propedeutics small animals- general exploration, handling, vital signs
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
1. use appropriate terminology
2. carry out an adequate management of the different animal species, knowing the methods of fastening
3. write a proper medical history of the animal
4. explore organs, devices or systems (semiotechnics) and interpret the results (semiology)
5. collect biological samples, analyze them and interpret the results obtained
what are the objectives of clinical propedeutics?
someone who knows the animal
who must we collect the clinical history of the animal from?
general (vital signs),
specific,
additional tests
what 3 factors does the physical exploration include?
diagnosis,
treatment,
prognosis
what 3 factors does the clinical judgement include?
no, they usually say that it is good, but you cannot trust this
should we trust the owner when he says that his animal is good?
usually not, but it can be
is sedation necessary for the physical exploration?
sometimes, it depends on the animal
do we keep the owner with us for the physical exploration?
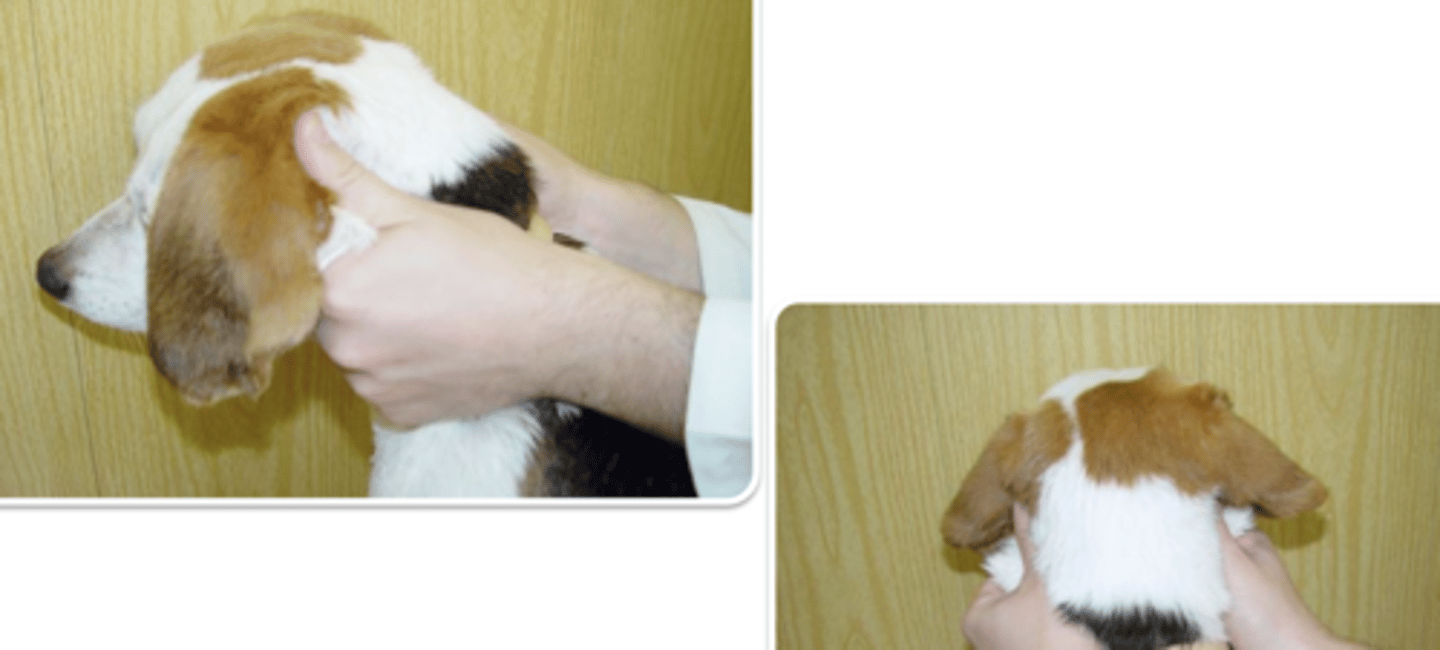
skin fold under the ears
what is the best way to immobilize the animal by the head?
brachiocephalic breeds, because it might cause eye prolapse
for what breeds might immobilizing using skin fold under the ears be dangerous? why?
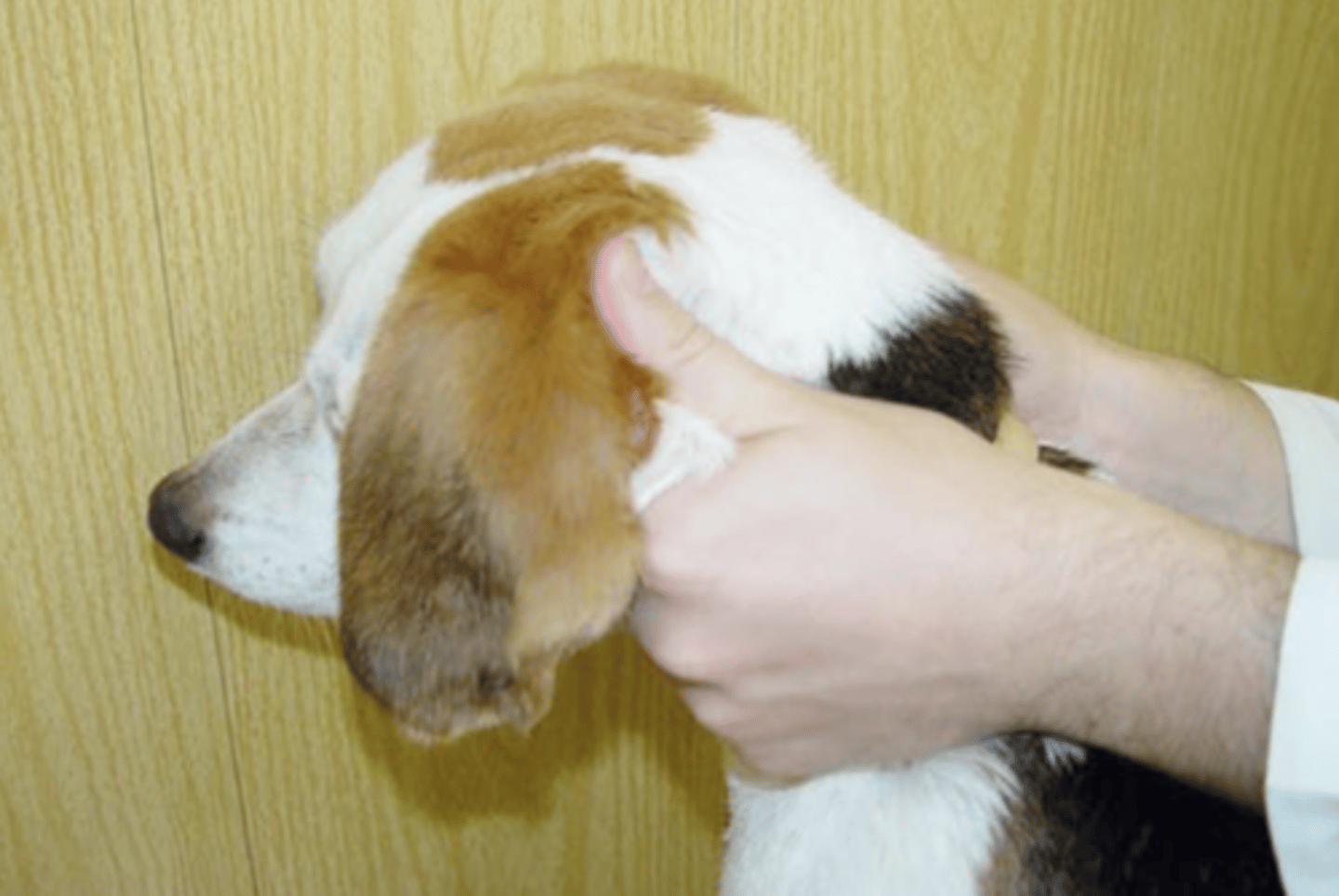
skin fold under the ears, to immobilize the animal's head
what is the vet doing? why?
from behind the dog, while it is sitting
how do we put on a muzzle?
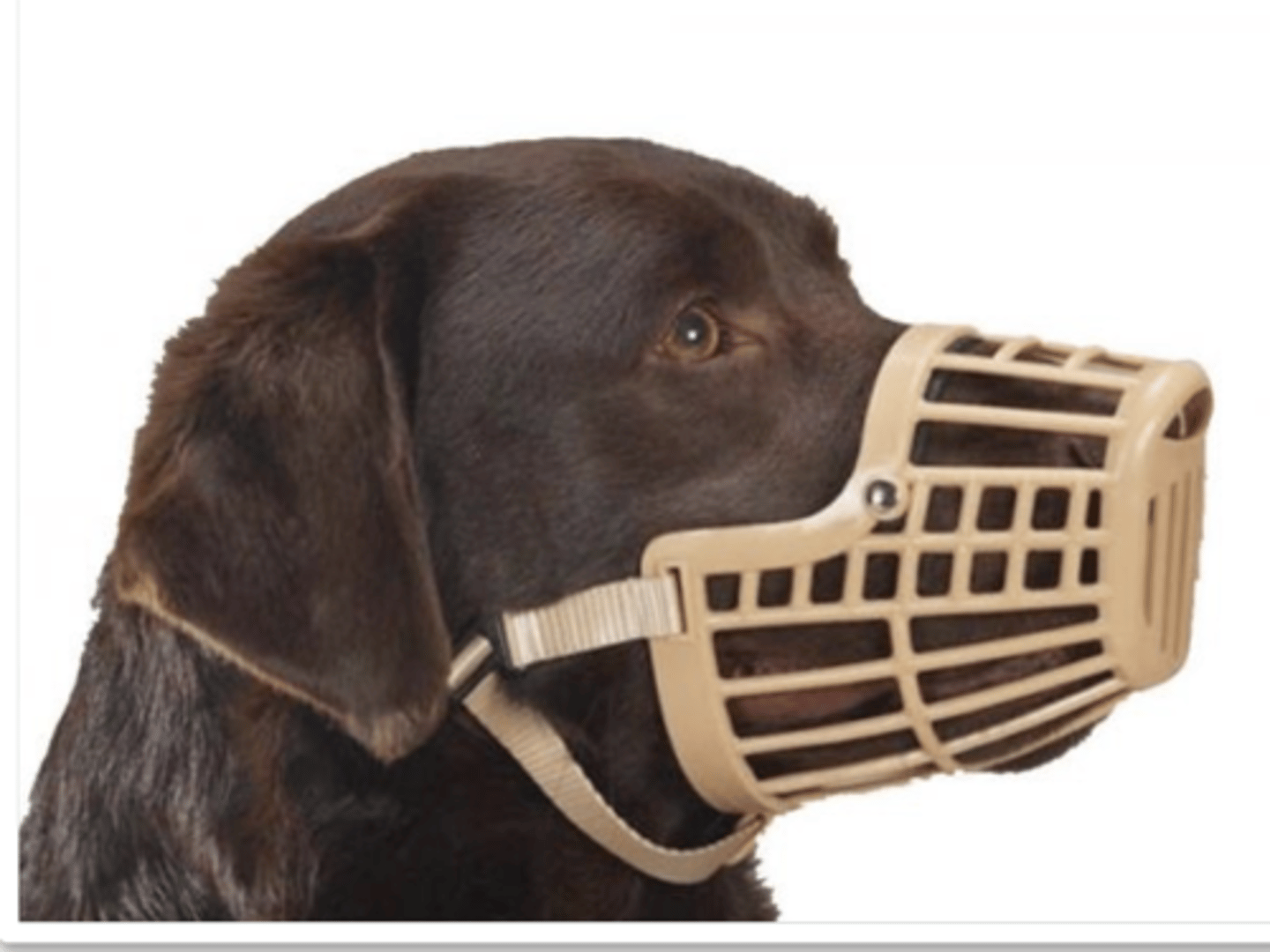

when the dog is vomiting, panting, and during hot weather
when can muzzles be dangerous?
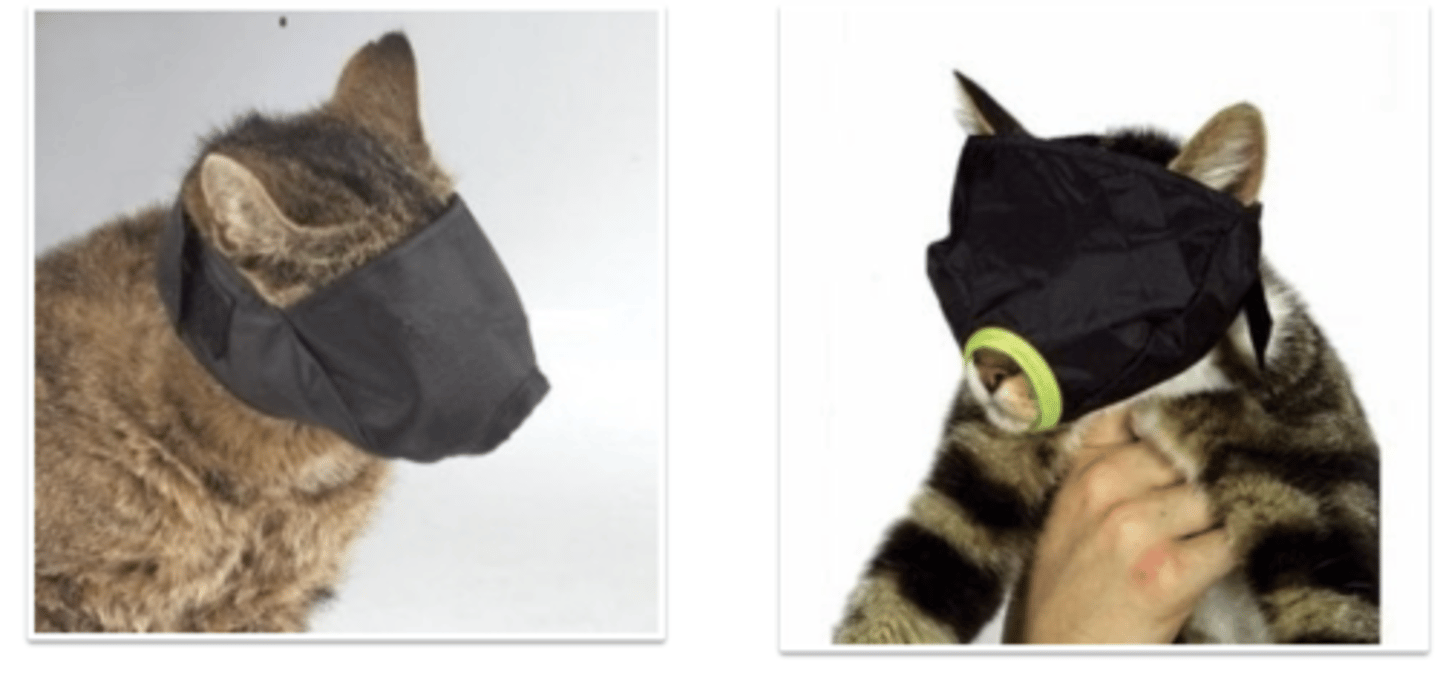
cover their eyes with a face cover
what can we do for cats to make them less stressed?
it makes the cat less stressed because it cannot see
what is this for?

use a gauze bandage to make your own muzzle
if there is no muzzle or not the correct size of muzzle, what do we do?
on top of the table
where is the physical exam done?
hands in front of front legs and behind the back legs
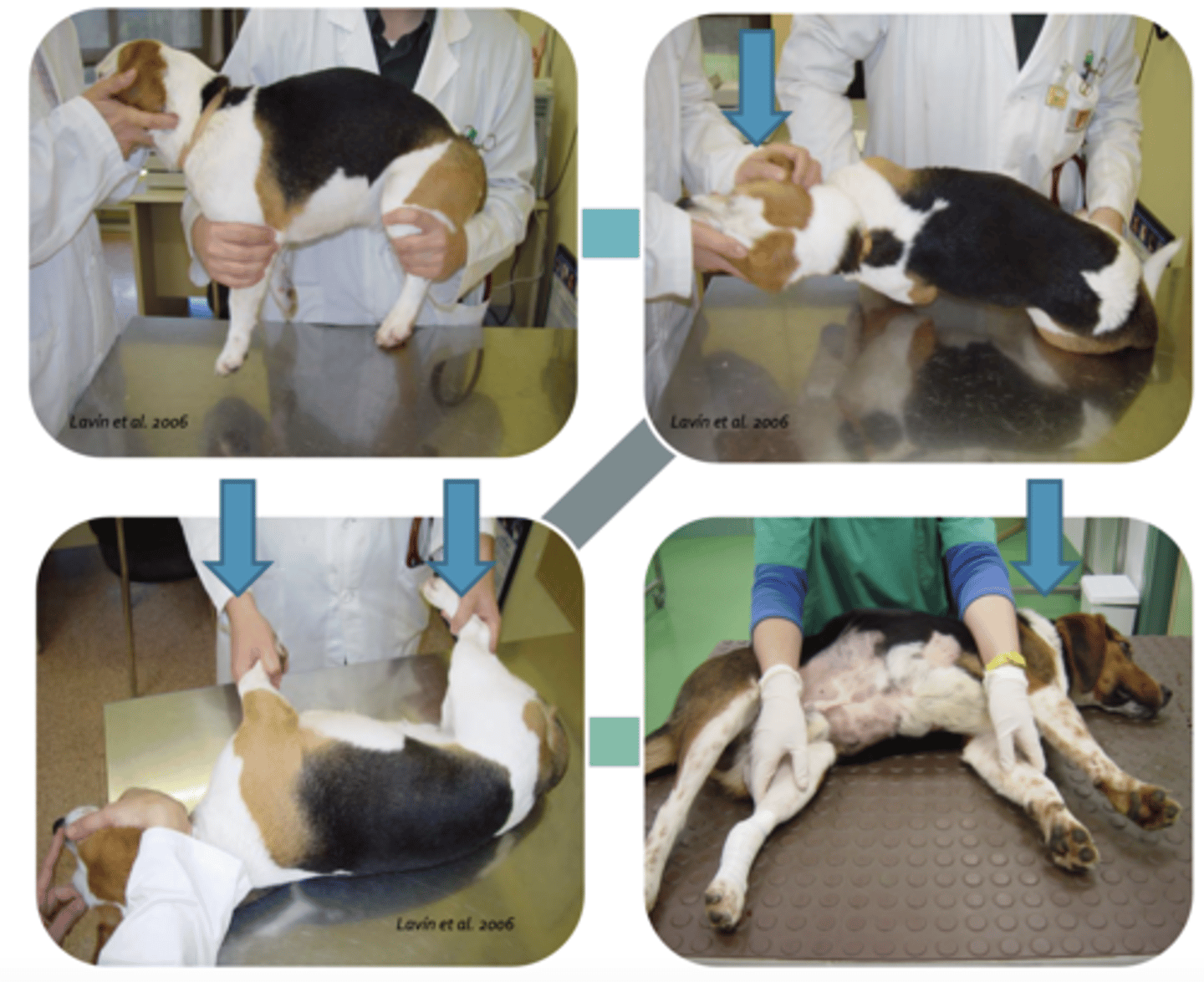
what is the best way to raise the dog onto the table?
grab legs on the opposite side of the dog while it stands, pull towards you. use someone else to support the head. hold inner legs once in the correct position
how do we perform a lateral decubitus?
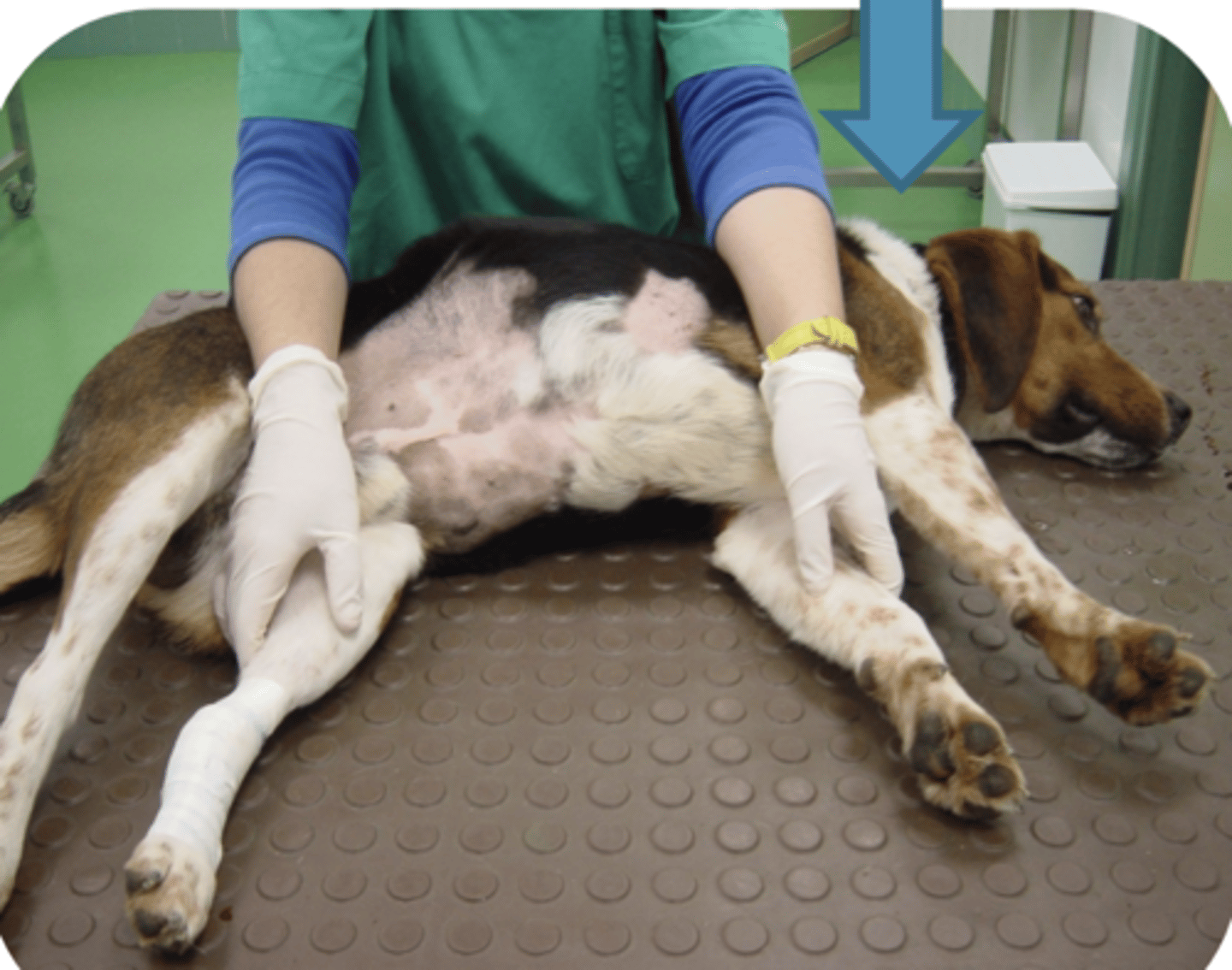
lateral decubitus
what is this called?
it is a containment cage, which presses the cat to the side of the cage for injections. it is very easy
what is this for?
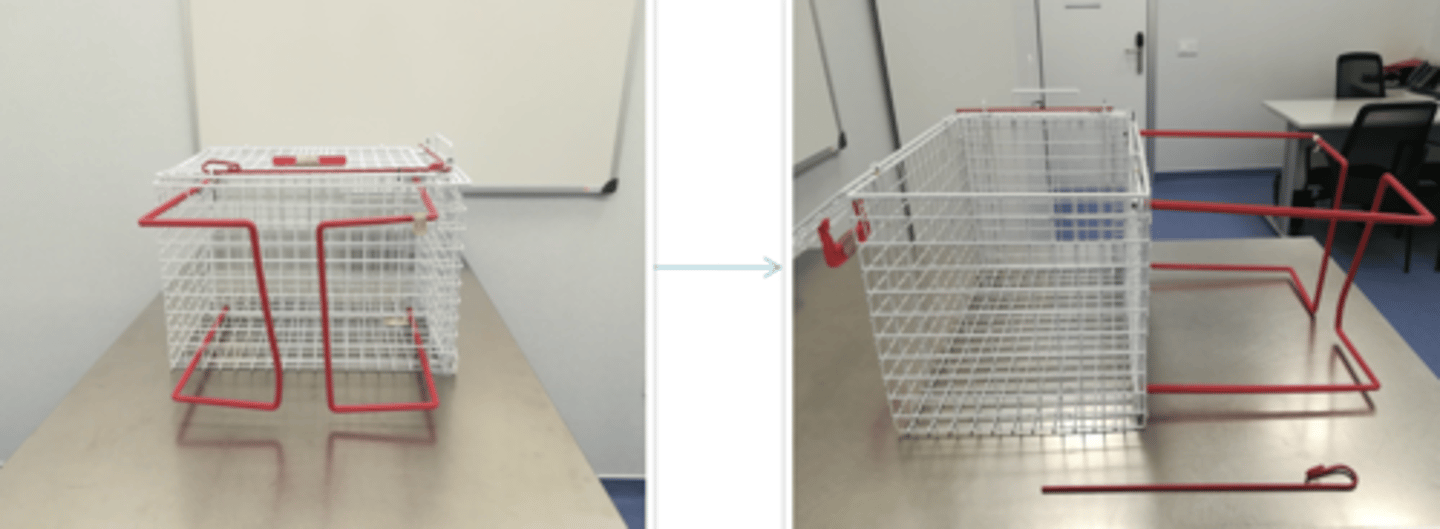
skin of the neck and back legs
for injecting the cat without the containment cage, what parts of the body do we hold?
overall status,
postural attitude,
behavior,
vital signs
what info do we get with the general exploration?
head, neck, skin, thorax, abdomen, urinary and reproductive systems, muscle and orthopedic systems, neurologic system
when performing a topographic exploration, what do we explore?
inspect without touching
we always _____ before touching the animal
objective exploration by the means of sight that allows to show qualitative and quantitative changes that can provide valuable information to guide the diagnosis
what is inspection?
inspection
what is the first semiological maneuver to be performed?
inspection of the entire body of the animal
what is a general inspection?
inspection reduced to a certain place or region of the animal's body
what is particular inspection?
inspection exclusively using eyes
what is a direct inspection?
an inspection using a device or lens, magnifying glass, specula, or endoscope
what is an indirect inspection?
palpation
what is the word for exploration by means of the sense of touch?
exploration by means of the sense of touch
what is palpation?
hands
direct/immediate palpation involves touching the animal with....
instruments such as catheters, probes, hammer, specula
indirect palpation involves touching the animal with....
using both hands
can be:
- direct: both hands perform the maneuver at the same time
- indirect: one hand performs the maneuver and the other holds an instrument
what is a bimanual palpation?
palpation performed on the exterior of the animal
what is external palpation?
palpation performed through a cavity such as rectal, oral, vaginal, etc
what is internal palpation?
palpate with the palm of the hand on the surface of the body
types: pressure, with back of the hand, pinching, sliding, friction
how do we perform a superficial palpation and what are the types?
palpation performed with the tips of the fingers, or through an instrument. it is to get information about pain sensitivity
what is a pressure palpation?
to subjectively assess the temperature of the animal (not accurate)
why would we choose to palpate with the back of our hand?
to determine the superficial planes on deep planes
what is the purpose of sliding palpation?
sliding the fingertip over the skin trying to perceive deformations under it.
used in dermatology
what is friction palpation?
to feel an internal organ such as stomach, intestine, uterus, bladder, etc
what is deep palpation for?
cats, because they have less abdominal strength. easy to feel foreign bodies
which, cats or dogs, is it easier to perform a deep palpation of internal organs?
a maneuver in which the patient's body is struck briefly to produce a sound/vibrations
what is percussion?
vibration
the blow of percussion produces a _______ of the tissues that form the organs and their contents, producing noise of different intensity and tones, depending on the circumstances
a percussion performed with the hand either immediately (fingertip, fist, etc), or mediate, digit-digit maneuver, in which a finger of one hand acts as a plesimeter and the index and ring finger of the other hand acts as a striker element
what is a manual percussion?
percussion performed with percussion instruments (ex: hammer)
what is an instrumental percussion?
large species (bovine, equine, etc)
in what species is an instrumental percussion more common?
hammer:
- rubber tip (used to percuss soft parts)
- metal (used for hard parts of the body)
pleximeter:
- interposed between the body of the patient and the hammer
- concentrates vibrations to give a concrete noise
- different shapes and materials
- thickness not greater than 2 mm
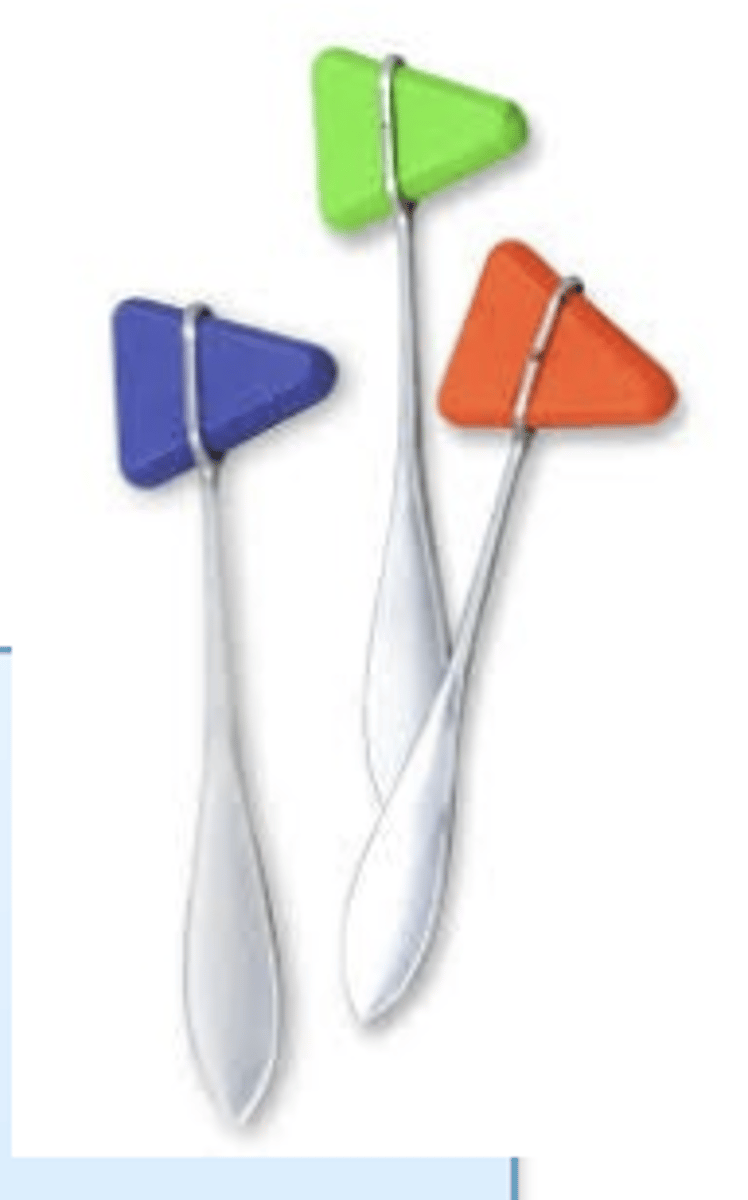
list the percussion instruments
pleximeter, used for intrumental percussion (usually on large animals)
what is this? what is it for?
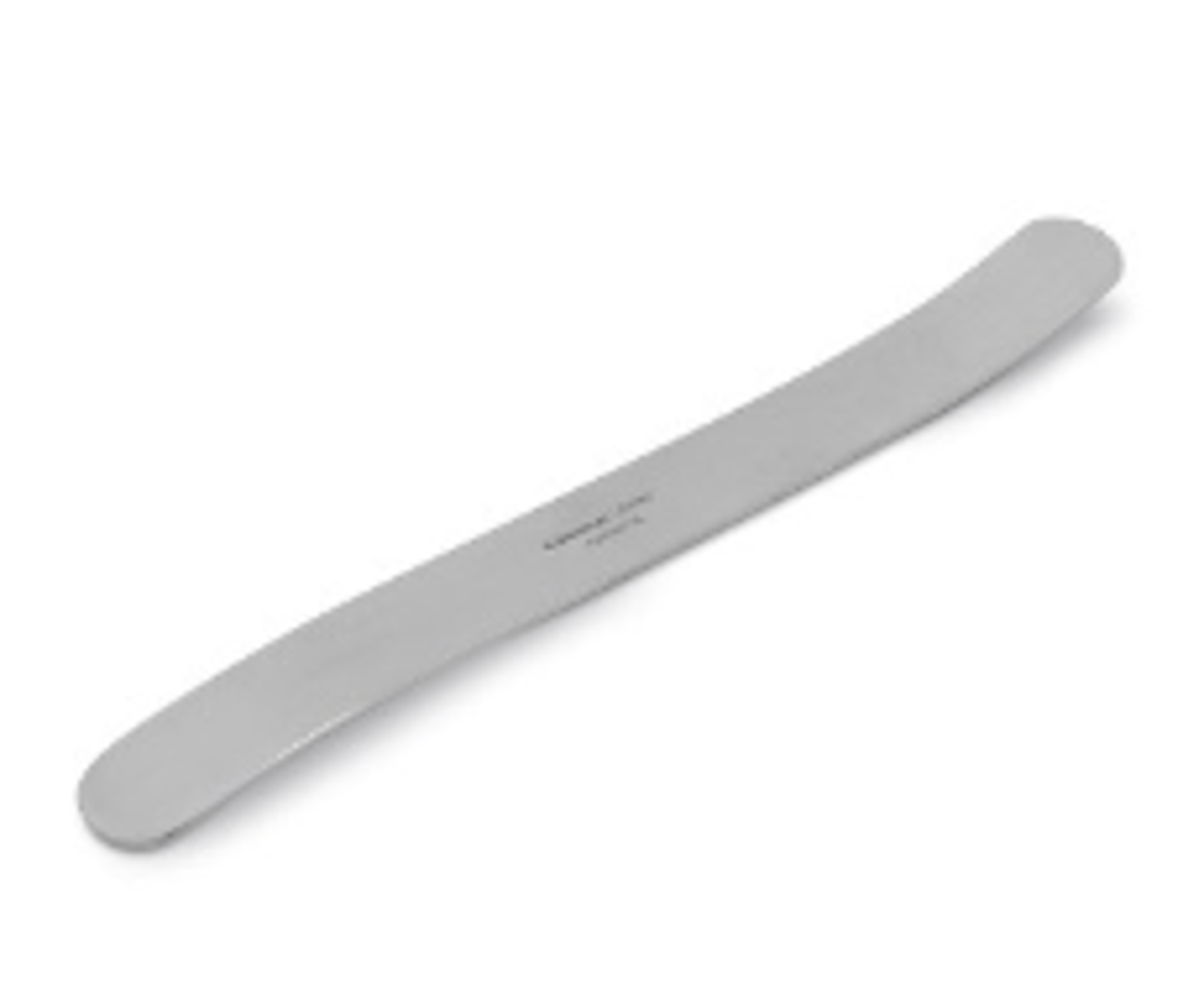

rubber tip hammer, used for instrumental percussion of soft parts of the body
what is this? what is it for?
percussion of abdomen- sounds like a basketball,
confirmed with an xray
what is the diagnostic test for bloat (abdomen full of air)?
hearing
auscultation is exploration through the sense of ______
acoustic manifestation
auscultation is the perception of the _________ __________ originated by normal or pathological vital processes
direct application of the ear on the body's surface
what is direct/immediate auscultation?
auscultation using instruments (stethoscope)
what is indirect/mediate/instrumental auscultation?
anatomic position of the animal's body and each part of the animal's body
what is postural attitude?
-rigid
-paresis/paralysis
-antialgic
-orthopneic
what are the different abnormal postures?
an abnormal position of the animal that they are doing to avoid pain
what is an antialgic postition?
paresis
what is the word for absence of movement?
leaning on something to help breathe
or standing in a way that makes breathing easier
seen in dyspneic patients
what is an orthopneic position?
the way the animal interacts with the environment and vital acts (eating, drinking, urinating, walking, etc)
what is attitude?
lack of interest/enthusiasm
what is apathy?
decreased level of alertness or consciousness
what is obtundation?
polaquiuria
what is the word for frequent urination but in small amounts?
comatose
what is the word for the animal not being responsive?
animal does not respond to stimuli
what does obnubilated mean?
stunned/confused and slow to act
what does stuporous mean?
we should be able to feel but not see
should we be able to see and feel the animal's spinous and transverse processes, ischiatic tuberosity, ribs, and coxal tuberosity?
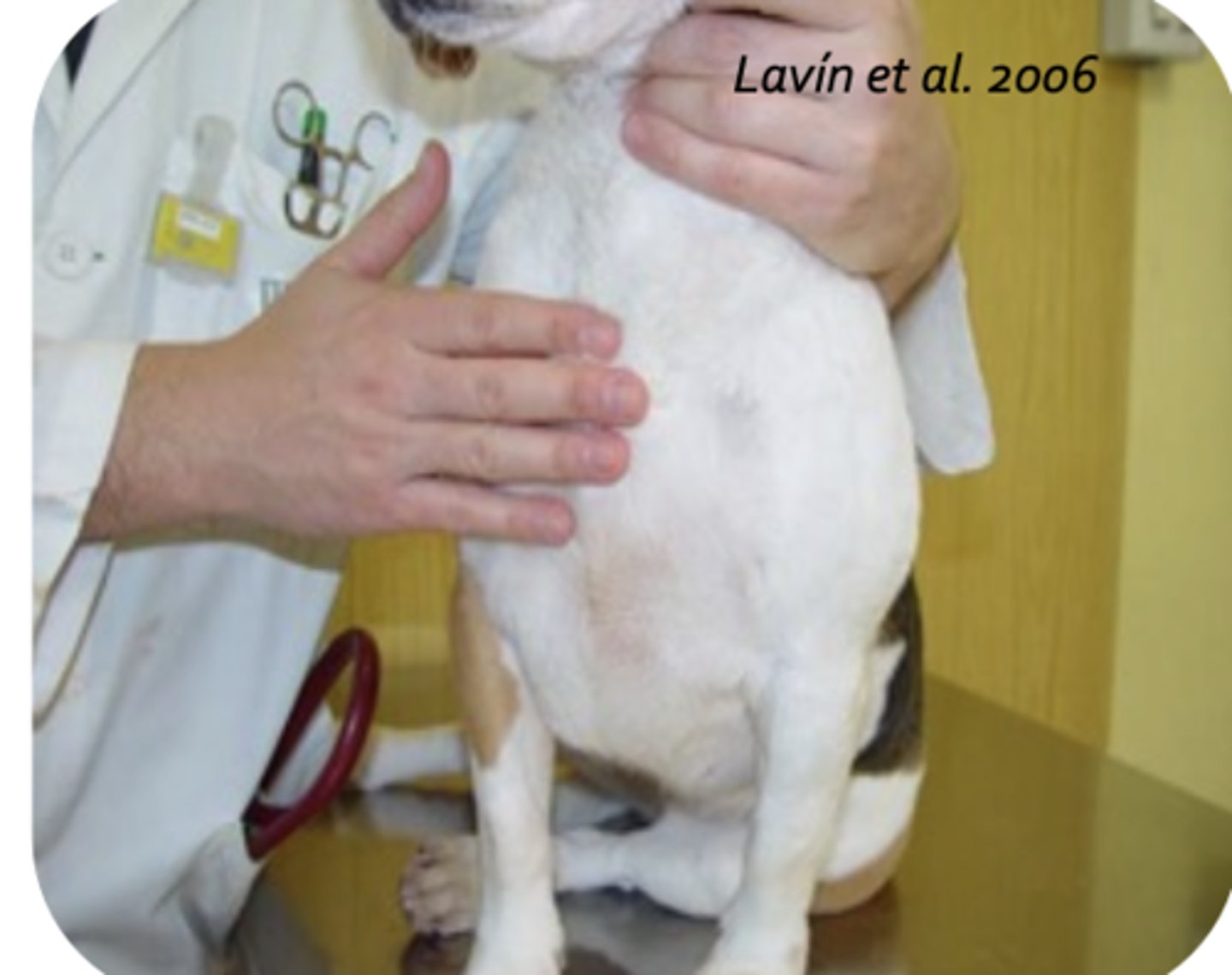
pectoral muscle
what is being palpated?
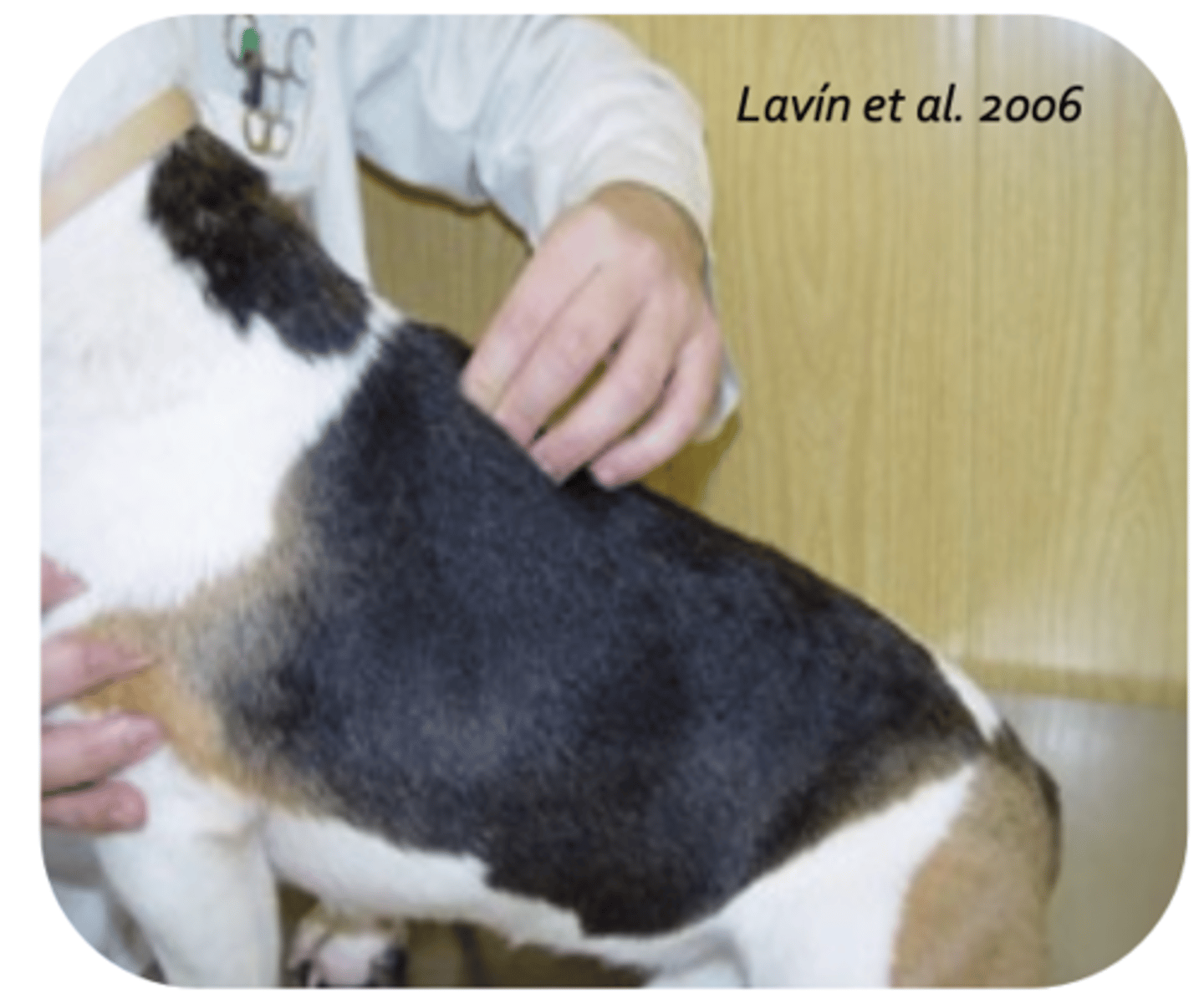
spinous processes
what is being palpated?
transverse processes
what is being palpated?
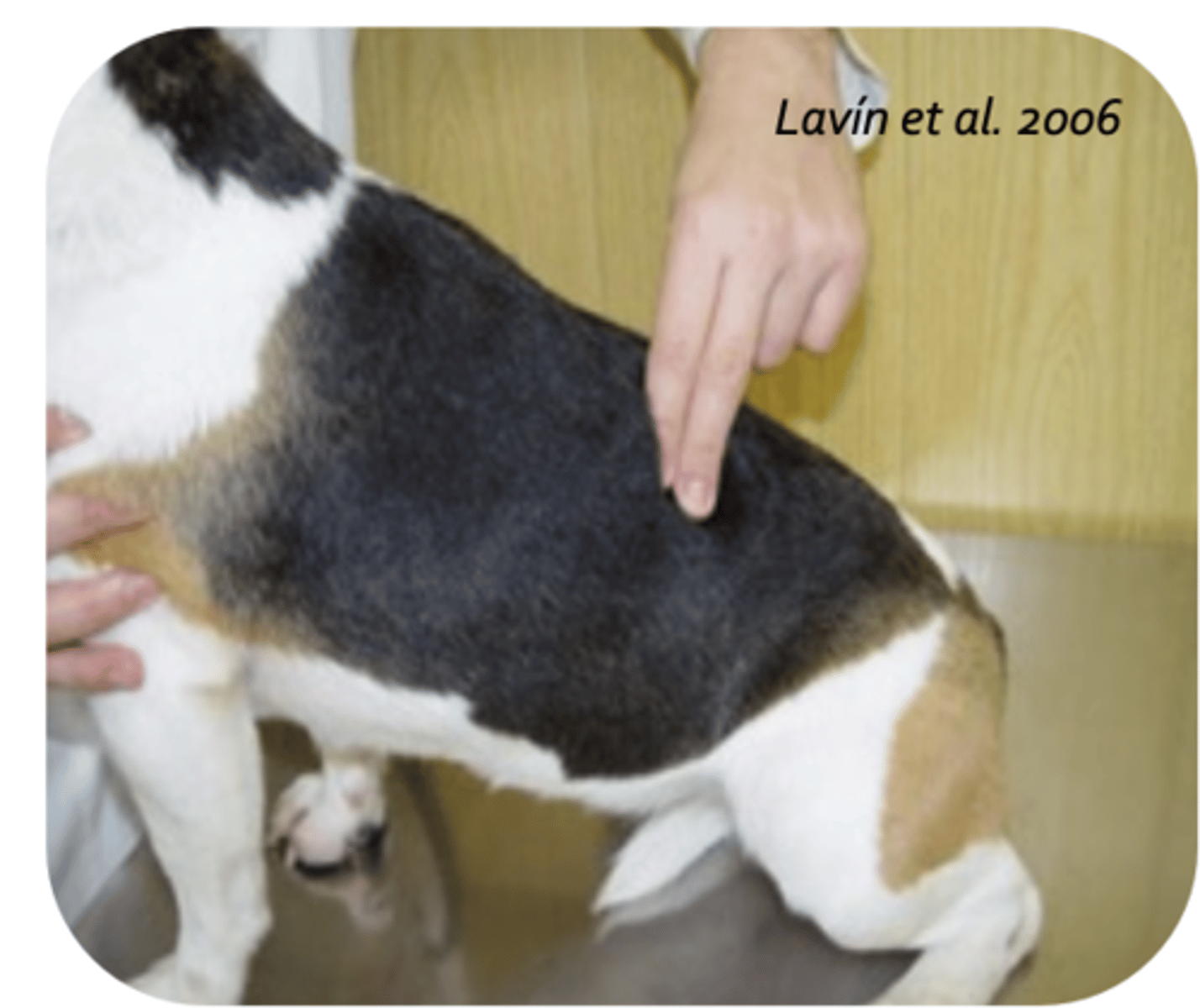
ischiatic tuberosity
what is being palpated?
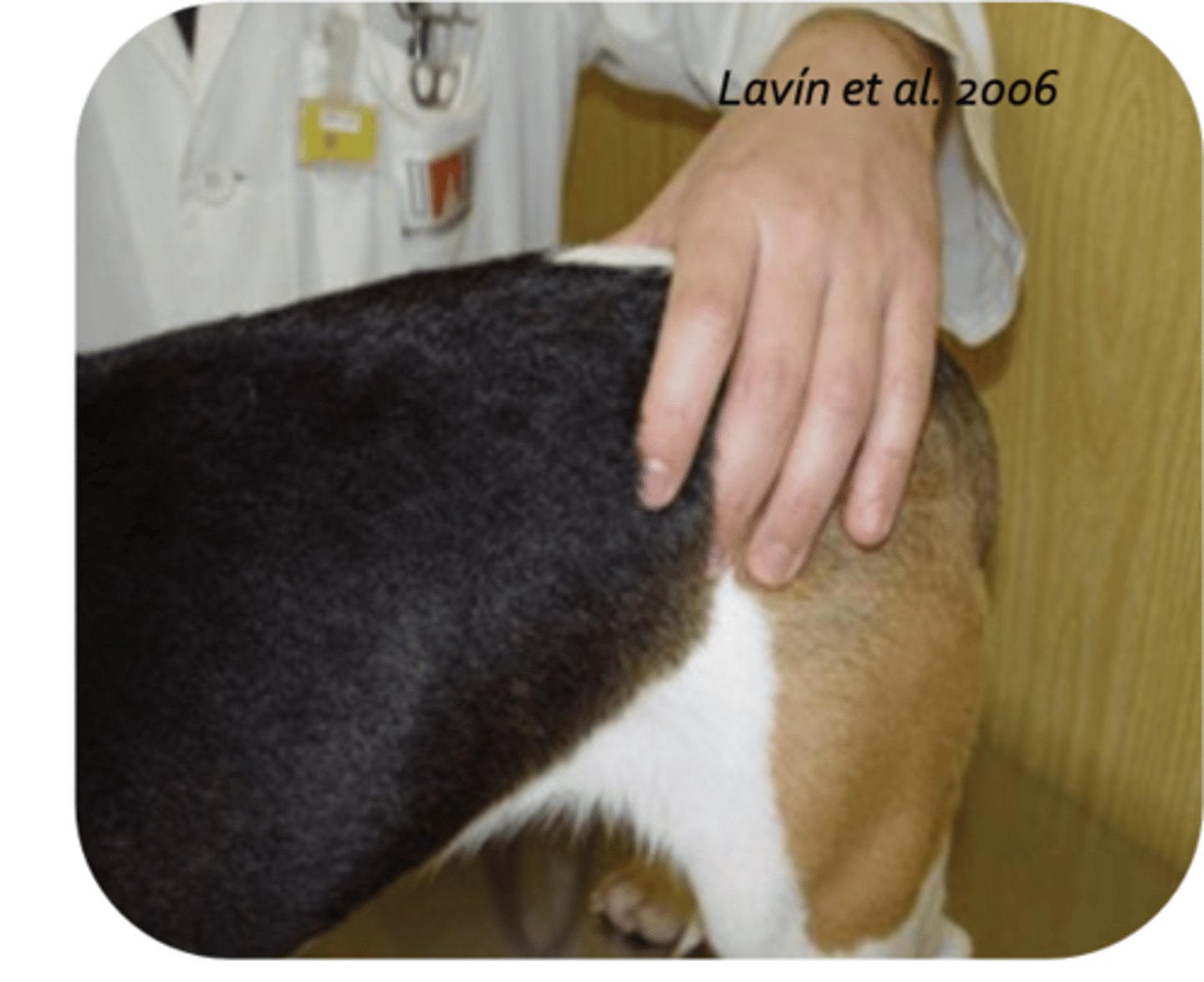
coxal tuberosity
what is being palpated?
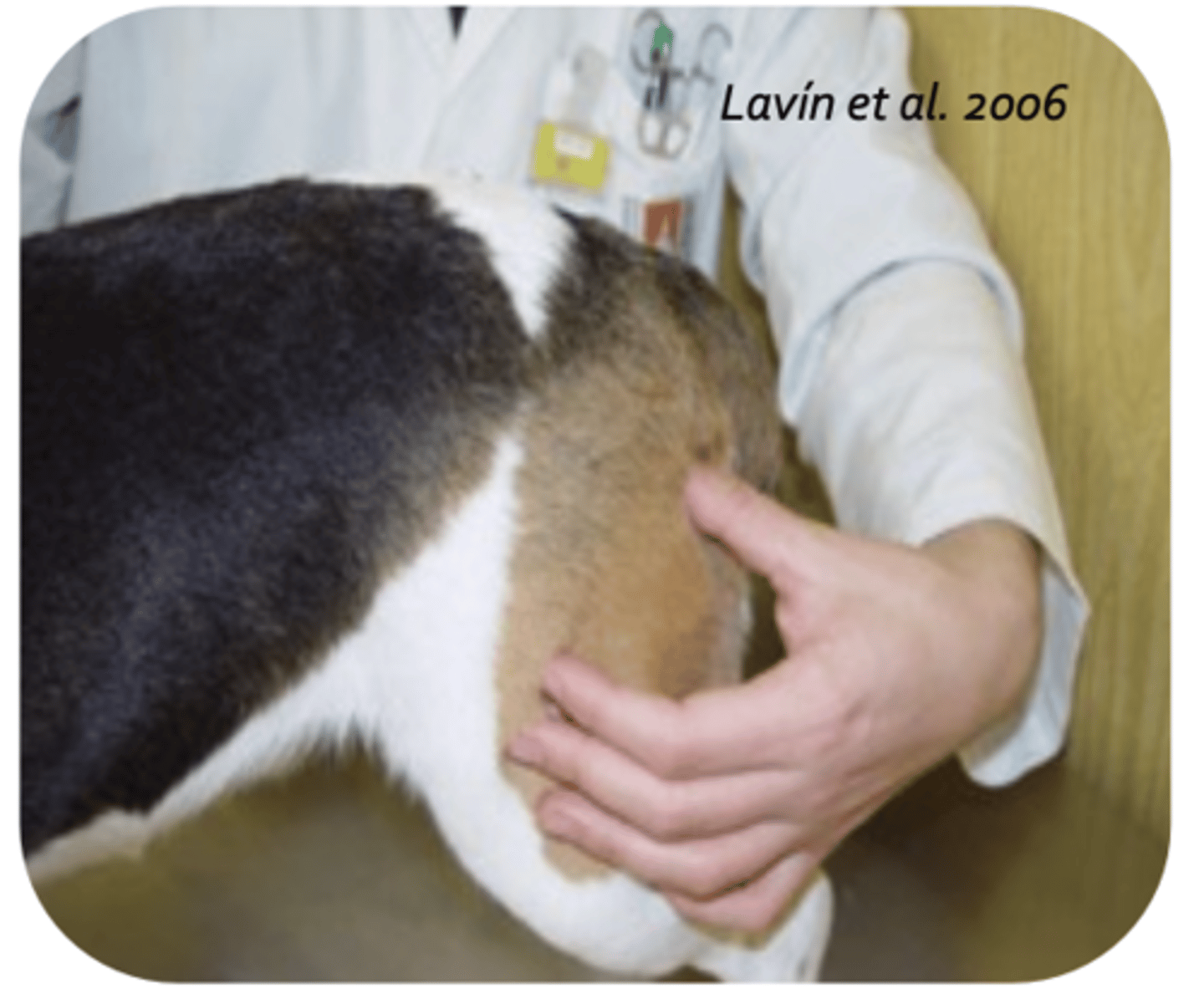
ribs
what is being palpated?
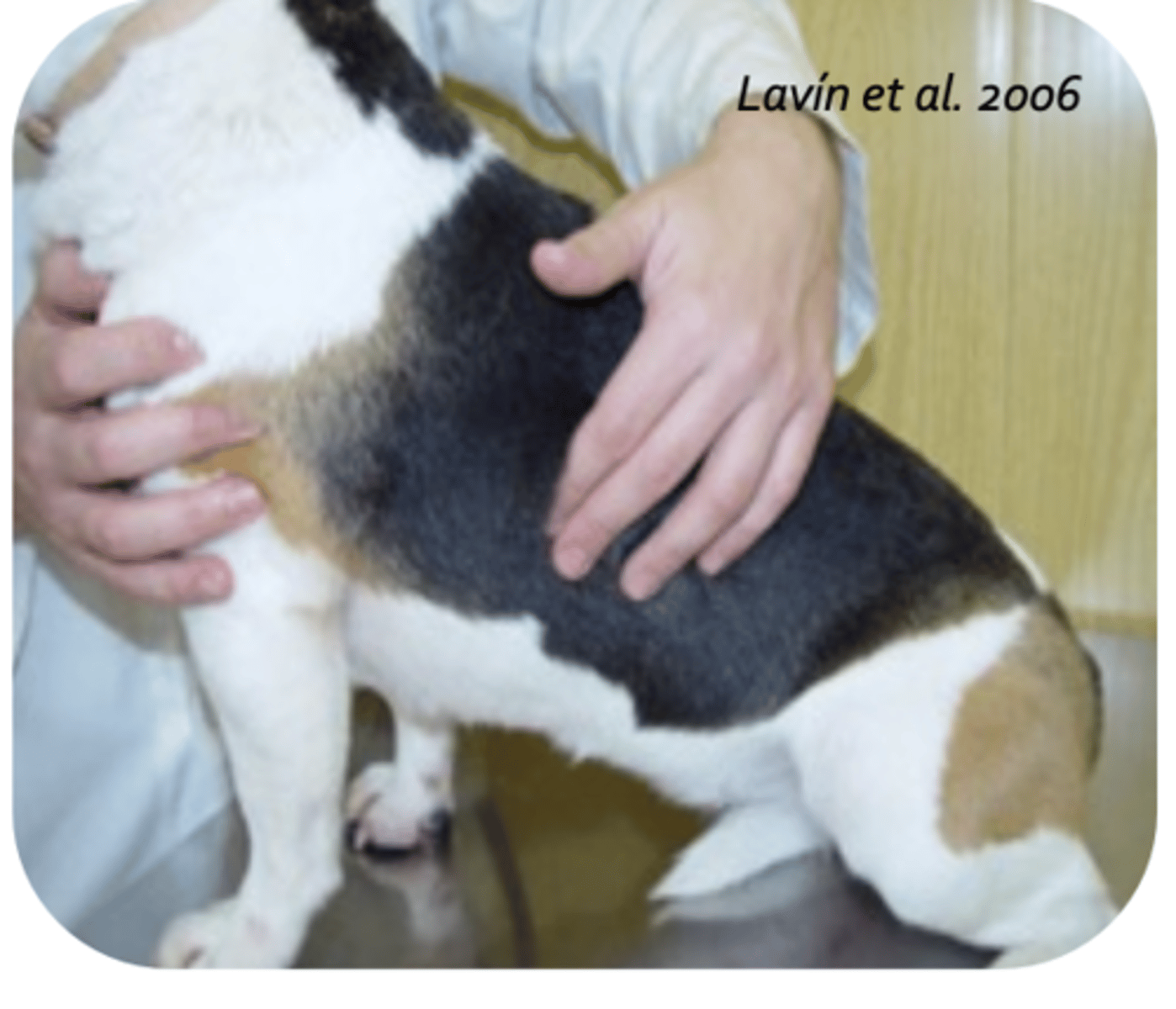
3
on a BCS scale from 1-5, which is ideal?
ribs not easily seen, but felt
describe the ideal BCS
acute
if the weightloss is quick, this is a ______ disease
chronic
if the weightloss is slow, this is a ______ disease
hydration status
the skin fold test is used to test the animal's ______
60-160 bpm
(lower for large breeds, higher for small breeds)
what is the normal dog heart rate?
130-230 bpm
what is the normal cat heart rate?
higher
do young animals have a higher or lower heartrate?
heart rate
the pulse should match the _____
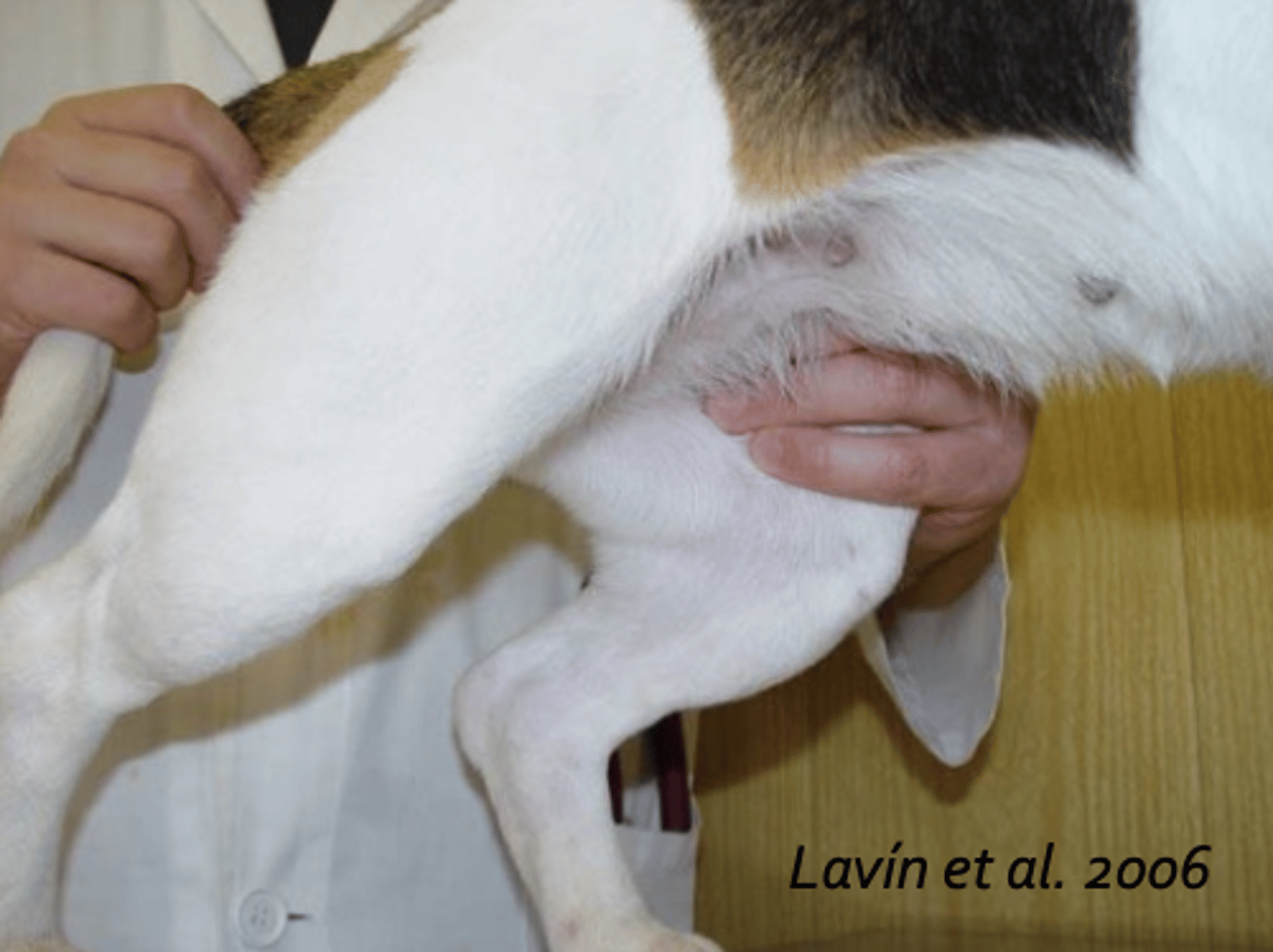
femoral artery
for dogs and cats, what vessel do we use to detect the pulse?
put 1-2 fingers (no thumb) on the femoral artery on the medial back leg
how do we find the pulse of a dog/cat?
pink, wet, brilliant, smooth
a healthy animal should have mucous membranes that look like.....
less than 2 seconds
the CRT (capillary refill time) should be how long?
4 or 5
on a 9 point scale, an ideal weight (BCS) would be_______
use sight and palpations
what do we do to give an accurate body condition score?
6 or 7
on a 9 point scale, an overweight animal would be_______
8 or 9
on a 9 point scale, an obese animal would be_______
1, 2 or 3
on a 9 point scale, an underweight animal would be_______
checking the pulse with the femoral artery
what is the vet doing?
no, they should be light pink
should the mucous membranes be dark?
costal
if the animal is doing abdominal respiration, this signals he is in pain
which is normal- abdominal or costal breathing?
10-40 bpm
what is the normal respiratory rate of a dog?
20-40 bpm
what is the normal respiratory rate of a cat?
snout, ear base, axila, groin
where can we take the external temperature of the animal?