AQA GCSE Biology Bioenergetics
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Write the word equation for photosynthesis
carbon dioxide+ water -> oxygen + glucose
Write the symbol equation for photosynthesis.
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Name 4 factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis.
LIGHT INTENSITY
CARBON DIOXIDE CONCENTRATION
TEMPERATURE
CHLOROPHYLL
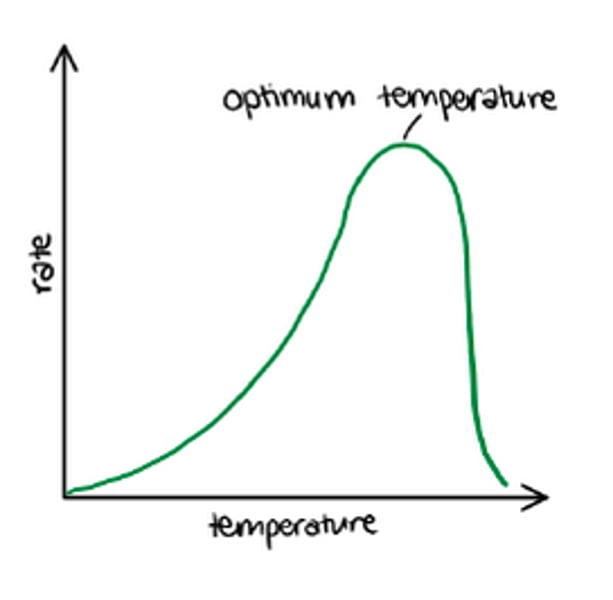
Draw a graph to show how temperature affects the rate of photosynthesis.
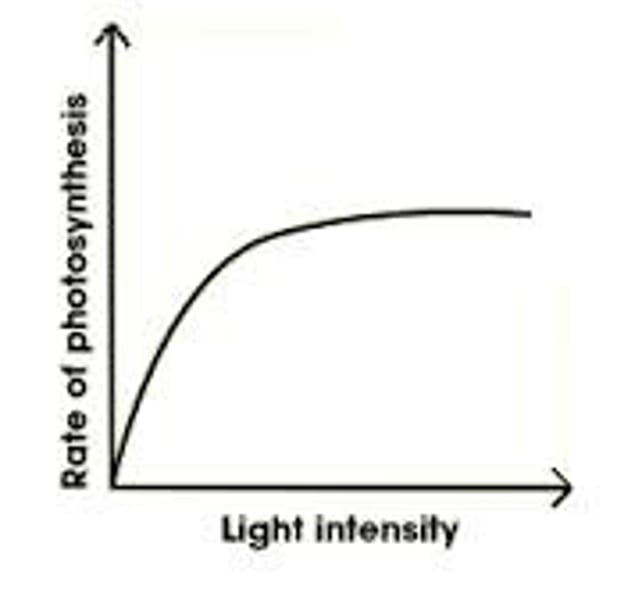
Draw a graph to show how light intensity affects the rate of photosynthesis.
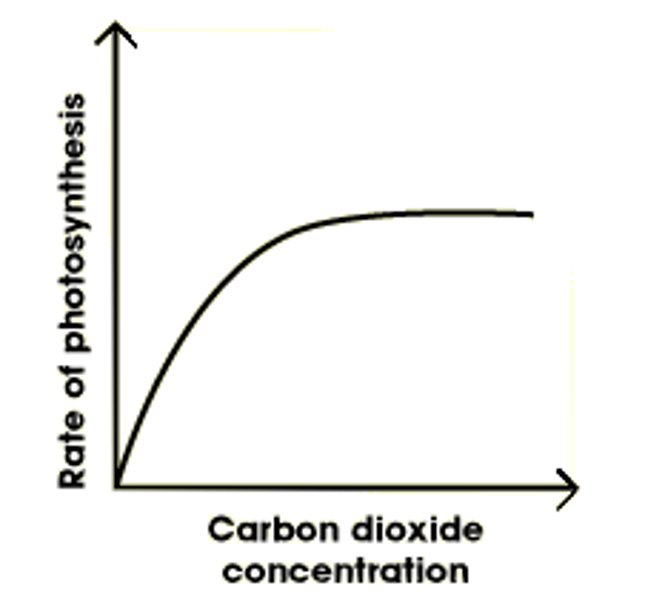
Draw a graph to show how the level of carbon dioxide affects the rate of photosynthesis.
Describe AND explain the graph of temperature versus rate of photosynthesis.
- increasing temperature increases rate of photosynthesis (because temperature increases the speed of chemical reactions)
- increasing the temperature too much causes the rate to fall again (because the enzymes have denatured)
Describe AND explain the graph of light intensity versus rate of photosynthesis.
the higher the light intensity the higher the rate of photosynthesis but it plateaus if the other factors are not in supply
Describe AND explain the graph of carbon dioxide level versus rate of photosynthesis.
the more co2 available the higher the rate of photosynthesis but it plateaus when other factors are limiting
Name the law that is used to link light intensity and distance.
INVERSE SQUARE LAW
Give the equation that shows the relationship between light intensity and distance.
light intensity = 1 / distance squared
Give 5 uses of the glucose made in photosynthesis.
respiration... making cellulose... making amino acids...stored as oils or fats... stored as starch
What is respiration?
respiration is the process of transferring energy from glucose, which goes in every cell
Why is respiration exothermic?
because overall it transfers energy to the environment
The energy transferred in respiration is used for all living processes. Give 3 examples.
to build up larger molecules from smaller ones ... to allow the muscles to contract... to keep the body temperature steady...
What is aerobic respiration?
respiration using oxygen
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water
What is the symbol equation for aerobic respiration?
C6H12O6 +6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O
Where do most of the reactions for aerobic repiration occur?
inside mitochondria
What is anaerobic respiration?
respiration without oxygen
When does anaerobic respiration take place in muscles?
when you do vigorous exercise
Which type of respiration transfers the least energy? Explain your answer with reference to the oxidation of glucose.
anaerobic respiration transfers less energy because glucose is not completely broken down (oxidised)
Give a word equation for anaerobic respiration in muscles.
glucose -> lactic acid
Give a word equation for anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast.
glucose -> ethanol + carbon dioxide
What is anaerobic respiration in yeast cells called?
FERMENTATION
Why is fermentation economically important?
because it helps the food and drink industry
Why do you need more energy when you exercise?
because you respire more and quicker
Describe what happens to the heart rate, breathing rate and breathing volume during exercise and explain why this happens.
heart rate goes up... breathing rate goes up... and breathing volume increases... this is so that more oxygen and glucose gets to the muscles for them to do more respiration, so more energy can be transferred
What is meant by the term oxygen debt?
when you finish exercising anaerobically you will be breathing faster
this provides the extra oxygen needed to convert lactic acid back to glucose in the liver
Describe the role of oxygen in the removal of lactic acid from the muscles.
oxygen reacts with the lactic acid to convert it backl to glucose
Describe the role of the blood and the liver in the removal of lactic acid from the muscles.
the blood carries away lactic acid from the body to the liver where it is made back into glucose
What is metabolism?
metabolism is all of chemical processes that occur inside a living organism
What is the difference between starch, glycogen and cellulose in terms of their function?
starch is a store of glucose in plants, glycogen is a store of glucose in aminals (stored in the liver and in muscles), and cellulose is used in plant cell walls
Describe how proteins are made.
protein is made up of large numbers of amino acid molecules