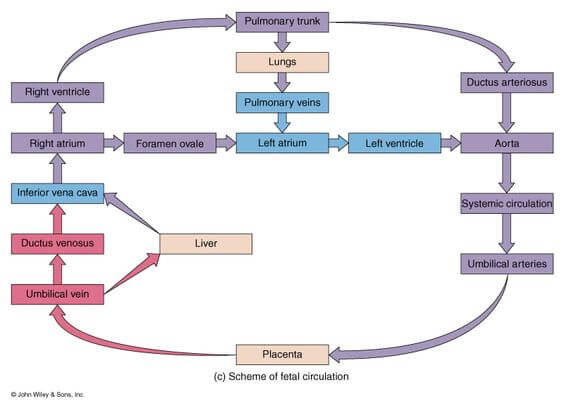
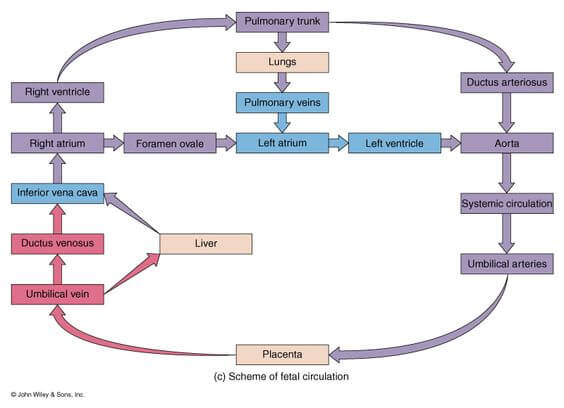
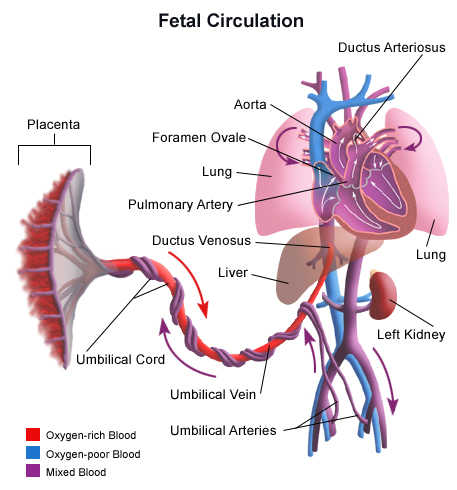
fetal circulation
composed of placenta, umbilical cord and umbilical artery and vein; placenta issued for gas and nutrient exchange, bypassing the mature lungs and liver via the umbilical vein
placenta
a temporary organ that connects the baby to the uterus during pregnancy; develops shortly after conception and attaches to the wall of the uterus; umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood from this organ to fetus and umbilical arteries carrying deoxygenated blood from the fetus bring it back here.
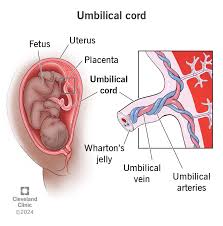
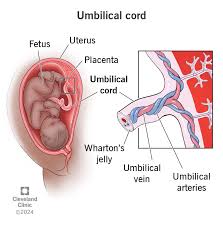
umbilical cord
a structure that connects a developing fetus to the placenta during pregnancy; composed of two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein surrounded by Wharton’s jelly and an amniotic membrane
umbilical artery
two blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta; located within the umbilical cord which connects the fetus to placenta; transports waste and CO2 from the fetus to the placenta for removal
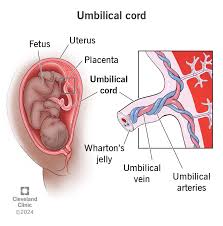
umbilical vein
a blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus during pregnancy
fetal heart
3 notable differences from adult heart — foramen oval, ductus arteriosus and ductus vensous; circulation of blood involves the ductus venosus shutting blood from the umbilical vein past the liver to the inferior vena cava, while the foramen oval moves blood from the right atrium to the left atrium, and the ductus arteriosus directs blood from the pulmonary artery to the aorta