Ch. 46 Male and Female Animal Repro Systems
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Land animal evolution breakthroughs
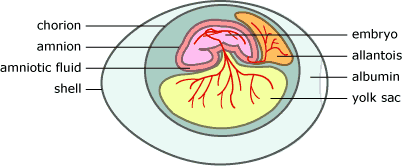
Amniotic egg - freed reptiles of need to return to water, internal fertilization
Amniotic egg
Can do gas exchange w/o drying out.
Amnion – top left, prevents drying
Allantois – top right, holds wastes and provides oxygen
Yolk sac – below, nutrients to yolk
Chorion – around, surrounds the above 3
Fertilized, multicellular, very complex. We could call it an ovum
cloaca
Opening for digestive, repro and excretory (uric acid in birds) system
Mammalian embryos are
viviparous
Viviparous
develop within the female reproductive tract
Viviparous mammalian embryos
Include marsupials and eutherians
marsupials
Complete development in pouch, nourish w/ milk
eutherians
Placental nourishment w/in uterus, nourished w/ milk after birth
Male repro tract structures
testes, seminiferous tubules, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, prostate and Cowper's glands, urethra, penis
testes
produce sperm cells and testosterone
seminiferous tubules
produce immature sperm cells
epididymis
matures and stores sperm cells in coiled duct
vas deferens
duct that carries sperm from epididymis to urethra
seminal vescicle
secretes fructose into semen as food for sperm
prostate
secretes alkaline buffer to semen to protect sperm from acidic environment of vagina
Cowpers glands
secretes mucus into semen to protect sperm from acidity in urethra
urethra
a tube that carries urine and semen out of the body
penis
delivers sperm to the female reproductive tract and expels urine
sperm parts
head, midpiece, tail
sperm head
nucleus and acrosome – vesicle w/ digestive enzymes to get through egg
sperm midpiece
full of mitochondria for tail energy. Sperm swim in their own food (O2 and fructose) to power cell resp/ATP production
sperm tail
move sperm to egg
exocrine
male repro glands are all _____. All push material to the outside
Gametogenesis
gamete development. Can be spermatogenesis or oogenesis
spermatogenesis
Division of spermatogonium into haploid differentiated spermatozoa that can all be used. Mitosis and 2 meioses. Spermatogenesis depends on the pulsatility of GnRH secretion
oogenesis
Division of oogonium into one haploid ovum and 3 haploid polar bodies that cannot be used. Mitosis and 2 meioses.
seminiferous tubules
Site of sperm production and spermatogenesis in testes
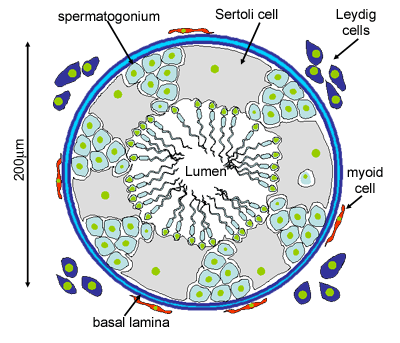
Sertoli cells
w/in seminiferous tubules, support sperm development
Leydig cells
outside seminiferous tubules, produce testosterone
hormones involved
GnRH, FSH, LH
GnRH
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone - stimulates release of gonadotropins
FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone - stimulates growth of ovarian follicles in females and sperm production in males
LH
Luteinizing hormone - triggers ovulation in females and stimulates testosterone production in males
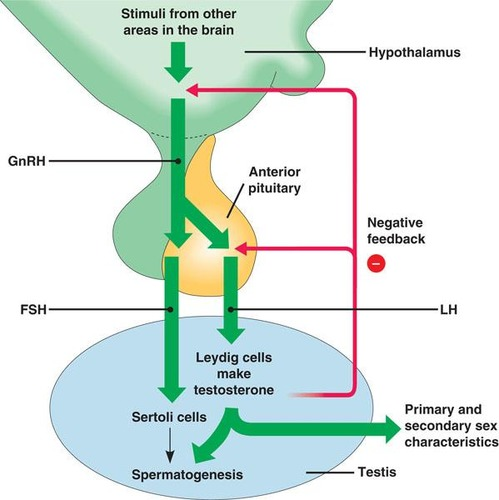
Testosterone
promotes spermatogenesis through the release of these hormones. Promotes development of sex characteristics. Inhibits GnRH and LH in a negative feedback loop of its own production
pulsatile
As a result of the negative feedback loop, testosterone, LH, and GnRH are all
female repro tract structures
ovary, oviduct (fallopian tube), uterus, cervix, vagina, clitoris
ovary
site of oocyte storage and development
oviduct/fallopian tube
transports oocyte from ovary to uterus. Site of fertilization
uterus
lined by endometrium. hollow chamber in which embryo develops
cervix
base of uterus that opens into vagina
vagina
sex organ that produces lubricants, birth canal
clitoris
sexual arousal organ
Fertilization occurs in the
fallopian tubes
ovary structures
Potential ovum, follicle, antrum, Graafian follicles, corpus luteum, ovum, liberated ovum is ovulation
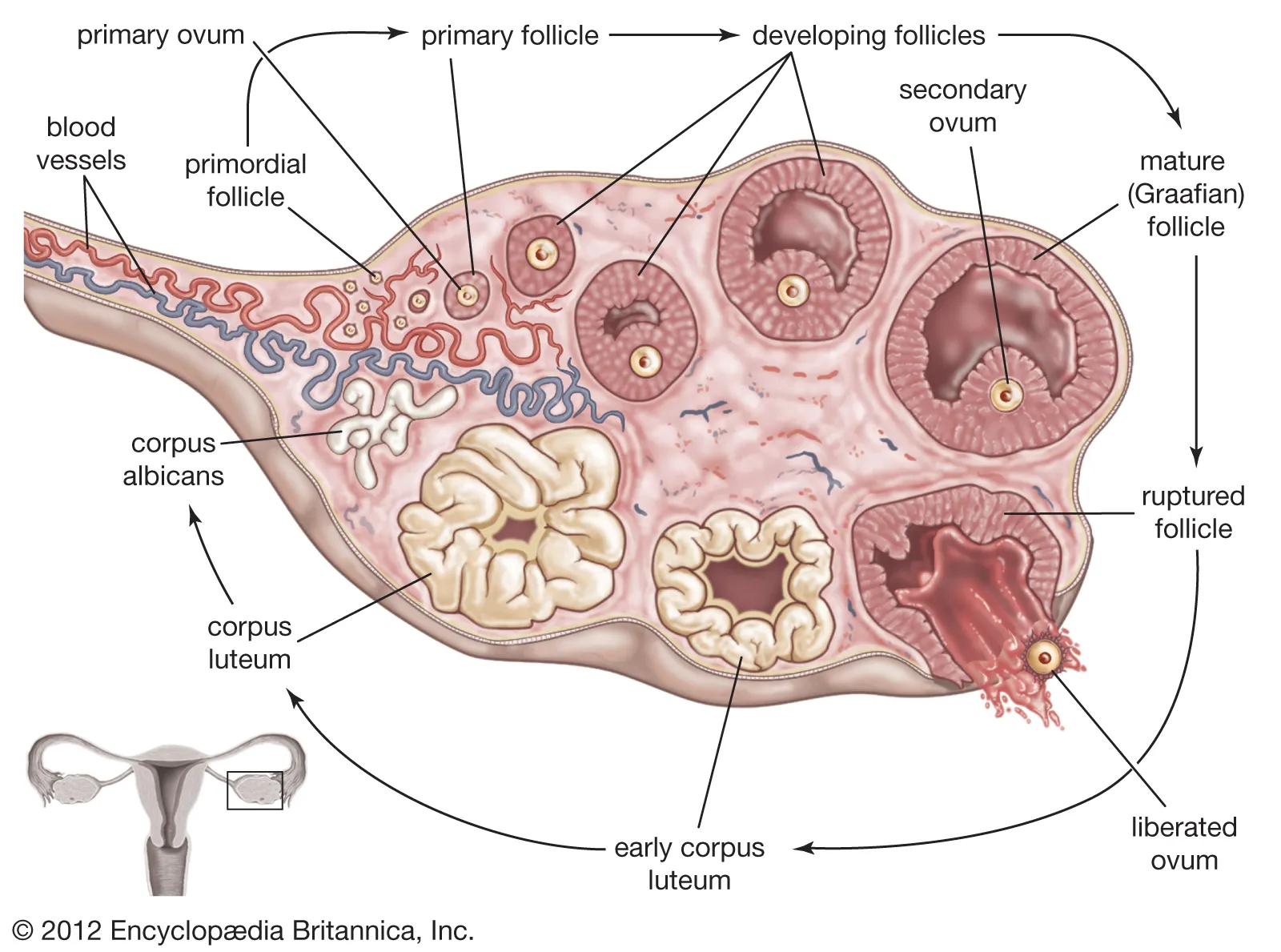
Potential ovum/egg cells
stimulated by hormones to develop. Once they do, cells around them will start to appear.
follicle
grows bigger and bigger around the egg (also big)
antrum
in mature follicle. Chamber that inflates with fluid. The egg is now surrounded by cells and so are the follicles. Once the antrum is full it bursts and releases egg (ovulation).
Graafian follicles
Mature follicles
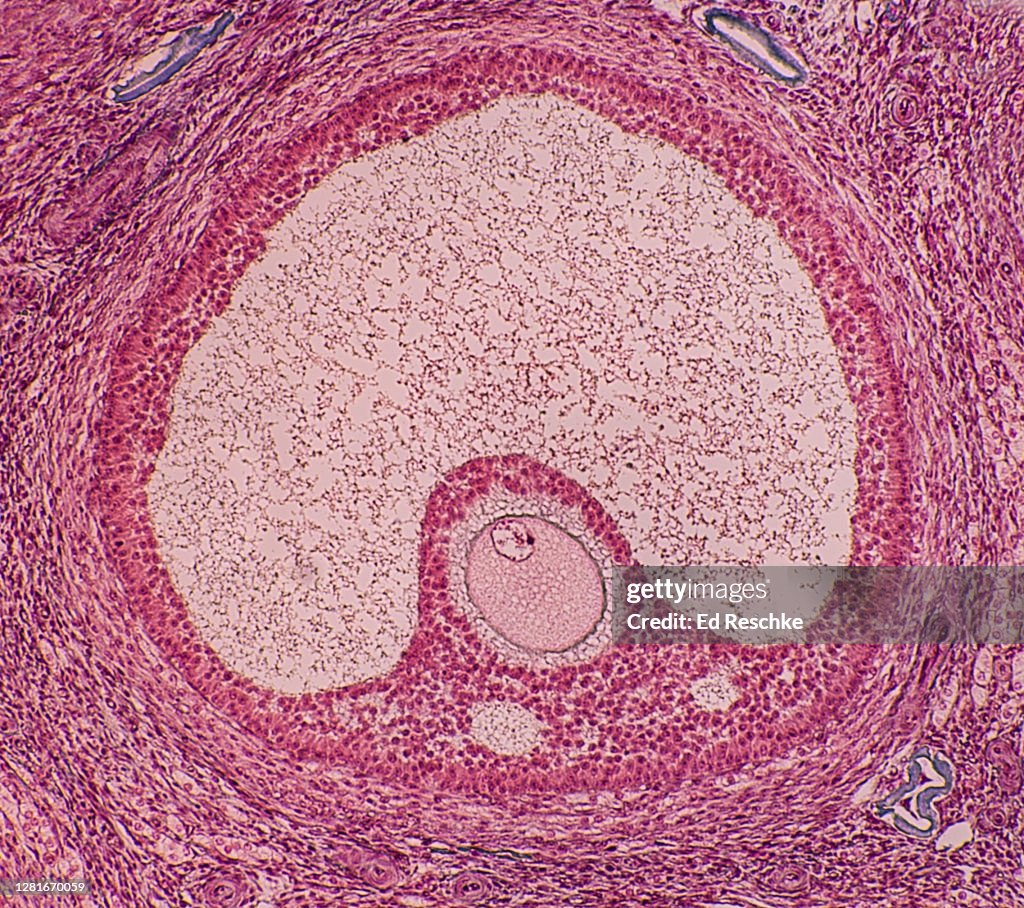
corpus luteum
Once the follicle bursts, what’s left is the corpus luteum that still makes hormones, shrinks, and scars eventually
ovum
The female reproductive cell or egg produced by the ovaries, which can be fertilized by sperm.
ovulation
liberated ovum. Involves mitosis, through cleavage. Mitosis without growth. Much smaller than the egg and zygote. They get smaller with every division.
oogenesis
Ovary w/ sequential development. Results in a big cell and a little one that dies off. 2nd division doesn't occur until after fertilization. Meiosis is the same but at each of them only 1 cell is destined to become an ovum/egg cell. 1st division: unequal cytokinesis, one becomes a polar body and will die. Same for 2nd division. Eggs are big. Bigger than the normal cell. Oogenesis results in a big cell and a little one that dies off. 2nd division doesn't occur until after fertilization.
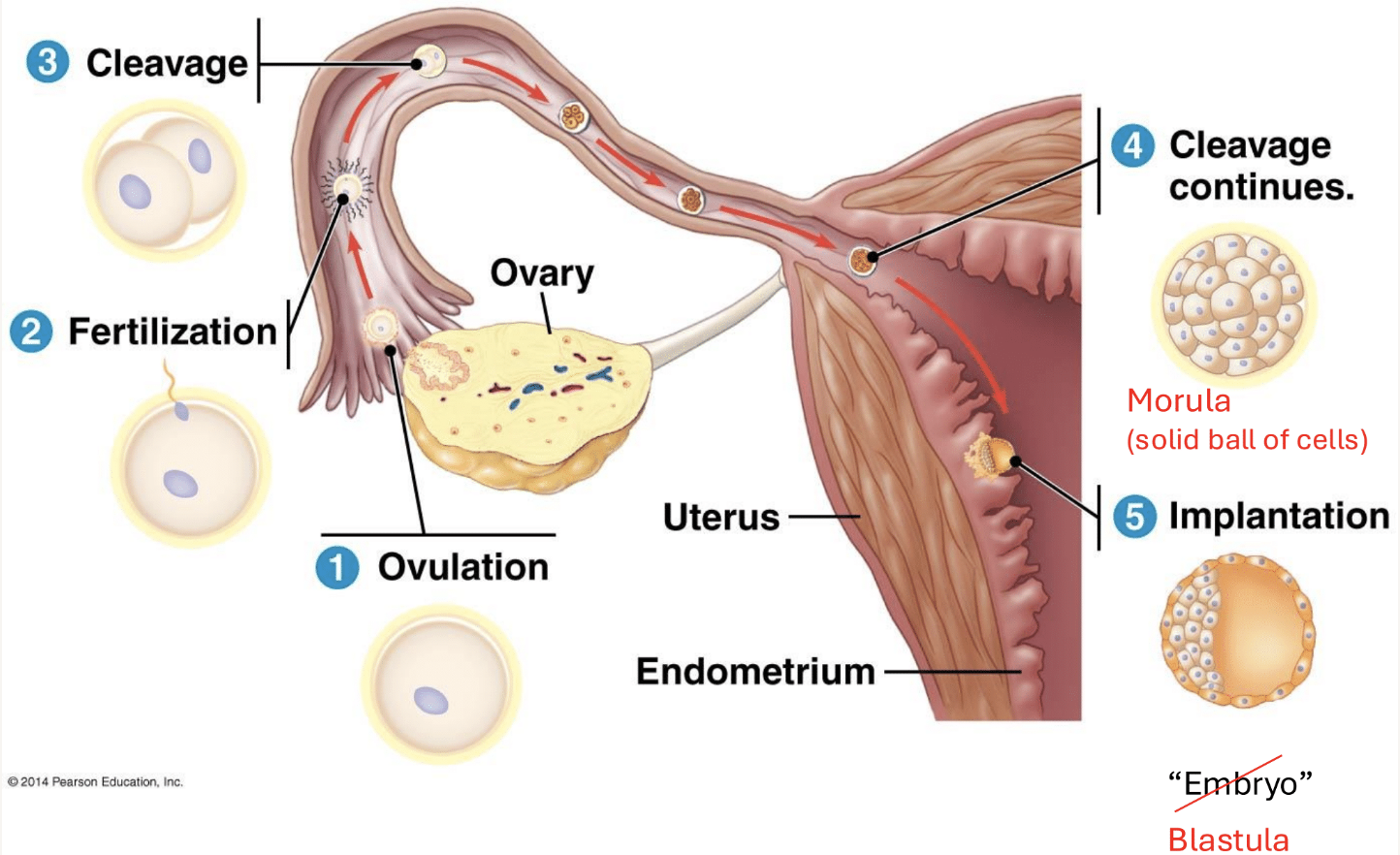
morula
solid ball of cells (totipotent)
blastocyst
ball of 100 clearly divided cells (totipotent).
blastula
future embryo and placenta (some differentiation already – pluripotent, not multipotent yet)
hormones involved
GnRH, FSH, LH, estradiol, progesterone
GnRH
tropic hormone secreted by neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus
Gonadotropins
stimulate the release of ovarian hormones (estradiol and progesterone). FSH and LH.
estradiol
form of estrogen produced by the ovaries that regulates the menstrual cycle
progesterone
steroid hormone produced by the ovaries that regulates the menstrual cycle and maintains pregnancy
tropic hormones
Remember tropic hormones stimulate the release of other hormones.
GnRH is tropic and released by hypothalamus
Hormones in context of ovulation in ovaries
notice specific spikes / characteristics. Be able to tell which line is which hormone. Could think of order as ELFP. Estrogen before ovulation, LH and F high and low during, progesterone after.
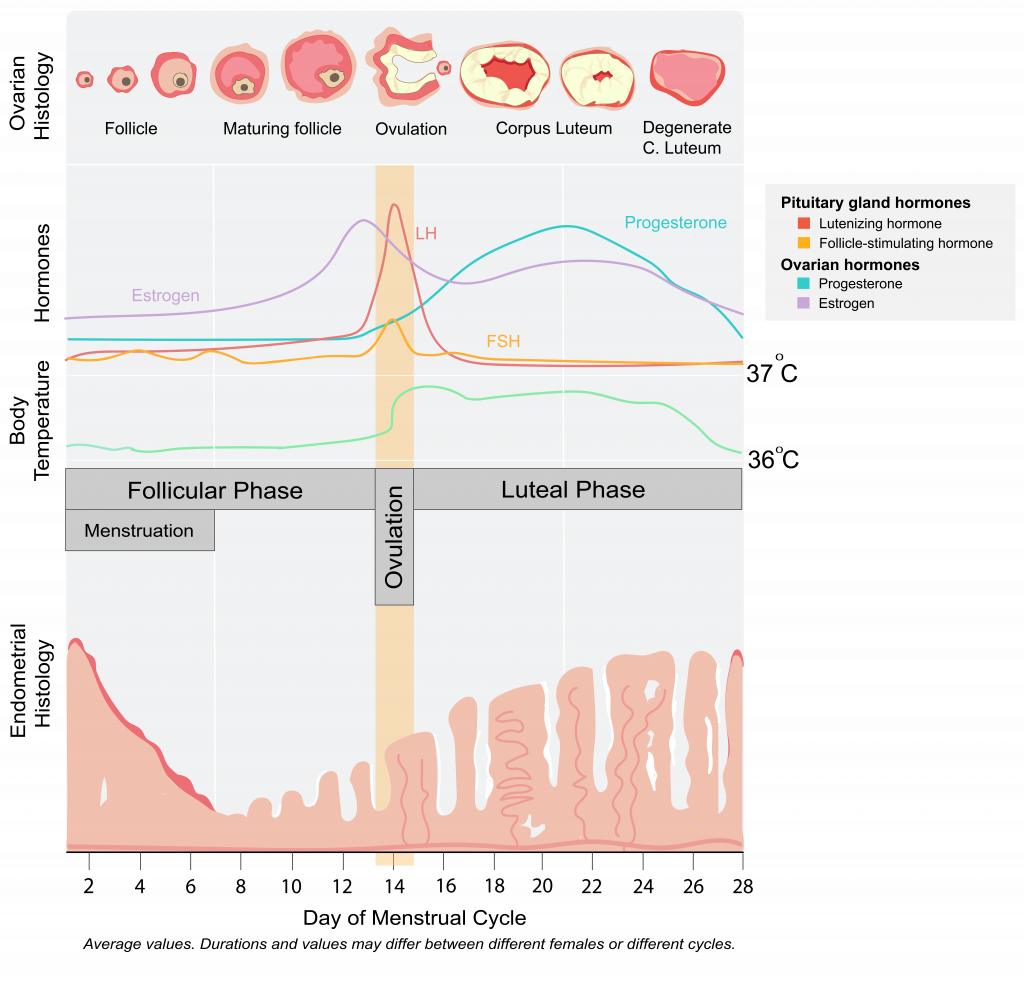
Hormones in context of uterus
Secreted in different amounts throughout menstrual cycle to trigger other hormones
estrogen
Estrogen is a steroid – a lipid – hydrophobic – intracellular receptor. Binds in cytoplasm and sends signal directly to DNA in the nucleus. Directly influences gene regulation/expression.
pregnancy
carrying one or more developing embryos or fetuses in the uterus
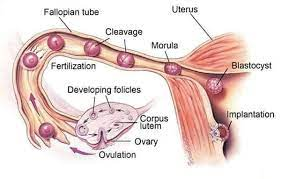
sperm path
(Male) testis→epididymis→vas deferens→urethra/penis→(Female) vagina→uterus→Fallopian tube // FERTILIZATION
zygote path
(Fallopian tube→uterus) divides/cleavage→blastula(100-ish cells) implants in endometrium of uterus→embryo and placenta develop→birth
twins form when
Identical are monozygotic, one zygote splits into two genetically identical cells, share placenta
Fraternal are dizygotic, two eggs fertilized by two separate sperm, genetically distinct but develop at same time, separate placentas
endometriosis
Cells of the uterine lining migrate to an ectopic location
menopause
Repro tract aging. Ovulation and menstruation stops. Ovaries no longer sensitive to FSH and LH
Where everything occurs in the repro tract
Ovulation, fertilization, cleavage, implantation. Cleavage is mitosis without growth
ectopic pregnancy
embryo implants in the wrong place - cervix or fallopian tubes. Not survivable for the embryo.
placental circulation
for transport of nutrients, gasses and wastes by both passive and active transport b/t cap beds
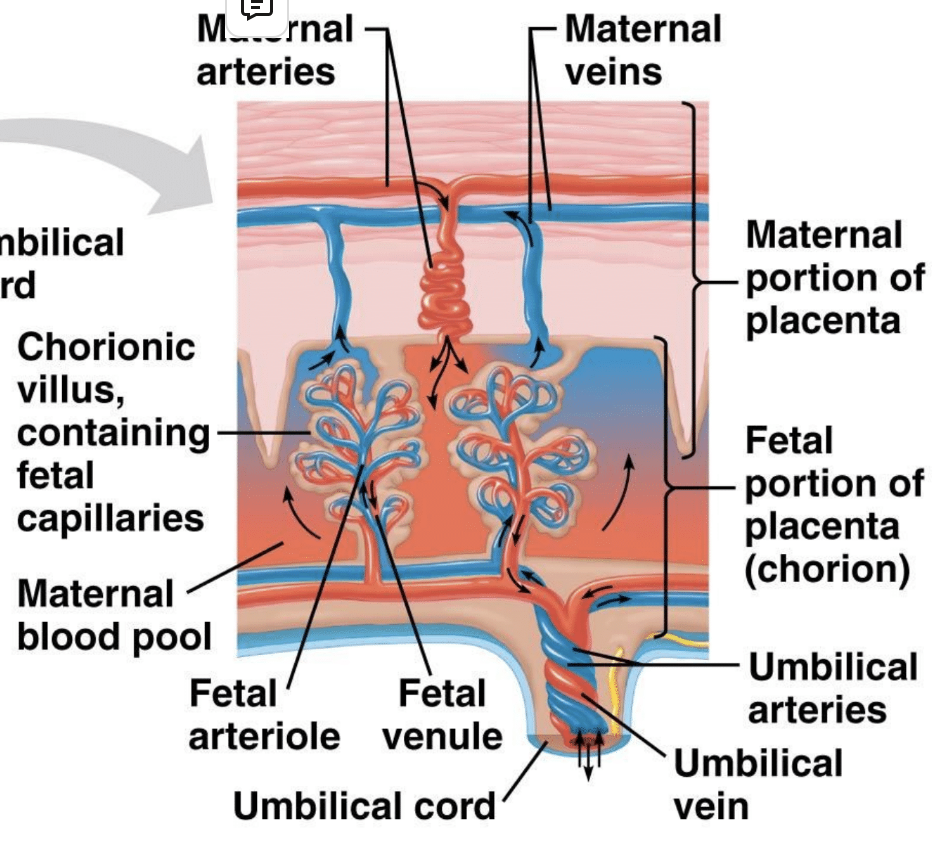
contraception
Deliberate prevention of pregnancy
surgical
vasectomy (M) tubal ligation (F)
vasectomy
vas deferens are tied and cut
tubal ligation
fallopian tubes are tied and cut, cauterized, or banded
in vitro fertilization
a medical procedure where an egg is fertilized by sperm outside the body