Male Reproductive System
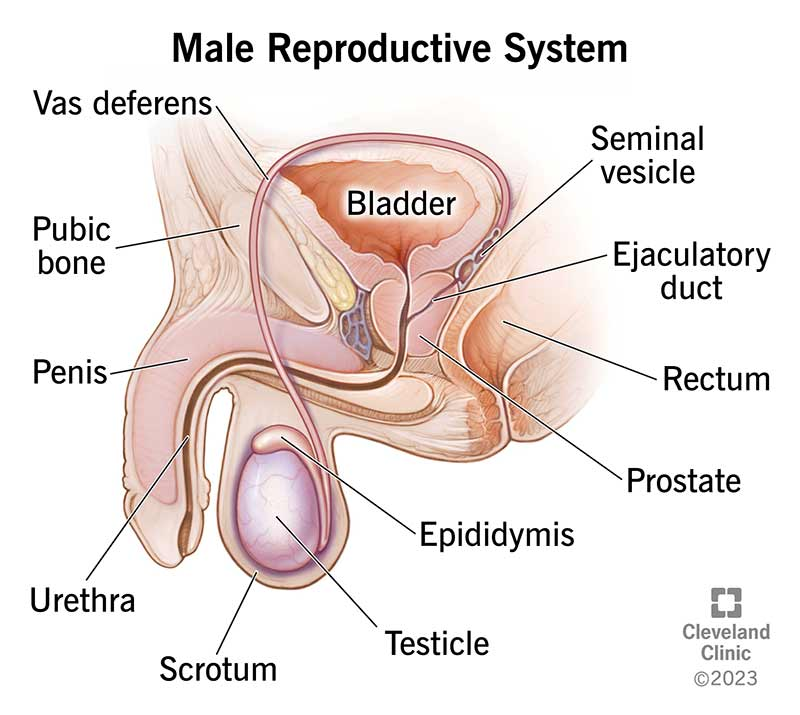
Path of SPERM: 1. Testicles 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Seminal Vesicle 5. Prostate Gland 6. Bulbourethral (Cowper’s) Gland 7. Urethra | SPERM: male sex cell |
|---|---|
SEMEN: thick fluid from the seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands that protect and nourish sperm | |
ERECTION: erectile tissue fills with blood and the penis become rigid (erect) | |
EJACULATION: process by which sperm exits the body when muscle contractions push semen out through the urethra | |
NOCTURNAL EMISSION: or “wet dream” ejajulation occurs during sleep; normal during puberty; sign of reproductive maturity. |
Male Reproductive System
SCROTUM |
|
|---|---|
TESTES |
|
EPIDIDYMIS |
|
VAS DEFERENS |
|
SEMINAL VESICLES |
|
PROSTATE GLAND |
|
BULBOURETHRAL/ COWPER’S GLANDS |
|
URETHRA |
|
PENIS |
Erectile tissue is sponge-like tissue that fills will blood causing erection Circumcision is the removal of the foreskin covering the tip of the penis. Health benefits of circumcision include a lower risk of certain STIs, UTIs, and penile conditions. |