gentrification
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Positive impacts of gentrification
- Increase in wealthier individuals = more investment
- Housing is refurbished
- Decrease in crime
- Boost to local economy
- More tax revenue
- Renovation
What is gentrification?
The process of deciding urban area being revitalised and improved, leading to affluent people moving in and changing the areas character. Poor people are forced out.
Negative impacts of gentrification
- Communities forced out
- Divides within community
- Loss of social diversity
- Some old buildings demolished
- Resentment within communities due to new arrivals.
How do booms and recessions impact people and places
Recessions occur when technology is no longer new. Reduced economic activity is evident from falls in macro-economic indicators, such as GDP, households income.
Bankruptcies and unemployment rise.
As disposable income falls, households reduce their discretionary spending (e.g. they keep technology for longer)
During a boom, technological innovation is not evenly distributed. It is the core regions that benefit from economic growth, where the multiplier effect is strong. The greater economic opportunities available in the core regions help to explain the higher standards of living found there.
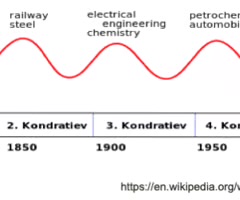
Kondratiev Waves
Kondratiev waves are cycles of economic growth and decline, each about 50 years long.
Kondratiev waves are linked with technological innovation, with each wave being associated with new industries that provide the basis for economic growth.
Waves of innovation
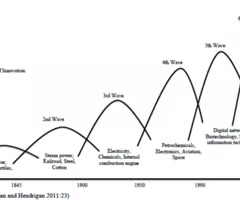
Similar to the Kondratiev graph, in that each wave is fuelled by a different technological innovation, however the height increases each time as income does.
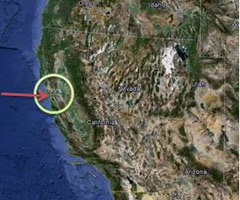
Example of an area that has benefited from globalisation - Silicon Valley, California
- An industrial area around the southern shores of San Francisco Bay in California
- The heart of the region is Stanford University
- High concentration of technology companies developed from the mid-20th century
- Known to be a centre of innovation, e.g. this is where Microsoft started in the mid 1970s
- Close to the major urban centre of San Francisco, which provides a good standard of living for people generating a high income
Suggest why some people have benefitted more than others form globalisation using an example.
Silicon Valley, California
Who benefits?
- High standards of living, being so close to San Francisco
- Desirable place to live - centred on Santa Clara Valley
- Benefits to the graduates of Stanford University, who act as a regular supply of skills to the research businesses - high standard of education, and plenty of employment opportunities post-uni
- High availability of venture capital for new startups. Nearly half of all the venture capital in the USA is spent in Silicon Valley and it has the most millionaires/billionaires in relation to the population of the region -- good opportunities for people who live and work there
- Agglomeration of law firms to ensure ideas are patented -- offers further employment opportunities to graduates
Who doesn't benefit?
- Migrants that have been drawn in due to the employment opportunities are disadvantaged - may have a poor quality of life as they have to work away from home
- Most production line workers are paid minimum wage, and have a high exposure to toxic chemicals
Methods used by the Gov at a national level to tackle social and economic inequalities (how do they play a part in reducing or exacerbating social inequality)
Taxation
- Income tax redistributes wealth to reduce social inequality -- progressive system where people with higher incomes pay a larger proportion of their incomes in tax. Essential items, e.g. food, may be exempt from tax to benefit poorer groups who spend a larger proportion of their income on tax
Subsidies - e.g. Free school meals, clothing allowances, help with university fees, or pensioners get subsidies for fuel and transport. Low wage earners, unemployed workers and those with a long-term disability are entitles to benefits
Planning - give priority to regenerating housing and services in poorer areas. Planning is often organised geographically and is targeted at the most deprived areas, which vary in scale from neighbourhoods to entire regions
Law - outlaws discrimination on racial, ethnic, gender and age criteria, and aims to give equal opportunities to all. The poorest groups of workers are protected by minimum wage legislation
Education - Governments provide funding for training and upgrading skills in order to raise skill levels and qualifications, improve employment prospects, and boost economic growth. There are also education programmes designed to improve personal health, (e.g. diet, obesity, smoking).
Rural services - concentrated in large villages and small towns to act as a hub for people in surrounding smaller settlements.