OCR BIOLOGY - cell division
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is the cell cycle
is an ordered set of events resulting in cell growth and division into 2 genetically identical daughter cells
sequence of evetns that occurs between one cell division to the next
stages in the cell cycle
G1 - growth phase, proteins are made
checkpoint cell - checks that the chemicals needed for replication are present and for any damages to the DNA before enter S phase
S - synthesis, cell replicates its DNA, ready to divide by mitosis
G2 - growth stage 2, cell keeps growing and proteins needed for cell division are made —— all
checkpoint cell - checks if all DNA has been replicated without any damage. cell can then enter mitosis
INTERPHASE (growth stage)
M - mitosis and cytokinesis
what is the significance of mitosis in life cycles
growth, tissue repair and asexual reproduction in plants, animals and fungi.
how is the cell cycle is regulated
use of checkpoints to control the cycle
G1 checkpoint cell - checks that the chemicals needed for replication are present and for any damages to the DNA before enter S phase
G2 checkpoint cell - checks if all DNA has been replicated without any damage. cell can then enter mitosis
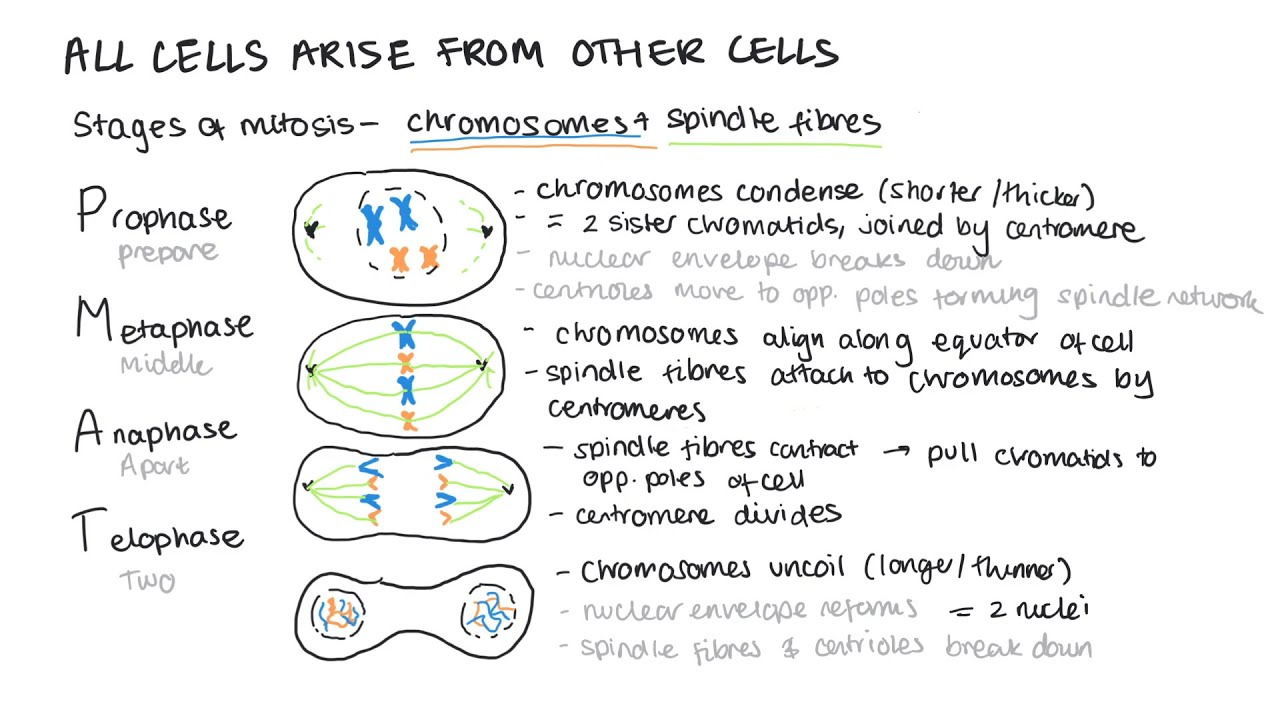
the main stages in mitosis
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
mitosis: 1- Interphase
cell carries out normal functions but prepares to divide
DNA is unravelled and replicated which doubles its genetic content
organelles are also replicated
ATP content is increased - provides energy needed for cells.
mitosis: 2- Prophase
chromosomes condenses so goes shorter and fatter
2 sister chromatid joined togather by centromere
centrioles (tiny bundles of proteins) starts moving to opposite poles of the cell forming spindle fibres (network of protein fibres)
the nuclear envelope breaks down and the chromosomes lies free
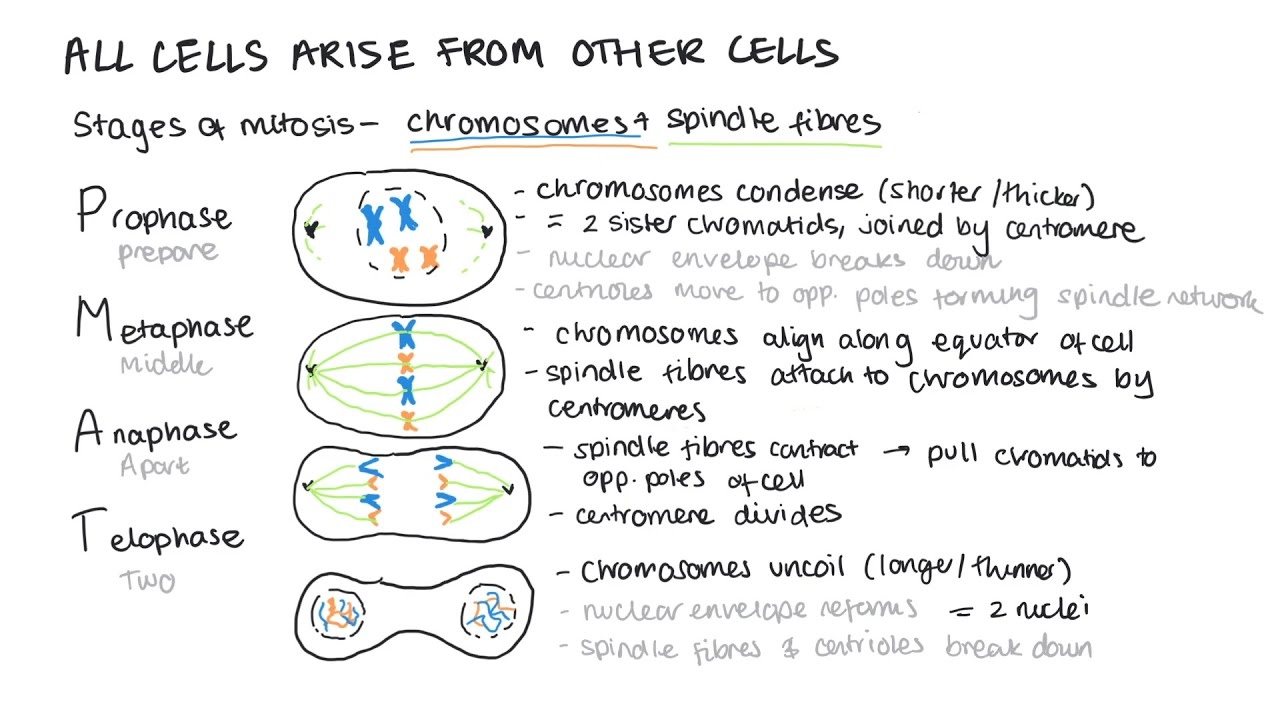
mitosis: 3- metaphase
the chromosomes becomes attached to the spindle by their centromere
the chromosomes are all lined up in the middle of the cell
at the M checkpoint the cell checks all chromosomes are attached to the spindle fibres before mitosis
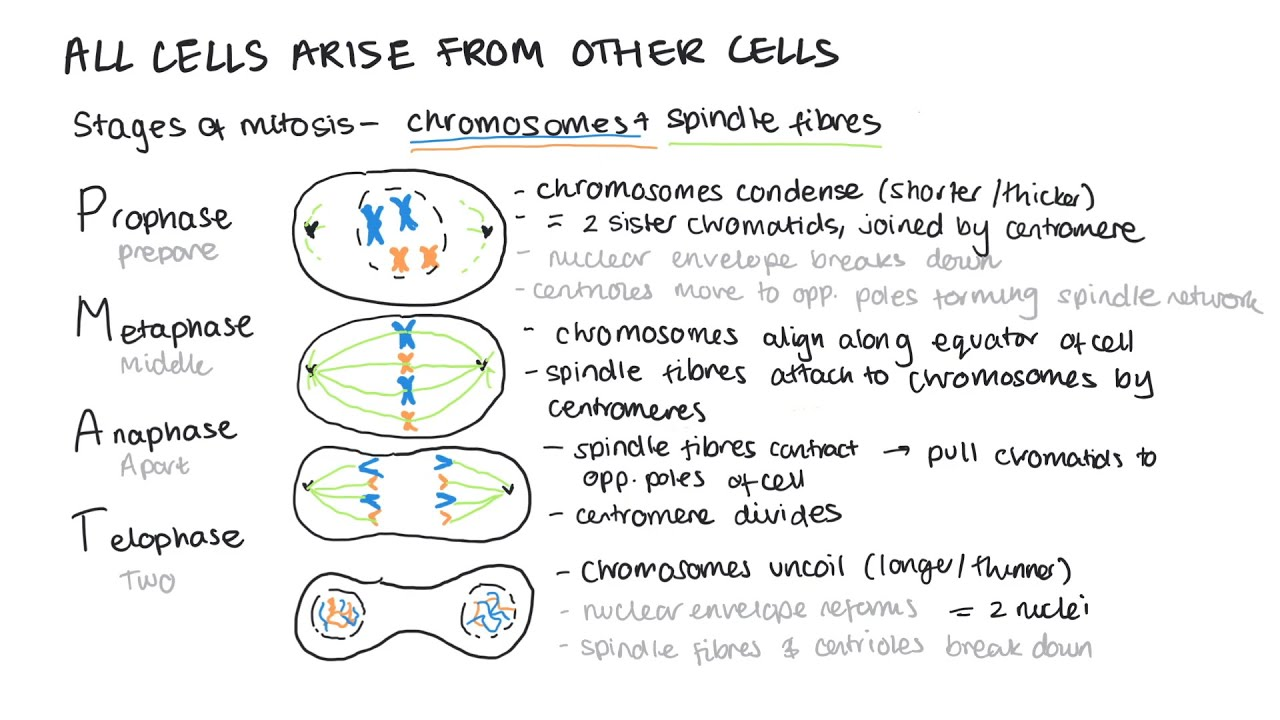
mitosis: 4- Anaphase
the centromere divides seperating sister chromatids
spindles contract pulling chromatids to the opposite end
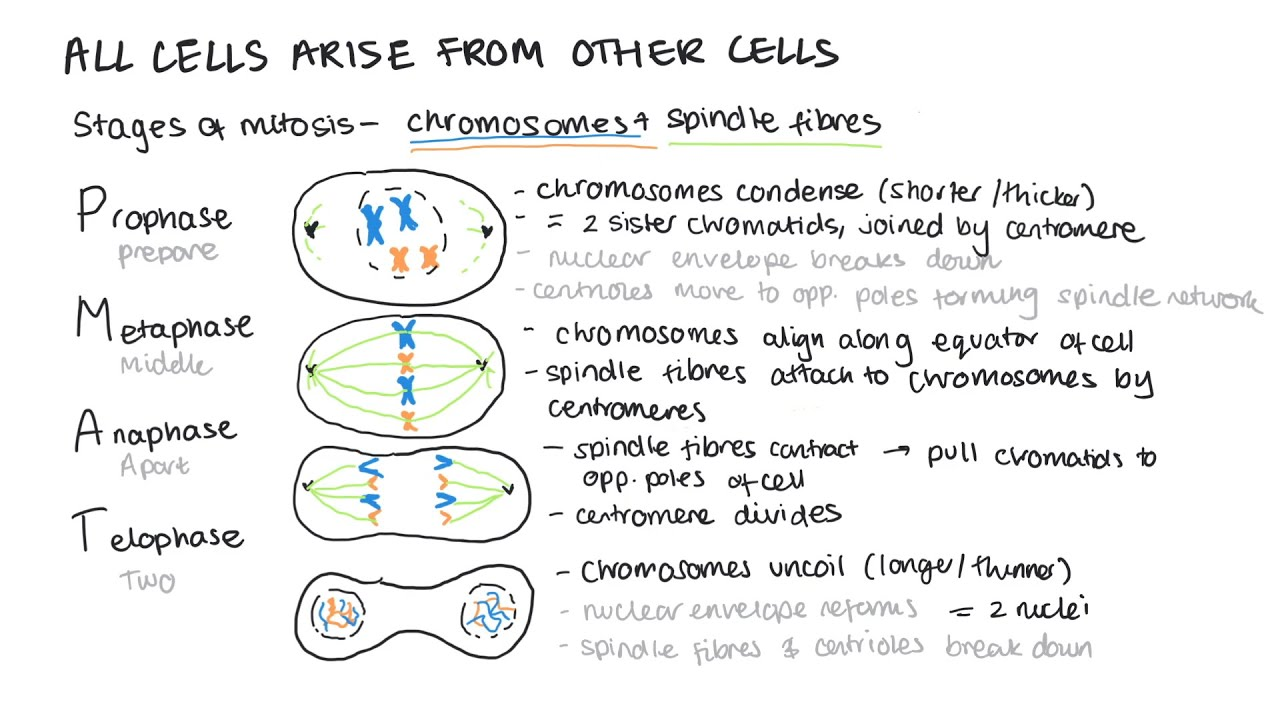
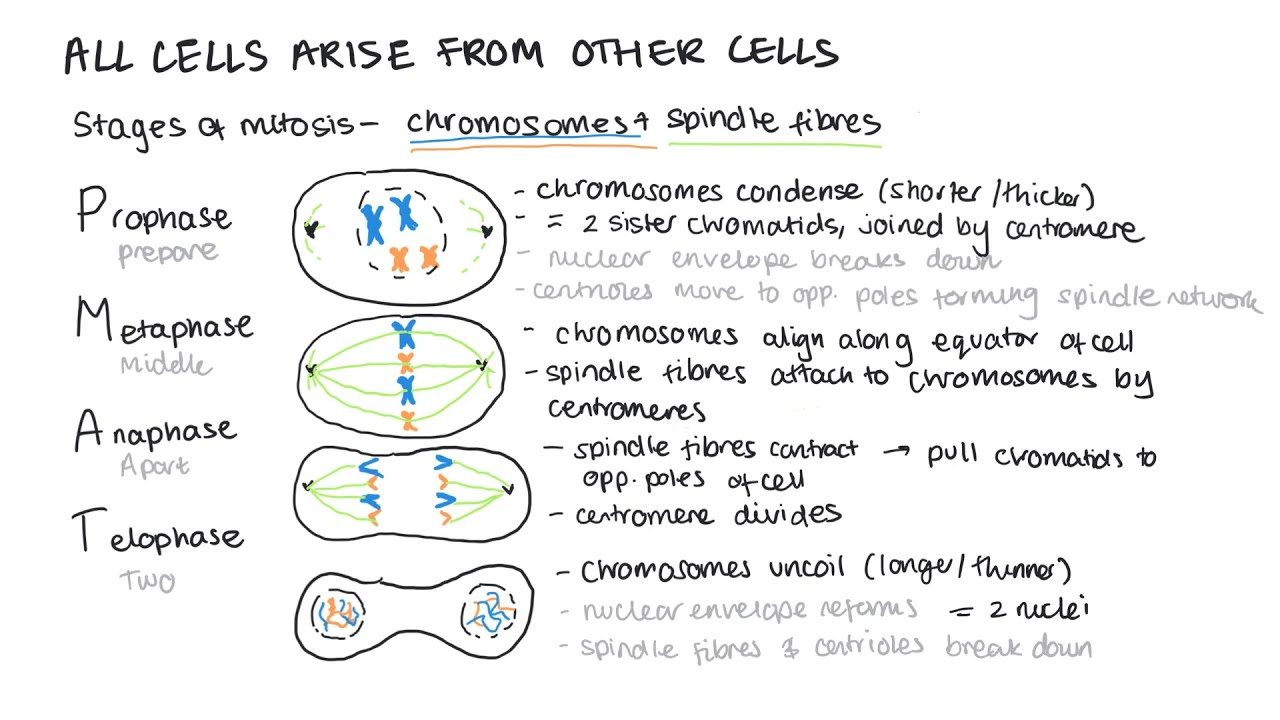
mitosis: 4- Telophase
chromatids reach the opposite poles
they uncoil and becoming long and thin
now chromosomes again
nuclear envelope forms around each chromosomes forming 2 nuclei
mitosis: 5- Cytokinesis
cytoplasm divides
cleavage furrow forms to divide the cell membrane
2 daughter cells genetically identical to each other made
cytokinesis begins at anaphase and finishes at telophase
seperate process from mitosis
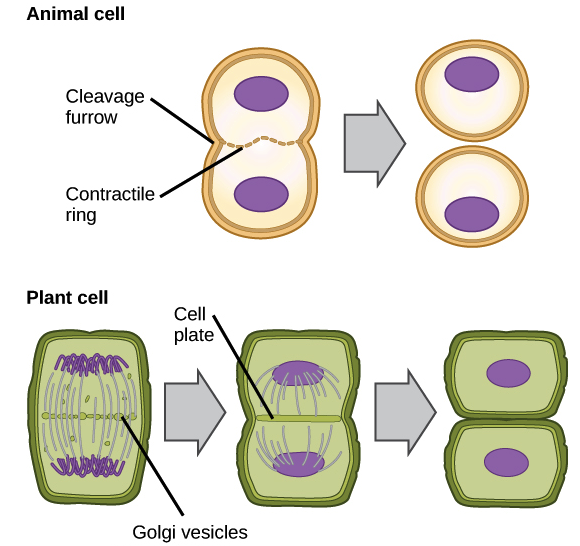
mitosis in plant cell
mitosis steps same until seperation
plant cells have cell walls so wont form cleavage furrow
vesicles from the golgi apparatus begins to assemble in the same place where metaphase plate was
vesicles fuse with each other dividing cell surface membrane into 2
define meiosis
form of cell division where the nucleus divides twice resulting in halving of chromosomes and producing 4 haploid cells from one diploid.
the significance of meiosis
produces haploid cells and genetic variation by independent assortment and crossing over.
used in gametes and is a reduction division
stages of meiosis
interphase
Meiosis I
prophase 1
metaphase 1
anaphase 1
telophase 1
Meiosis II
prophase 2
metaphase 2
anaphase 2
telophase 2
meiosis I: prophase I
Prophase I -
chromosomes condenses
nuclear envelope disintegrates homologous chromosomes pairs up forming a bivalent
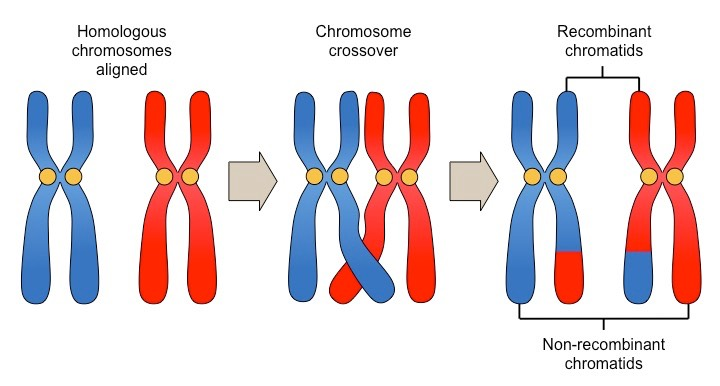
these chromosomes when moved through liquid cytoplasm the chromatids become entangled aka CROSSING OVER
due to this crossing over = chromatids have the same genes but different combinations of allele
spindle fibres form
meiosis I: Metaphase I
Metaphase I -
the homologous pairs of chromosomes assemble along the metaphase plate by spindle fibres from centromere instead of single chromosomes
orientation of chromosomes on metaphase plate is random
the maternal and paternal chromosomes can end up facing either pole aka INDEPENDANT ASSORTMENT results in different combinations of alleles facing towards the poles, this leads to genetic variation
meiosis I: Anaphase I
Anaphase I -
homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles and chromatids stay joined together
sections of DNA on sister chromatid becomes entangled during crossing over now breaks off and rejoins resulting in exchange of DNA. point where chromatids breaks and rejoins is called CHIASMATA
when genes get exchanged between chromatids - RECOMBINANT. genes being exchanged may be different alleles of the same gene meaning the the combo of alleles being exchanged will be recombinant chromatids will be a different allele combo from original chromatid.
causes genetic variation from new combo of alleles so sister chromatids are no longer identical
meiosis I: Telophase I
Telophase I -
chromosomes assemble at each pole and nuclear membranes reforms
chromosomes uncoil
cell undergoes cytokinesis and divides into 2
the reduction of chromosomes number from diploid to haploid is complete
Meiosis II: Prophase II
Prophase II -
chromosomes consists of 2 chromatids, condenses and becomes visible again
the nuclear envelopes breaks down
spindle formation begins
Meiosis II: Metaphase II
Metaphase II -
individual chromosomes assemble on the metaphase plate
chromatids are no longer identical due to crossing over - there is independent assortment and more genetic variation
Meiosis II: Anaphase II
Anaphase II -
chromatids of individual chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles after division of centromeres
Meiosis II: Telophase II
Telophase II -
chromatids assemble at the poles
chromosomes uncoil and form chromatins again
nuclear envelopes reform
nucleolus becomes visible
cytokinesis results in the division of 4 daughter cells making cells haploid as its reduction reaction
will be genetically different from each other and from parent cell due to crossing over and independent resortment.
specialised cell: erythrocytes
aka RBC
flattened biconcave shape = increase SA:volume
essential in transporting oxygen
dont have nuclei = increases space available for haemoglobin
flexible = squeezes through narrow capillaries
specialised cells: neutrophils
aka WBC
essential role in immune system
multi lobed nucleus = easier to squeeze through small gaps to get to sites of infection
granular cytoplasm = many lysosomes which contains enzymes used to attack pathogens
specialised tissue: squamous epithelialium
made of squamous epithelial cells
aka pavement epithelium = flat appearance
thin = squats/ flat cells make up it so its one cell thick
present when rapid diffusion across a surface is essential
forms lining of the lungs = rapid diffusion of oxygen into the blood
specialised tissue: ciliated epithelial cells
made up of ciliated epithelial cell
hair like structure of structure is called cilia = beats in rhythmic manner
lines up the trachea = mucus to be swept away from the lungs
goblet cells also present = releasing mucus to trap unwanted particles present in the air = prevents bacteria reaching alveoli once in lungs
specialised cell: sperm cells
male gametes
delivers genetic information to female gamete (ovum)
contains a flagella = capable of movement and has many mitochondria present so supplies energy needed to swim
acrosome = digestive enzymes released to digest protective layer around ovum and lets sperm penetrate through it - leads to fertilisation
specialised plant cell: palisade cells
present in mesophyll = contains chloroplasts to absorb large amount of light for photosynthesis
cells = rectangular box shapes, closely packed for continuous layer
thin cell walls = increases rate of diffusion of CO2
large vacuole = maintains turgor pressure
chloroplasts cna move within cytoplasm = to absorb more sunlight
specialised plant cell: root hair cells
present at surface of roots near growing tips
long extensions called root hairs
these increases SA of the cell
maximises the uptake of water and minerals from the soil
specialised plant cell: guard cells
forms small opening of leaves surface called stomata
necessary for CO2 to enter plant for photosynthesis
guard cell = loses water = less swollen due to osmotic forces = changes shape
stoma closes = prevents further water loss from the plant
cell wall of the guard = one side thicker so the cell dont change shape symmetrically as it changes volume
cartilage tissue
connective tissue
found on the outer ear, nose, and the end of bones
contains fibres of proteins and elastin and collagen
firm and flexible connective tissue
made up of chondrocyte cells embedded in extracellular matrix
prevents end of bones rubbing against each other
fishes have bones made up of cartilidge
muscle tissue
shortens in length in order for bones to move
different types of muscle fibres:
skeletal muscle fibres - attached to the bone
myofibrils - contains contractile proteins
xylem tissue
vascular tissue
responsible for transport of water and minerals throughout plants
composed of vessel elements - elongated dead cells
walls strengthened by lignin = waterproof - provides structural support for plants.
phloem tissue