Networks, Connections and Protocols (P1)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Network
More than one computer system connected together allowing for communication and sharing of resources.
LAN
A local area network has computer systems situated geographically close together, usually within the same building or small site.
Owned and managed by the network owner.
WAN
A wide area network has computer systems situated geographically distant to each other, possibly across a country or even across the world.
Owned and managed by third party communication channels like BT or Virgin Media
MAN
A metropolitan area network for computer systems across a town or city.
PAN
A personal area network for devices connected and used by an individual.
Client-Server network
A network where clients make requests to a server, which manages the request and responds.
Client is typically dependent on server to provide and manage information needed.
Server controls network security, backups and can be upgraded to manage higher demand.
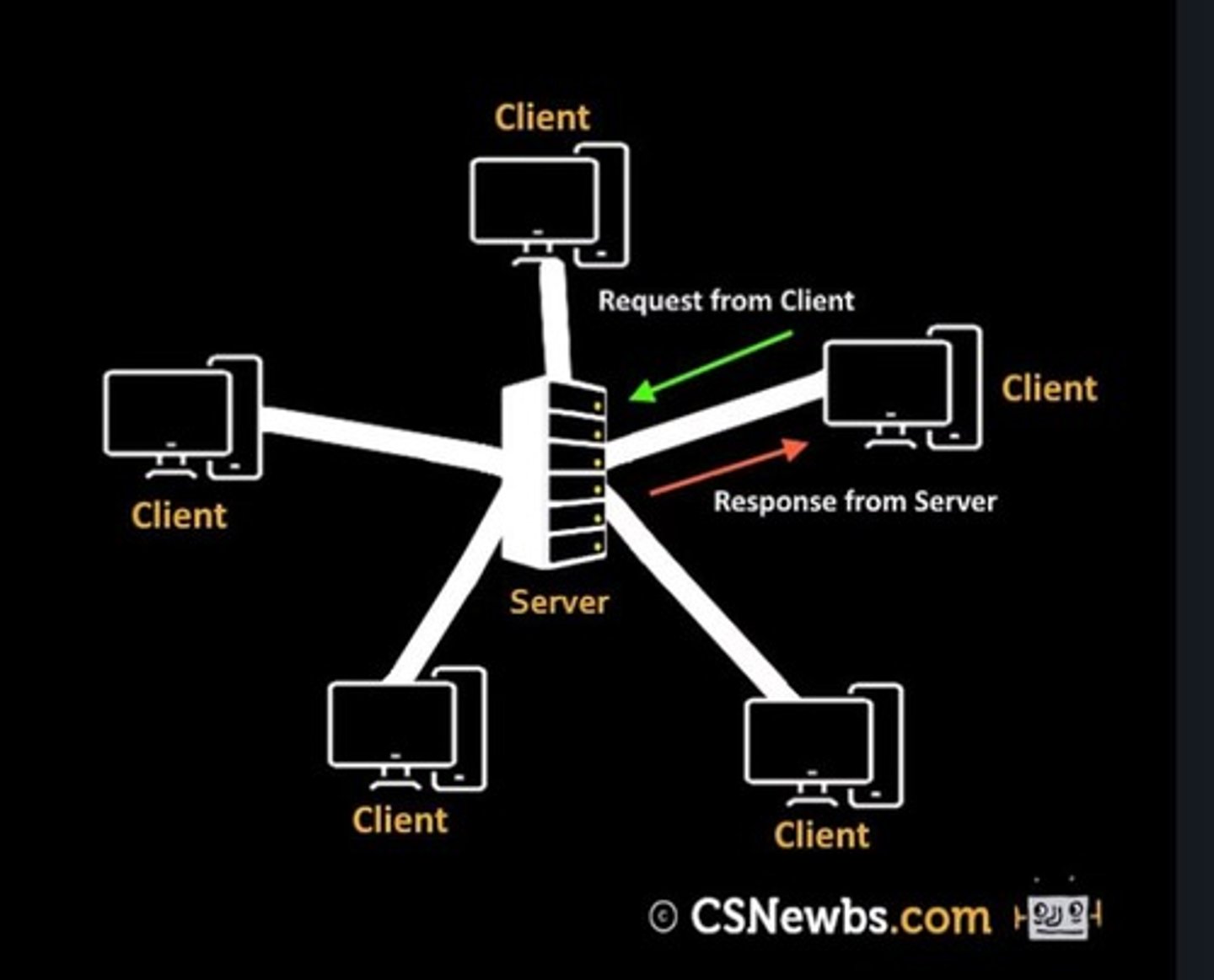
Client-Server network advantages
Network can be controlled centrally from server to easily backup and update software.
Hardware, software and resources can be shared across the network.
Clients can be easily added to the central server.
Client-Server disadvantages
Difficult to manage large amounts of traffic congestion - may cause network to shut down.
If fault occurs with the server, whole network will fail.
IT technicians may be required to manage and maintain the network.
Malware, such as viruses, can spread quickly across the network.
Peer-to-Peer network
A network where data is shared directly between systems without requiring a central server.
Each computer is equally responsible for providing data
Optimal for sharing files that can be downloaded
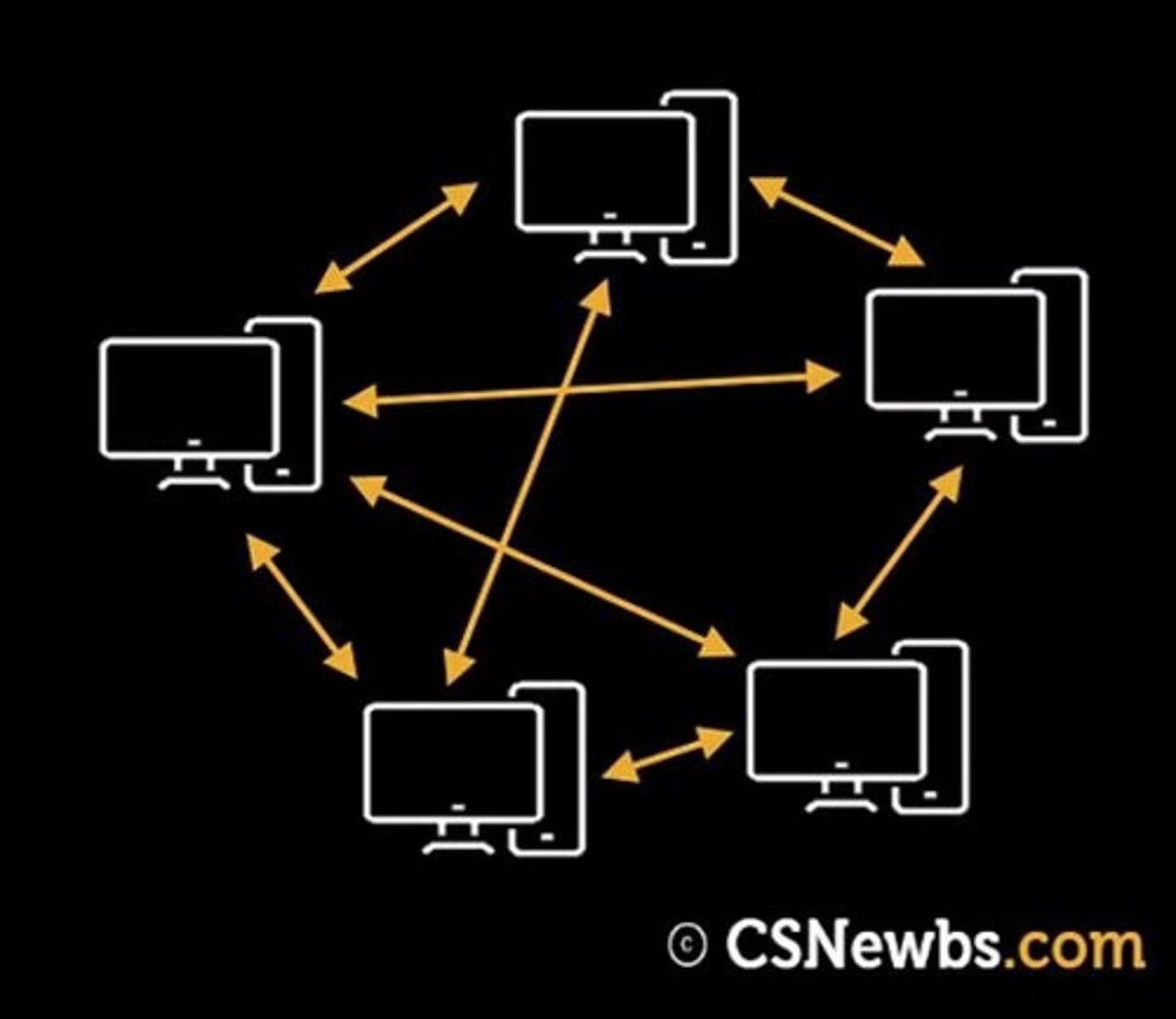
Peer-to-Peer network advantages
Simpler network to set up as no server is required.
Clients are not dependent on a server.
Perfect for quickly sharing files between systems.
Peer-to-Peer network disadvantages
Without a dedicated central server, managing security and backups must be done on each individual system.
Computer performance will decrease with more devices connected to the network.
Data packets
Files broken down into smaller parts for quick transfer across a network.
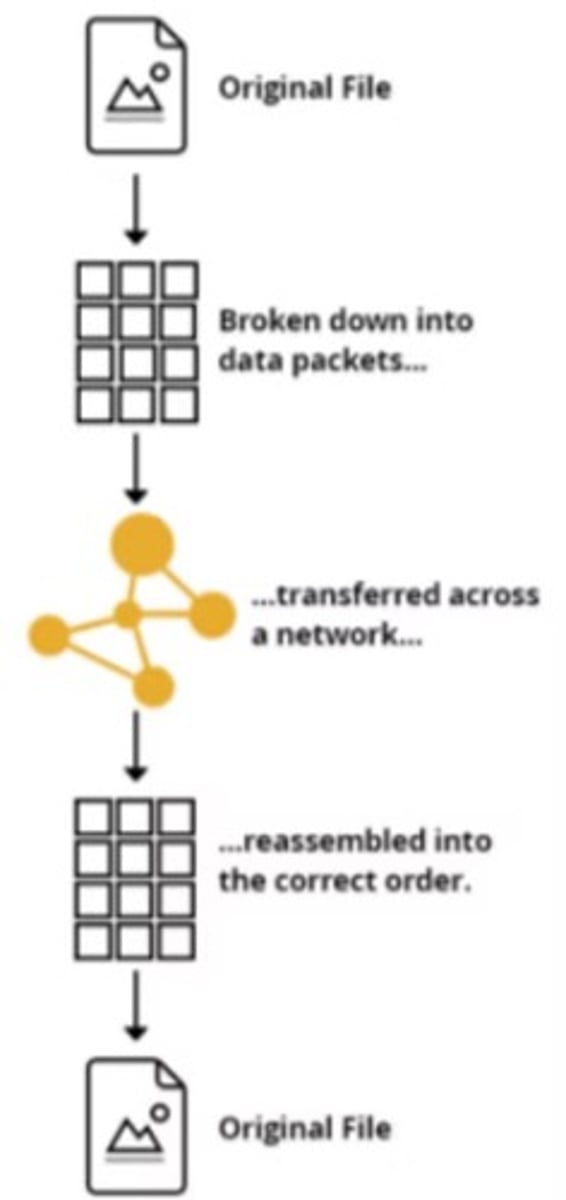
Transfer of data packets
Whole files are too large to transfer as one unit, so files are broken down into data packets.
Each packet of data is redirected by routers across networks until it arrives at destination
Data packets may split up and use alternative routes to reach destination address quicker.
When data packets have all arrived at destination, the data is reassembled back into the original file.
Network topology
Refers to the layout of computer systems on a local network.
Star Topology and how it works
A layout where each computer system is connected to a central device, usually a hub or switch.
Each computer is connected to a central hub or switch which looks at the destination address of data packets and transfer them directly to the intended computer within the network.
Star Topology network advantages
Increased security - data packets sent directly to and from the hub/switch in the centre.
New systems can be directly attached to central system - whole network isn’t disrupted.
Transfer speeds are generally fast - minimal network collisions.
Star Topology network disadvantages
Extra hardware (hub/switch) is required to be bought, installed and maintained.
If central system fails, the whole network will be unusable until fixed.
Mesh Topology and how it works
In a full mesh network, each computer system is connected to every other computer system.
Data packets are transferred to the destination address along the quickest path, from node to node. If one pathway is broken, there are many alternative routes that the packets can take.
Mesh Topology network advantages
If one cable or system fails, data packets can take alternative routes.
Can withstand large amounts of data traffic - many connections and pathways
New systems can be added without disruption to entire topology.
Mesh Topology network disadvantages
Network layout may be expensive to maintain and install.
Redundant cabling should be avoided - avoiding cabling and connections to systems that don’t require it.
Example of things that can affect performance of a network
number of users at same time
number of data collisions
interference (e.g. thick walls)
distance to travel / signal strength
amount of data to transfer
server / CPU performance
Main 3 factors affecting performance of a network
Latency (delay, how fast signals travel)
Bandwidth (max rate of data transfer)
Error rate (rate of corruption)
Wireless access point (WAP)
Provides a link between wireless and wired networks by creating a wireless local area network.
Router
Device used to transfer data packets between networks.
Alternative routes for data packets
Data packets may split up and use different paths to reach the destination address.
Nodes
Devices in a network topology diagram.
Routing table
A list used by a router to calculate the quickest and shortest route to transfer data.
Switch
a device used to connect devices together on a LAN (local area network).
MAC address
A unique identifier assigned to a network interface card for communications on a network.
Hub
An alternative to a switch that is slower and less secure as it forwards a copy of the received data to all connected nodes.
Network Interface Controller / Card (NIC)
An internal piece of hardware that is required for the computer to connect to a network.
Ethernet cable
Cables used typically on a LAN to transfer data between nodes and hardware such as switches.
Fibre Optic cables
Very fast but more expensive and fragile cables typically used to send data quickly along a WAN.
Coaxial cables
Older, slower, copper cables that are not used as much in modern times as they can be affected by electromagnetic interferences.
Internet
A global network of interconnected networks.
WWW
A way of accessing information on the internet.
Web server
A server that provides services on the internet and responds to the web browser's request to display a web page.
Domain name
A unique name (e.g. google.com) that must be registered with a domain registrar to host a website.
DNS (domain name system)
A server that stores a list of domain names and a list of corresponding IP addresses where the website is stored.
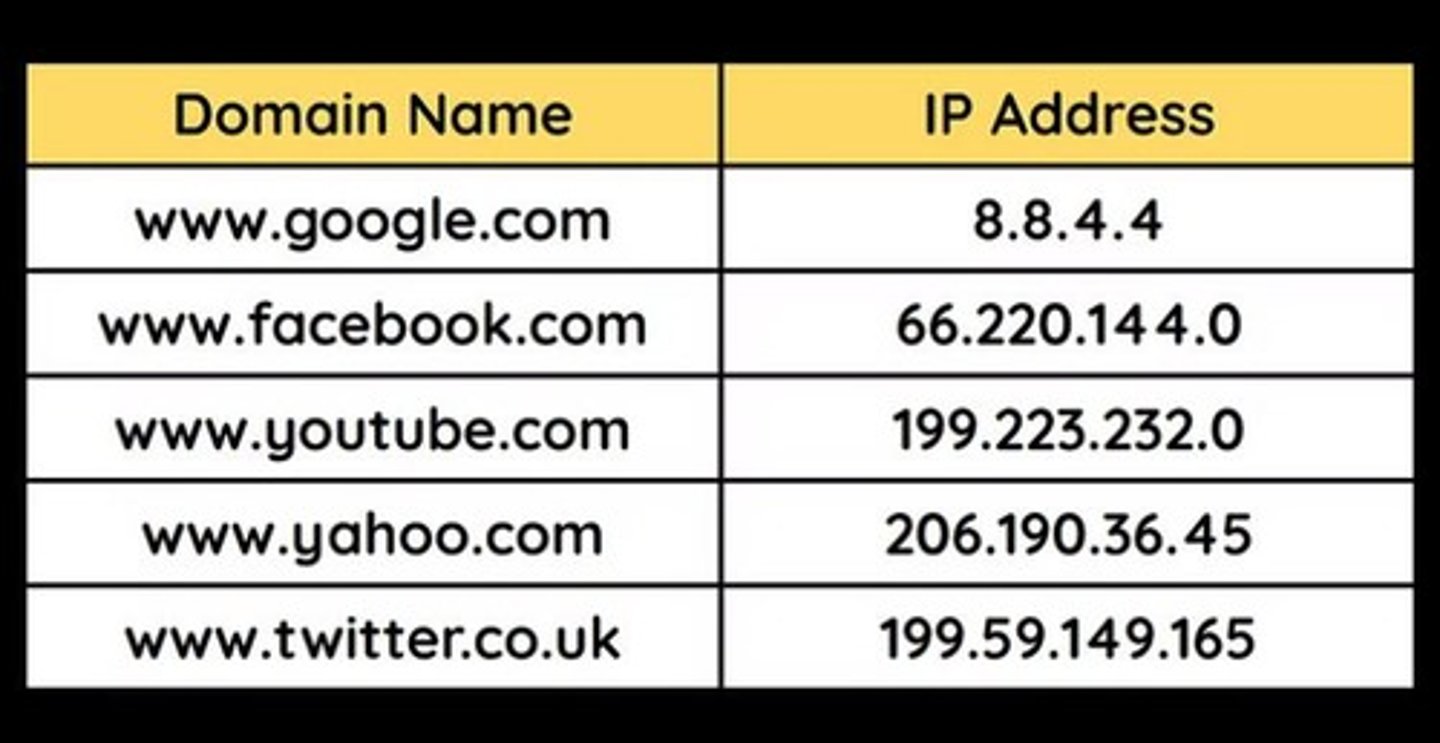
IP Address
Uniquely identifies a device on a network, and defines where it is located geographically.
The Cloud
Refers to the network of server accesses on the internet.
Hosting Company
A company responsible for keeping servers running and making data accessible and secure on the internet.
Wired Connections
Connections that use physical cables, such as copper or fibre optic wires, and require a network interface card (NIC).
Wireless Connections
Connections that use no cables but require a wireless network interface card (WNIC).
Protocol
A set of rules that allow devices on a network to communicate with each other.
IP (Internet Protocol)
A protocol responsible for routing and addressing data packets to ensure they reach the correct destination.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
A protocol that splits data from applications into smaller data packets that can then be sent across a network.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
A protocol used to transfer web pages and defines how web browsers work.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
A more secure version of HTTP that works with SSL to transfer encrypted data.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
A protocol used to transfer files across a network, for uploading or downloading files to/from a web server.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
A protocol used to send emails to a mail server and between mail servers.
POP (Post Office Protocol)
A protocol that deletes an email from the server once it has been downloaded to a device.
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)
A protocol that syncs messages with an email server to allow access from different devices.
IPv4
A 32-bit address that allows for over 4 billion unique addresses, represented in denary.
IPv6
A 128-bit address that allows for an undecillion unique addresses, represented in hexadecimal.
Protocol Layer
A sub part of a more complex task that provides a specific function to assist in data transmission.
Advantages of Layers
Self-contained layers make managing, repairing, and upgrading easier
Allows focus on specific parts of a protocol.