SCMT 3443 Exam 3
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Shrinkflation
also known as package downsizing or weight-out, is the process of items shrinking in size or quantity while the prices remain the same.
Measure
Concrete or objective attribute—often a single item or data point.
Metric
A relative attribute—often a combination of two or more measures, a percentage, or a comparison over time.
KPI
Key Performance Indicator: A metric viewed as particularly important to evaluate business performance.
Difference between Measure, Metric, and KPI
metric is usually multiple measures, and a KPI is a metric that businesses use to analyze things
Formula for Total Cost
First Cost+Landed Cost
Fill Rate
the percentage of orders that you can ship from your available stock without any lost sales, backorders, or stockouts.
On-Time Delivery
the ratio of customer order lines shipped on or before the requested delivery date / customer promised date versus the total number of order lines.
Order Cycle Time
the time it takes for a company to complete the order fulfillment process
Complete Orders
an Order that has been provisioned and for which all other related work has been carried out
Inventory Turns
a measure of the number of times inventory is sold or used in a time period such as a year. (you want this to be high)
Inventory Obsolescense
stock a business doesn't believe it can use or sell due to a lack of demand
Inventory Days Supply
an efficiency ratio measuring the average amount of time in days that a company or warehouse holds inventory before selling or shipping it.
Inventory Carrying Cost
the total of all expenses related to storing unsold goods.
Total Landed Cost
the total price of a product or shipment once it has arrived at a buyer's doorstep
Units Shipped per Employee
how many units each employee ships during a set period of time
Damage Frequency
how often products get damaged in the shipping process
Picking/Shipping Accuracy
total number of correct picks divided by total number of picks
Document/Invoicing Accuracy
accurate invoices/total number of invoices
OTIF
“On Time in Full”-combination of fill rate and on time delivery; commonly used metric at Walmart
Fixed Assets
things such as trucks, warehouses, and stores
What is owning your inventory considered?
an asset
S of SMART Acronym
Specific-Clearly defined and targeted to avoid misinterpretation
M of SMART Acronym
Measurable-Can be quantified for analysis, comparison, and tracking
A of SMART Acronym
Attainable-Reasonably achievable based on the situation
R of SMART Acronym
Relevant-Is directly related to desired performance/results
T of SMART Acronym
Timely-Provides prompt feedback, and can be done with the time frame given
Additional Qualities of a Good Metric
Concise, Minimize Effort, Avoid Conflict, Consistent
Profit-Leverage Effect
translates the cost savings in logistics to the sales equivalent required to have the same profit impact.
SCOR
Supply Chain Operations Reference Model-a "process reference" model that is used globally to measure supply chain activities across industries. It measures performance metrics in five categories: reliability, responsiveness, agility, cost, and asset management efficiency.
Showrooming
going to a bricks-and-mortar store like Best Buy to physically check out your purchase options and then using an online app or going home to use your computer so that you can find your selected item for a lower price online.
Webrooming
the opposite of showrooming. You go online to do your product research and comparison shopping. Then you head to the store to make your final decision and buy the product.
Distribution Channel
a set of interdependent organizations used by a selling organization to provide its products or services to the marketplace
Scenario Analysis
a systematic process for analyzing possible decisions by considering the outcomes under different sets of assumptions
Pilot Project
a small-scale preliminary study conducted to evaluate feasibility, duration, cost, adverse events, and improve upon the study design prior to performance of a full-scale research project.
Fulfillment Network
another way to say distribution channel, typically used in omnichannel and e-commerce networks
Digital Marketplace
a platform that facilitates electronic trade between buyers and sellers.(essentially just another word for e-commerce)
Difference between multichannel and omnichannel
In multichannel, a company has multiple means of getting products to customers, but the product will come from different sources. In omnichannel, a company has multiple ways to get a customer a product all from the same source. (Example. a store having separate apps for grocery and pharmacy would be multichannel and everything being on the same app would be omnichannel.)
The Strategic Profit Model(also known as the DuPont Model)
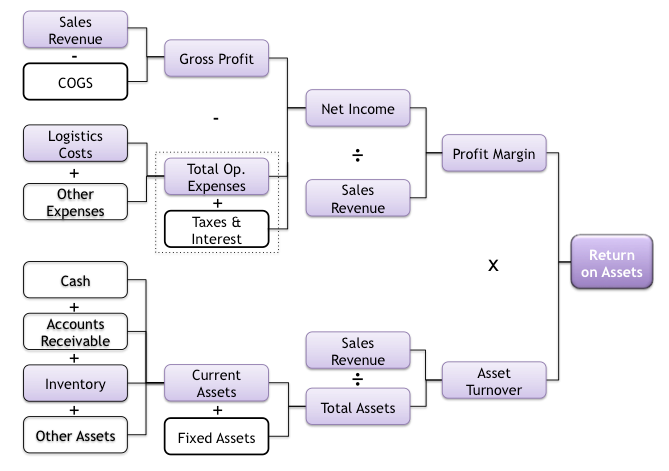
Multi-Channel Distribution
involves a business using more than one type of distribution channel. Ex. a clothing brand that sells its products through its physical stores, an online website, and a mobile shopping app.
Omnichannel Distribution
an approach to distribution that enables customers to buy and receive products from multiple sales channels that are seamlessly integrated. Regardless of the channel they’re on, your team or your products are only a click, an email, a direct message, or a phone call away. Ex. Amazon
OPD
Online Pickup or Delivery: inventory usually ordered on a mobile app that will either be picked up or delivered
DSV
Drop Ship Vendor-asking a vendor to hold inventory at a warehouse and fulfill orders for your company
Marketplace
giving a vendor/supplier a platform to sell; usually the company running the website earns only commission on these sales
Production Economies of Scale
when companies produce large amounts of products to store until the customer wants it
Form Postponement
a strategy that involves delaying giving a product its final form until the exact customer order comes in
Transportation Economies of Scale
You can ship in full truckloads. Inbound shipments are broken down and stored at the warehouse; outbound shipments are consolidated and shipped at the warehouse.
Warehouse
Facilities where raw materials, semi-finished goods or finished goods are stored for a short term or long term until they are ready to be used
Raw Materials
The individual materials used to create products before they are actually created
Picking List
Created by a WMS, a list that documents all cases or items that need to be picked from the warehouse shelves for specific orders
Value-Added Services a Warehouse can Provide
Mass Customization, Final Assembly, Product Repair
Distribution Centers
Combine inventory from multiple locations to mix and match to fulfill customer orders
Cross-Docking Facility
like DCs, act as mixing facilities. However, in a cross-dock operation, the goal is to keep the products moving—from inbound dock to outbound dock. In many instances, product is only in the cross-dock facility for two or three hours. Thus, cross-docks are often called "flow-through" warehouses.
Duties
a tariff or tax imposed on goods when transported across international borders.
AMR
Autonomous Mobile Robots: the robots found in warehouses that assist with moving freight around the building
Difference between a Public and Private Warehouse
private warehouses are typically owned by the company that operates out of them, and public warehouses typically have a landlord from a third party
What happens when you increase the amount of warehouses that you own?
most of your operating costs will increase
Tasks associated with the Arrival function of a warehouse
Receiving and Unloading, Storage Placement(putaway)
Tasks associated with the Shipment function of a warehouse
Order Selection(picking), Final Processing/Packaging, Checking and Verifying Orders, Consolidating and Staging, Loading and Shipping
Tasks associated with the Always/Day-to-day function of a warehouse
Administrative, Facility Maintenance, Equipment Maintenance
What does Receiving do in a WMS?
Confirms receipt, creates putaway label, directs stock to active reserve location
What does Order Picking do in a WMS?
Prioritizes orders, prints pick tickets for best sequence, prints labels for packing operations
What does Verification do in a WMS?
Uses bar code scanning, prints labels for shipping contents
What does Shipping do in a WMS?
Suggests shipping routes, creates shipping documents, calculates shipping costs
Reasons why a company puts a warehouse in a certain location
Transportation Access(Truck, Rail, Water, etc.), Availability of Workforce, Freeway Access, Land Cost and Taxes
5S Method
Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain
5S: Sort
Clearly separate necessary items from unnecessary; abandon the unnecessary
5S: Set in Order
Neatly arrange and identify things for ease of use
5S: Shine
Always maintain tidiness and cleanliness. Regularly scheduled clean-ups
5S: Standardize
Constantly maintain the 3Ss mentioned above
5S: Sustain
Create vehicles to enforce the above rules
Six Sigma
a set of management techniques intended to improve business processes by greatly reducing the probability that an error or defect will occur.
DMAIC
Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control: a methodology used within Six Sigma to improve a company’s operations
Perfect Order
Orders delivered without changes, damage, or invoice errors
Carbon Footprint
The total sets of greenhouse gas emissions caused by an organization, event, product, or person
Ecological Footprint
The amount of the environment necessary to produce the goods and services necessary to support a particular lifestyle
Greenhouse Gases
the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth.
Ways companies are trying to lower their emissions
moving towards electric vehicles, trying to avoid moving trucks with empty trailers, and not letting trucks sit with the engine idling while loading and unloading
Which is the most sustainable form of transportation
Ships
Which is the least sustainable form of transportation
Air(also most expensive)
Empty Backhaul
Moving a trailer back to point A from point B with no freight on board
Some ways to reduce transportations’ environmental impact
Better equipment planning, better training and habits, new technology
Cradle to Grave
considering the environmental impact of the product from the earliest supplier through to disposal.
Supply Chain Strategy of the Maturity stage of the product lifecycle
Minimize distribution costs and assure on-time delivery to a larger market.
Supply Chain Strategy of the Decline stage of the product lifecycle
Minimize distribution costs and plan for reverse logistics.
Sustainability Strategy of the Maturity stage of the product lifecycle
Minimize logistics and manufacturing footprint by reconsidering packaging, transportation modes, manufacturing and DC locations, and inventory levels
Sustainability Strategy of the Decline stage of the product lifecycle
Execute reverse logistics, re-use, and recycling. Minimize inventory to avoid obsolescence and disposal.
Scope 1
Emissions your company directly produces.
Scope 2
Emissions from purchased energy such as electricity and heating and cooling.
Scope 3
Emissions from everything else in the organization and its supply chain. This includes business travel and commuting, waste disposal, environmental impact of products sold, and purchased transportation and logistics services
Pros of E-Commerce Sustainability
Less driving to stores, reduces the waste of printed catalogues, reduces the amount of retail spaces and associated energy use, up-to-date inventory and tracking so you know item availability without going to a store, saving gas
Cons of E-Commerce Sustainability
Numerous deliveries to a remote location may be worse than one trip to the city to shop, more returns because we buy products without trying them on, damage in handling during shipping creating more waste, If few DCs, distance to deliveries may be very long, one package at a time: more pollution
Which metrics fall under the Customer Service category
Fill Rate
On-time delivery
Order cycle time
Complete orders
Customer complaints
Which metrics fall under the Asset Management category
inventory turns
Inventory obsolescence
Return on assets
Inventory days' supply
Economic value added
Which metrics fall under the Cost category
Inventory carrying cost
Total landed cost
Outbound freight
Warehousing labor costs
Administrative
Which metrics fall under the Productivity category
Units shipped per employee
Equipment downtime
Order productivity
Warehouse labor productivity
Transportation labor productivity
Which metrics fall under the Quality category
Damage frequency
Order entry accuracy
Picking/shipping accuracy
Document/invoicing accuracy
Number of customer returns
Which metrics are found on the Income Statement(Revenue)
Order fill rate
Order cycle time
On-time delivery
Which metrics are found on the Income Statement(Cost of Goods Sold)
Inbound transportation
Inventory obsolescence
Inventory damage
SMI/Consignment costs of suppliers
Which metrics are found on the Income Statement(Other Operating Costs)
Warehousing cost
Transportation cost
Logistics administration
Technology cost