5.1 Introduction to Soil Systems
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is a soil profile?
A visual representation of the different horizons present in a soil system
What is a layer known as on a soil profile?
Horizon
What are the 6 main horizons?
O horizon
A horizon
E horizon
B horizon
C horizon
R horizon
Describe the O horizon
Organic horizon (uppermost layer)
Composed of mainly organic matter e.g. leaf litter, decaying plant material, organic debris
What is the function of the O horizon?
Rich in nutrients and serves as a site for nutrient cycling and organic material decomposition
Describe the A horizon
Topsoil
Mineral matter mixed with humus
Darker in colour
What is the function of the A horizon?
Important for plant growth as it contains nutrients and provides favourable environment for root development
Describe the E horizon
Eluvial/leached horizon
Leaching or removal of nutrients due to downward movement of water
Lighter in colour
Describe the B horizon
Illuvial/deposited horizon
Where minerals and nutrients leached from upper horizons accumulate
Has different colours, textures or chemical properties compared to horizons above and below it
What do the properties of C horizon influence?
Development and characteristics of upper horizons
Describe the R horizon
Bedrock
Unweathered
Unaffected by biological activity
What does the R horizon represent?
The original geological material from which the soil formed
Who does the soil profile help?
Scientists, farmers, land managers to understand:
properties and fertility of soils
informed decisions for land use, crop selection, soil conservation practices
What are the storages in a soil system?
Organic matter
Organisms
Nutrients
Minerals
Air
Water
What are the inputs of soil systems?
Organic matter
Inorganic matter from rock material
Precipitation
Infiltration
Energy
What are the outputs of soil systems?
Leaching
Uptake by plants
Mass movement
Soil erosion
What are the transfers in soil systems?
Biological mixing
Leaching
Eluviation
Illuviation
Translocation
What are the transformations in soil systems?
Decomposition
Weathering
Nutrient cycling
Humification
Mineralisation
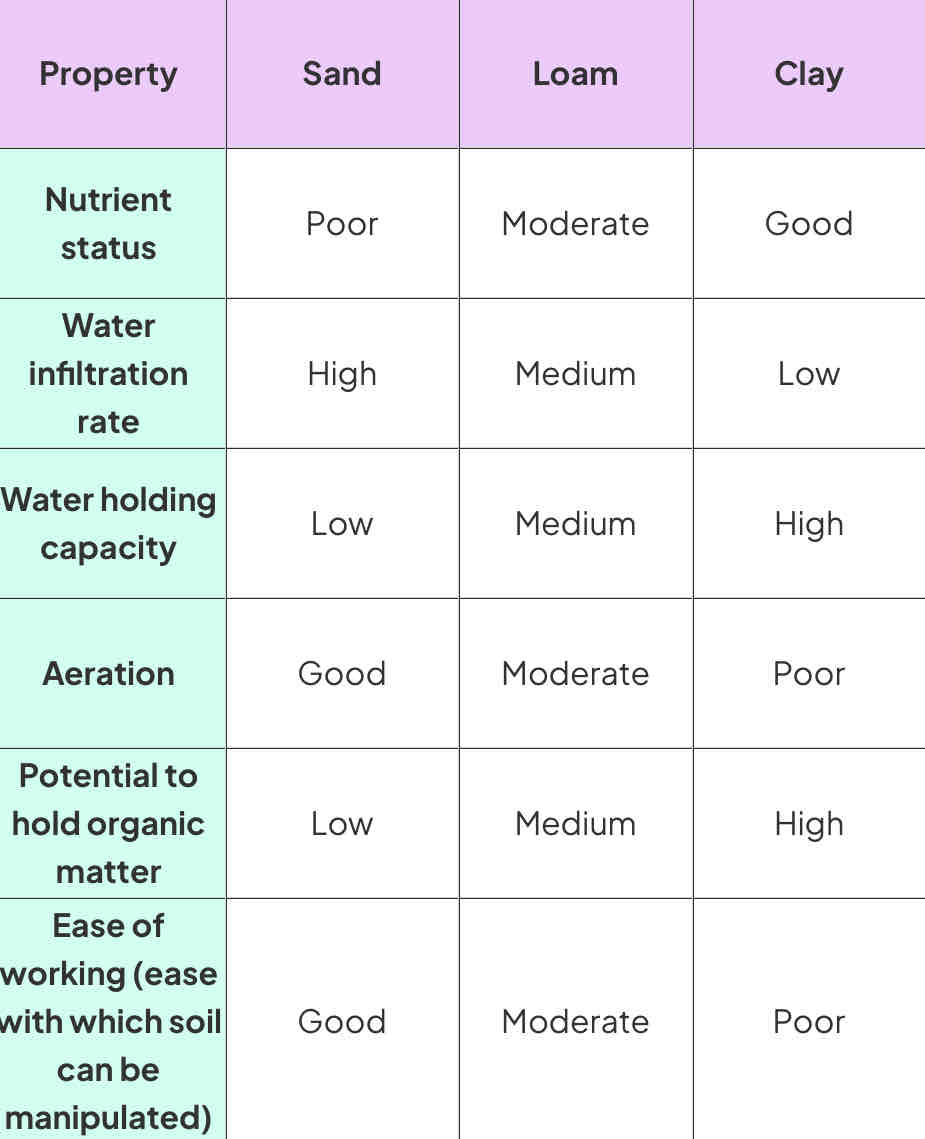
Describe sand soils
Large particles of sand (silica etc)
Low organic matter and nutrients (as sand particles don’t have high capacity for nutrient retention)
Good drainage due to large pore spaces between sand particles, allowing water to move quickly through soil
Low water holding capacity as sand particles limited ability to retain water
Air spaces due to large particle size, facilitating oxygen availability for plant roots + soil organisms
Low microbial activity and diversity of organisms
Low potential to hold organic matter as sand particles don’t have strong binding capacity
Describe clay soils
Composed of small clay particles with minerals e.g. silicates, aluminium oxides
High nutrient content and strong cation exchange capacity
Poor drainage due to compactness and small particle size
High water-holding capacity
Limited air spaces, restricting oxygen availability for roots + organisms
Supports diverse soil organisms due to retained water and nutrients
Strong potential to hold organic matter
Describe loam soils
Composed of balanced mix of sand, silt, clay, diverse mineral content
Moderate nutrient content with adequate cation exchange capacity for nutrient retention + availability
Moderate drainage, balancing water movement and retention
Moderate water-holding capacity, allowing plants to access water while preventing water logging
Balanced air spaces for root respiration and soil organism activity
Supports diverse biota, including microorganisms and earthworms
Moderate potential to hold organic matter, facilitating decomposition and nutrient cycling
Soil properties summary table
How do soils influence plant growth?
Structure + properties affect nutrient content, water availability, air spaces, biota → promote plant growth
Why is nutrient content important in soil?
Provides essential elements needed for plant growth
How do water holding capacity and drainage affect plants?
Provides water for photosynthesis, while drainage prevents water logging, which can harm plants
Why are air spaces important in soil?
Ensure oxygen is available for plant roots and soil organisms to breathe
What role do soil organisms (biota) play in soil health?
Help recycle nutrients, break down organic matter and form relationship with plants (e.g. nitrogen-fixing bacteria)
How does organic matter affect soil fertility?
Adds nutrients to soil and improves its structure, helping plants to grow
How do different soil types affect primary productivity?
Balance of nutrients, water, air spaces, biota, organic matter determines how well a soil can grow
What is soil structure?
Refers to how soil particles are arranged, which impacts plant growth
What is soil texture?
Size of soil particles e.g. sand, silt, clay
How does soil texture affect plants?
Influences moisture content, aeration, nutrient retention and root penetration
What are properties of clay soils?
Holds nutrients well but can become waterlogged and shrink during droughts
What are sandy soils good at?
Excellent drainage but may not hold onto nutrients well
What happens to silt soils if ploughed when wet?
Can become compacted, harming growth
Why are loam soils considered ideal for cultivation?
Balanced texture, good drainage, moisture retention and aeration, making them highly productive for plant growth