A and P test 1
1/242
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
243 Terms
What is the function and purpose of the endocrine system?
Maintain homeostasis by sending chemicals and hormones through the body (slower/longer term)
What do the hormones do (endocrine system)
Controls growth,
development,
metabolism/energy
reproduction
stress response
long term body regulation
With which system does the endocrine system work closely?
The nervous system.
(nervous system=fast/short term)
What transport system does the endocrine system use?
The cardiovascular (blood) system.
What are target cells?
What the hormone can speak to
Cells that have receptors for specific hormones.
(if the cell doesn't have the receptor, the hormone will NOT impact (respond to) it)
Do hormones respond to all cells?
NO
If it doesn't have a receptor, it won't impact it
What are the types of hormones based on solubility?
Water-soluble and lipid-soluble hormones.
Water vs Lipid Soluble Hormones
Lipid-soluble can move in and out of the cell at will, while water CANNOT (the water soluable needs a transport molecule or 2nd messenger/receptor)
What is up regulation?
Absence of hormones in the body will trigger the body to make more receptors for more target cells (more sensitive)
What is down regulation?
The decrease in the number of receptors for a hormone on target cells. (less sensitive)
What role do water-soluble hormones play as 1st messengers?
They bind to receptors on the cell surface to initiate a response. (bc they cant just move in and out)
What are cAMP and calcium in the context of hormone signaling?
They act as 2nd messengers in the signaling pathway.
How do lipid-soluble hormones function?
They diffuse through the cell membrane (dont need second messenger)
What is negative feedback in the endocrine system?
A process that reduces the output of a system to maintain homeostasis.(most common)
What is positive feedback in the endocrine system?
A process that increases the output of a system. (usu short term)
What controls hormone secretion?
hormonal signals, neural signals, changes in blood chemistry.
(change in blood, brain, hormones...)
Where is the pituitary gland located?
Below (inferior) the hypothalamus at the base of the brain.
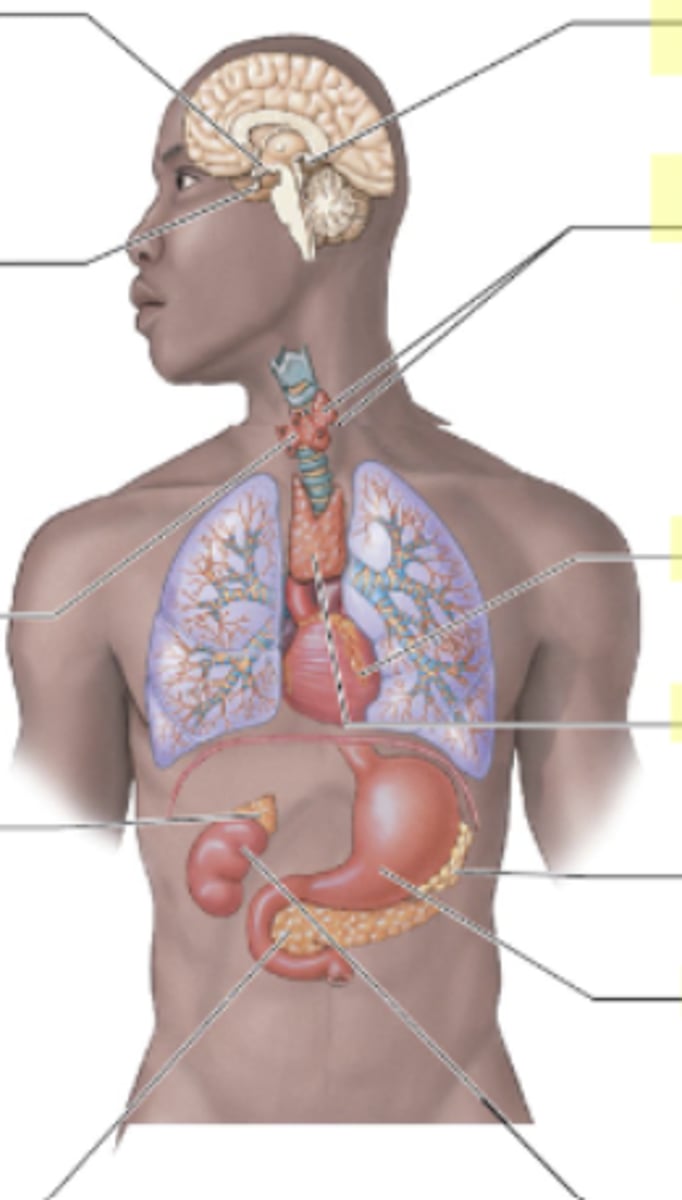
QUESTION ON TEST- "If a patient has this and this issue, which endocrine organ might that impact?"
Pituitary gland
What is the difference between anterior and posterior pituitary?
The anterior pituitary produces hormones, while the posterior pituitary stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus.
Anterior Pituitary
Hormones are made and released here
Released: GH, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH (MSH)
Posterior Pituitary
Hormones are stored and released here
Released: ADH and Oxytocin
What are the targets of the hormones released by the pituitary gland?
TSH-thyroid
ACTH-adrenal cortex
FSH/LH-gonads (overies/testes)
PRL-mammary glands (milk production)
GH-most tissues+liver, bone, muscle
Where is the hypothalamus located?
Above the pituitary gland in the brain.
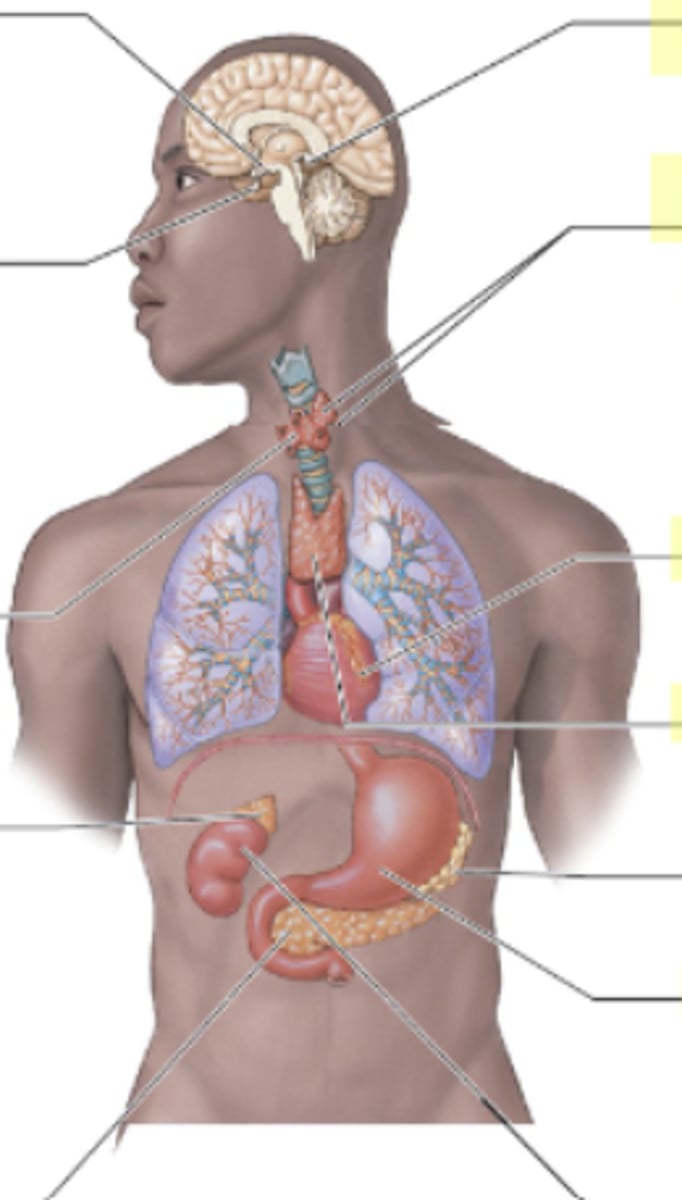
What does the hypothalamus control?
Everything (main control center) Speaks to pituitary which sends messages to rest of body
What are the two types of regulatory hormones?
1. Releasing Hormones (RH)
2. Inhibiting Hormones (IH)
What is the style of hypothalamic regulation?
Hypothalamus-> RH/IH-> pituitary -> target glands
Where is the thyroid located in relation to other structures?
The thyroid is located in the front of the neck,
Butterfly shaped
wraps around the trachea.
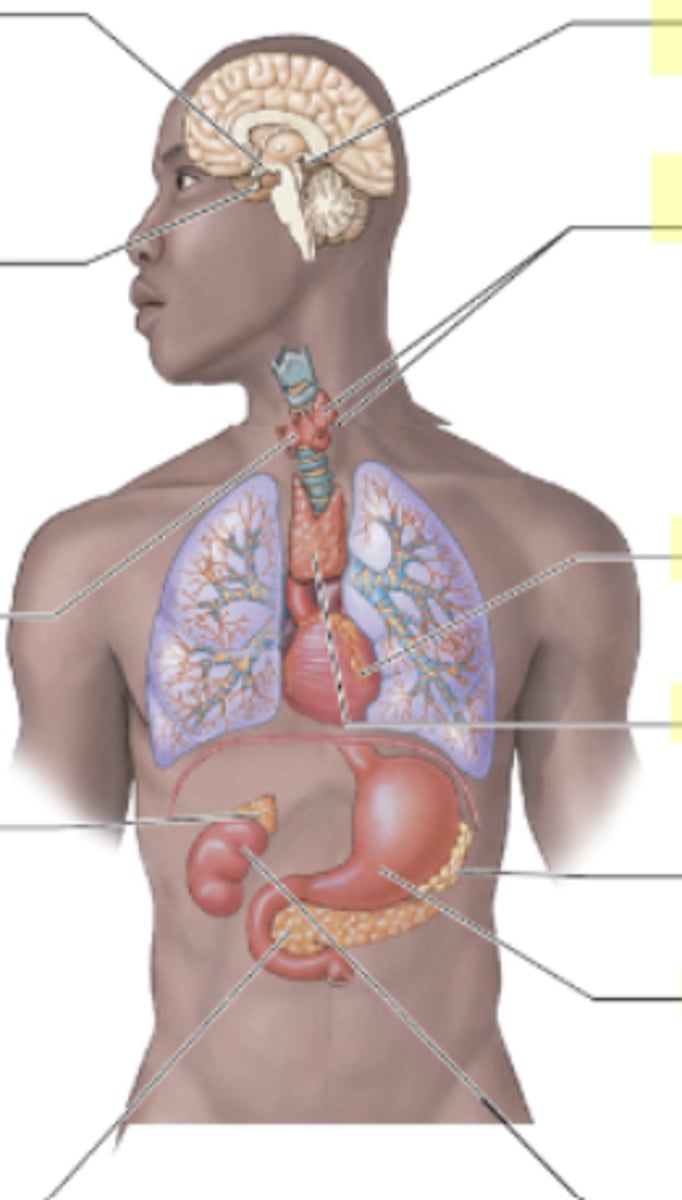
What does the thyroid gland secrete?
T3, T4, calcitonin
What nutrient is vital for the synthesis of thyroid hormones?
Iodine is vital for the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Where are thyroid hormones synthesized and stored?
Thyroid hormones are synthesized in the follicular cells and stored in the colloid. (till needed, then its passed through capillary)
What mediates thyroid activity?
Thyroid activity is mediated by TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone).
What do thyroid hormones do?
T3 and T4 help to create homeostasis in the body (Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism and influence growth and development with calcitonin)
Where is the parathyroid gland located in relation to other structures?
The parathyroid glands are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
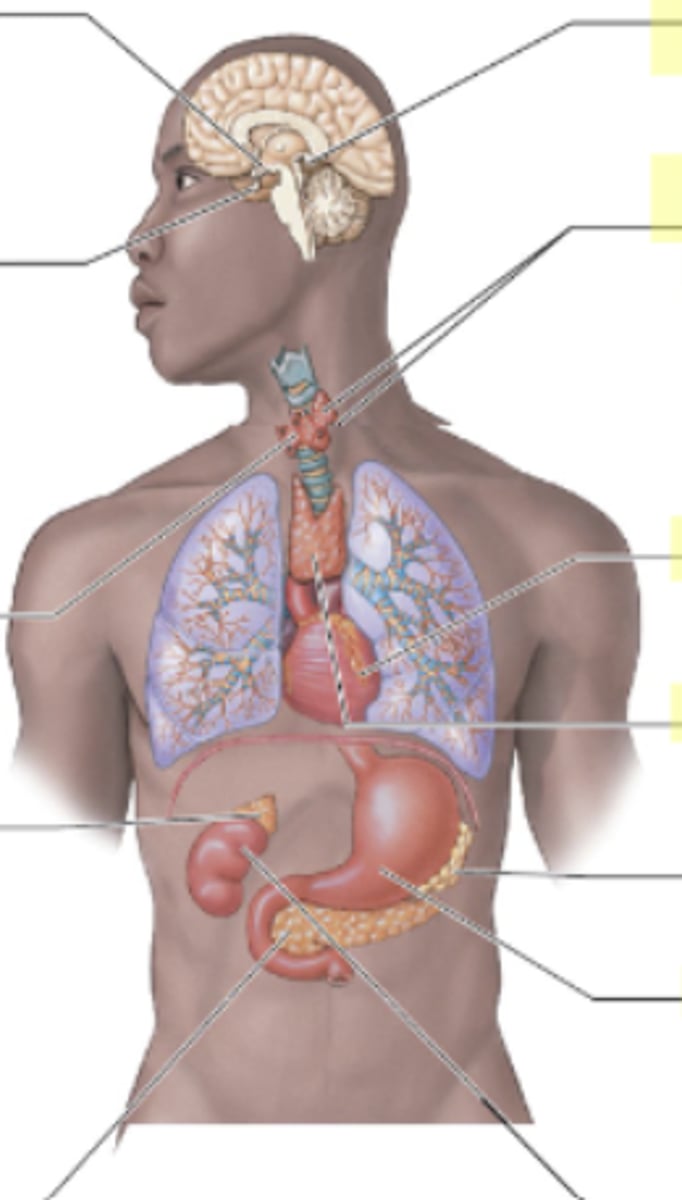
What hormone is secreted by the parathyroid and what is its role?
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulates calcium levels in the blood.
Where is the adrenal gland located in relation to other structures?
The adrenal glands are located on top of each kidney.
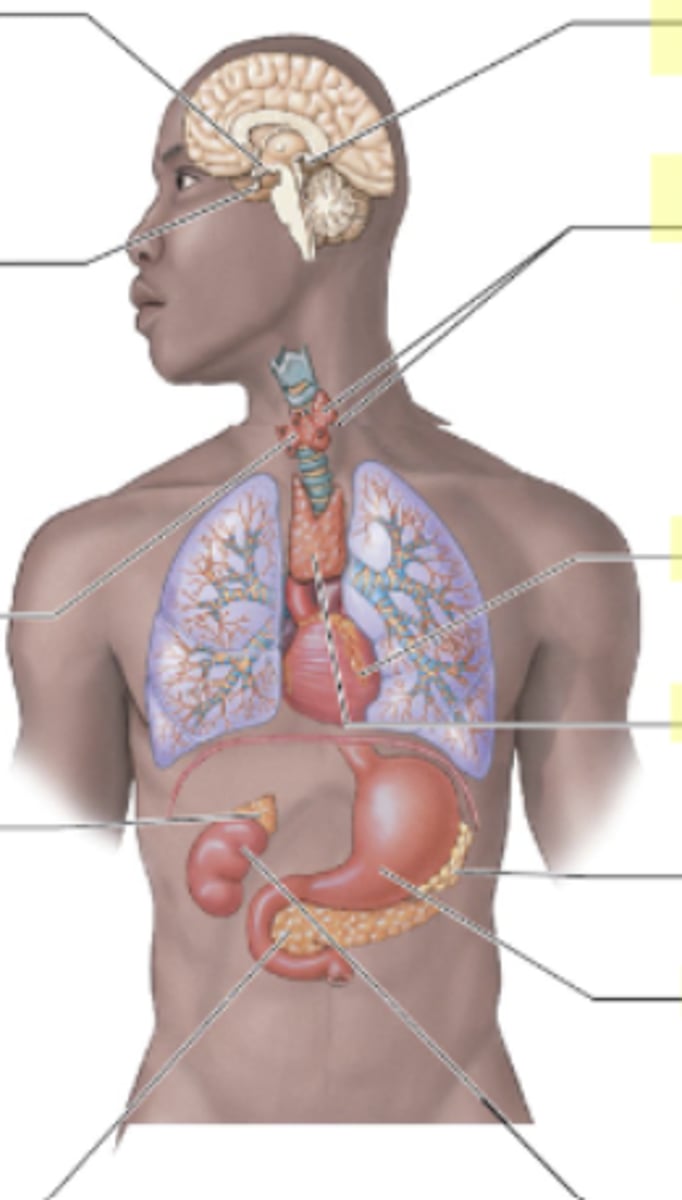
What are the two parts of the adrenal gland and their roles?
The adrenal cortex (outer) secretes steroid hormones, and the adrenal medulla (inside) secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine
epinephrine and norepinephrine
fight or flight response
Where is the pineal gland located in relation to other structures?
The pineal gland is located in the brain, near the center.
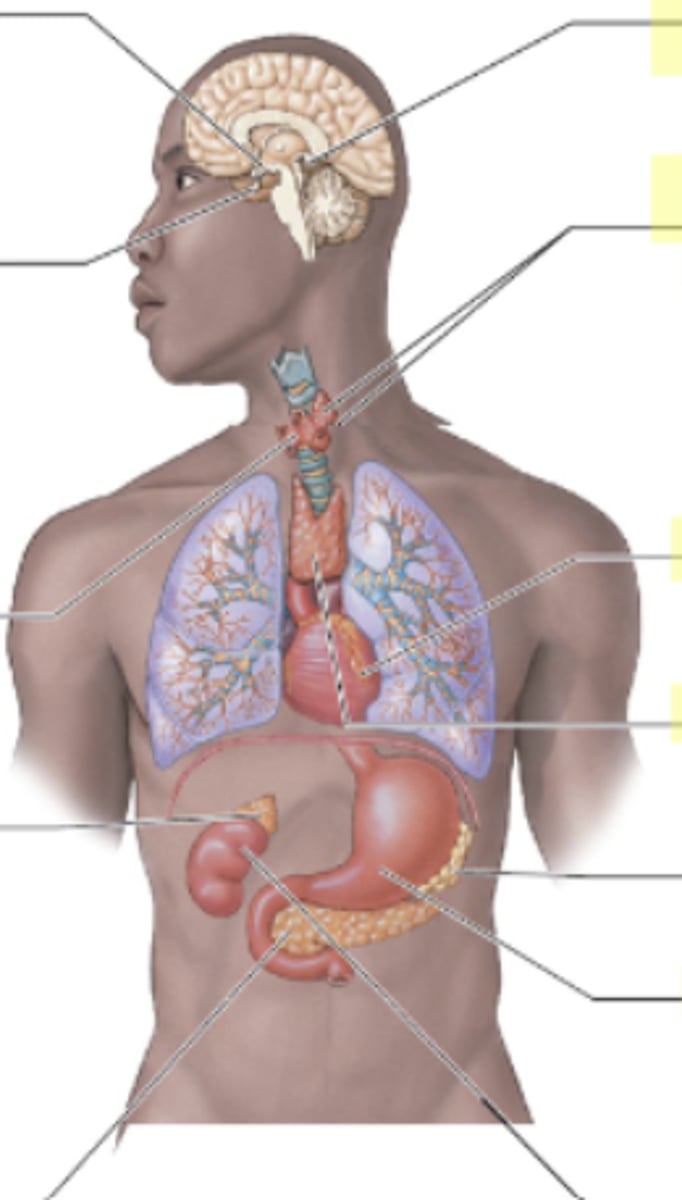
What hormone does the pineal gland secrete and what is its role?
The pineal gland secretes melatonin, which impacts sleep and healing, and menstrual cycles
Where is the pancreas located in relation to other structures?
The pancreas is located behind the stomach, slightly to left
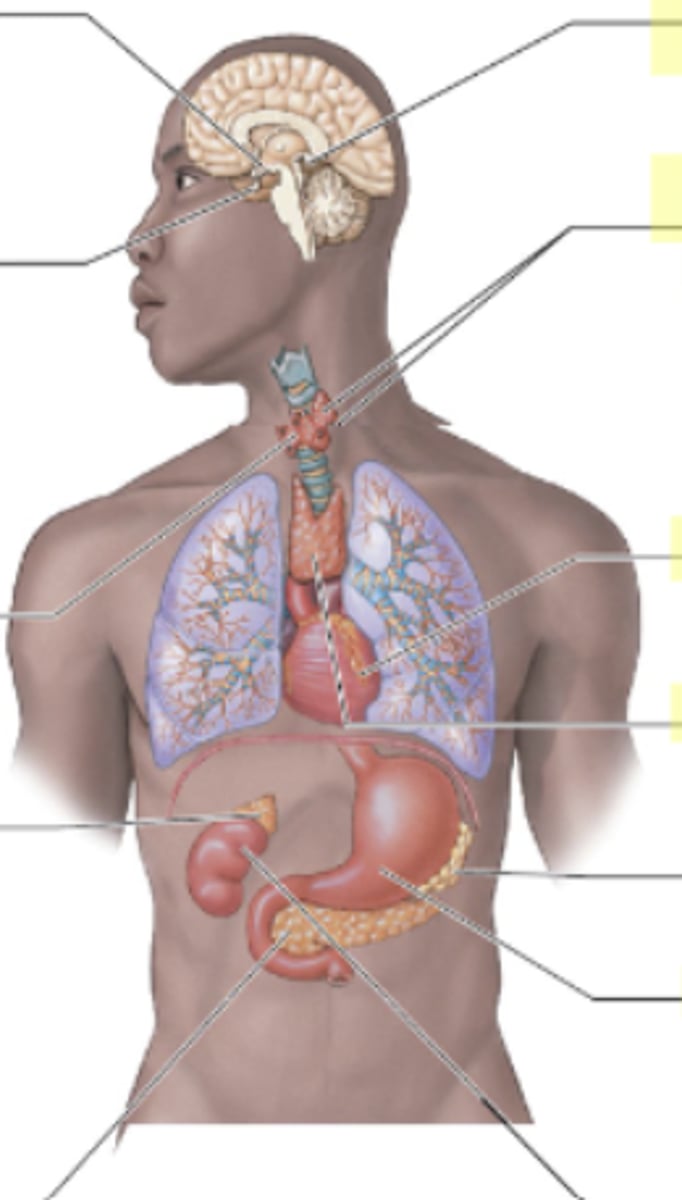
What are the two types of cells in the pancreas and what hormones do they secrete?
Alpha cells secrete glucagon (increase bg), and beta cells secrete insulin (decrease bg).
How do the cells in the pancreas raise or lower bg?
What are the definitions and types of diabetes?
Diabetes is characterized by high blood sugar; types include Type 1 and Type 2 and gestational
Type 1 diabetes and treatment
Autoimmune disorder (destruction of beta cells)
Requires insulin for treatment
Type 2 diabetes and treatment
diet, exercise...
Gestational diabetes and treatment
Pregnant patients
Diet and exercise
There is fetal risk
What are the risks of hyperglycemia?
Risks include damage to organs, nerves, and blood vessels. High blood glucose
What hormones are produced by the gonads?
The male gonads produce testosterone, and the female gonads produce estrogen and progesterone.
What is the role of hormones secreted by the intestines?
Intestinal hormones regulate digestion and nutrient absorption.
Where is the placenta located and what hormones does it produce?
The placenta is located in the uterus during pregnancy and produces hormones like hCG, estrogen, and progesterone. It supports fetus, softens cerviz, relaxes pelvic
Intestines Hormones roles
(secretin and cck) regulate digestion and w pancreas and gallbladder
What is the role of vitamin D in the skin?
Vitamin D is synthesized in the skin, processed by liver/kidneys, and helps raise calcium
What does adipose tissue release and what does it do?
Relases Leptin- inhibits hunger.
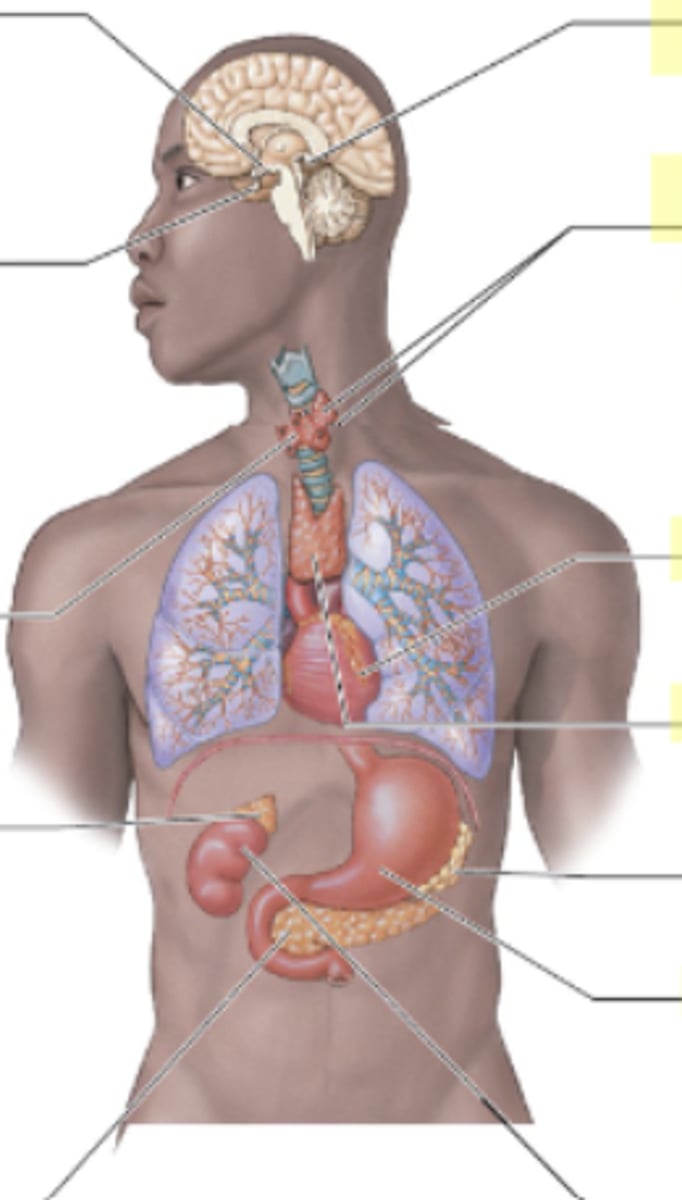
What are the two endocrine roles of the kidneys?
The kidneys produce erythropoietin and renin.
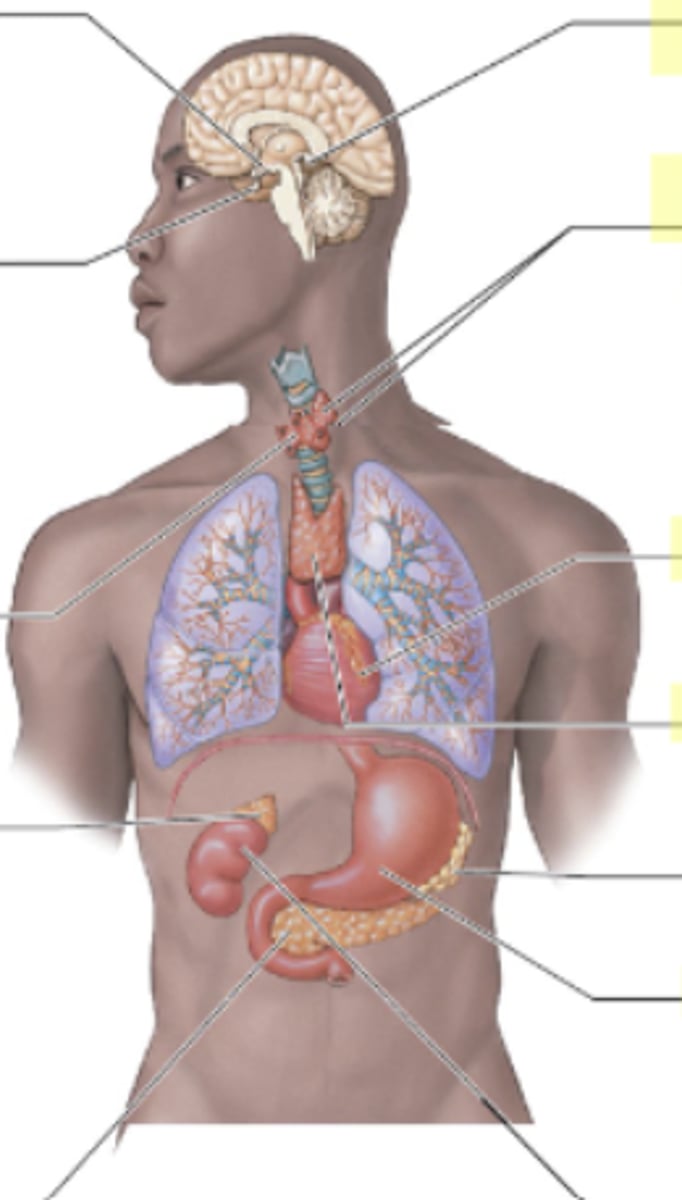
What is the endocrine role of the heart?
The heart secretes atrial natriuretic peptides (ANP and BNP) to regulate (lower) blood pressure.
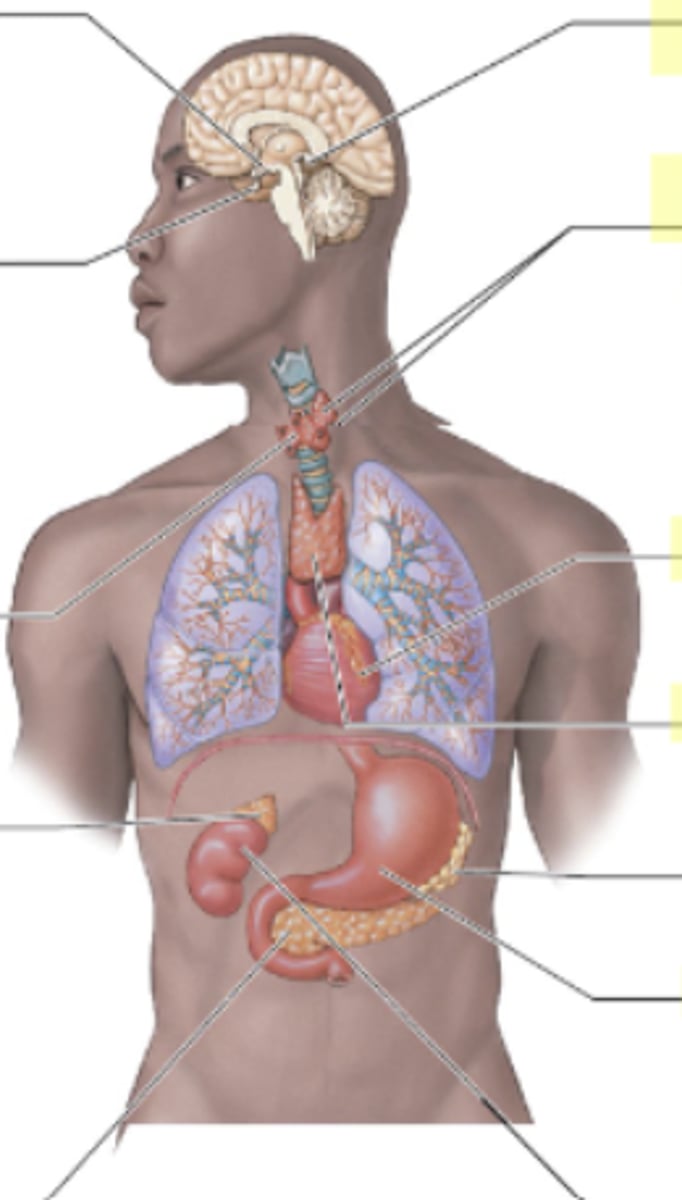
What is the role of the thymus?
Mature of T-cells (WBC) for the immune system.
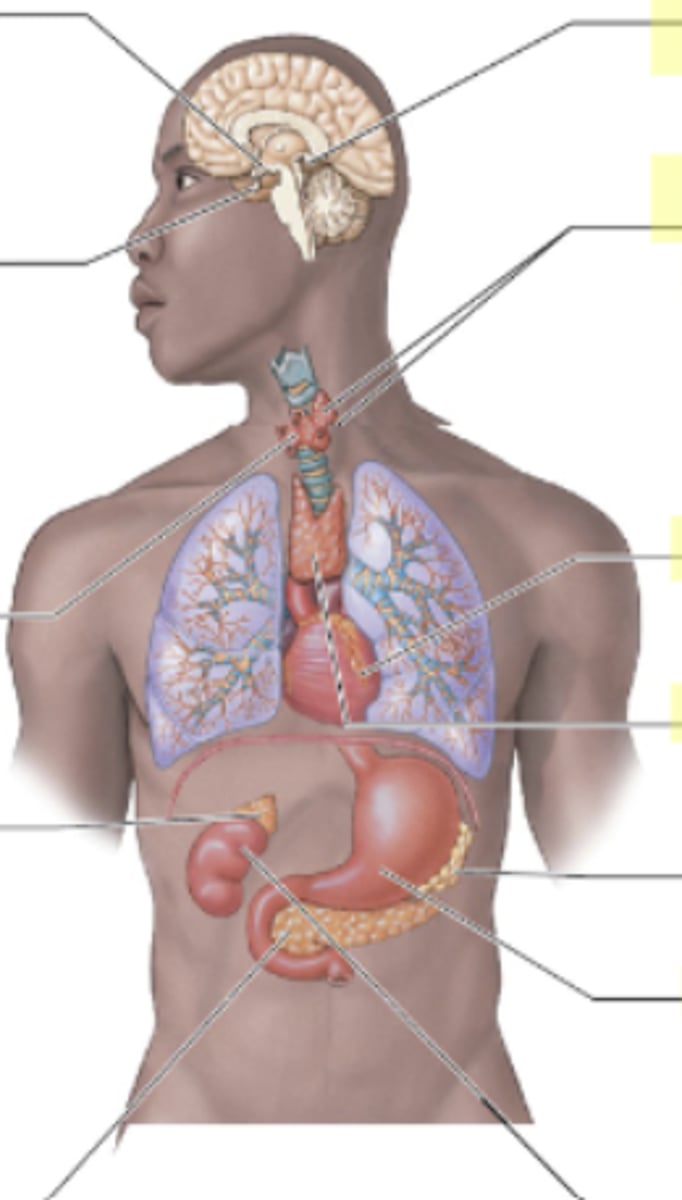
How do the hormones interact?
Antagonistic: result depending on the other hormone
Synergistic: additive effect
Permissive: One hormone is needed for the other to work fully
Integrative: they produce diff results
What do growth hormones impact?
Growth hormones impact growth, metabolism, and body composition.
What are the phases of General Adaptation Syndrome?
The phases are
1. Alarm-immediate response (epinephrine),
2. Resistance-longer than a few hrs (glucocorticoids),
3. Exhaustion-failure to resolve
What hormonal changes occur with aging?
Normal: menopause, changes in GH, thyroids (energy and focus)
Abnormal: disease level problems
LOCATION:
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
Thyroid Gland
Adrenal Gland
Pancreas
Pineal Gland
Parathyroid Glands
Heart
Thymus
Adipose Tissue
Digestive Tract
Kidneys
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
Thyroid Gland
Adrenal Gland
Pancreas
Pineal Gland
Parathyroid Glands
Heart
Thymus
Adipose Tissue
Digestive Tract
Kidneys
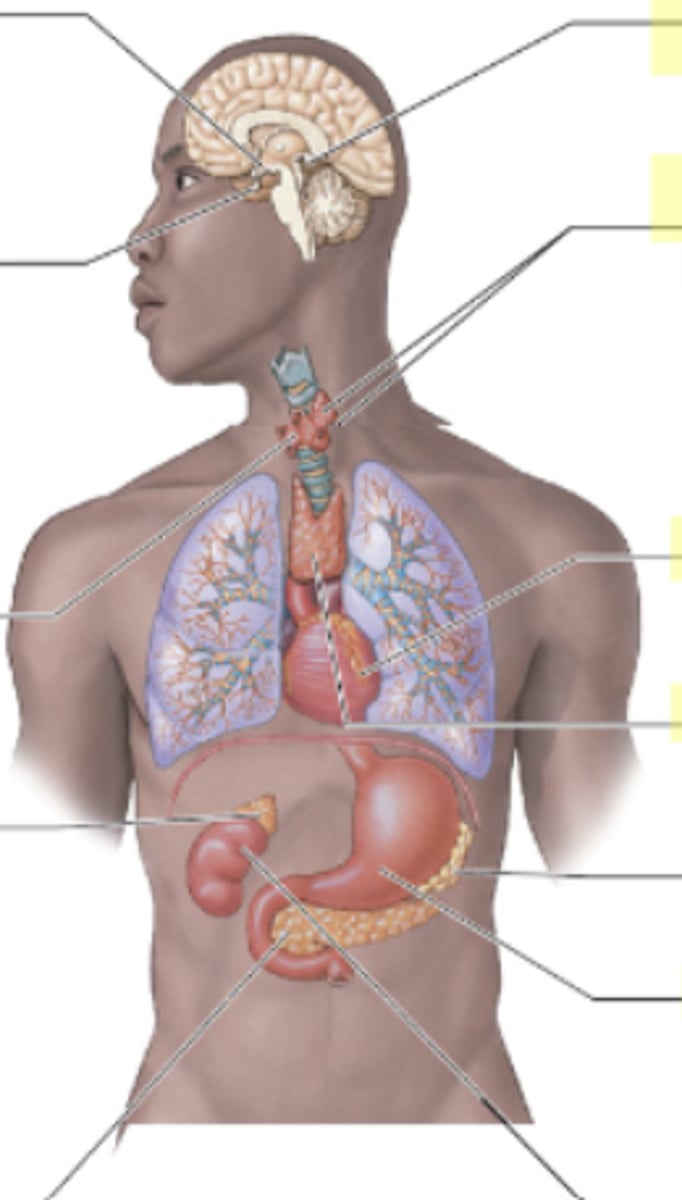
Cardiovascular components
blood (connective tissue), heart (pump), blood vessels (pipes)
What are the functions of blood?
1. Transport -gases/nutrients/wastes/hormones all over the body,
2. Regulation- PH/temp/fluid
3. Protection -clotting/immune
What is the normal blood volume in adults?
The normal blood volume is approximately 5 liters.
1 LITER =
1000 mL
What is plasma and its role?
Plasma is the liquid component of blood, its more than half of its volume, and it transports nutrients, hormones, and waste.
Contents of blood
RBC, WBC, platelets, plasma
Hematocytoblasts pathway in bone marrow
Hematocytoblasts -> myloid stem cells -> RBC, most WBC
Lymphoid stem cells become lymphocytes
What are blasts and bands in blood?
immature cells
Erythrocytes: requirements, role, shape
RBC- has Hgb
Carries oxygen throughout body
Requirments: iron, amino acids, B12, folate, EPO
Bioncave no nucleus - lives about 120 days
What is the role of hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin carries oxygen in red blood cells.
What causes anemia?
Cause: Low RBCs, low Hgb, or abnormal Hgb
Common causes: blood loss, Hb deficiency, B12/folate deficiency, genetic disorders
Symptoms: fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pale skin Significance: Less O2 to tissue → decreased cellular respiration → decreased ATP production
Where are red blood cells formed? DONT UNDERSTAND NEED CLARIFICATION)
Red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow from hematocytoblasts.
How are WBCs produced?
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs)
GM-CSF stimulates Granulocyte and Monocyte production
What are the types of white blood cells? (Leukocytes)
The five types are neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes.
What is the role of neutrophils?
1st responders (most of WBC-short lifespan)
Neutrophils respond to acute infections through phagocytosis and degranulation.
Dead neutrophils=pus
What is the role of eosinophils?
Pest control
Eosinophils are involved in allergic reactions and asthma.
Release enzymes at injury site to help resolve inflammation
What do basophils do?
Alarm system
Basophils release histamine (dilates blood vessels) and heparin (prevents blood clotting) during allergic responses.
What is the role of monocytes?
Presentation
Largest
Monocytes become macrophages and dendritic cells to present antigens.
Release Cytokines (immune response)
What are the roles of lymphocytes?
Special ops team
Lymphocytes are involved in adaptive immunity.
3 types: B cells, T cells, NK cells
What is leukopenia? Leukocytosis? Leukemia?
Low WBC count
High WBC count
Cancer of WBCs indicated by extreme leukocytosis
What is the role of platelets?
Thrombocytes
Helps w blood clotting.
Lifespan 7-10 days
What are the three phases of hemostasis?
When s/o stops bleeding
The three phases are vascular, platelet, and coagulation.
Vascular phase
Triggered by vessel damage=sticky
Platelet phase
platelets attach to exposed surfaces
forms platlet plug
clots itself
Coagulation phase
Blood clotting
NEEDS Calcium and Vitamin K
Has 3 pathways
Coagulation phase: 3 Pathways
1. Extrinsic
2. Intrinsic
3. Common
Extrinsic pathway
Outside bloodstream (in vessel wall)
Bgins when releases Factor III
Activates Factor X
Intrinsic pathway of coagulation
Inside bloodstream
Begins w proenxymes being exposed to fibers at injury site
Activates factor X w other enzyme
Common pathway factors
Begins w factor X
Activates prothrombin activator, produces blood clot
Thrombin vs prothrombin
Prothrombin = inactive precursor;
Thrombin = active enzyme
Fibrinogen vs fibrin
Fibrinogen = soluble;
Fibrin = insoluble strands (clot)
Clotting is controlled by:
Natural anticoagulants like antithrombin, heparin, protein C, plus intact endothelium chemicals.
Fibrinolysis
Clot breakdown by plasmin (dissolves fibrin)
Surface antigens
A, B, D(Rh)
What are the blood types based on surface antigens?
Blood types include A, B, AB, and O, determined by the presence of specific antigens.
How do we know if someones blood is positive or negative?
If it has the D (Rh) antigen
Agglutination
Clumping of RBCs when antibodies bind antigens.
Universal donor:
Universal recipient:
Donor= O-
Recipient= AB+
What is Rh incompatibility?
Rh incompatibility occurs when an Rh-negative mother carries an Rh-positive fetus.