BIBC 100 Midterm 1
1/165
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
Nucleic Acids
make up genetic information and encode proteins
Lipids
energy, signaling, structural organization
Proteins
drive metabolic reactions, build/repair body tissues, maintain pH, can act as transporter or energy
carbohydrates
energy storage, has structural components, virus transmission info, certain mechanisms
water O-H bond length
0.96 Angstrom
water bond angle H-H
105 degrees
Hydrogen Bonds
hydrogen with an electronegative atom on a different molecule
Can C-H form H bonds?
No
Ion Hydration
negative or positive dipoles on water cause them to attract to an ion and “hydrate” them, forming a cage around ions and breaking up the crystal lattice
Ion-Ion Interactions
two oppositely charged ions (metal cation + nonmetal anion)
Van der waals Interactions
occur with any two atoms in close proximity via random electron movement that produces dipoles
Van der Waals Diameter
the distance between two atoms where the repulsive and attractive forces of two atoms is equal
hydrophobic interactions
nonpolar molecules in a polar solvent tend to group together, face inwards
Entropy (s)
number of microstates, description of disorder
Do biological systems minimize nonpolar surfaces? why/why not?
yes, because this decreases the number of ordered water molecules, making there be more free-moving molecules and increasing entropy
Polar Molecules
Hydrophilic, atoms with differing electronegativity
Nonpolar Molecules
Hydrophopbic, atoms with similar electronegativity
what kind of interactions can polar molecules do
all except hydrophobic
what kind of interactions can nonpolar molecules do
hydrophobic, van der waals
Amphipathic molecules
polar and nonpolar, can do all weak interactions
generic amino acid structure
alpha carbon + carboxyl + amino + hydrogen + sidechain
L-AA
amino —> carboxyl
D-AA
carboxyl —> amino
Ka formula
Ka = (H+ * A-)/(HA)
Henderson-Hasselbalch
(A-)/(HA) = 10^(pH-pka)
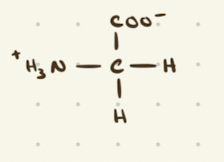
Glycine
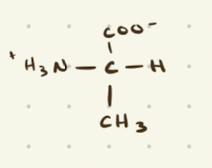
Alanine
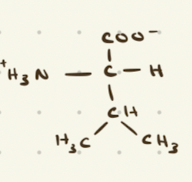
Valine
Leucine

Isoleucine
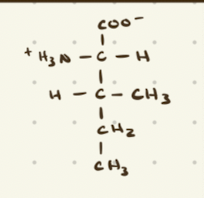
Methionine
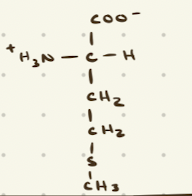
Proline
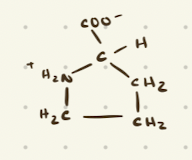
Nonpolar Aliphatic Amino Acids
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Proline
Aromatic Amino Acids
Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan
Phenylalanine
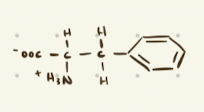
Tyrosine
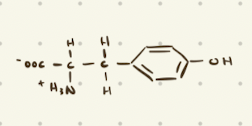
Tryptophan
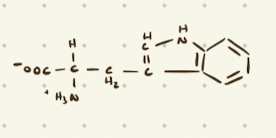
Polar, Uncharged Amino Acids
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine
Serine
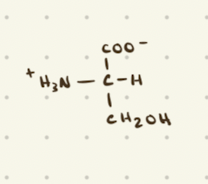
Threonine

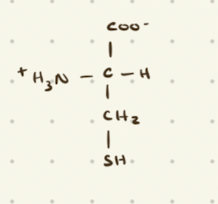
Cysteine
Asparagine
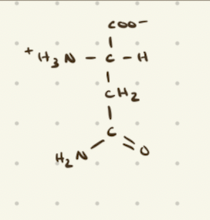
Glutamine
Positively charged, basic amino acids
lysine, arginine, histidine
why is histidine special?
only AA with a side chain ionizable at a physiological pH, so it’s commonly used in catalysis reactions
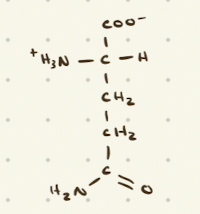
Lysine
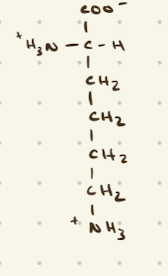
Arginine
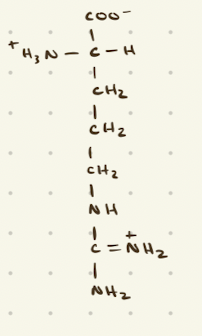
Histidine
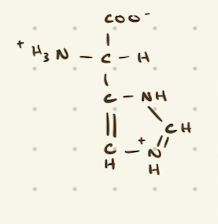
Negatively Charged, Acidic Amino Acids
aspartate, glutamate
Aspartate
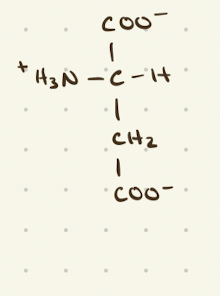
Glutamate
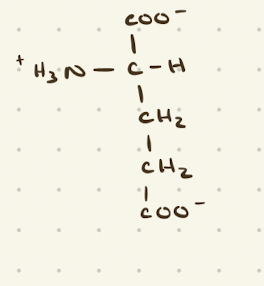
Zwitterions
molecules with positively charged and negatively charged groups so it nets out to zero charge
Isoelectric Point
the pH at which the net electric charge equals zero
if pH=pI…?
amino acid is in zwitterion form and the least soluble
pI formula for non-ionizable sidechains
pI = (pk1+pk2)/2
pI formula for ionizable sidechains
pI = (pKR + pKL)/2
ionizable amino acids
Tyr, Cys, Lys, His, Arg, Glu, Asp
what does it mean for an amino acid to be ionizable
have a third buffer zone
Alanine 3
Ala
Arginine 3
Arg
Asparagine 3
Asn
Aspartic Acid 3
Asp
Cysteine 3
Cys
Glutamic Acid 3
Glu
Glycine 3
Gly
Glutamine 3
Gln
Histidine 3
His
Isoleucine 3
Ile
Leucine 3
Leu
Lysine 3
Lys
Methionine 3
Met
Phenylalanine 3
Phe
Proline 3
Pro
Serine 3
Ser
Threonine 3
Thr
Tryptophan 3
Trp
Tyrosine 3
Tyr
Valine 3
Val
Are amino acid modifications during translation?
No, post-translational
AA that do phosphorylation
Thr, Ser, Tyr, His
AA that does Ubiquitination
Lys
AA that does Acetylation
Lys
AA that does carboxylation
Glu
AA that does Glycosylation
Ser, Thr, Asn
AA that does Lipidation
Gly, Cys
phosphorylation
enzyme regulation, protein interactions, signal transduction
ubiquitination
protein degredation
acetylation
epigenetic regulation, histone structure, DNA interactions
carboxylation
increase calcium affinity
glycosylation
protein stability, recognition
lipidation
target proteins to membranes
what do disulfide bonds link together
cysteine
ramachandran plot dark blue
no steric clash
ramachandran plot light blue
minor steric clash
ramachandran plot white
not allowed
how do secondary structures result
hydrogen bonding
alpha helix
spiral structure
how many residues per turn alpha helix
3.6 residues per turn
how many h bonds per turn alpha helix
3-4
best helix former?
alanine