Soils Final Exam - Video Quiz Questions
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
What is "Soil Ventilation" and why is it important?
carbon dioxide is released and oxygen enters soil via soil pores.
it is important because it allows roots to conduct respiration and obtain energy
From largest to smallest name the three types of particles that make up what is called soil.
1 - Sand
2 - Silt
3 - Clay
Decaying bi-products (processed organic material) from plants and animals make up which important non-mineral component of soil?
humus
An unconsolidated layer of parent material or crumbled, hard, unweathered rock is called ______________________?
regolith
A soil horizon that is defined by nutrient leaching that leaves behind a relatively coarse and sandy layer is called _______________________?
E-Horizon
A soil where the OH- ions outnumber the H+ ions is called _____________________.
Alkaline
List four processes described in the text that commonly lead to the degradation of soil quality.
1) Erosion that removes topsoil
2) The accumulation of salts in improperly irrigated soils in arid regions
3) When people cultivate soils and harvest the crops without returning organic residues and mineral components
4) Contamination of a soil with toxic substances or pollution
How do you distinguish between the O-Horizon and the A-Horizon?
O-Horizon contain largely unprocessed organic matter, while A-Horizon contains more humus (processed organic matter)
According to the text, what are the five main roles of soil in an ecosystem?
1) A medium for plant growth
2) Regulator of Water Supplies
3) Recycler of Raw Materials
4) Habitat for Soil Organisms
5) Engineering Medium
A Soil Infiltration Test provides data that is most directly related to which soil property
Soil Permeability
The term that describes water's ability to stick to solid surfaces
Adhesion
When one water molecule attaches to another water molecule, it is called _____________________.
Cohesion
The process of nutrient ions continually moving from areas of greater concentration toward the nutrient-depleted areas of lower concentration around the root surface is called __________________________?
Diffusion
What causes most soil nutrient leaching?
Gravitational Water
What term is given to water that is stored and moves upwards through micropores in the soil?
Capillary Water
The term for a soil's state when the gravitational water has drained away but a decent amount of useable capillary water remains is _______________________.
Field Capacity
Even though there may be an adequate amount of water (enough to prevent wilting) remaining in the soil after it has reached the permanent wilting point, why do plants remain wilted in the day and night even though water is still present in the soil?
The remaining water is capillary water and is held to tightly to the soil by adhesion to be available to plants to prevent wilting.
Why might a soil rich in iron (but NOT with too much iron) still be unable to provide enough iron to a plant that requires this mineral?
Because the iron is not in an available form for the plant roots to take it up
Can plant roots ingest soil particles if they are small enough?
NO
No matter how fine, plant roots cannot ingest soil particles and require nutrients to be dissolved in a soil solution for uptake.
As a society, is our reliance on soils likely to increase or decrease in the decades ahead?
Increase.
Population increase will require more food growing medium. More sites for soil engineering. Carbon storage. Water filtration.
Rocks that are composed of primary mineral, such as feldspars, and are generally dark-colored mineral that contian iron and magnesium and are more easily weathered than other types of rocks belong with which category of rock?
Igneous rocks
The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rock at or near the Earth's surface is called?
Weathering
Rock abrasion by ice and rock cracking from plant roots are both examples of ______________________ weathering.
Physical
Salt dissolving in water is an example of what type of chemical weathering process?
Dissolution
Chemical reactions in which a compound like iron loses electrons is called _________________.
Oxidation-Reduction
Poorly sorted rock fragments like talus or cliff rock debris (detritus) that are detached from high areas and carried downslope by gravity is termed ________________.
Colluvium
Colluvial Debris
What are the three general classes of alluvial deposits?
-Floodplains
-Alluvial Fans
-Deltas
What is the difference between 'glacial till' and 'basal till'?
Glacial till is the materials deposited by glaciers in an unstratified mixture of debris which vary in size from boulders to clay. This is the material that is 'along for the ride' on the glacier and is dropped/deposited when the glacier melts.
Basal till is a finer ground material that is made by the glacier itself grinding/scraping on bedrock and leaving behind a dense, concrete-like layer that is difficult for plant roots to grow into.
The greater the amount of precipitation a climate has the greater the amount of chemical weathering.
True
What are 'lacustrine' deposits?
Materials deposited in lakes that remain after the lakes have dried up.
What is the most influential soil forming factor
Climate
What are the five major soil forming factors?
1 - Parent Material
2 - Climate
3 - Vegetation
4 - Topography
5 - Time
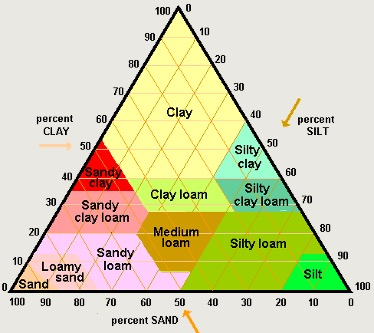
"A" horizon sample - 40% sand, 40% silt, and 20% clay.
What is the soil texture?
medium loam
Terms commonly used in association with wetland soils
Sapric
Peat
Muck
Soluable salts can build up in the upper soil horizons in some regions because of a lack of ___________________.
This can also lead to a build up of carbonates and certain types of cracking clays.
water
What do earthworms eat?
Soil particles and organic residues`
In general, we would expect to see the least amount of soil moisture on slopes that face the _________________
South
Do erosion rates of soils depend on climate, slope and vegetation type?
Yes
How is Colluvium transported?
gravity
How is Glacial till transported?
glacial ice
How is Alluvium transported?
Flowing water
Rank the soil horizons (A, E, B, C, R) in order of (1) most biological activity to (5) least amount of biological activity.
1 - A
2 - B
3 - C
4 - E
5 - R
What size of soil particle exhibits a greater amount of adsorption and microbial colonization than the others?
Clay
Positively charged ions are called _________________.
cations
What type of silicate clay has the greatest cation exchange capacity?
Vermiculite
Organic (humus) colloids usually unsuitable for making building or road foundations?
True
How is the Cation Exchange Capacity affected by soil pH?
It increases with higher pH levels
Isomorphic substitution is the process where
one atom replaces another atom of similar size without disrupting the crystal structure of a clay mineral.
Silicate clays have an overall positive charge.
False
they have a negative charge.
Most of the nutrients important to plant growth are cations and have a positive charge.
True
What prevents cations from permanently bonding with clay particles?
A Hydration Sphere
Nutrients like nitrogen phosphorus and potassium are more easily available for plant uptake when soil pH is more acidic.
False
These nutrients are more available in more alkaline pH.
Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) is an important measurement because it determines the amount of cations available for ________________.
plant uptake
The total number of negative colloid charges per unit mass is termed ___________________________
cation exchange capacity
What type of soils typically have the lowest amount of colloids?
Sandy Soils
Cations are more susceptible to leaching out of the soil than anions.
False
Generally, anions are more susceptible to leaching than cations.
A molecule's ability to hold onto ions is referred to as _____________________.
chelate
OR
adsorpton
Root systems have a _____________ charge
Negative
Clay particles have a strong __________________ charge
negative
If a nutrient is not attached to a soil particle surface, what is likely to happen to it when it rains?
It will leach downward in the soil
Which of the following elements would form a stronger chemical bond with a clay particle?
a. Potassium
b. Hydrogen
c. Calcium
d. Sodium
C
Can anions attach to clay particles?
NO
The presence of several organisms that can carry out the same ecological task is termed ______________________.
Functional Redundancy
Earthworms belong to which trophic level in a Soil Food Web?
Primary Consumer
Secondary Consumer
Higher Level Consumer
The term given to fungi, bacteria, and other forms of microflora that carry out the decomposition of dead plant and animal debris is _____________________.
Saprophytic feeders
______________________ is much more prevalent in forest soils than in grassland soils.
Fungi
Fungi utilizes a different style of growth that allows it to transport nutrients along long hairlike threads than can stretch for miles. This is an example of what type of growth?
Filamentous
What produces exudates?
roots
What is the rhizosphere and where does it occur in soils?
Area in soil that is significantly influenced by living roots.
Typically occurs within 2 MM from the root surface.
What is a mycotoxin?
a toxin produced by fungi
When fungal hyphae penetrate the root cell wall and form small, highly branched structures that transfer (1) mineral nutrients from the fungi to the host plants and (2) sugars from the plant to the fungus, we refer to those highly branched structures as ___________________.
Arbuscules
Termites are most commonly found in _____________________.
Grasslands (Savannas)
Microbes (Microbial Activity) consist of very small living things that include
Bacteria
Fungi
Protozoa
What do earthworms eat?
Detritus
Soil Organic Matter
What sex are earthworms primarily?
neither male or female
Earthworm casts are high in ________,__________ and organic matter.
Bacteria
Available Plant Nutrients
Roots typically occupy about __________ percent of the soil volume, but may be responsible for 30% of the soil respiration in a soil.
1%
The rhizosphere is exceptionally rich in soil nutrients because of ____________________.
Exudate Interactions
Bacteria is present in much higher concentrations in grasslands and agricultural soils than in forests because of the high concentration of _________________ in grasslands and agricultural soils.
roots
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is an example of a _____________________
Genetically Engineered Microorganism
In general, the following practices have led to a DECREASE in biodiversity & populations (Select ALL that apply)
Soil Fumigants
Moldboard plowing
In general, the following practices have led to an INCREASE in biodiversity & populations (Select ALL that apply).
Organic Mulches
Zero Tillage
Animal manures & composts
What physical indicators are observable from plants that are deficient in nitrogen?
Yellowish-green color
Which of the following environments would we likely see the most denitrification activity?
Wetlands
The process of nitrification consists of two steps. The first step is conversion of ____________________________ to Nitrite.
Ammonium
Soluble Organic Nitrogen accounts for about _____________________ percent of the total organic nitrogen in soils.
0.3-1.5%
Nitrite is a highly useful form of nitrogen for plants. They require a large amount of nitrite for their growth and tissue development
False
Which of the following forms of nitrogen is most easily lost in the soil by the process of soil leaching
Nitrate
Why are nitrites and nitrates much more easily leached out of soils than ammonium?
because they are negatively charged and easily leached by gravitational water
Nitrogen-fixing nodules contain large amounts of _______________________
Bacteria
The four major forms of sulfur are sulfides, sulfates, organic sulfur, and _____________________
elemental sulfur
How do plants adsorb atmospheric nitrogen in it's N2 form?
They don't
What molecule typically forms a reaction with ammonium to form nitrite?
Oxygen
Describe two ways in which too much nitrogen in an aquatic environment can be a problem
Algae blooms from excessive nitrogen blocks out the sun for submarine organisms. When it decomposes, the organisms that eat the dead algae also consume massive amounts of dissolved oxygen in the process, further damaging the aquatic environment.
The term given for two organisms that mutually benefit from a close relationship with each other (like we see with Venom in the Spider-man comics), is ______________________.
Symbiosis
Nitrogen fixing bacteria require large amounts of _______________________ to perform the work of breaking N2 apart into useable nitrogen. The plant provides this to them and in exchange the plant gets access to nitrogen in an available form.
water
What processes are capable of breaking a nitrogen triple bond?
lightning
bacteria
hot lava flows
What important trend began shortly after World War II, which dramatically affected the global nitrogen cycle?
Dramatic Increase in the Use of Synthetic Nitrogen Fertilizer
Ammonium is likely to increase it's volatilization into an ammonia gas in environment that _________________.
Increases in Soil Alkalinity
Denitrification occurs more frequently in soils that are limited in _____________________.
Oxygen