Geography midterm study guide
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Geography
Studying the world, what it looks like, and cultures
Investigate human and natural phenomena around the world
Look at hour human and physical occurrences connect the earth
Regional analysis
Physical geography
Geography is a spatial science - we study things in relation to their space on earth
The branch of geography dealing with natural features and processes
Human geography
Studying specific systems (ex. Trade, politics, etc.)
The study of how people interact with the physical world around them
Includes the way they use resources, adapt to climate change, and develop regional cultures
Spatial
Geography is a spatial science, we study things in relation to their space on earth
Absolute location
Accepted grid system (longitude and latitude) (section, township, range)
Relative location
Position in relation to other places/ things (situation ~how something is situated)
Absolute direction
North, east, south, west
Relative direction
Near east, far east, out west, back east
Absolute distance
How many mikes/km away
Relative distance
More relevant to human experience (time, money, etc)
Scale (in terms of study)
How big or small a study is ~ how general or specific it is (agriculture, travel, etc))
Scale (for a map)
It's relationship to real world distances (ex. 1in on a map = 1mile in the world)
Tobler’s first law of geography
Everything is specially related, but relationships are stranger when things are near one another
Accessability
How easy/difficult it is to overcome a distance
Connectivity
Things that help connect different areas- roads, TV, cellphones, etc.
Globalization
Increasing interconnection of more people and parts of the world
Spatial diffusion
The process of the spread of an idea or thing
Spatial distributions
The study of how things ave arranged or spread out across a geographic area ~ Form the root of regions
Spatial associations
The relationships and patterns that exist between geographical phenomena and how they are distributed across space~ arise from spatial distributions that are closely related
4 types of regions
Administrative, formal, functional, perceptual
Administrative region
A geographical region designated for the exposes of administration and governance (ex-country)
Formal region
A well-defined area with a common characteristic that is consistent throughout the region (ex. Corn belt)
Functional region
A type of region that is defined by a specific social or economic attribute (ex. Circulation area for the Bismarck tribune)
Perceptual region
An area that's defined by people's feelings, beliefs, and attitudes about a place rather than geographical boundaries
Maps (uses)
When the area we are trying to look at is too big
Show distributions of things over earth
Measuring distances between locations
Illustrating the sizes and shapes of countries
Communicates spatial data about earths surface
Maps (weakness)
They distort shape, size, distance, and direction because its hard to show a 3D world on a flat map
Longitude
Vertical (up and down) lines 0 to 180 degrees
Latitude
Horizontal ( side to side) (lines get shorter as you go-the line for the equator is the longest)
Equal-area projection map
A map projection that shows regions that are the same size on the earth the same size on the map but may distort the shape, angle, or scale
Used for longitude and latitude
Conformal projection map
A map that favors preserving the shape of features on the map but may greatly distort the size of features
Azimuthal equidistant projection map
A map that shows earth's surface from a given point, preserving both distance and direction from the center point
Robinson projection map
Shows the poles as lines rather than points and more accurately portraying high latitude lands and water to land ratio
General maps
A map that displays a variety of natural and human made features of general interest and are intended for widespread public use
Thematic maps
Portrays the geographic pattern of a particular subject matter in a geographic area
Lithosphere and main processes
A thin but strong solid shell of rocks, the outer, lighter portion of earth's crust
Processes: plate techtonics, earthquakes, volcanos
Atmosphere and main processes
Player of gasses surrounding the planet primarily composed of oxygen and nitrogen
Processes: radiation, convection, regulating temperature, movement of air masses
Biosphere and main processes
The zone of earth where life exists (includes the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere)
Processes: photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition
Hydrosphere and main processes
Refers to all water on earth and the main processes within it
Processes: evaporation, condensation, precipitation, runoff, infiltration, and Transpiration
Coriolis effect
An effect whereby a mass moving in a rotating system experiences a force acting perpendicular to the direction of motion and to the direction of motion and the axis of rotation
Population geography
Provides the concepts and theories to understand and forecast the size, composition, and geographic distribution of the human population
Rates
Record the frequency of the occurance of an event during a given time frame for a designated population
Cohort
Refer data to a population group untied by a common characteristic
Crude rates
Relates to the total population without regard to the age or sex of a population
Birth rate
Annual number of live births per 1000 population
Death rate
Also known as mortality rate, the annual number of deaths per 1000 population
Total fertility rate
Average number of children each woman has
Replacement fertility rate
Level needed to ensure replacement of each generation
Rate of natural increase
Crude birth minus crude death, then converted to a percentage
Doubling Time
The time it takes for the population to double
Migration
Movement of people
Types of migration
Emigration - movement of people out of a place
Immigration - movement of people into a place
Demographic equation
Formula for determining population change from year to year that takes into account the factors of births, deaths, immigration, and emigration
Ecumene
Habitable areas
Non-ecumene
Inhabitable areas
Population Density
Number of people per area they occupy
Crude density
Number of people per unit area of land
Physiological density
Population per arable land
Agricultural Density
Excludes city population from physiological density
Population Profiles (population pyramid)
A graph that shows the distribution of a population by age and gender
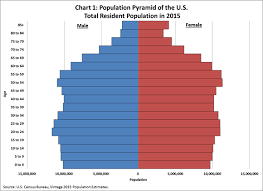
Population Distributions
A map that shows population density around the world
Projections
If y holds true the x will be true in the future
Predictions
We think this is going to happen (projections can be predictions)
Demographic transition
Stages of population growth and decline - birth and death rates start high , death rate decreases, they both decrease, population eventually declines
Overpopulation
Judgement of whether the environment can support the present population - many variables such as carrying capacity, technology , and trade
Cultural Geography
A common way of life - can be small scale or large scale
Convergence
A culture becoming more alike
Divergence
Cultures becoming more distinct
Culture traits
units of learned behavior
Culture complex
Combination of traits
Culture system
Shared traits/complexes in a population
Culture region
portion of the earth’s surface with shared characteristics
Culture realm
Culture region at broadcast extent
Subsystems of culture (I/FWP)
Ideas/folk, work, place - technological, sociological, ideological
Innovation
Change of ideas within a cultural group itself
Spatial diffusion
Process by which an aspect of culture spreads to another area - people move or information spreads - barriers can arise
Acculturation
One culture group changes dramatically by adopting another culture
Language
An organized system of speech by which people communicate with and understand each other
Religion
Value systems that involve worship and faith of sacred/divine or a unified system of beliefs that own people into single moral community
Universalizing
Faiths that seek to spread beliefs to everyone
Ethnic
Strong territorial/cultural identification
Traditional religion
Small, very local, often close nature
Principal religion
Ex. Judaism, Christianity, Islam, etc
Human interaction
Communication and interdependencies between people
Spatial interaction
Human interactions. Looked at through the places involved
Distance decay
Principle that states that interactions decrease as distance increases
Critical distance
Distance where variables associated with interaction override our willingness to interact
Barriers to interaction (and examples)
Anything that can inhibit movement of ideas, technology, or people
Ex. Distance, cost, religion, language, government
Individual activity space
The space within which we move freely to do daily tasks
Variables that affect activity space
Stages in life, mobility, opportunities
Contagious diffusion
Spread person to person - the more people who have it the faster it spreads
Hierarchical diffusion
Ideas spread at high levels first, then move down
Push factors
Things that makes someone want to leave a place
Pull factors
Things that make someone want to come to a place
Place utility
How much use can be made of a place
Migration field
Areas that dominate in/out migration for a place
Step migration
A big migration done in small steps
Chain migration
One group leaves, another follows, etc.
Political geography
Study of the organization and spatial distribution of political phenomena
State
Political unit that is part of the federal government or- independent political unit holding sovereignty over a territory
Nation
Independent political unit holding sovereignty over a territory Or- community of people with a common culture or territory