Review lab
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
which anatomical plane divides into superior inferior portion
transverse/horizontal/axial plane
when 2 muscles do functionally opposing actions?
antagonist
In anatomical position, where are your palms facing?
anterior
if body is lying prone, what does it mean
lying face down
Your wrist is what to elbow
distal
shoudlers up and end in anatomical position?
depression of scapula
muscular agonist of depression?
pectoralis minor, inferior head of trapezius
muscle antagonist for depression
superior trapezius, levator scapuluae
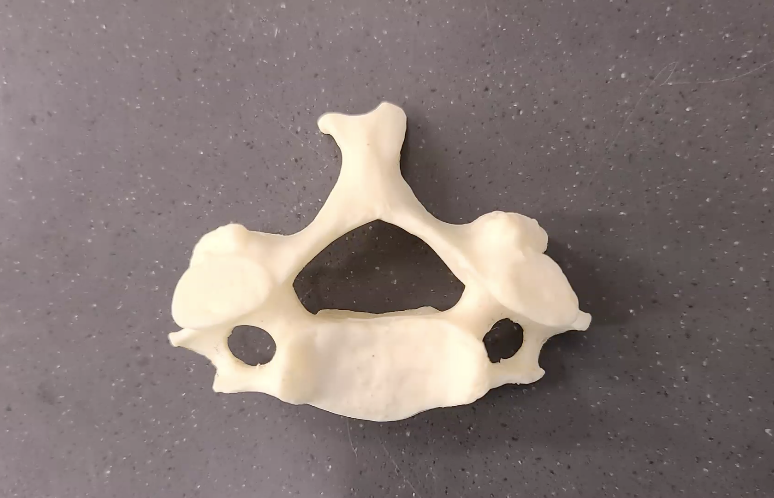
what type of vertebal is this
cervical vertebrae
the openings: transverse foramen, vertebral arteries travel through these
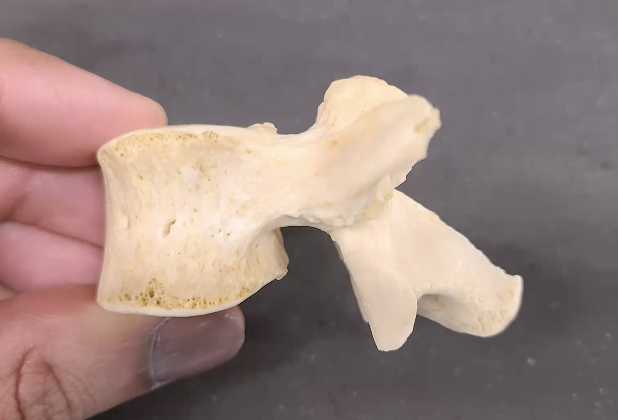
what view is this
left lateral view
the small bone stickimg out: spinous process
the small bone next to the larger bone sticking out: inferior articular process
what are the fingers touching?: verteberal body
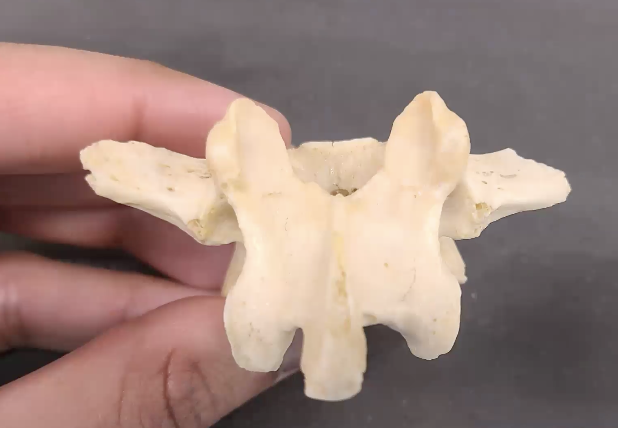
what view is this
posterior view
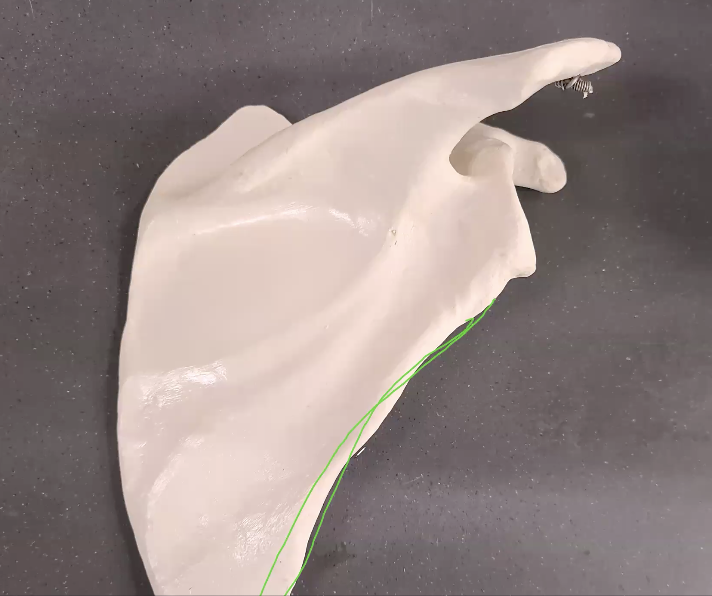
which side scapula?
right scapula (cup like socket facing right side) and posterior view
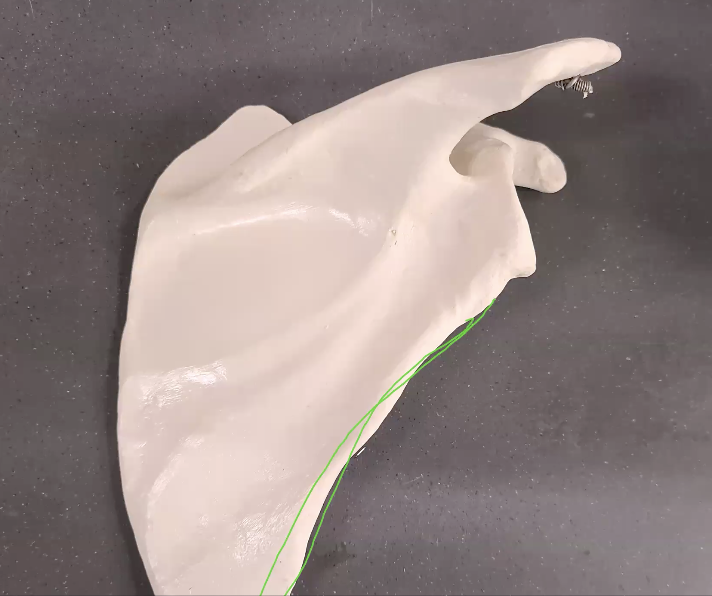
what is the green line
lateral border
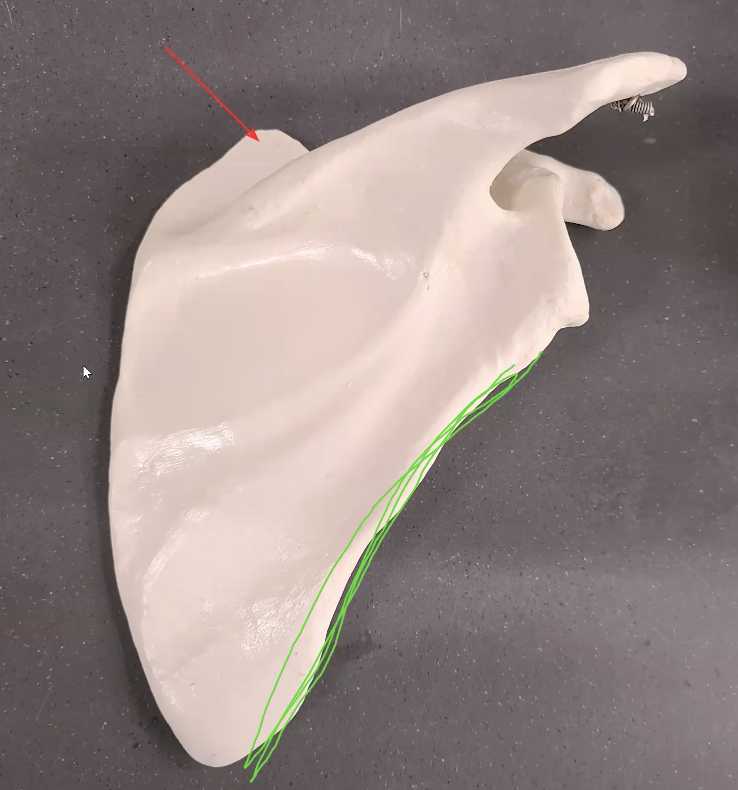
what is the red line pointing at
superior angle
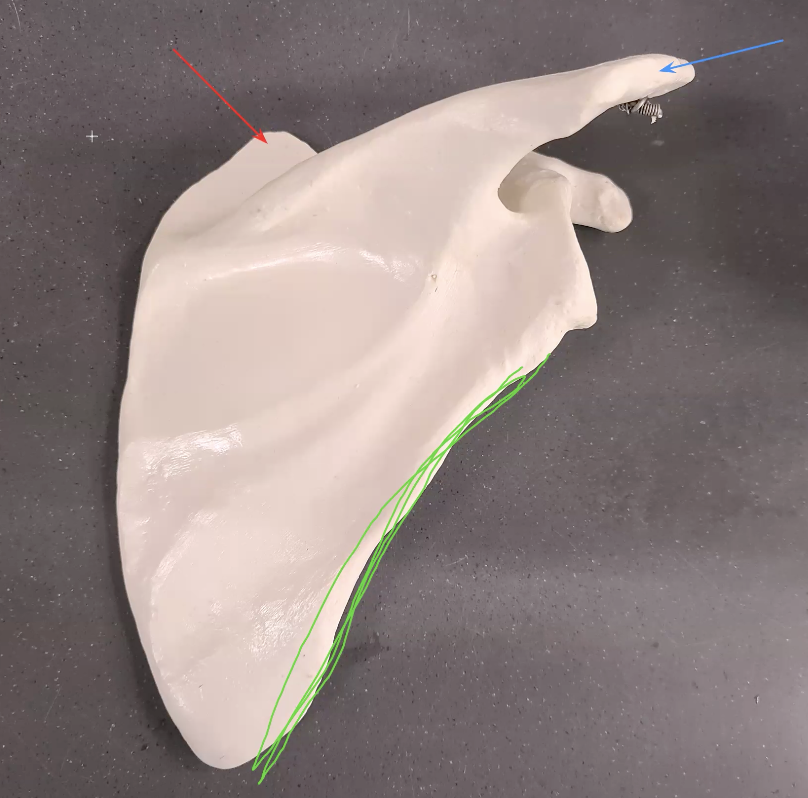
what is the blue arrow pointing at
the acromium process
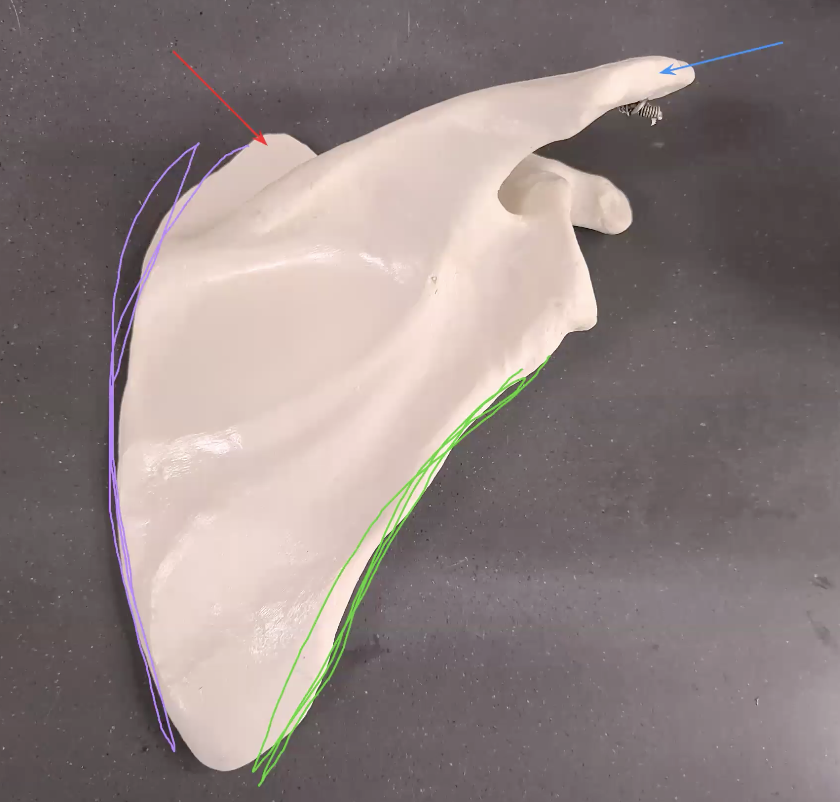
what is the pink line going around
medial border
what are the rector spinaluaue collectively dping
spinal extension
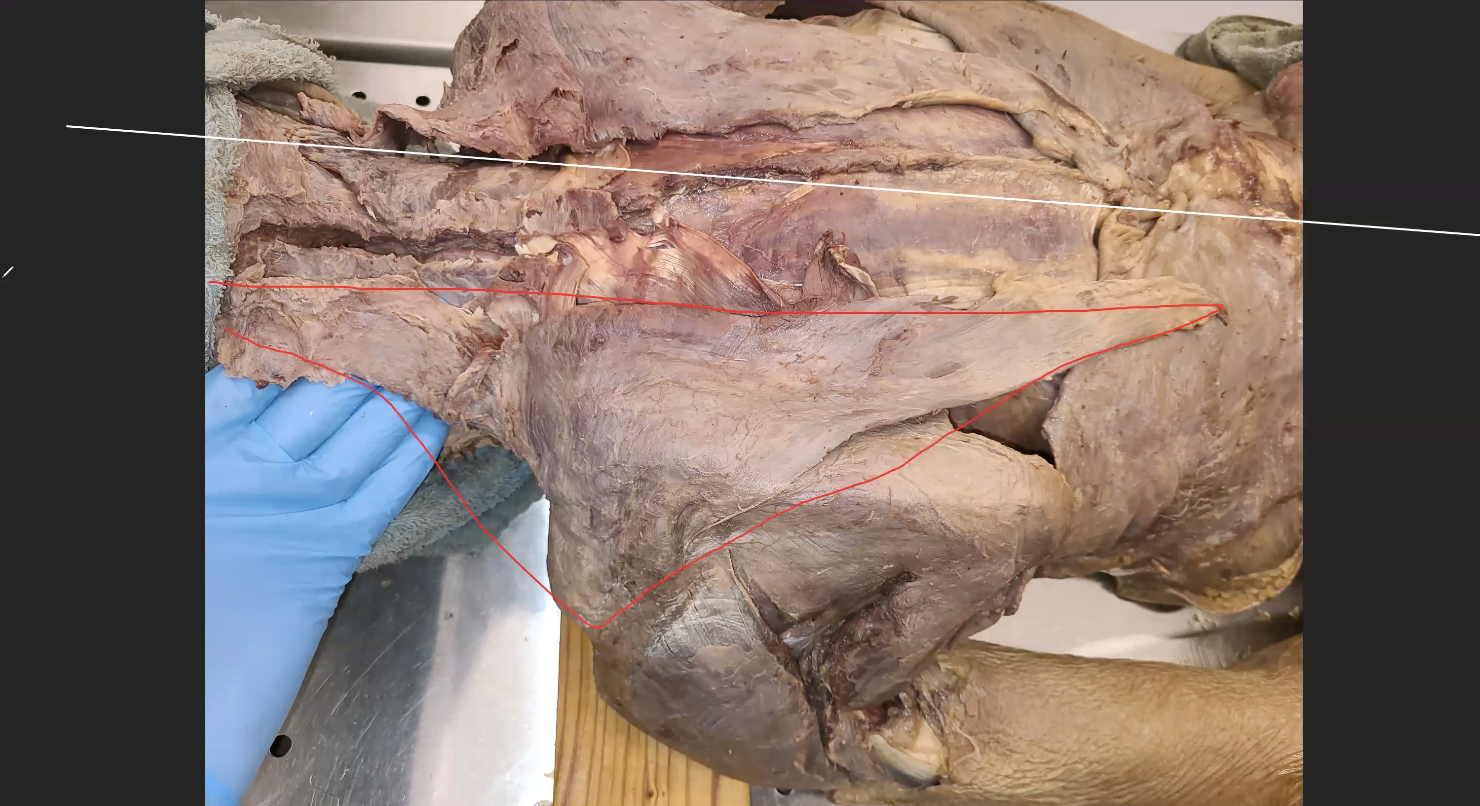
what is the red line muscle
trapezius
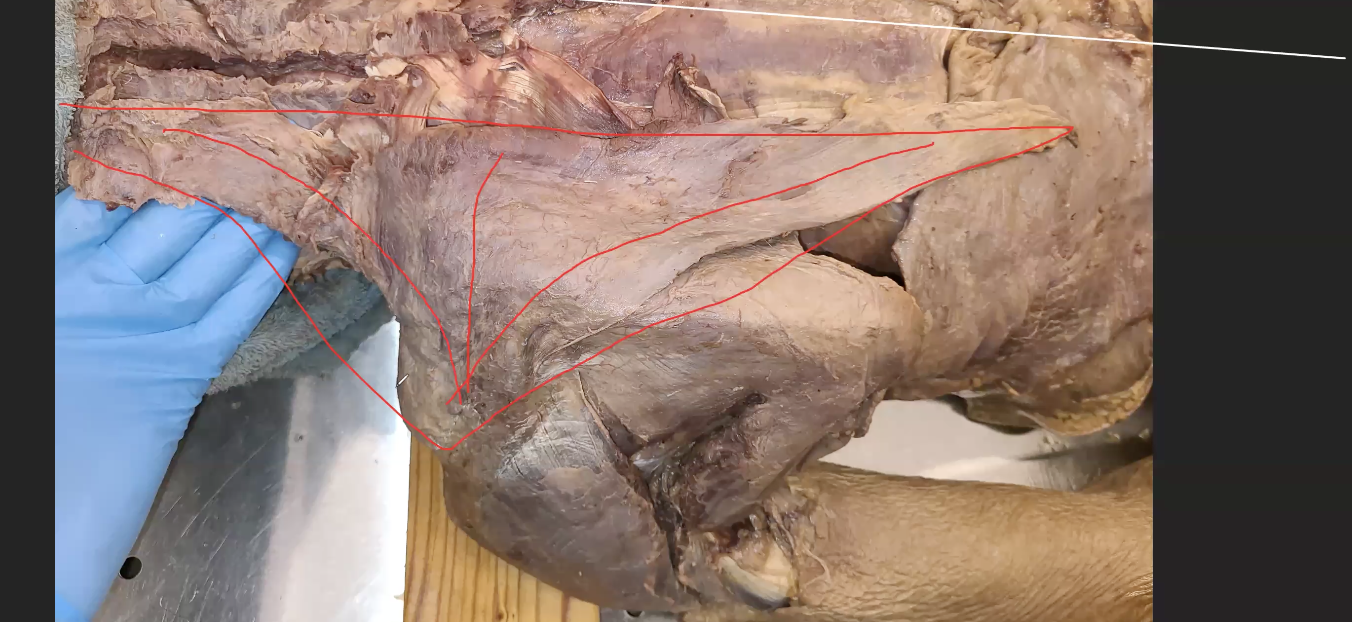
the 3 heads of trapezius
inferior head, middle head and superior head
what is an action that occurs when all 3 heads work in trapezius as a unit
scapular retraction
what are 4 movements must all neutralises in order for scapular retraction to occur
elevation and depression of scapula
super and inferior rotation of scapula
what does the middle head only do
retraction of scapula
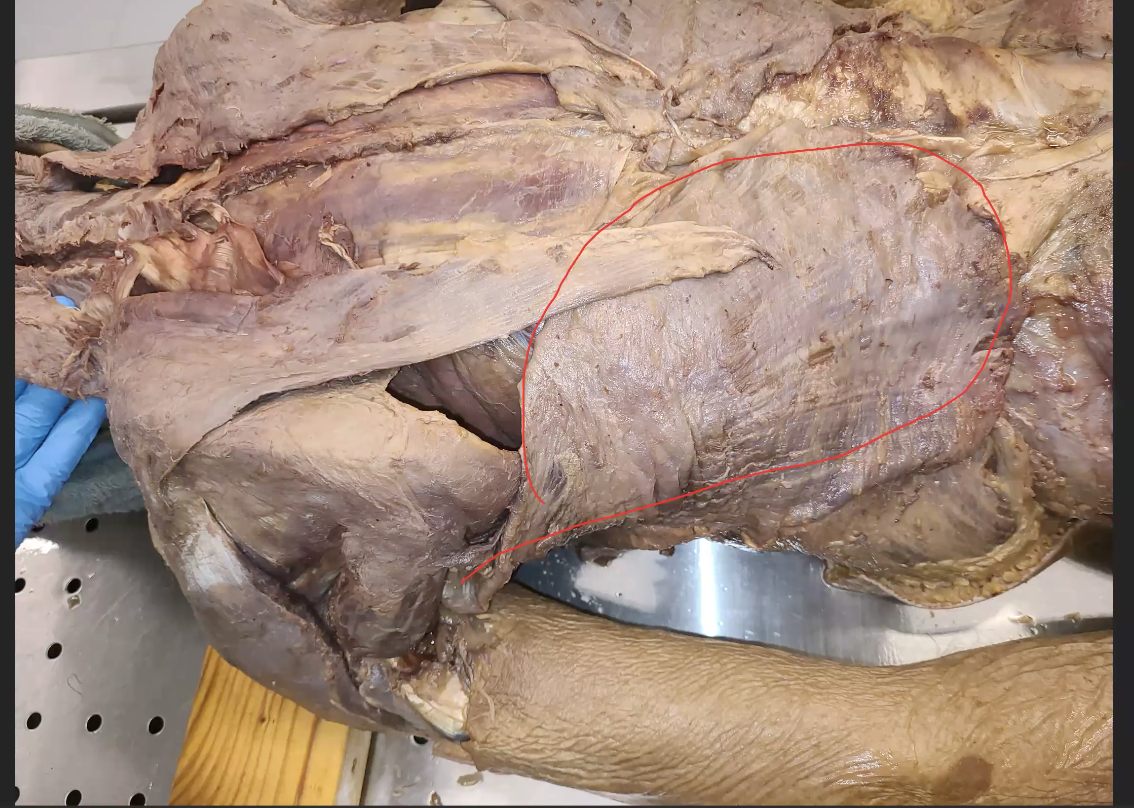
what is outlined in red
latissmus dorsi
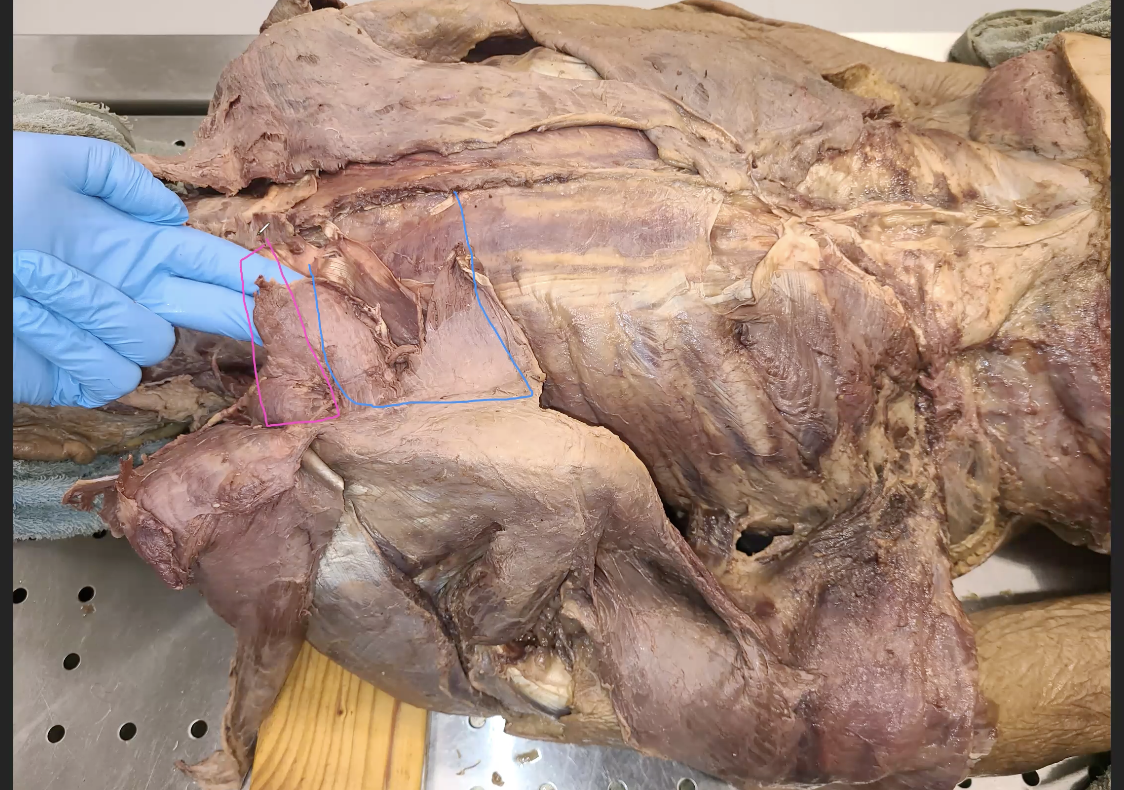
What is in the blue
rhomboid major
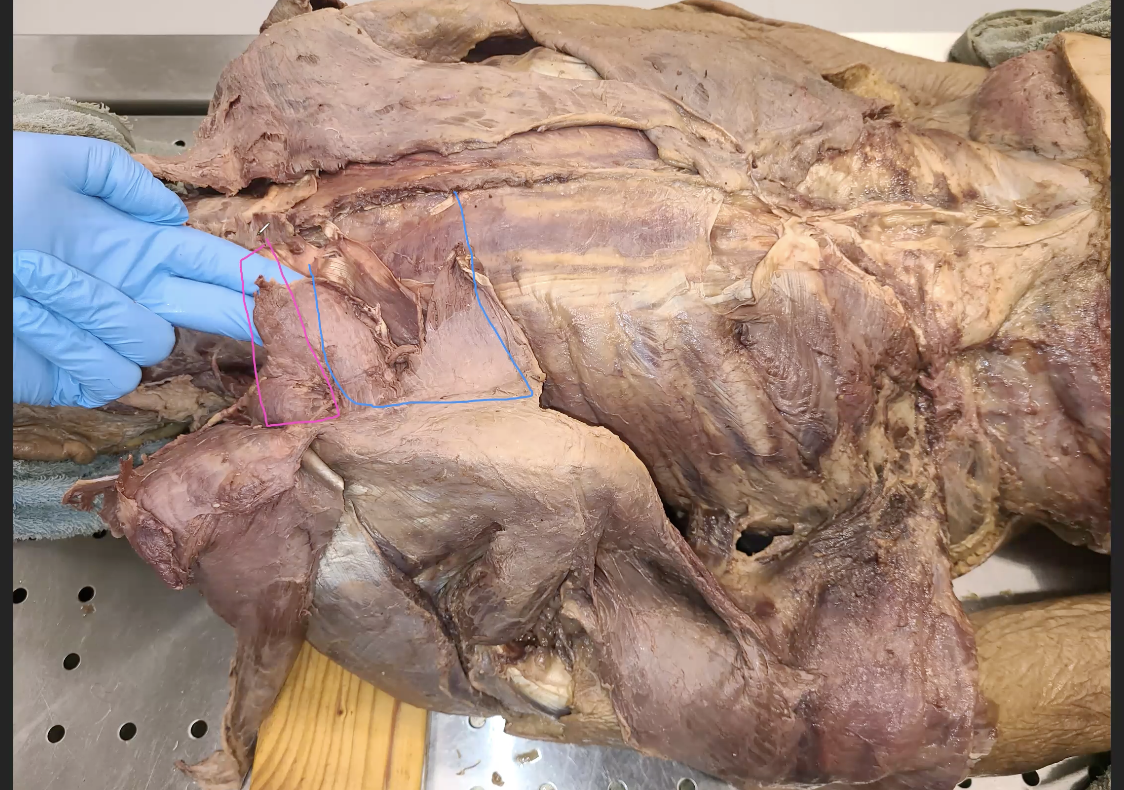
What is in the pink
rhomboid minor
what is a primary action for rhomboid minor and major
scapular retraction, inferior rotation
they are synergistic to trapezius
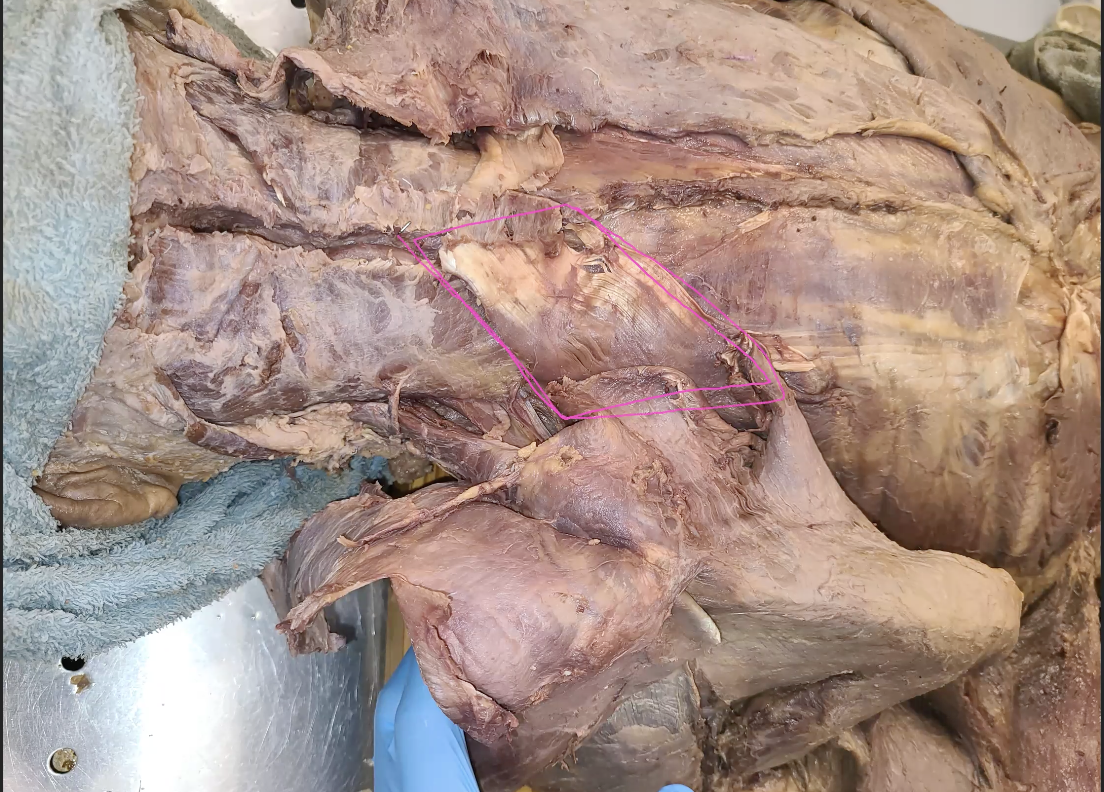
what is circled in pink, directly under rhomboids (shiny tendons)
serratus posterior superior
what does serratus posterior superior do?
elevation of ribs
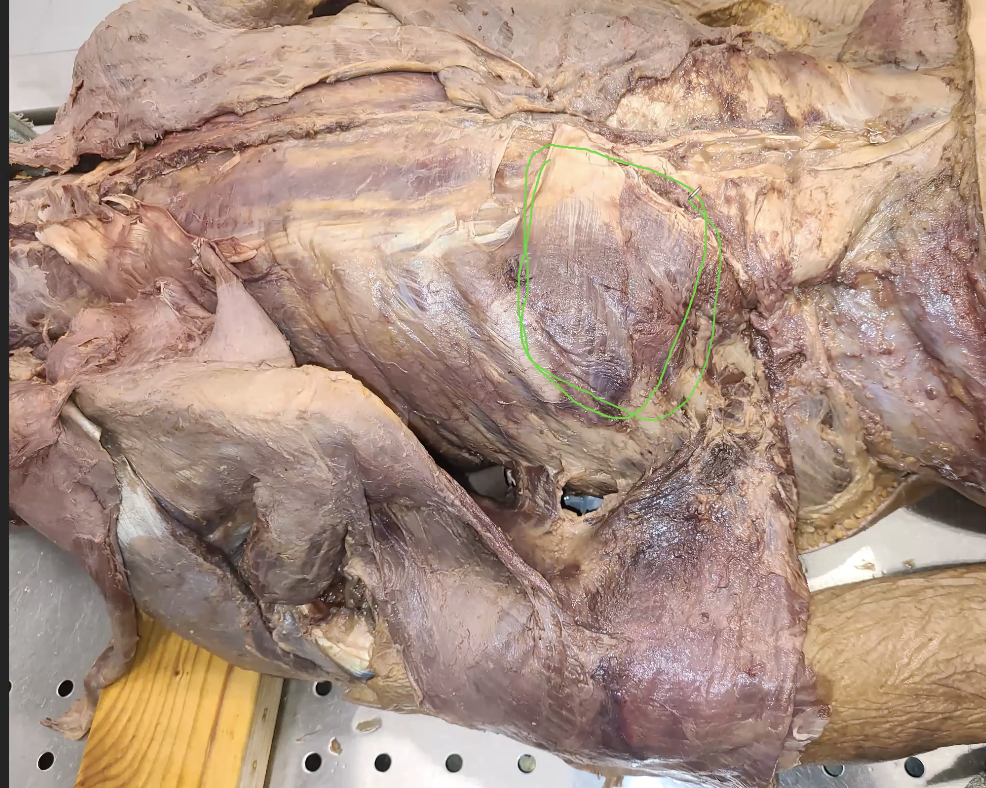
what is outlined in green
serratus posterior inferior
what does serratus posterior inferior do
depression of ribs
serratus posterior inferior and posterior superior are what to eachother?
antagonists
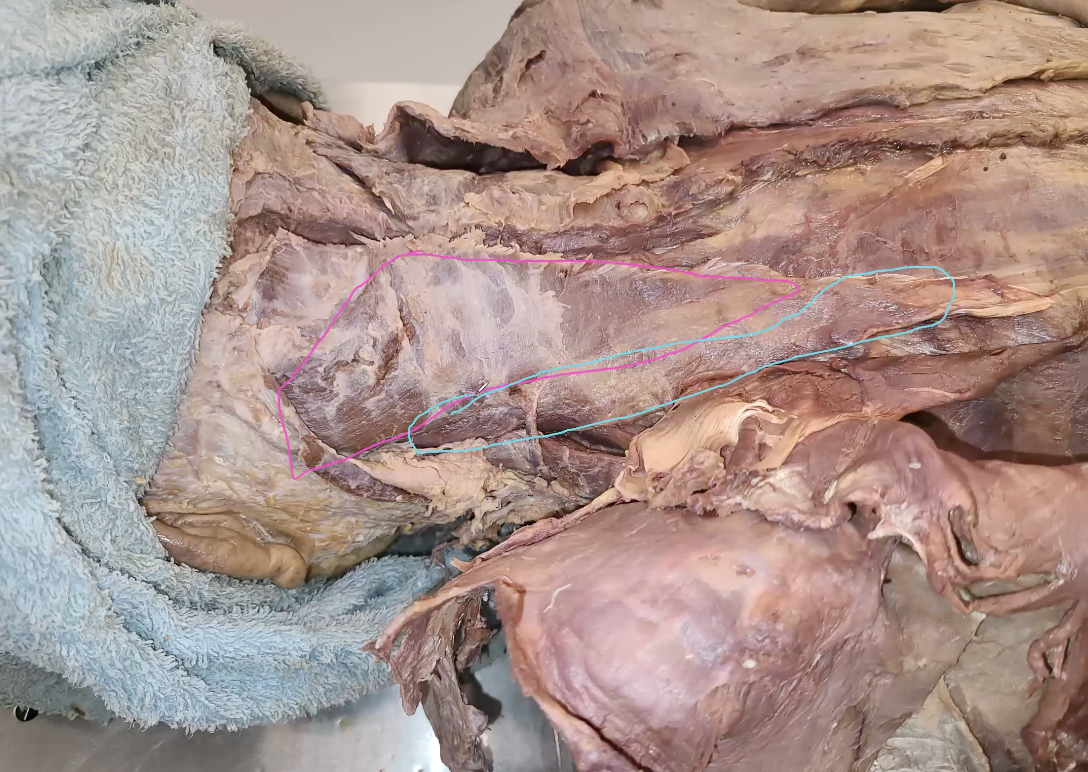
after reflecting the serratus posterior superior, what is the one in the blue
splenius cervices
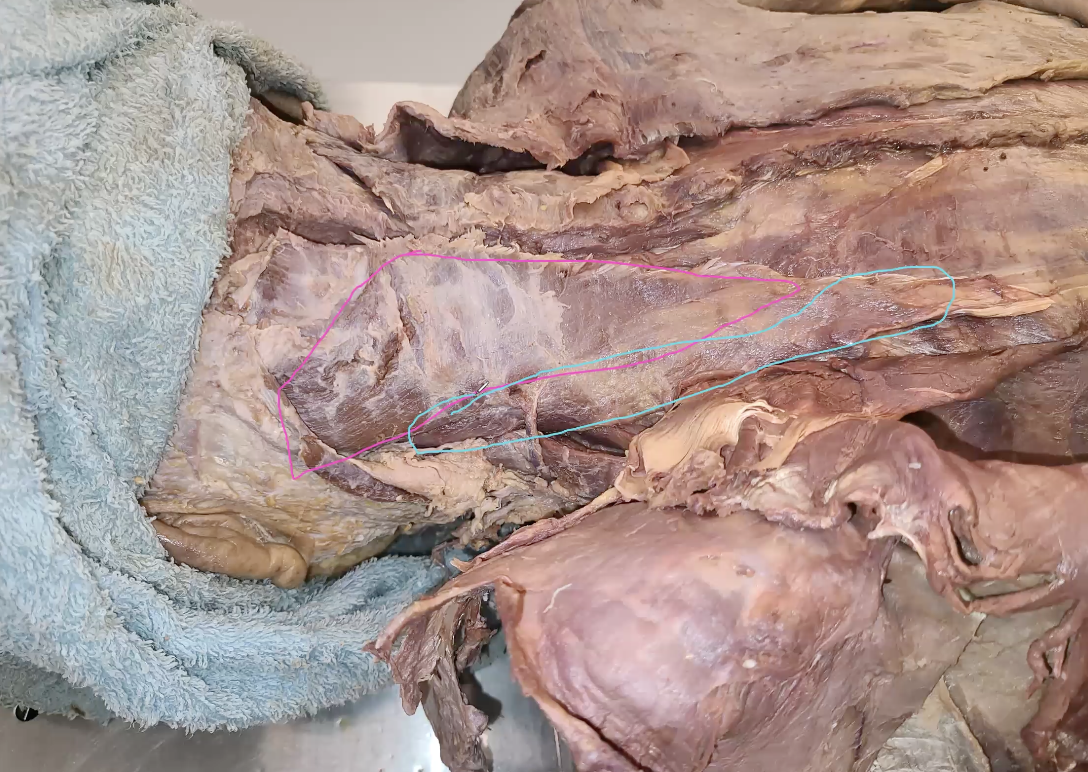
what is the one in the pink?
splenius capitus
when splenius cervices and splenius opitus are contracting unilaterally, what are the 2 potential movements that can occur?
same lateral flexion of cervical spine (always same side)
same side lateral rotation
splenius cervices and splenius opitus are contracting bilaterally?
extension of cervical spine
twisting spine to the right, what muscles are doing this?
right internal oblique
right illiocastis/longissmus
twisting spine to the left, what muscles are doing this?
left external oblique (abdominal wall)
left spinal stabilisers (back)
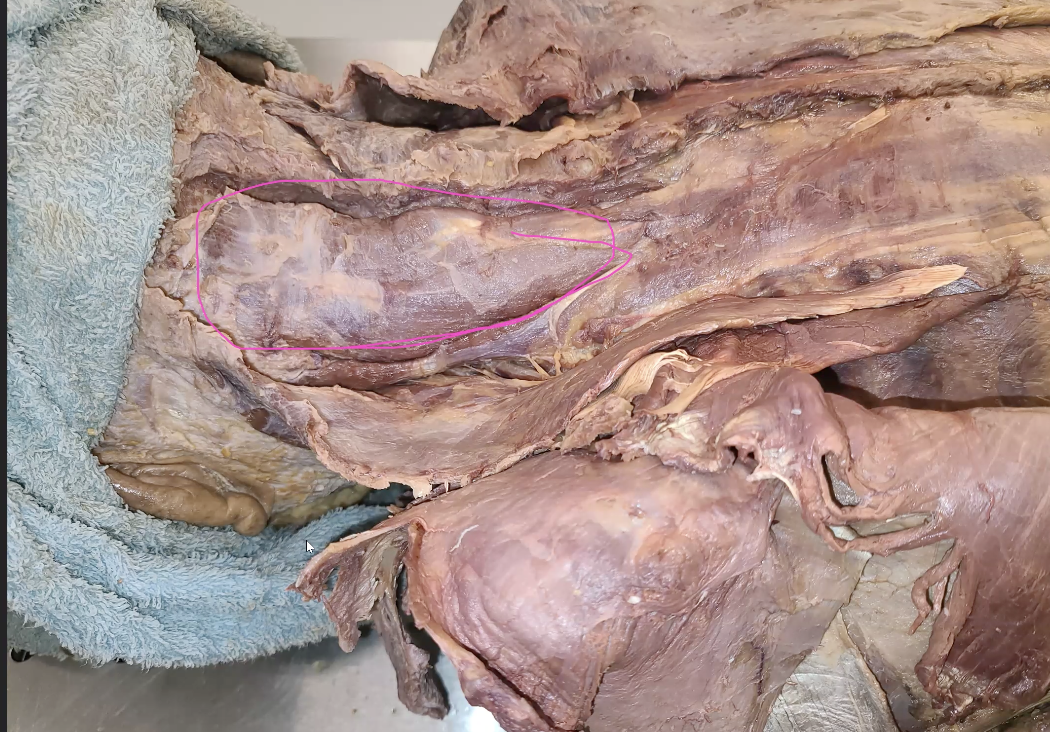
what is the pink that is outlined
semispinalis
deep to splenius muscles
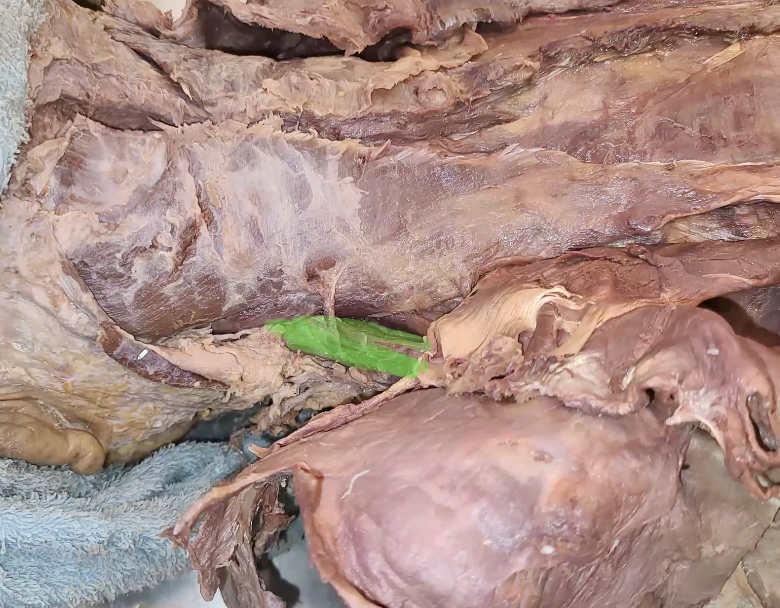

green highlight?
levator scapulae
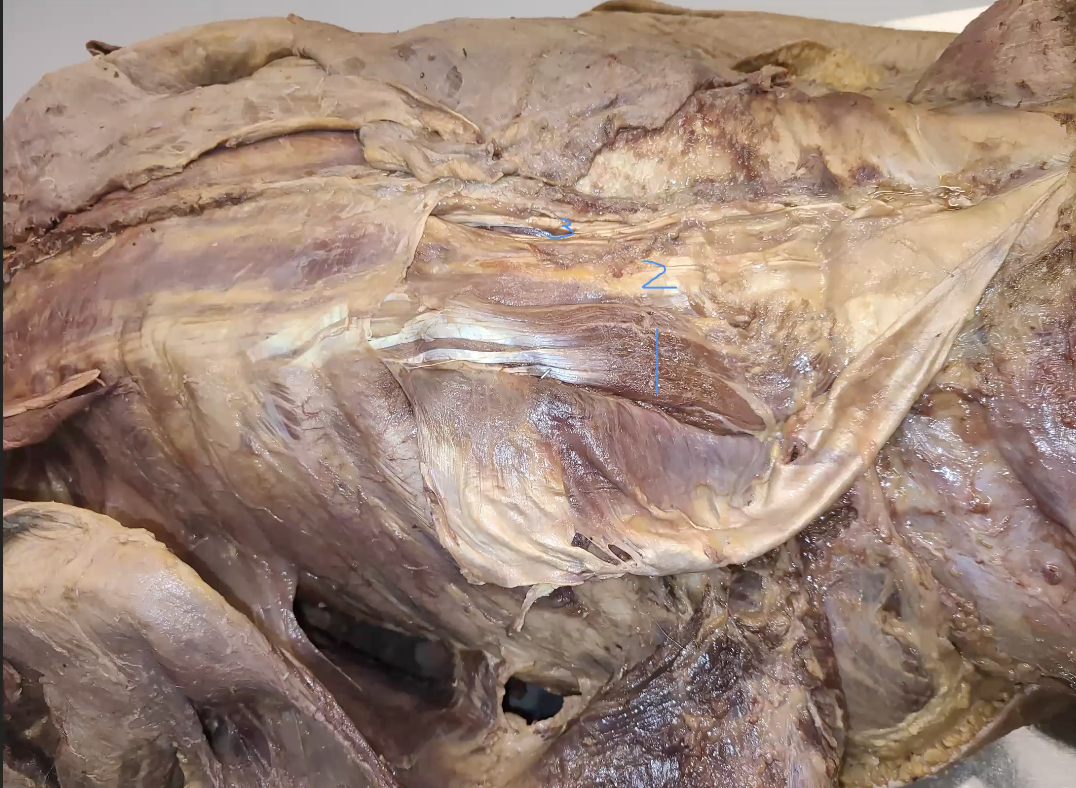
what is 1,2,3
1: illiocostales
2: longissmus
3: spinalus
what do 1,2,3 do bilaterally
spinal extension
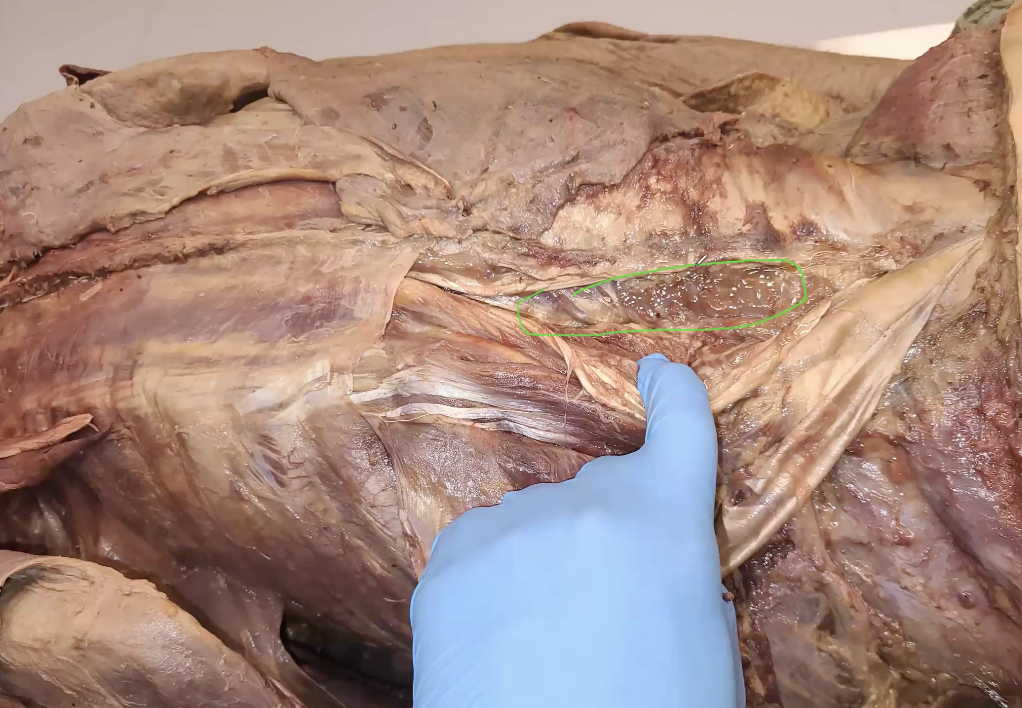
circled in green? found in lower back
multifitus
when spinal stabilisers in back are working bilaterally, what are they helping with?
extension of spine
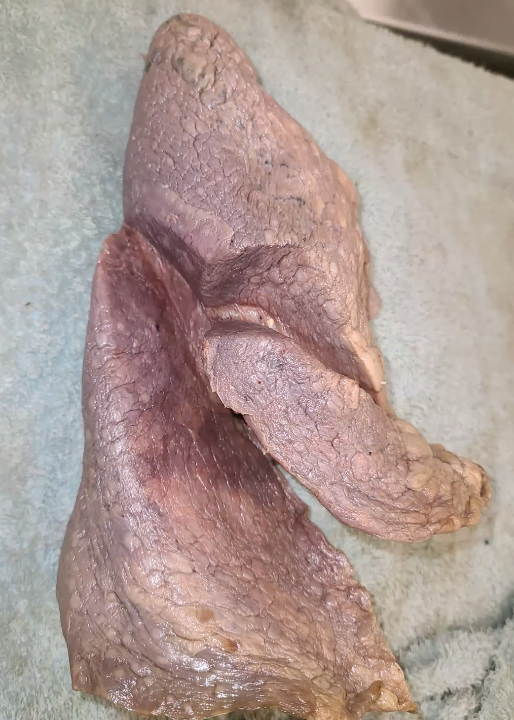

which lung is this?
right
lateral view
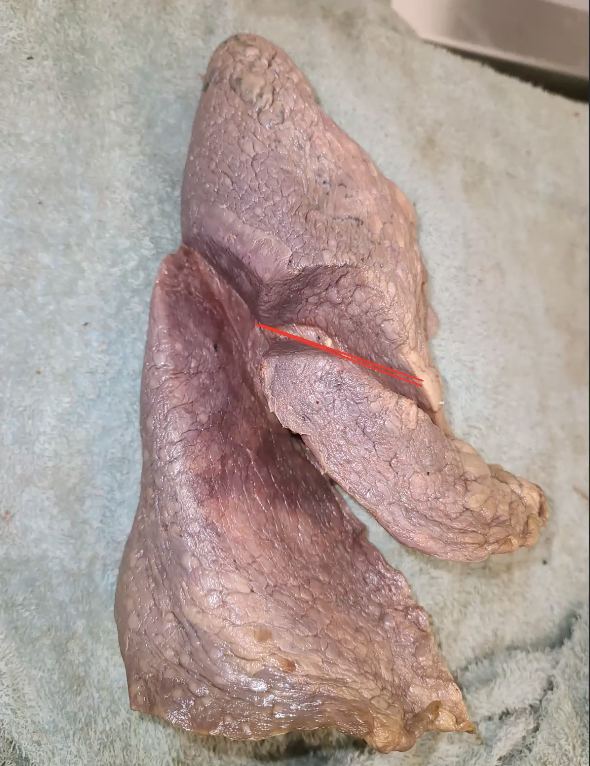
what is the red line?
transverse/horizontal fissure (not found on left)
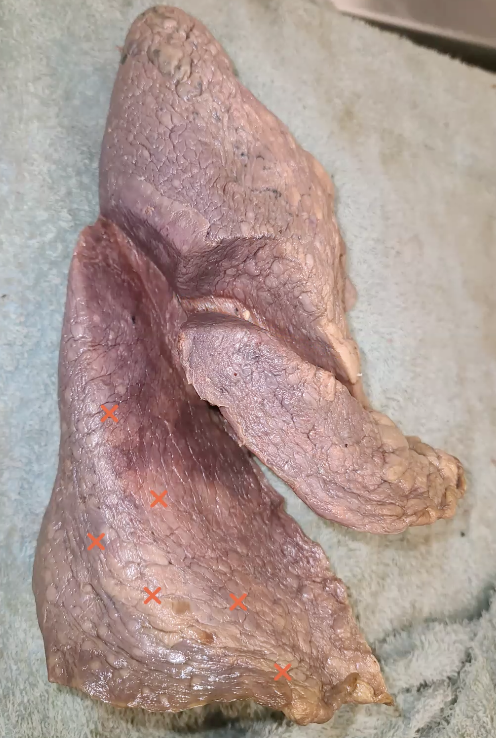

which lobe are these x’s on?
Inferior lobe
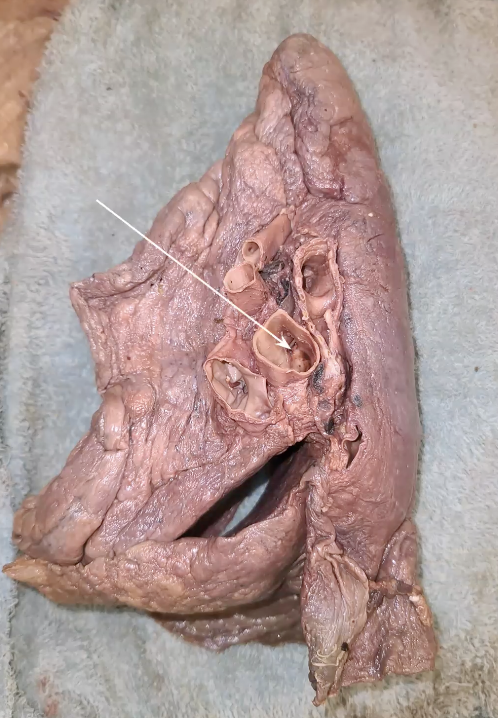
what kind of opening is this? if you press on the wall, it would collapse initially.
pulmonary artery
first chamber and valve the blood would encounter
left atrium and mitral/bicupsid valve
pulmonary artery is direct branch to what blood vessel
pulmonary trunk
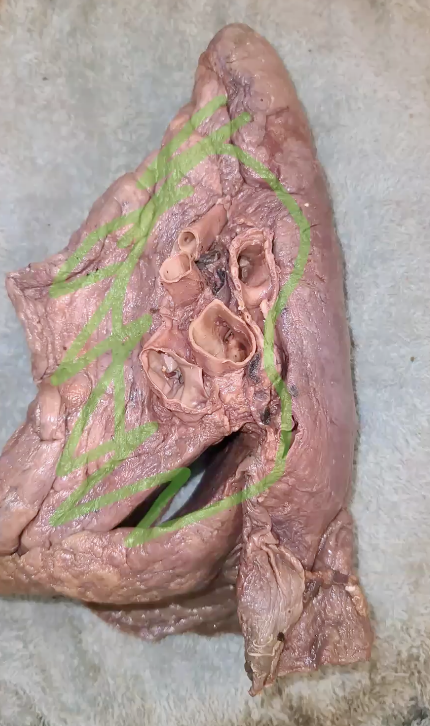
what surface is this?
mediastinal surface
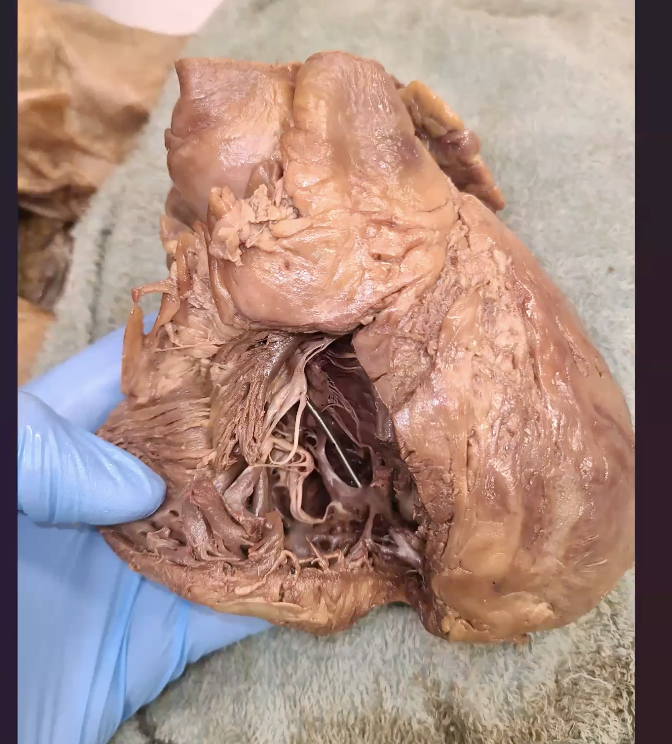
which valve is this?
right ventricle
which valve do u travel through to get to right ventricle?
tricuspid valve
which valve do u go to exit the right ventricle?
pulmonary valve
blood flow (first half)
blood comes into right ventricle through the tricuspid valve to pulmonary valve to pulmonary trunk
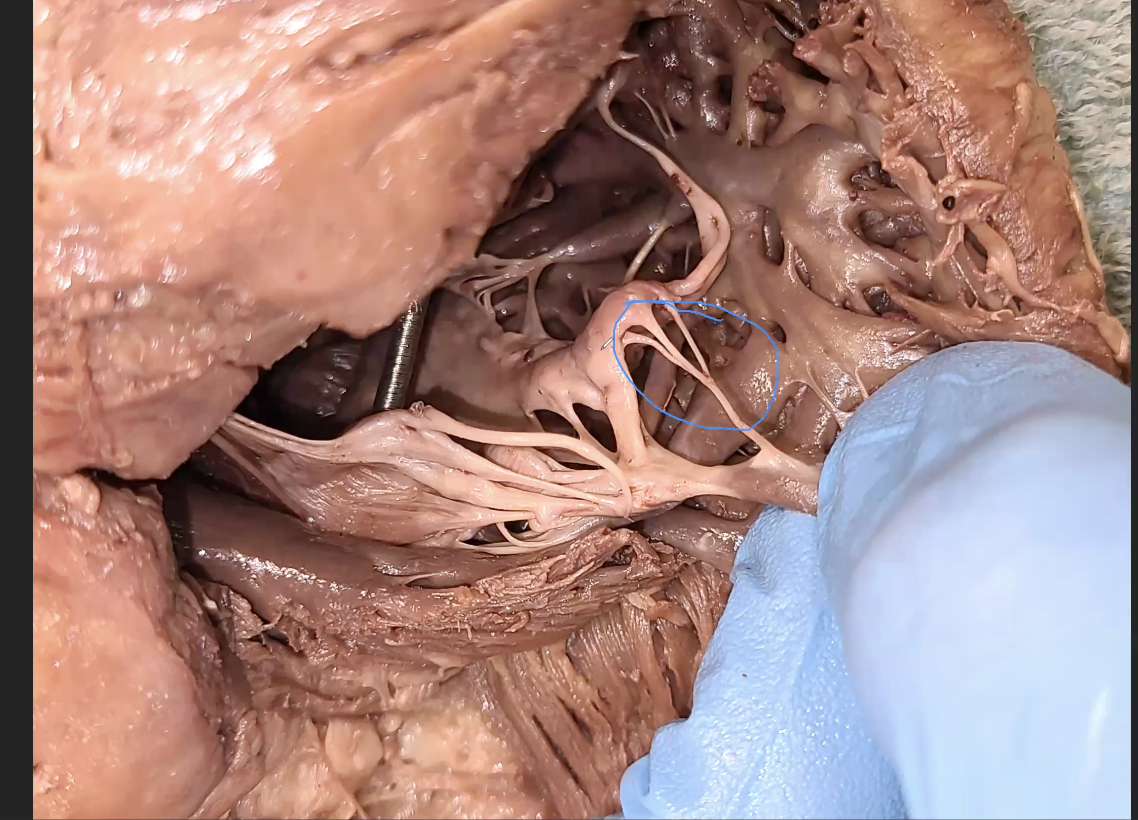
what is the blue circled
chordae tendineae
muscles that are being pinched?
papillary muscles
papillary muscles are specific to which 2 valves?
tricuspid and bicuspid valves
opening for fetal heart?
foramen ovale
sealed off after your born ?
fossa ovalis
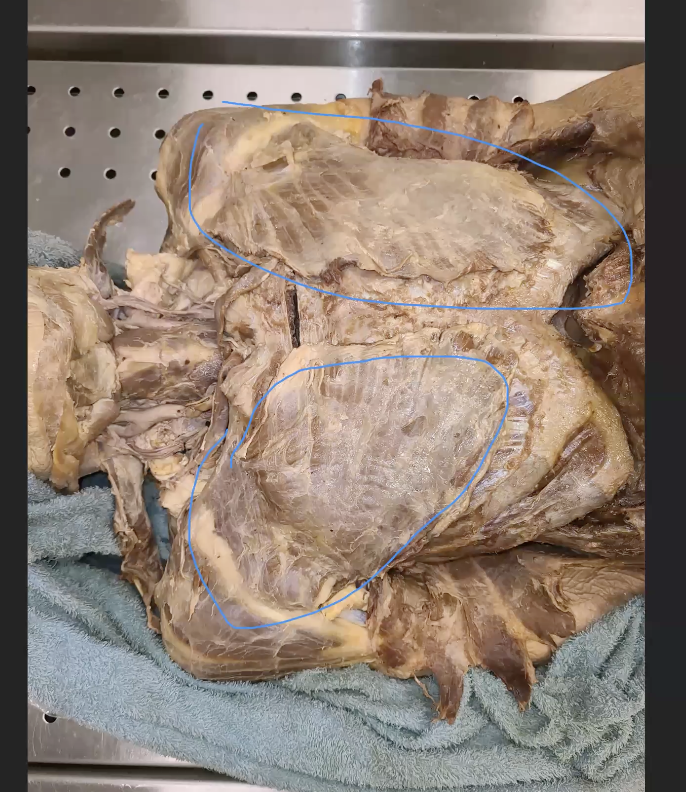
what is this blue circled?
pectoralis major