Male Reproductive System
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Path of SPERM
The sequence of structures through which sperm travels in the male reproductive system.
SPERM
Male sex cell responsible for fertilization.
SEMEN
Thick fluid produced by the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands, which nourishes and protects sperm.
ERECTION
The process in which erectile tissue fills with blood, causing the penis to become rigid.
EJACULATION
The process by which sperm exits the body through muscle contractions, pushing semen out through the urethra.
NOCTURNAL EMISSION
Also known as a "wet dream," it is the occurrence of ejaculation during sleep, particularly common during puberty.
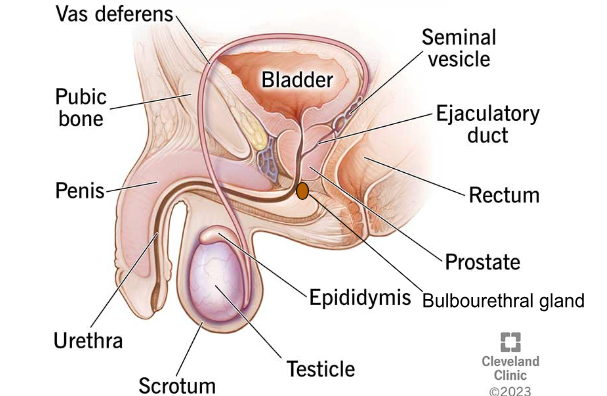
SCROTUM
The external pouch that holds the testes and epididymis.
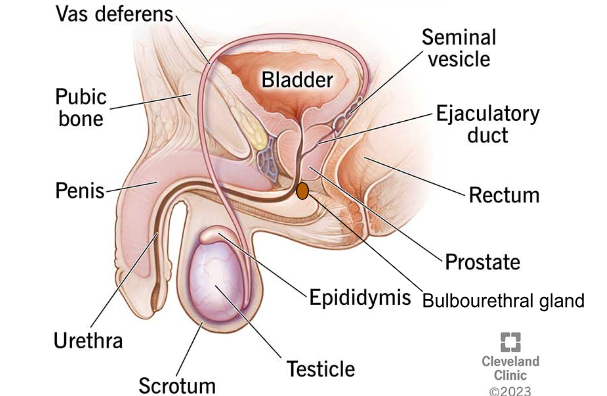
TESTES
The male reproductive organs that produce testosterone and sperm.
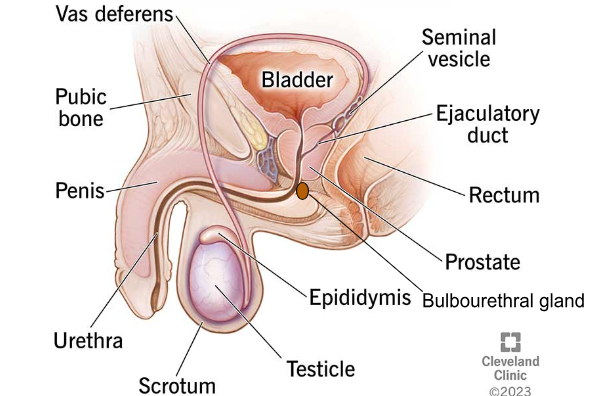
EPIDIDYMIS
The tube located on the back of each testicle, where sperm matures and is stored.
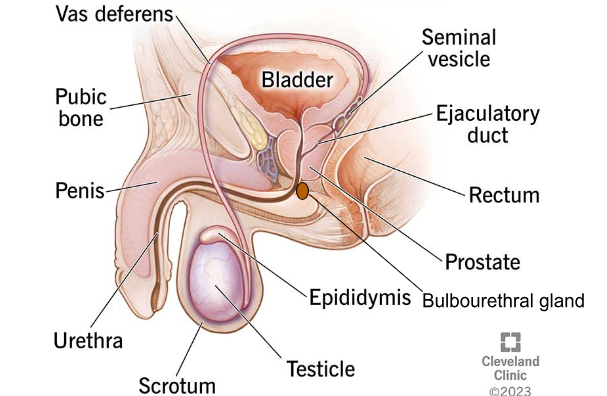
VAS DEFERENS
The tube that transports sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
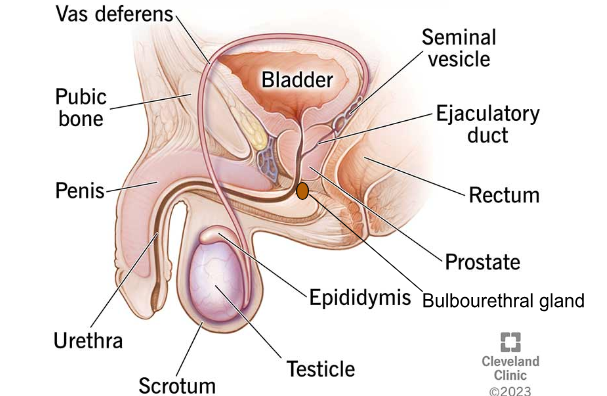
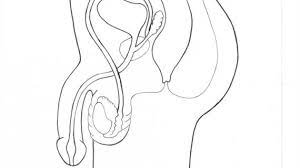
SEMINAL VESICLES
Glands that produce fluid to nourish sperm.
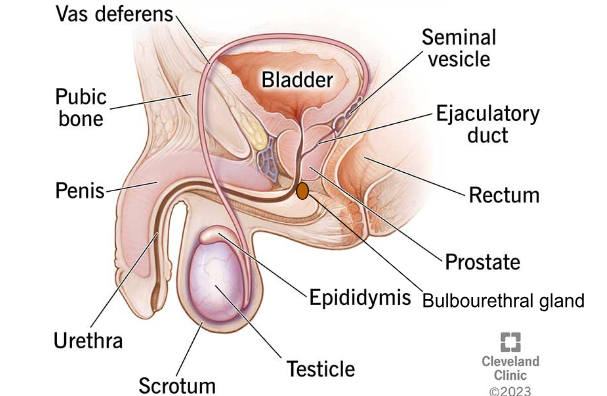
PROSTATE GLAND
Gland that produces fluid to nourish sperm and increases the pH level of semen.
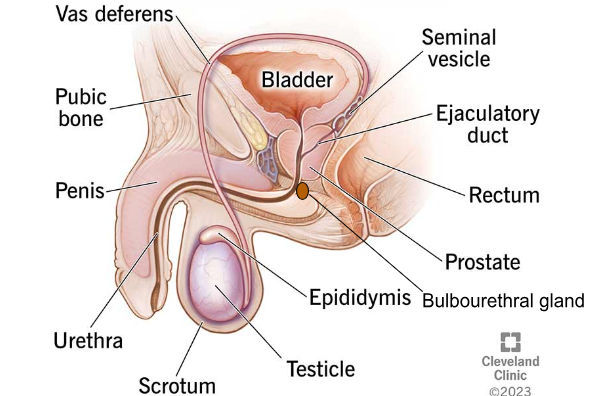
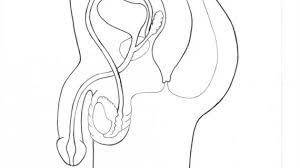
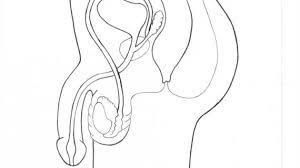
BULBOURETHRAL/COWPER'S GLANDS
Glands that produce fluid to lubricate the urethra and neutralize acid from residual urine.
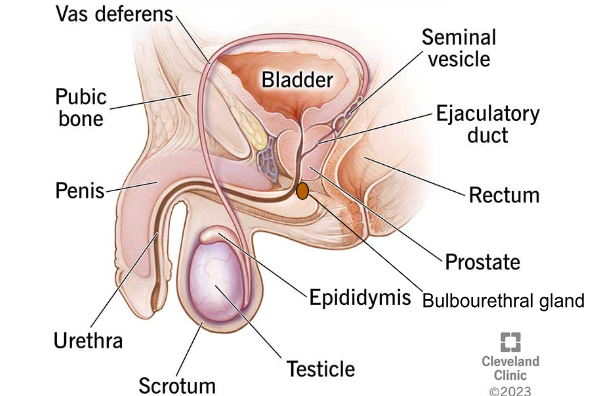
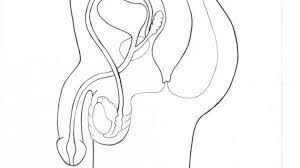
URETHRA
The tube that transports urine from the bladder and expels semen from the body.
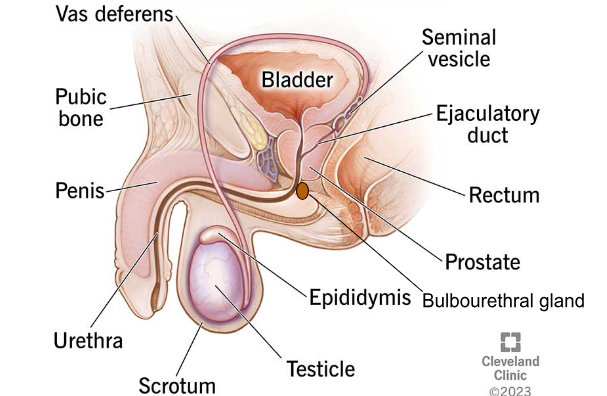
PENIS
The external organ composed of erectile tissue.
Erectile tissue
Sponge-like tissue that fills with blood, causing an erection.
Circumcision
The removal of the foreskin covering the tip of the penis.
Health benefits of circumcision
Lower risk of certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs), urinary tract infections (UTIs), and penile conditions.