anatomy 403: neuro 5: diencephalon, cerebral cortex, and limbic system
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
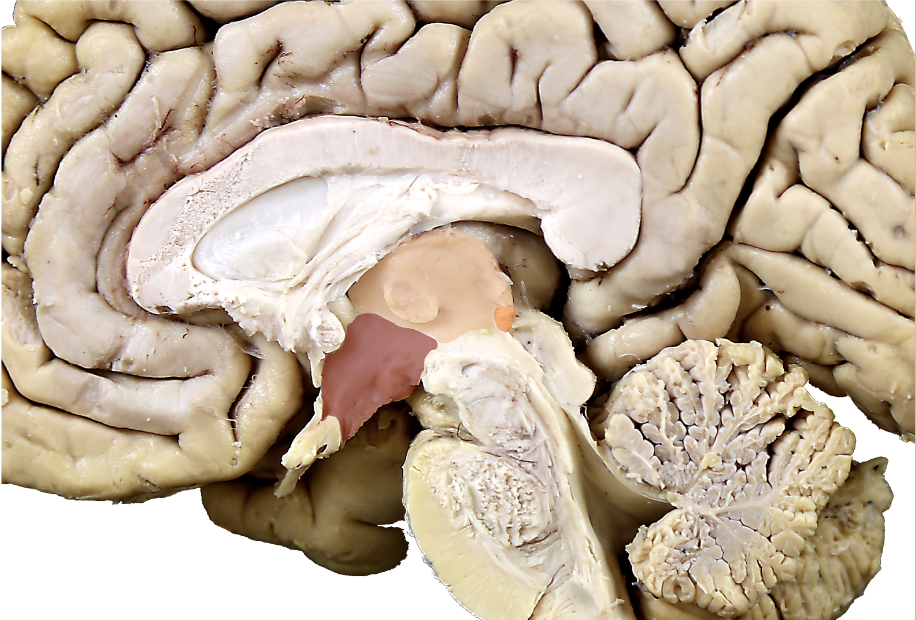
what are the regions of the diencephalon?
epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus, ventral thalamus
what structure is in orange?
epithalamus (pineal gland and habenula)
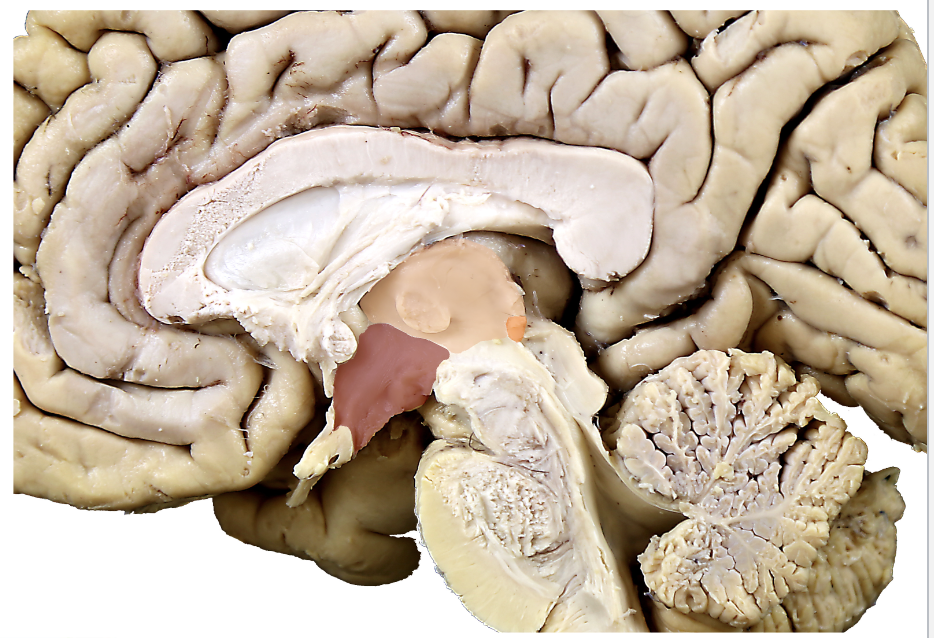
what structure is in red?
hypothalamus
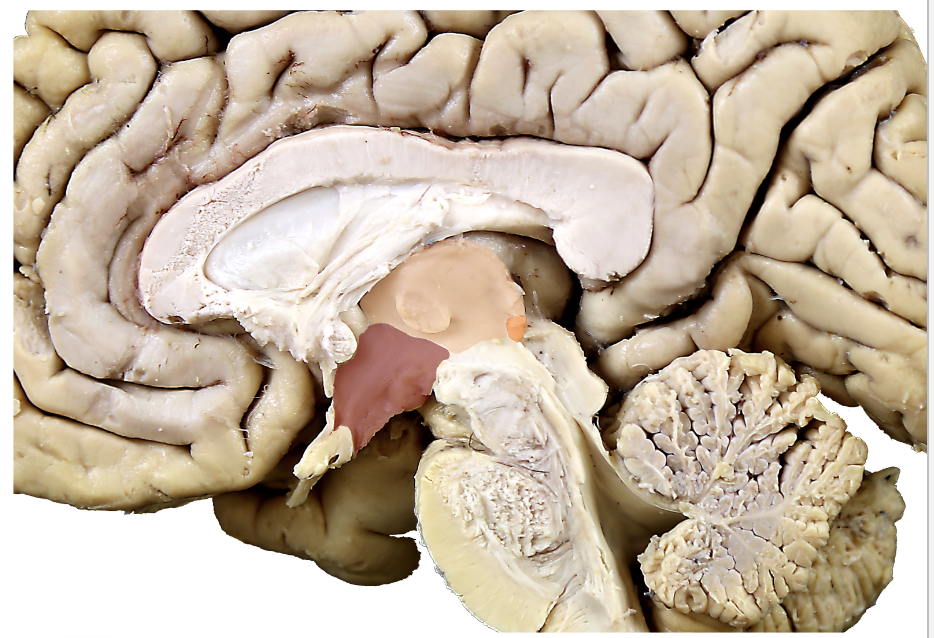
what structure is in pink?
thalamus
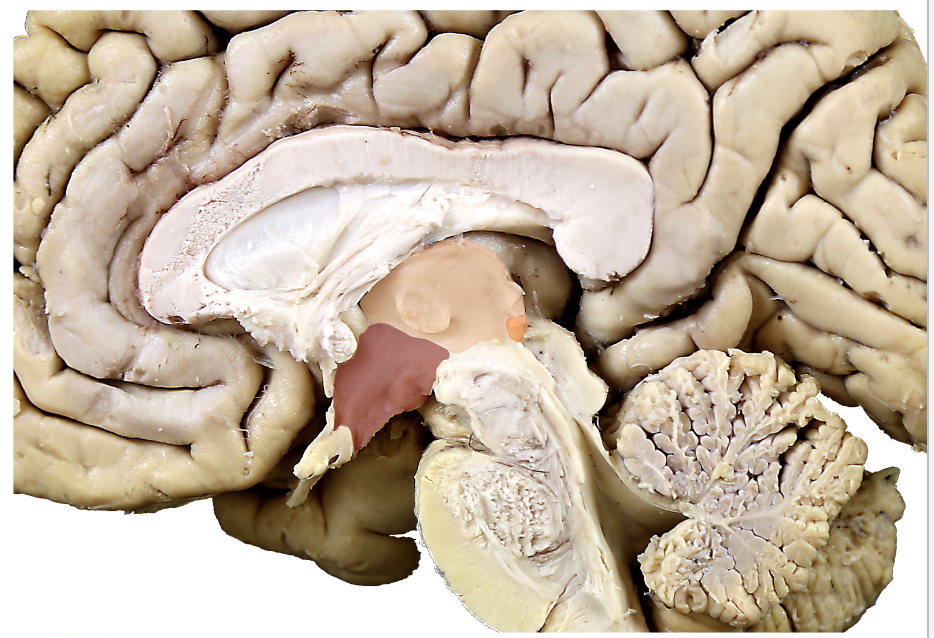
dorsal thalamus
usually referred to as the thalamus
all sensory information passes through the thalamus prior to cortex with one exception of _______
olfaction
dorsal thalamus
largest part of the diencephalon
midline structure
2 hemispheres: connected by the ________
connections: motor, sensory, and limbic cortex, reticulating activating systems of the brain stem
massa intermedia
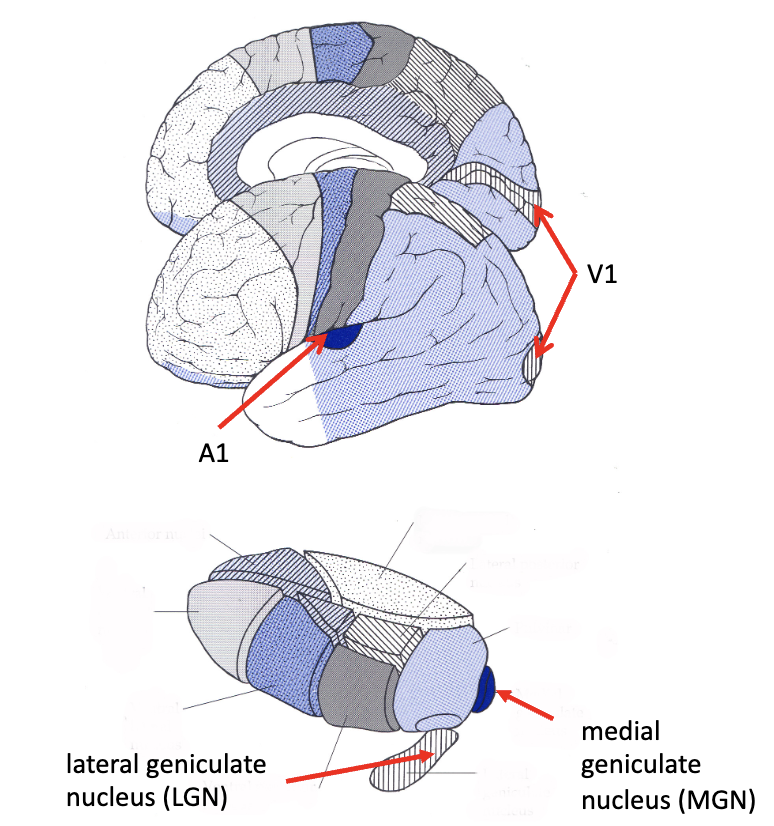
sensory thalamus
_______
afferent: inferior colliculus
efferent: auditory radiations
medial geniculate
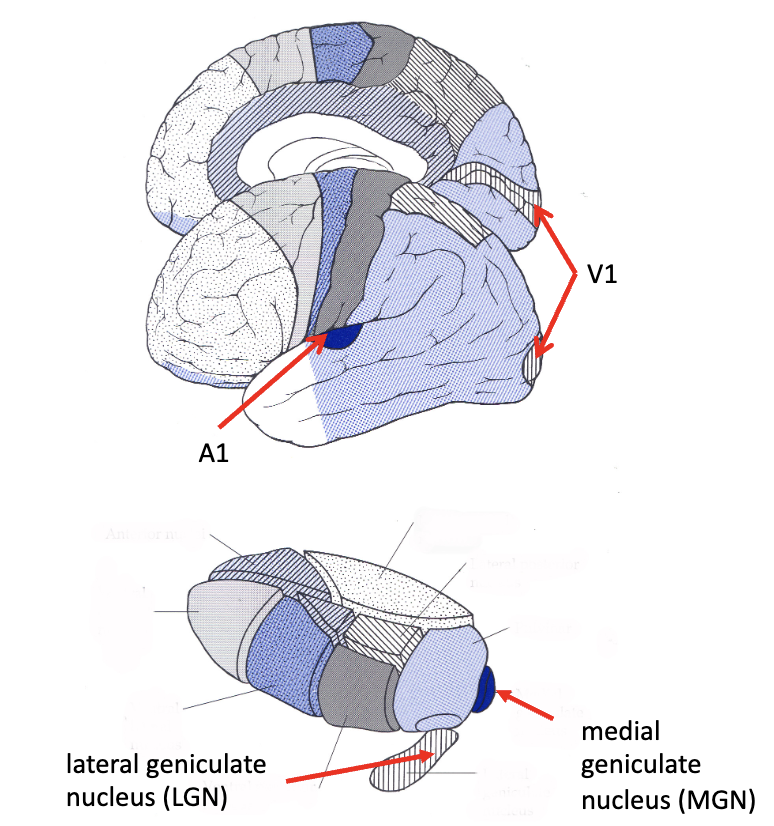
sensory thalamus
________
afferent: optic tract
efferent: optic radiations aka geniculocalcarine tract
lateral geniculate
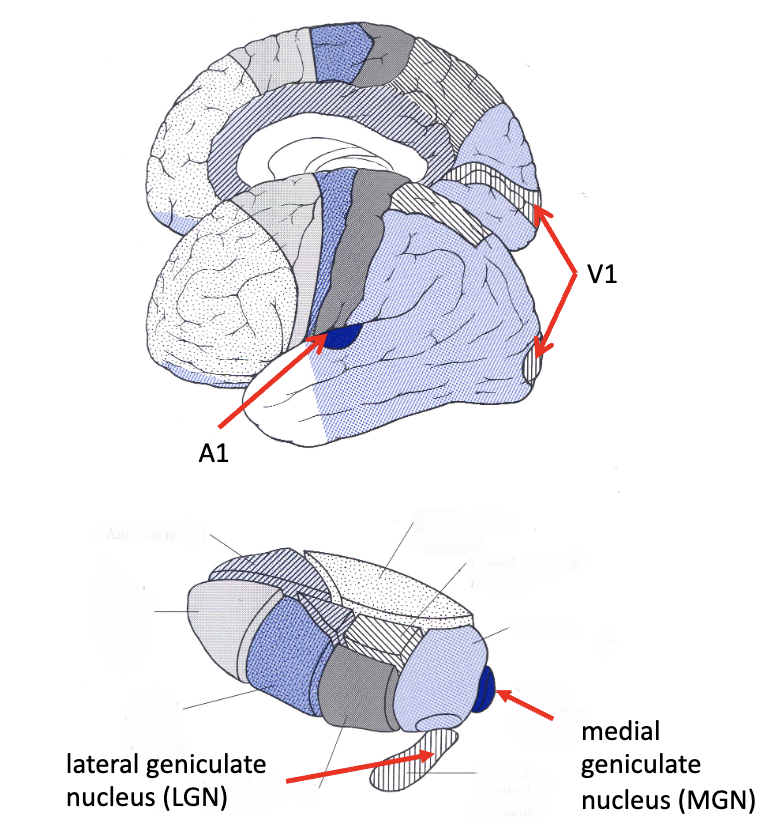
sensory thalamus
what is the A1 portion of the brain?
primary auditory cortex
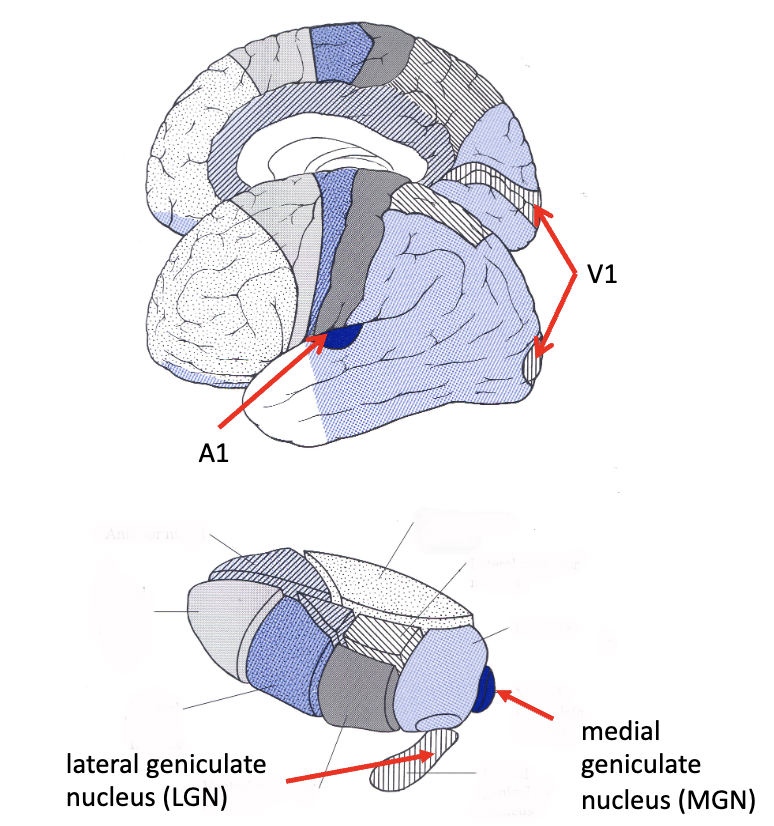
sensory thalamus
what is the V1 portion of the brain?
primary visual cortex
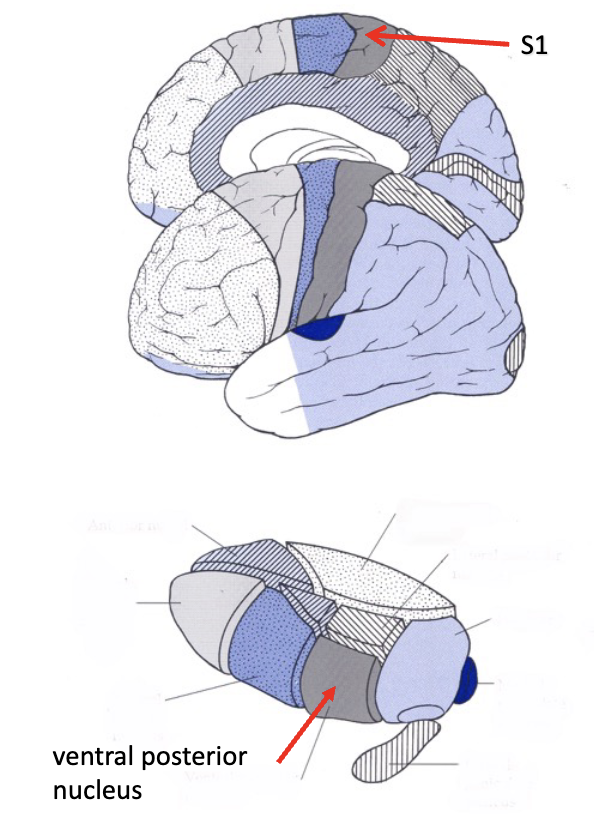
sensory thalamus
ventral posterior
afferent systems: ________, _______
efferent systems: somatosensory cortex via the internal capsule and S1 (primary sensory cortex)
medial lemniscus, anterolateral system
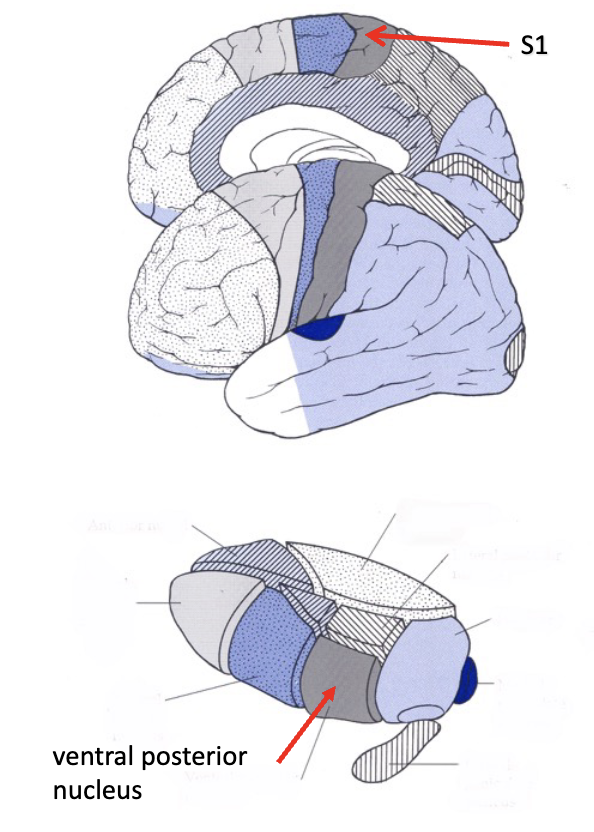
sensory thalamus
what does the medial lemniscus sense?
fine touch and proprioception
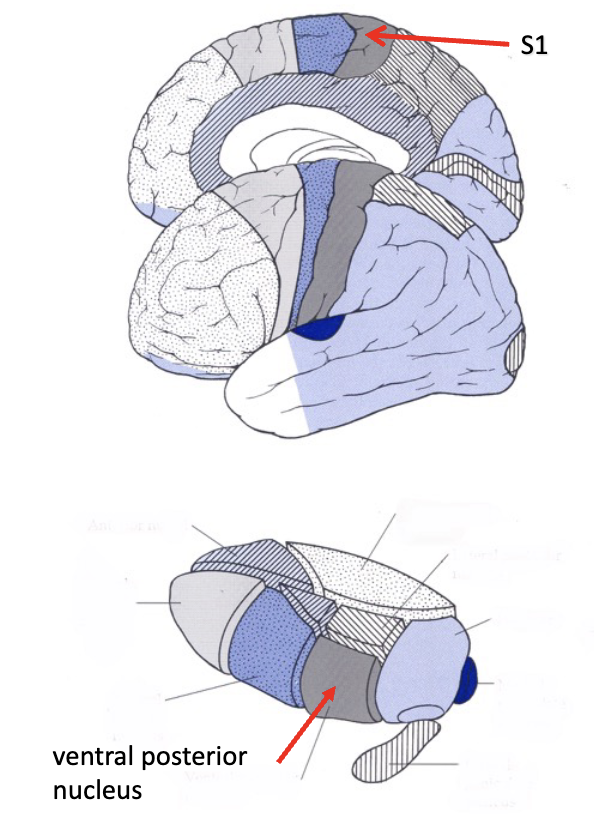
sensory thalamus
what does the anterolateral system sense?
temperature, gross touch, pain
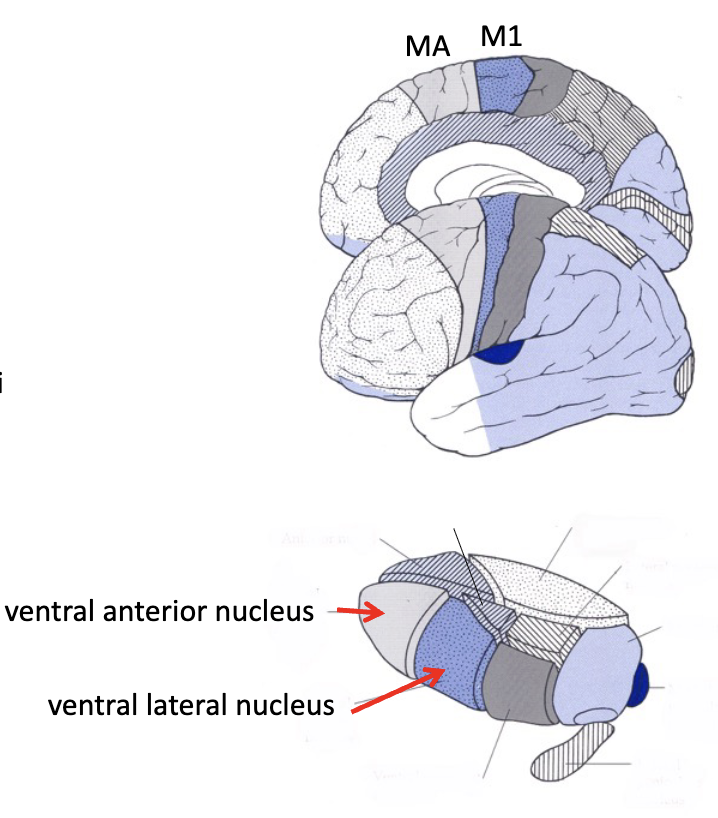
motor thalamus
ventral anterior and ventral lateral
part of the ______
receives info from basal nuclei (ganglia) and reports back to motor cortex
basal nuclei loop
hypothalamus
sends and receives hormonal and other molecular signals via the vascular system, as well as neural signals
main functions:
control of the ________
control of the autonomic nervous system and variety of survival behaviors
pituitary gland
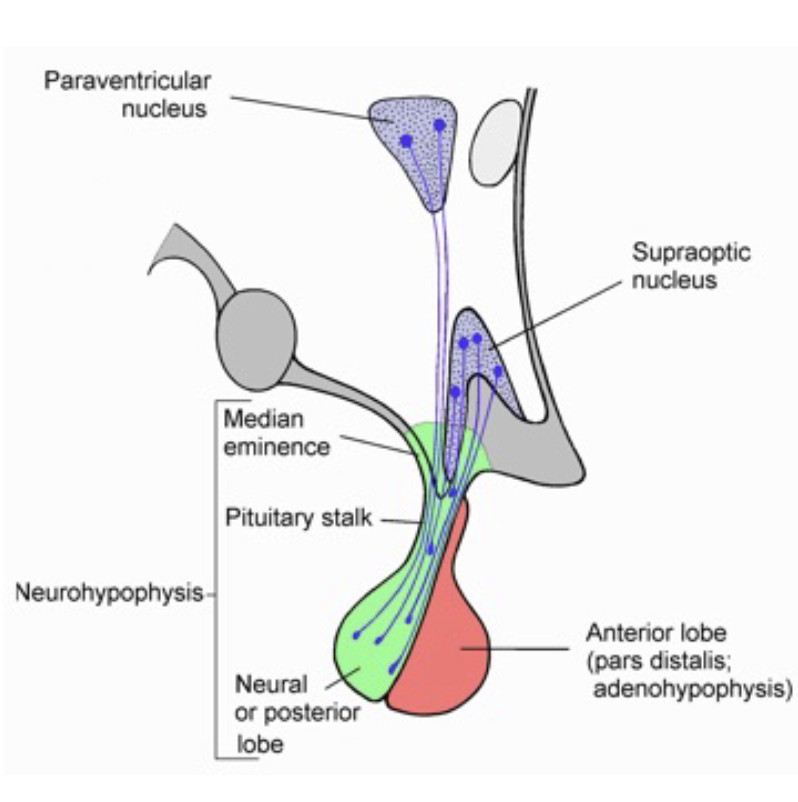
hypothalamus
control of the pituitary gland
the ______ and ______ nuclei contain neurons that produce oxytocin and vasopressin that release these peptides onto the capillaries of the posterior pituitary
paraventricular, supraoptic
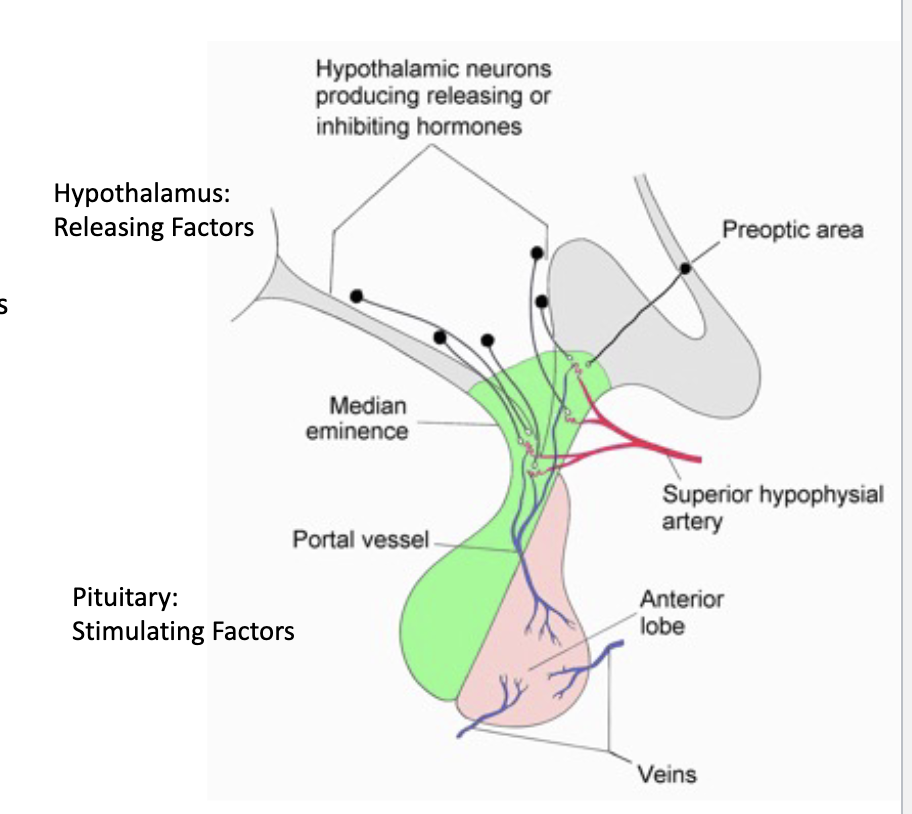
hypothalamus
control of the pituitary gland
the hypothalamus control the _____ by secreting releasing factors into the _______portal system
unlike many other endocrine tissues, the anterior pituitary is so dependent on the hypothalamus, that it is not transplantable
anterior pituitary, hypophyseal
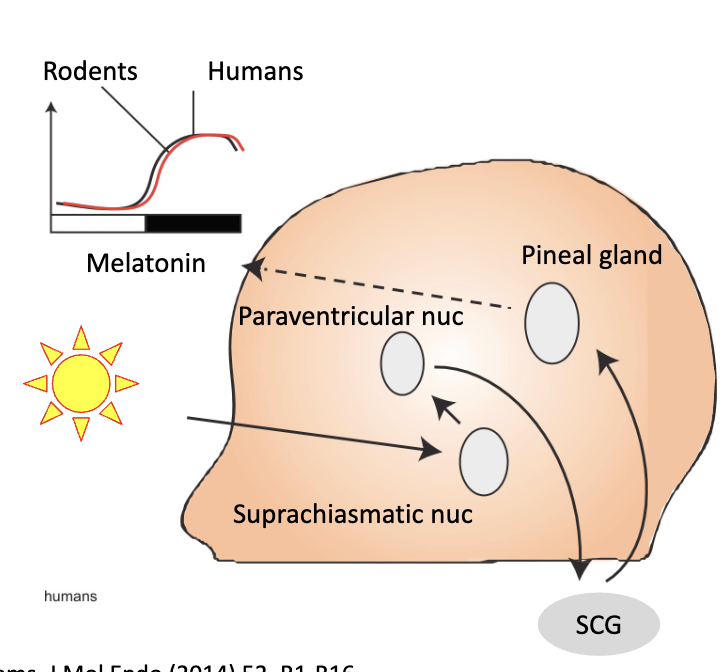
hypothalamus - circadian rhythms
what is the process?
retina → suprachiasmatic nucleis → paraventricular nucleus → intermediolateral cell column → superior cervical ganglia → pineal gland → melatonin secretion
hypothalamus - thermoregulation
__________
heat conservation, shivering, construction of blood vessels
destructions reults in hypothermia
sympathetic nervous system
posterior nucleus (dorsal hypothalamis area)
hypothalamus - thermoregulation
__________
heat dissipation, sweating, dilation of blood vessels near the body surface
destruction results in hyperthermia
parasympathetic nervous system
anterior nucleus (median preoptic area)
cerebral cortex
in human, the vast majority of the cortical hemisphere occupied by _______
unique to mammals
gray matter = neurons arranged in layers
white matter = myelinated fiber tracts
neocortex
cerebral cortex
what matter are neurons found arranged in layers?
gray matter
cerebral cortex
what matter are myelinated fibers tracts?
white matter
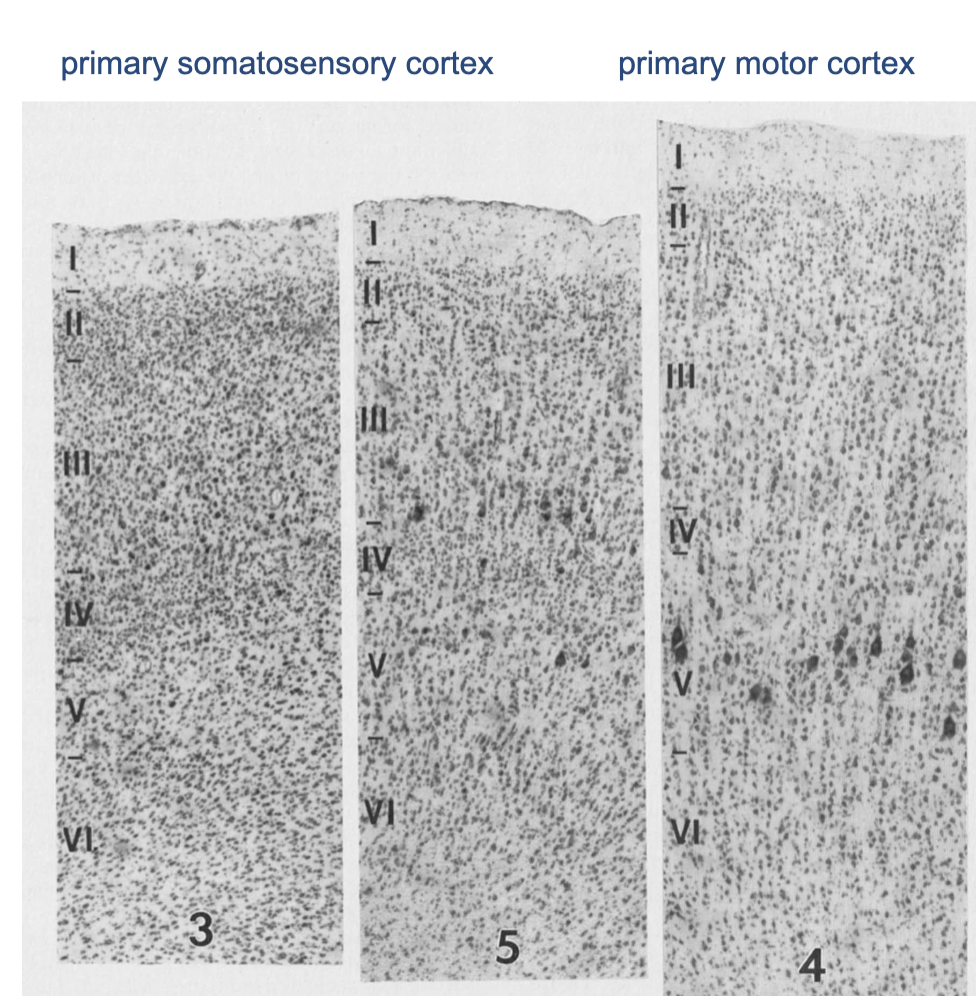
cerebral cortex
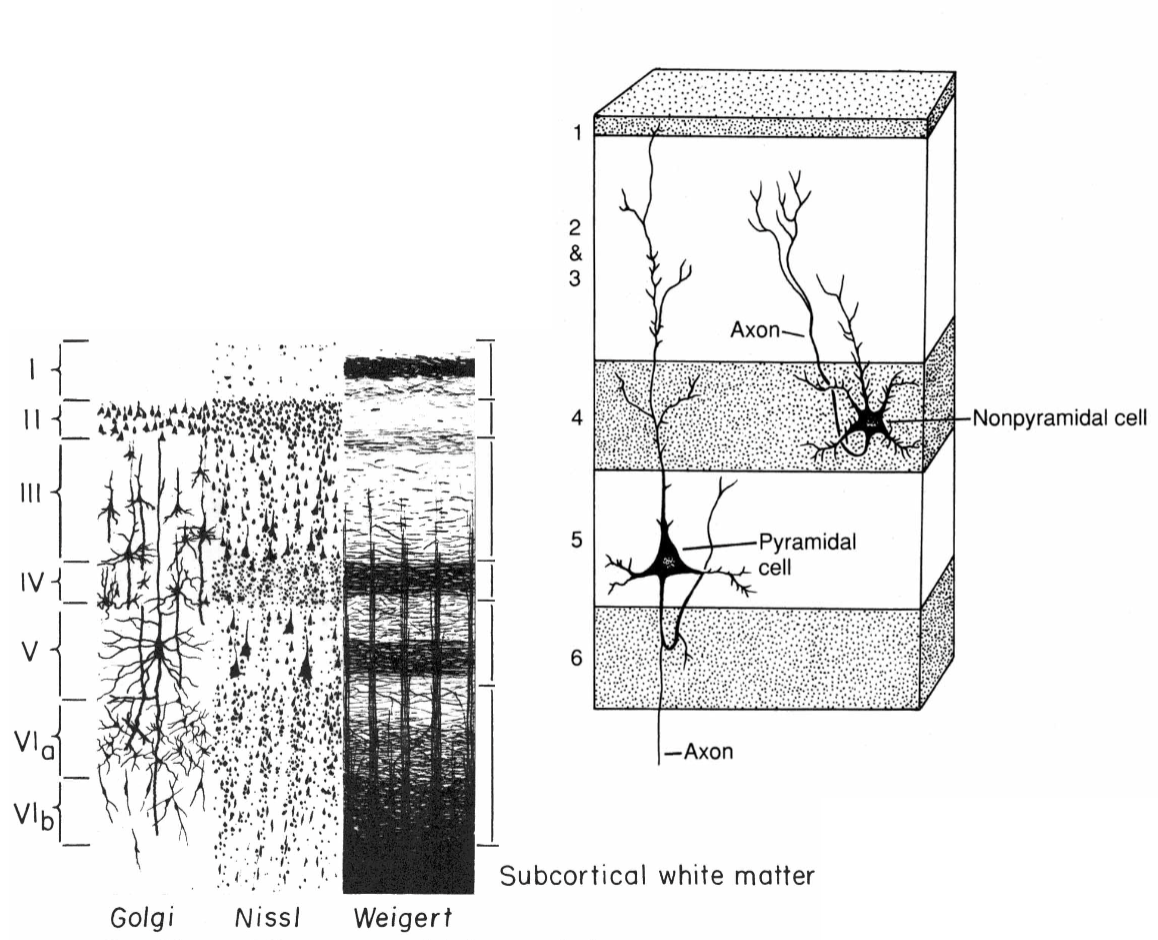
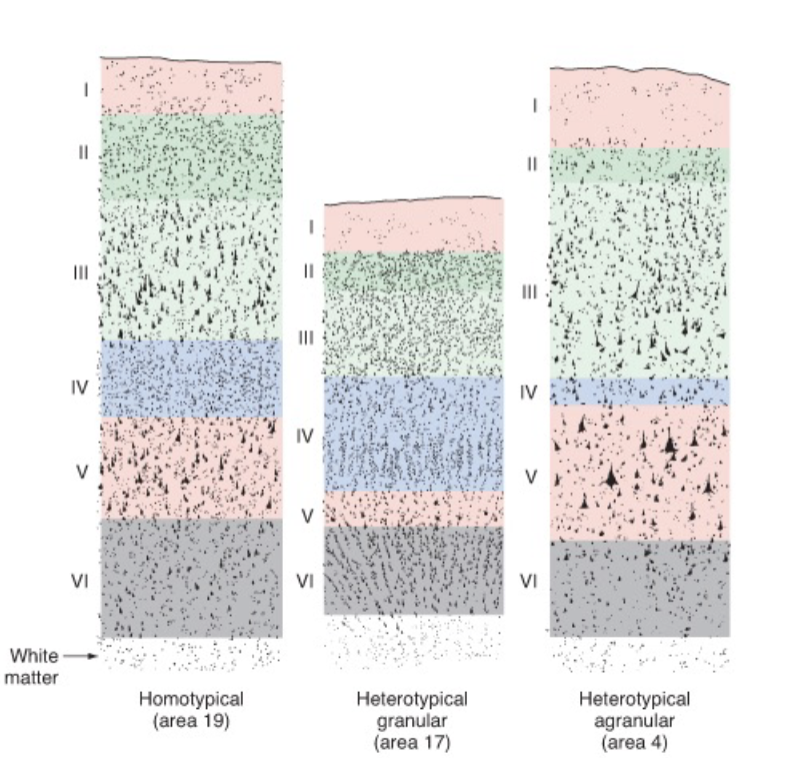
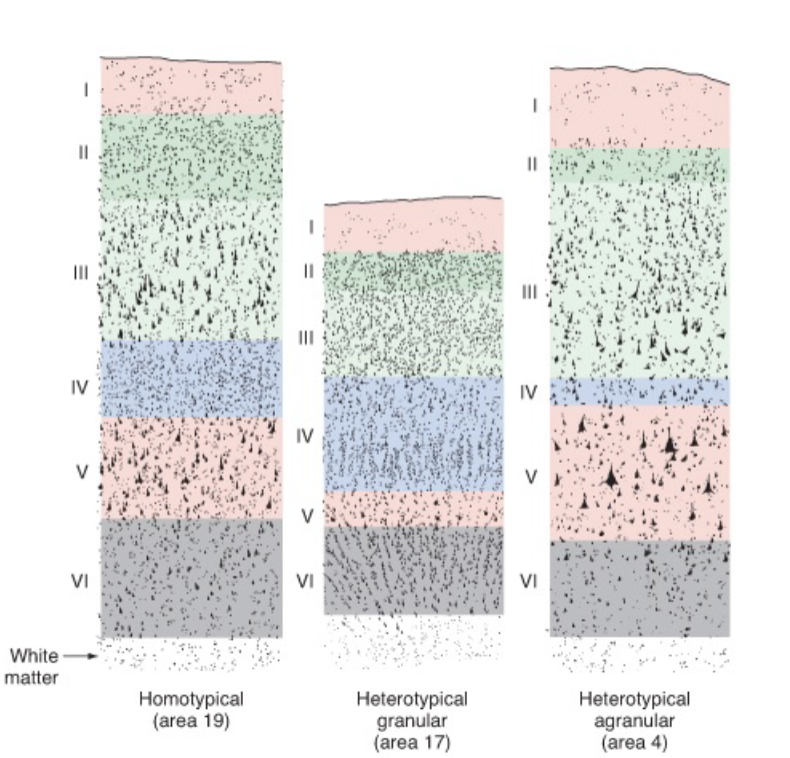
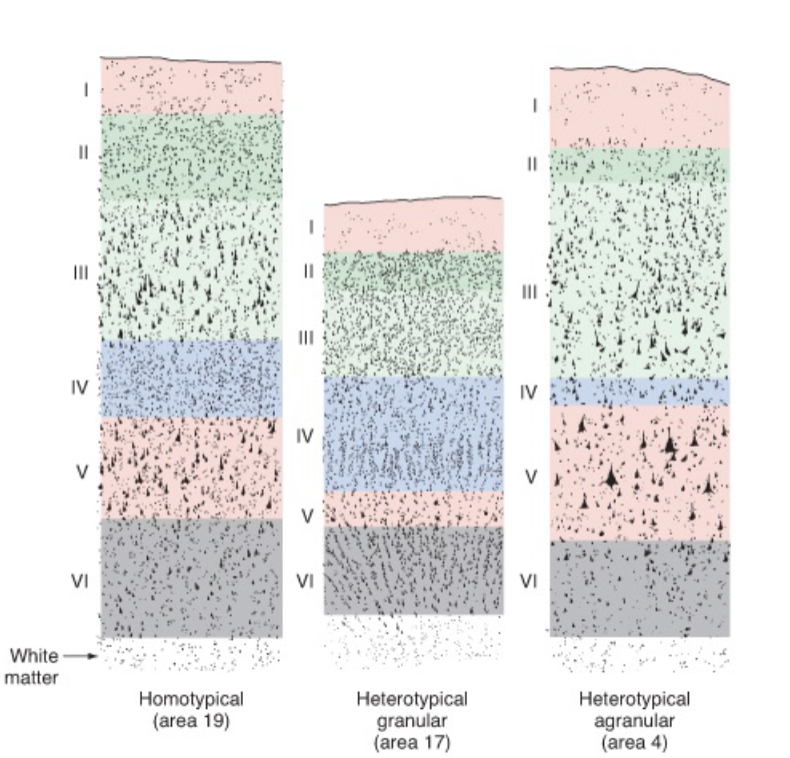
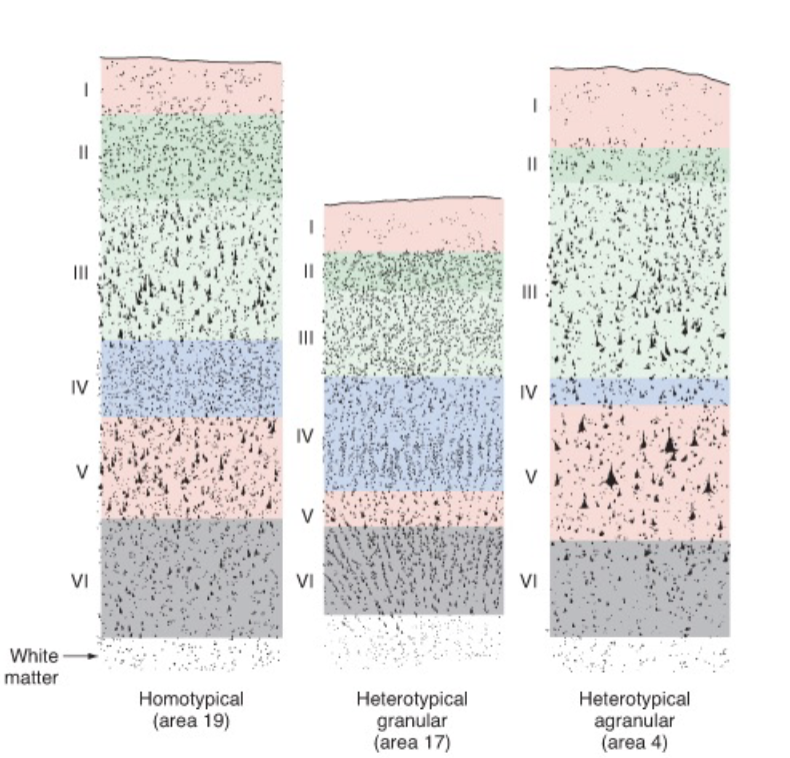
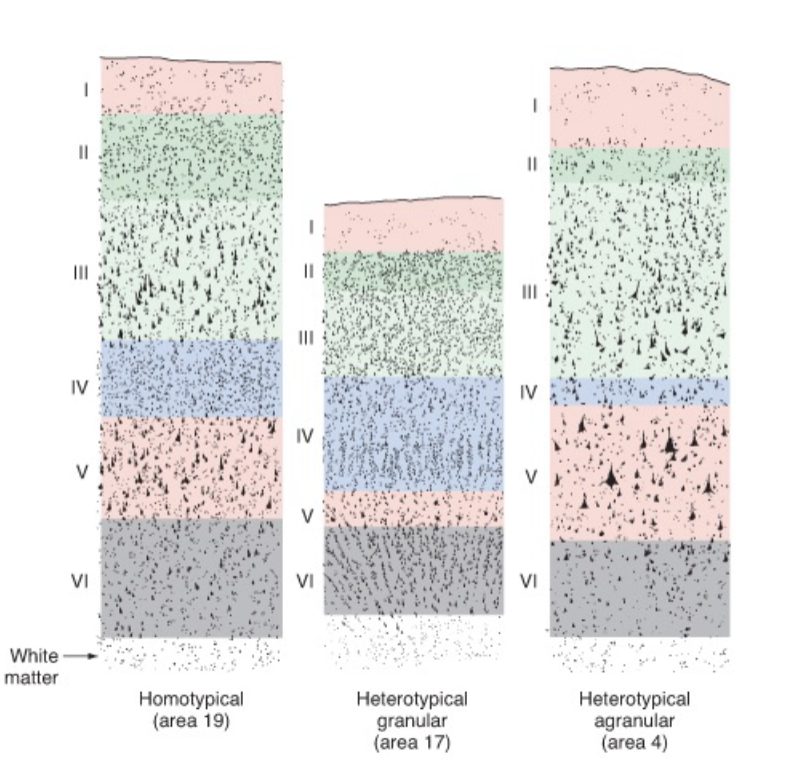
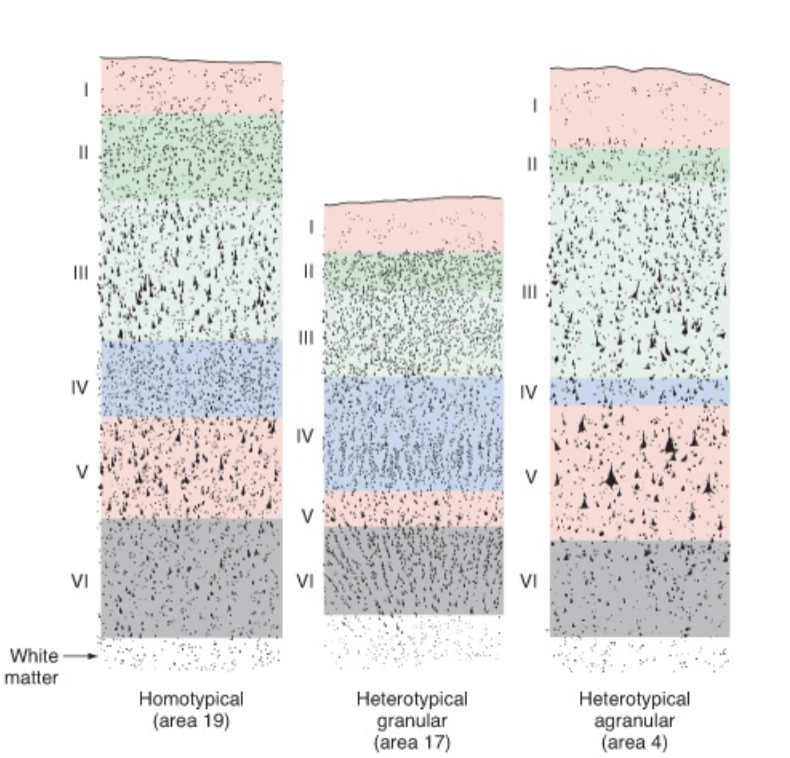
basic 6-layered organization is conserved across all mammals
______ (new, 6 layers_
______ (middle 4/5 layers)
______ (other) cortical areas
neocortex, mesocortex, allocortex
cerebral cortex
layer 4 is the ______ zone of thalamocortical axons
recicpient
cerebral cortex
layers 3, 5, and 6 are the ____ layers, sending axons to other cortical or subcortical targets
output
cerebral cortex
I: molecular
II: external granular
III: external pyramidal
IV: internal granular
V: internal pyramidal
VI: fusiform
just put ok
ok
cerebral cortex
what is layer 1 called?
molecular
cerebral cortex
what is layer 2 called?
external granular
cerebral cortex
what is layer 3 called?
external pyramidal
cerebral cortex
what is layer 4 called?
internal granular
cerebral cortex
what is layer 5 called?
internal pyramidal
cerebral cortex
what is layer 6 called?
muliform (fusiform)
cerebral cortex
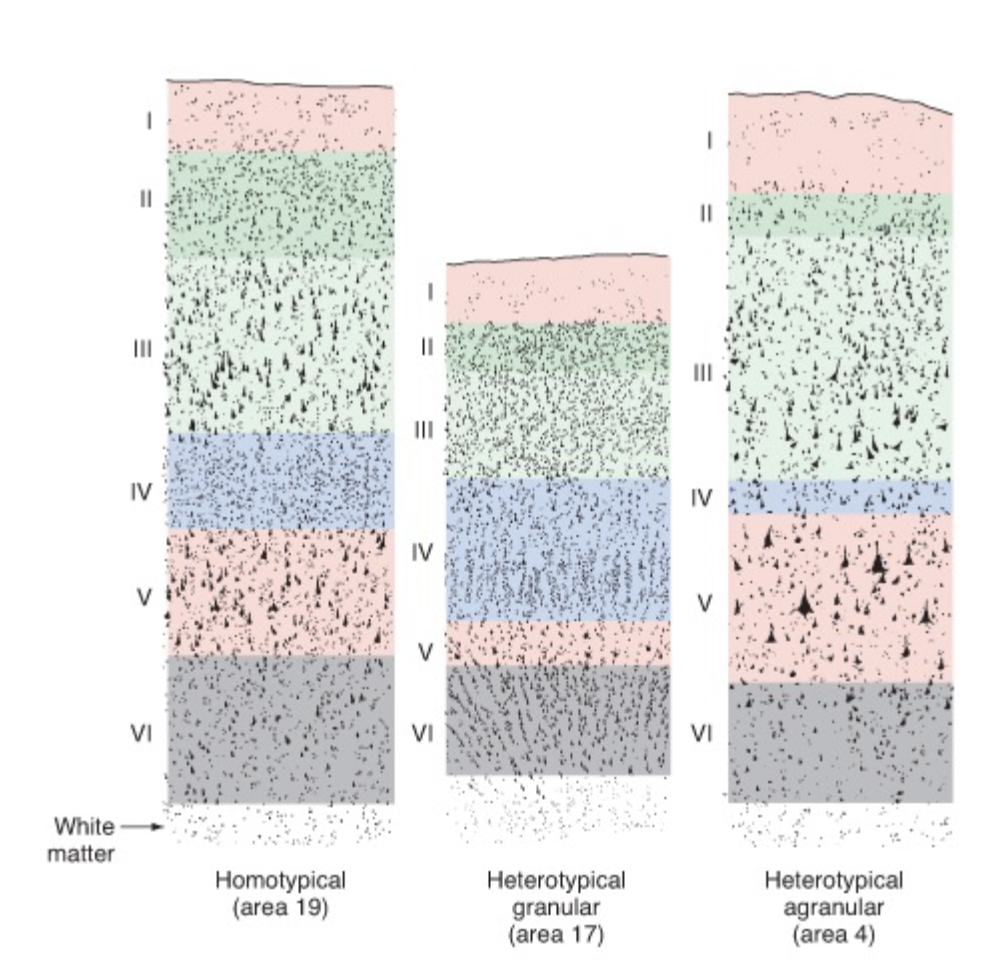
what makes up layer 1?
apical dendrites of pyramidal neurons
cerebral cortex
what makes up layer 2?
recipient zone of diffuse thalamic projections and other subcortical nuclei (basal forebrain, brain stem, and hypothalamus)
cerebral cortex
what makes up layer 3?
cortico-cortical projections
cerebral cortex
what makes up layer 4?
recipient zone of precise, topographically organized projections from specific thalamic nuclei
cerebral cortex
what makes up layer 5?
is the principal output layer to the subcortical (bigger)
cerebral cortex
what makes up layer 6?
output to thalamus
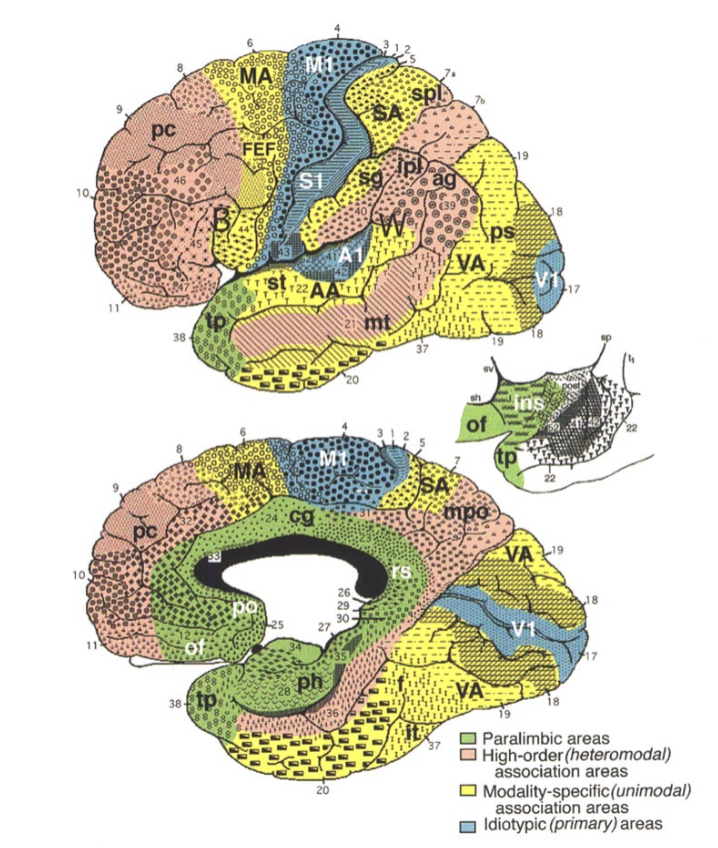
cerebral cortex
primary ______ areas: M1, S1, A1, V1
motor and sensory
white matter
what are the three types of connections within the brain?
commissural, projection, association
white matter
projection fibers project out of cortex to subcortical targets in the ______
connections between the brain and lower centers
internal capsule
white matter
commissural fibers span both cerebral hemispheres in the _________
interhemispheric
corpus callosum
white matter
association fibers are on the same side of the hemispheres
arcuate fasciculus and _____
intrahemispheric
cingulum
limbic system
function: regulation of emotional behavior (anger, rage, sexual activity)
pathways to and from the hypothalamus and limbic system ____ each other
parallel
limbic system
the ________ receives information about the prefrontal association cortex, the amygdaa, and ventral tegmental area
sends informationn to the globus pallidus and substantia nigra
it is thought to be our _____ system and associated with addiction and pleasure
nucleus accumbens, reward
limbic system
hippocampal formation and amygdala
often described as being “inside” the _______
hippocampal formation may be viewed in the floor of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle
telecephalon
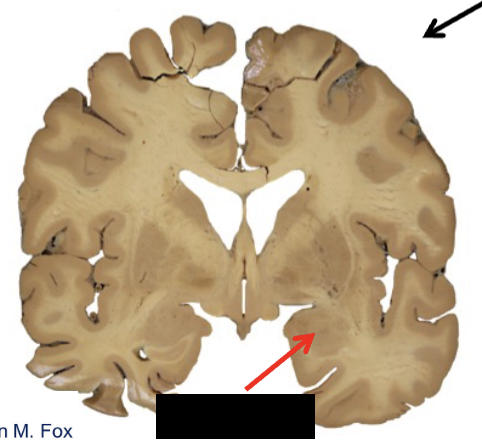
limbic system
what structure is this?
amygdala
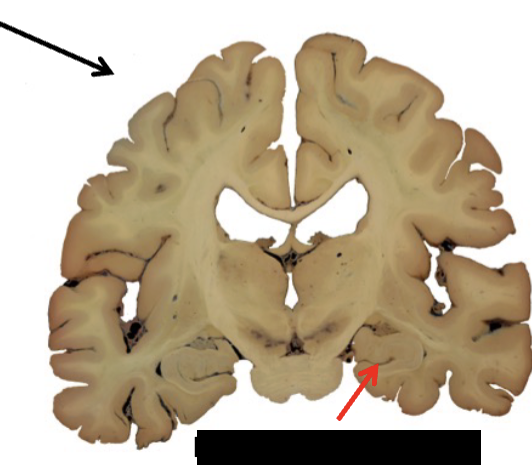
limbic system
what structure is this?
hippocampal formation
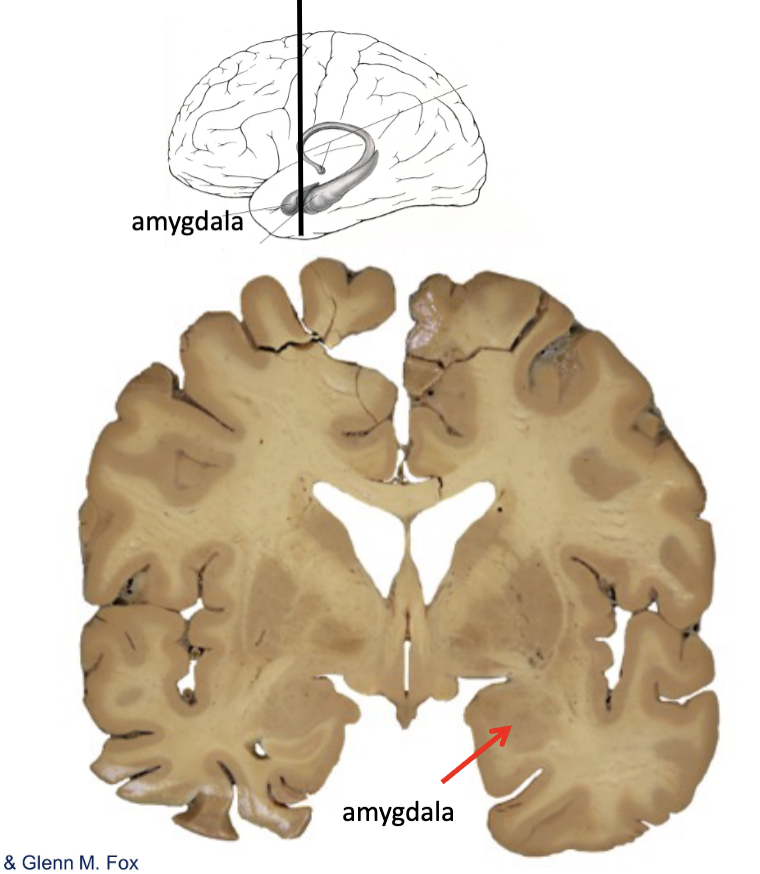
limbic system
the amygdaloid complex contains multiple nuclei
lcoated in the _____ lobe, rostral of the hippocampal formation, at the anterior end of the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle
function: general limbic emotions and behaviors, fear, anger, satiety, and environmental contexts
stimulation: fear, rage
_____: highly variable responses, passivity, and hypersexuality
temporal, ablation
limbic system
what are the three parts of the hippocampal formation?
dentate gyrus, hippocampus, and subiculum
limbic system
dentate gyrus layers from superficial to deep?
molecular, granular, polymorphic
limbic system
hippocampus layers from superficial to deep?
polymorphic, pyramidal, and molecular
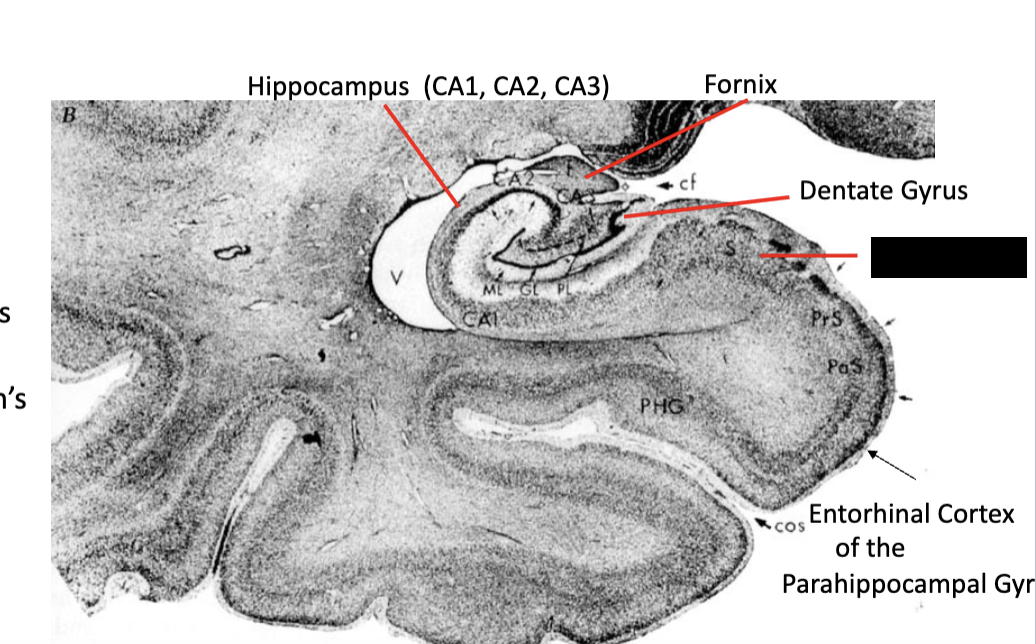
limbic system
what structure is this?
subiculum
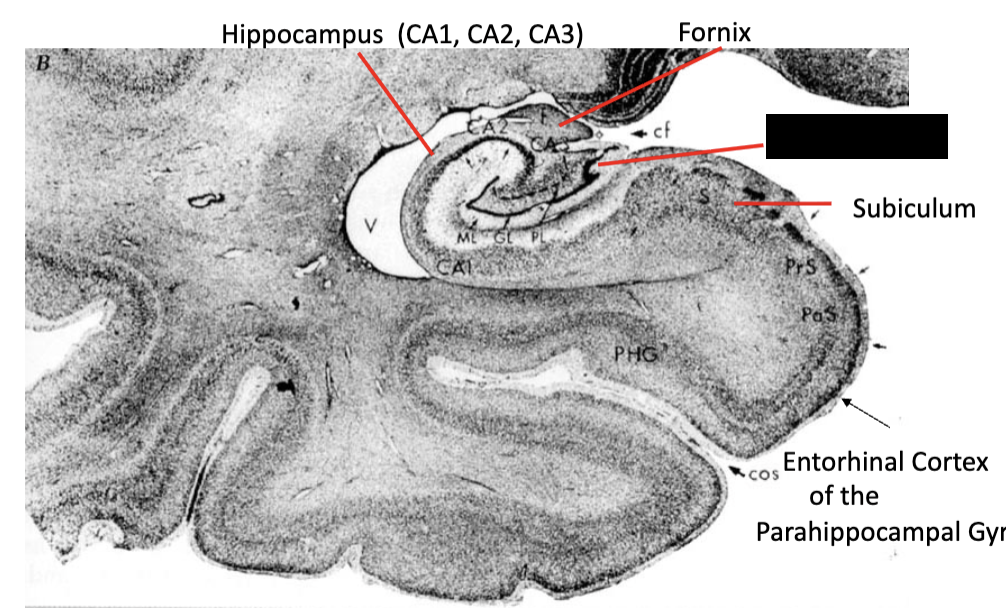
limbic system
what structure is this?
dentate gyrus
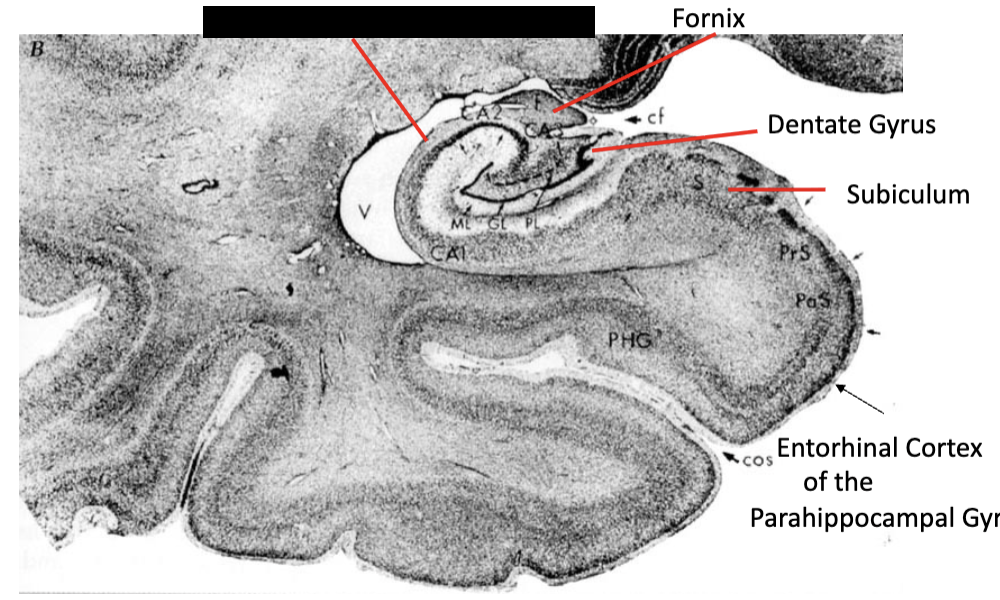
limbic system
what structure is this?
hippocampus (CA1, CA2, CA3)