IB Physics HL (Units we have done so far)
1/218
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
219 Terms
Velocity
Change in displacement over time
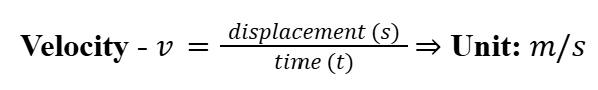
Acceleration
Change in velocity over time
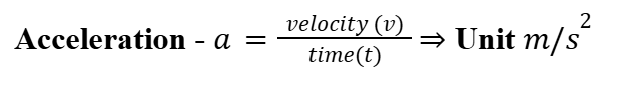
S.U.V.A.T. Equations
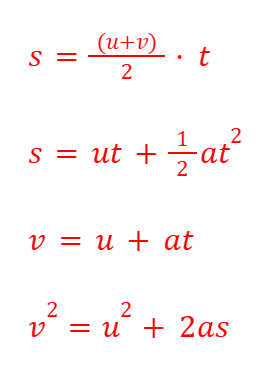
Vectors
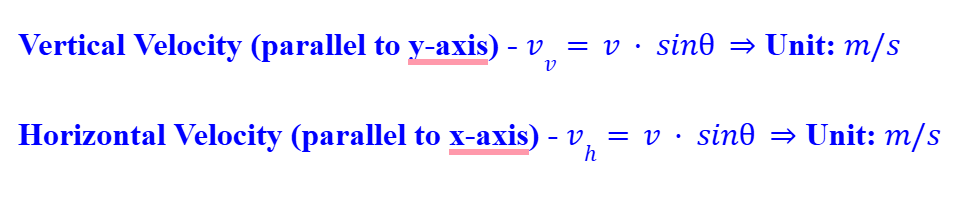
Normal Force
The Force applied is mass times acceleration.
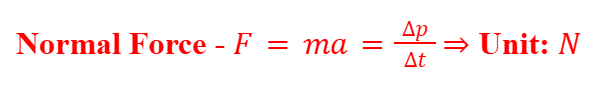
Weight

Density
The density of an object is the mass per unit volume.
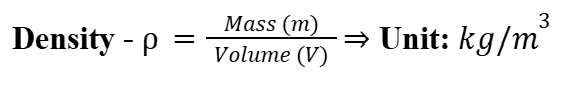
Buoyancy Force

Spring Constant
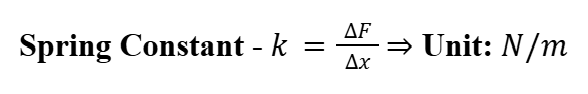
Hooke’s Law
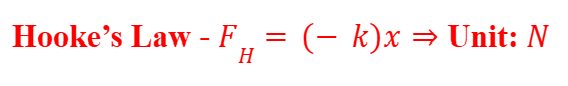
Static Friction
The friction force experienced when the object is at rest.
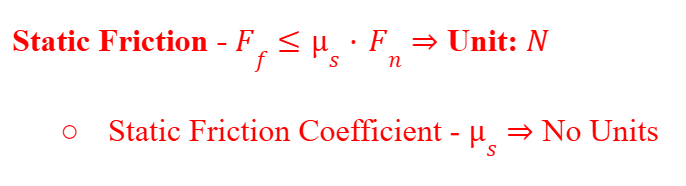
Dynamic Friction
The friction force experienced when the object is in motion.
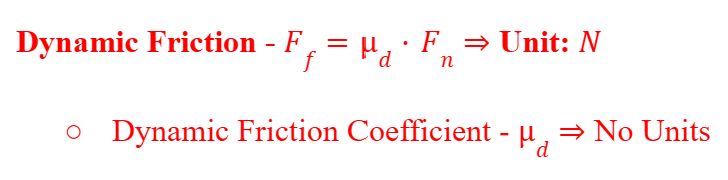
Viscous Drag
The drag force experienced by a solid sphere in a fluid

Linear Velocity
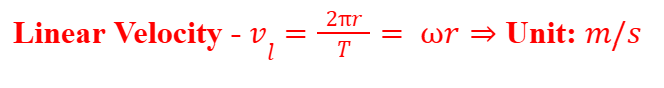
Angular Velocity
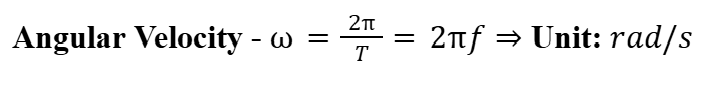
Angular Acceleration
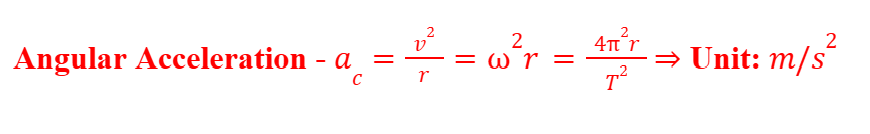
Centripetal Force
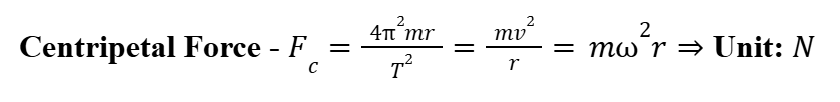
Impulse
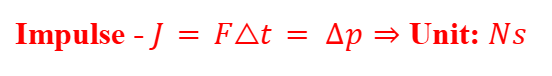
Elastic Collisions
All Kinetic Energy and Momentum of one object passes to the colliding object (Kinetic Energy is conserved).
Inelastic Collisions
Kinetic Energy is not conserved in the collision.
Explosions
The momentum of the projectile is equal and opposite to the momentum of the firing device (recoil).
Work
The work done on an object is the force applied to move the object in the direction of the force.
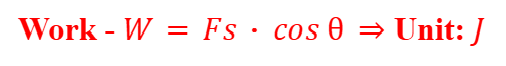
Kinetic Energy
The kinetic energy is the energy stored in the body when it is in a state of motion.
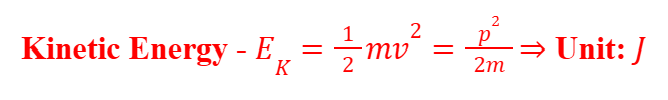
Gravitational Potential Energy
The gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in a body due to the effects of gravity.

Elastic Potential Energy
The elastic potential energy is the energy stored in any elastic body i.e. a body that returns to its original shape after the external force is removed.
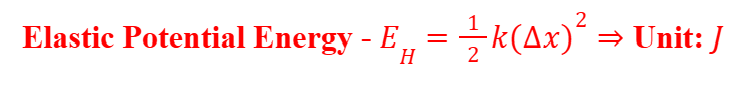
Conservation of Energy
Kinetic Energy = Potential Energy
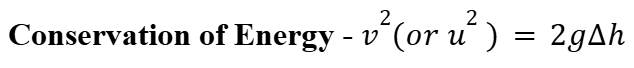
Power
The work done per unit time
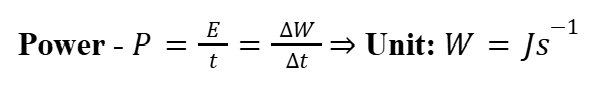
Power needed to maintain a constant velocity

Efficiency
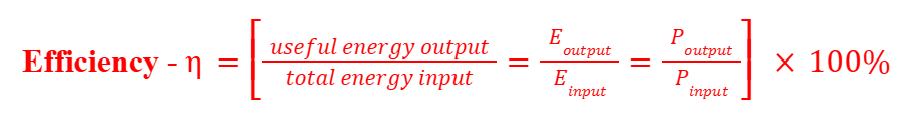
Energy Density
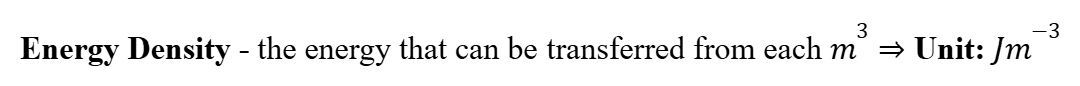
Torque (in formula booklet)
A measure of the rotational force applied to an object, calculated as the product of the force and the distance from the pivot point.
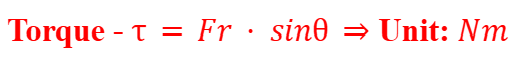
Couple
A couple is a pair of equal-sized forces that have different lines of action but are parallel to each other and act in opposite directions, either side of the axis of rotation.
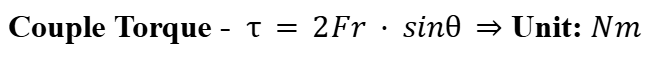
Angular Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration
The change in angular position of a rotating object, measured in radians. Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular displacement, while angular acceleration is the rate of change of angular velocity.
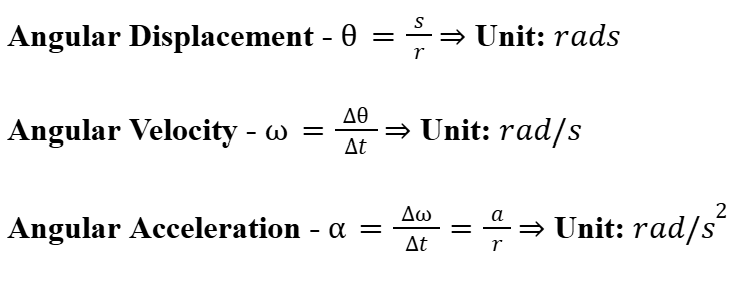
Angular S.U.V.A.T. Equations
A set of equations that relate angular displacement, angular velocity, angular acceleration, and time for rotational motion, similar to linear S.U.V.A.T. equations.
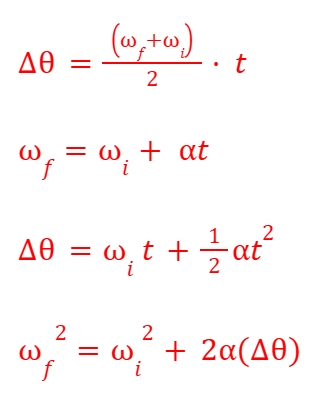
Moment of Inertia
A measure of an object's resistance to changes in its rotation, calculated as the sum of the products of each mass element and the square of its distance from the axis of rotation.
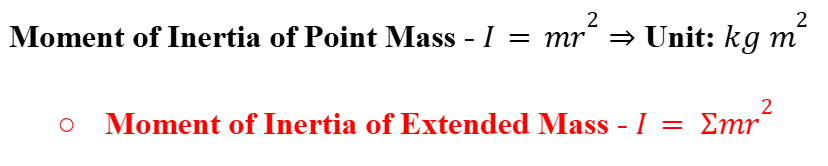
Moment of Solid Cylinder, Disk or Ring

Moment of Solid Sphere

Second Law of Rotational Motion

Angular Momentum
The angular momentum of any closed/isolated system is conserved if there is no resultant torque.

Angular Impulse
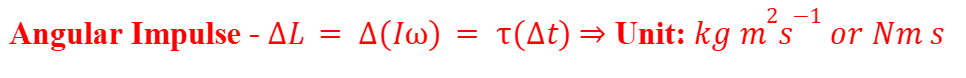
Rotational Kinetic Energy
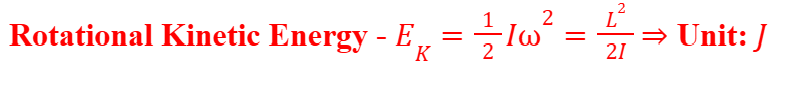
Conservation of Energy down a Slope
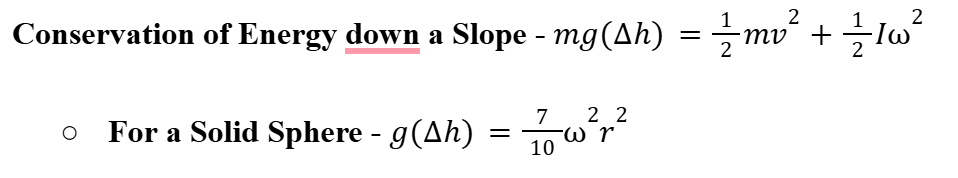
1 Revolution per Second in Rad/s
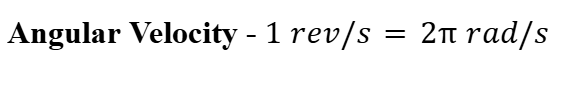
Reference Frame
A reference frame is a set of coordinate axes and clocks at all points in space. A non-accelerating frame is called an inertial frame of reference.
Galilean Distance Transformation

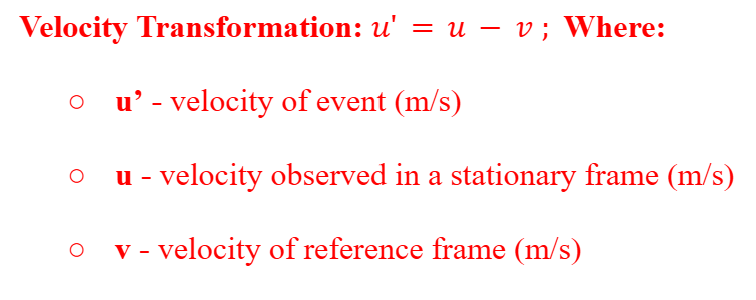
Galilean Velocity Transformation
Galilean Time Transformation

Postulates of Special Relativity
All laws of physics remain the same in all inertial frames.
The speed of light in a vacuum is constant in all frames.
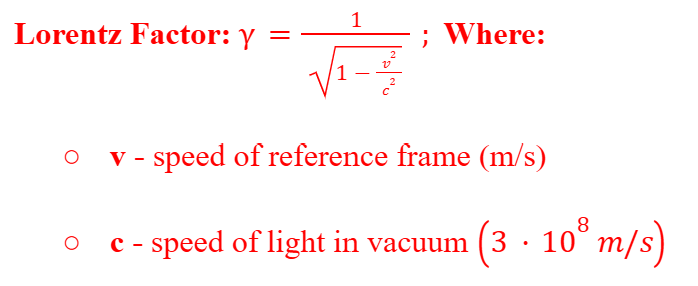
Lorentz Factor
Relativistic Distance Transformation

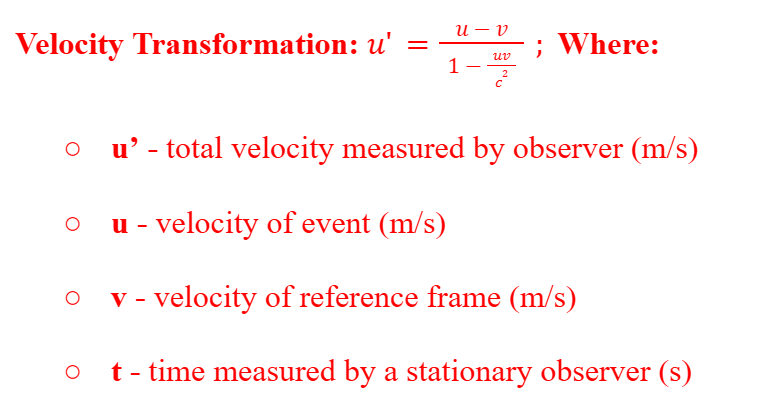
Relativistic Velocity Transformation
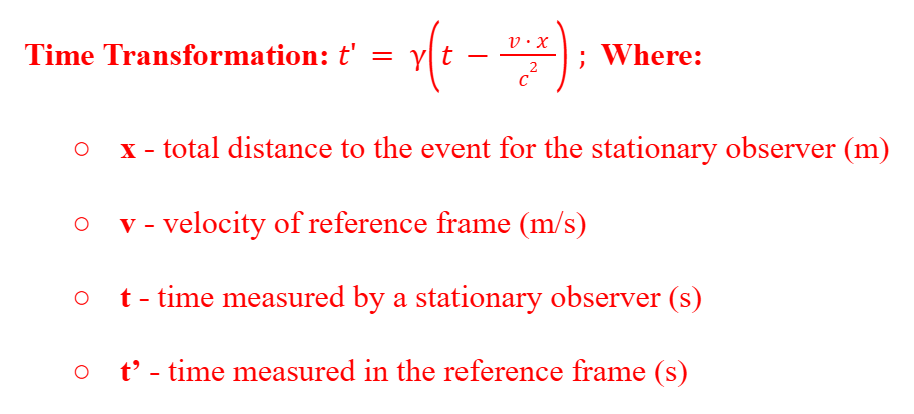
Relativistic Time Transformation
Spacetime Interval
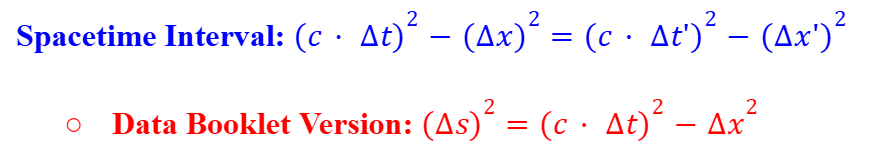
Spacetime Coordinate Differences

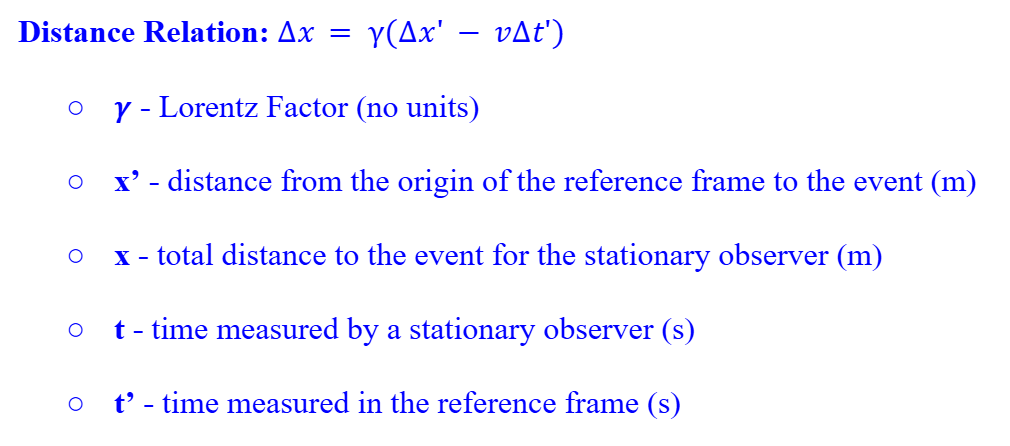
Distance Relation
Time Relation

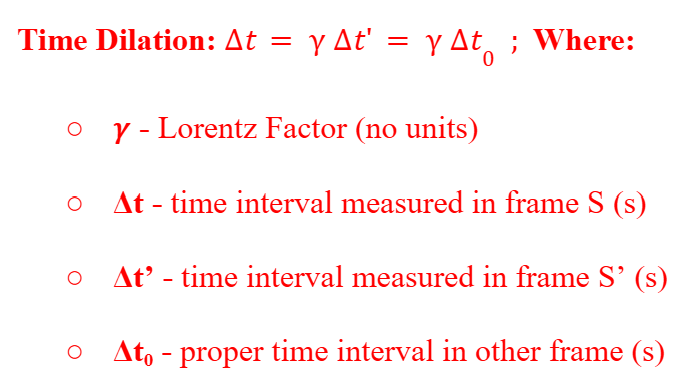
Time Dilation
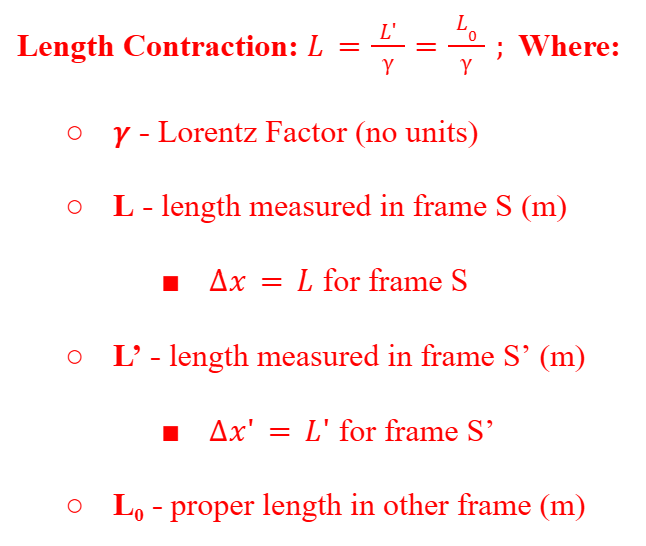
Length Contraction
Proper time and Proper Length
A proper time interval is the time between two events that take place at the same point in space.
A proper length is the length measured when the object is at rest. The object's rest frame is the reference frame where the object is at rest. Only the lengths in the direction of motion are contracted.
Simultaneity
If two events occur simultaneously in frame S’ with a time interval of 0, then the following equation is the time interval in frame S.
If x' = 0, the events will not be simultaneous in other frames.
If x = 0 i.e. the simultaneous events occur at the same point in space, thus they are simultaneous in all frames of reference.

Angle of the Wordline
The angle of the wordline cannot exceed 45o.

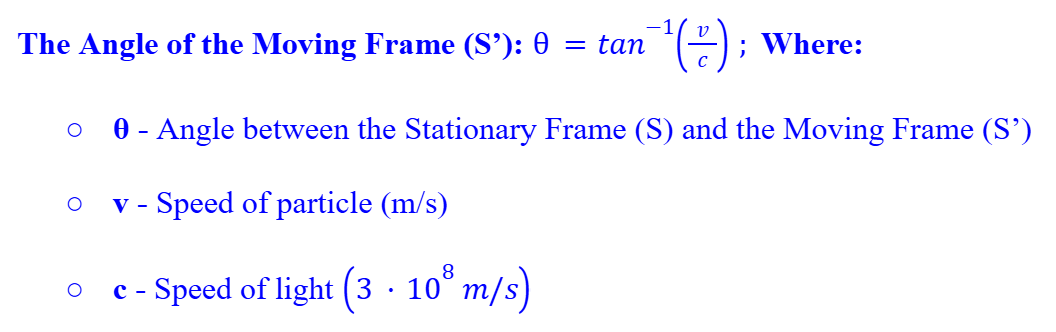
Angle of Moving Frame
The angle of the moving frame cannot exceed 45o.
Causation in Spacetime Diagrams
An event ‘E’ can cause event ‘L’ if the time separating ‘E’ and ‘L’ is greater than or equal to the travel time of a photon from the position of ‘E’ to ‘L’.
Scale Relation of Axes in Different Frames
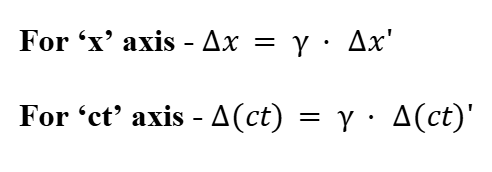
Length Contraction in Spacetime Diagrams
Draw a line parallel to the (ct)’ axis at the start and end of the length in the moving frame and extrapolate it towards the x-axis in the stationary frame to find the proper length.
Draw a line parallel to the (ct) axis at the start and end of the length in the stationary frame and extrapolate it towards the (x’)-axis in the moving frame to find the contracted length.
Lengths are only contracted when in the direction of the velocity.
Time Dilation in Spacetime Diagrams
Draw a line parallel to the x-axis from the start and end points of (ct)’ in the moving frame and extrapolate it towards the (ct) axis to find the proper time.
Draw a line parallel to the (x’)-axis from the start and end points of (ct) in the stationary frame and extrapolate it towards the (ct)’ axis to find the dilated time.
Simultaneity in Spacetime Diagrams

Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to heat an object by 1K or 1oC without resulting in a change of state.
Heat Energy

Average Kinetic Energy

Law of Conservation of Heat
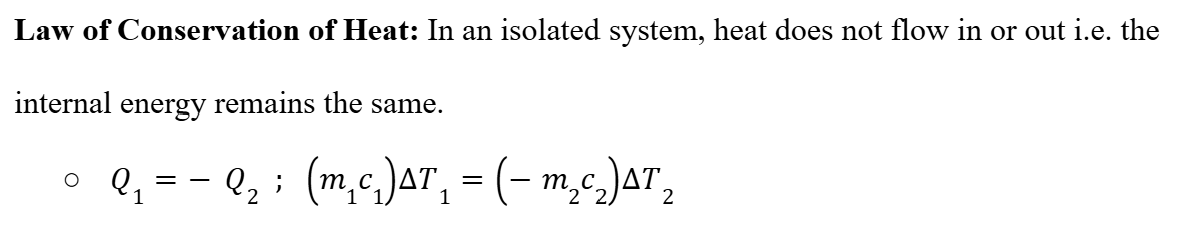
Internal Energy Formula
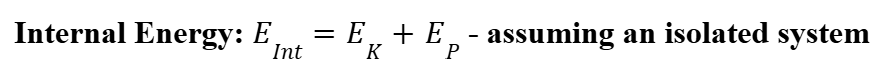
Specific Latent Heat

Specific Latent Heat Equation

Total Heat Energy
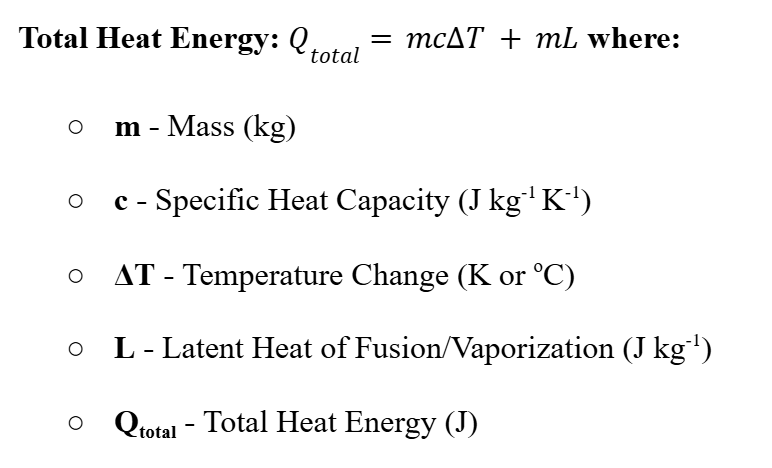
Thermal Conduction
Heat transferred through direct contact. Needs a medium.
Thermal Convection
Heat transferred through fluid motion due to temperature differences. Needs a medium.
Thermal Radiation
Heat transferred through electromagnetic waves like visible light and infrared radiation. Does not need a medium.
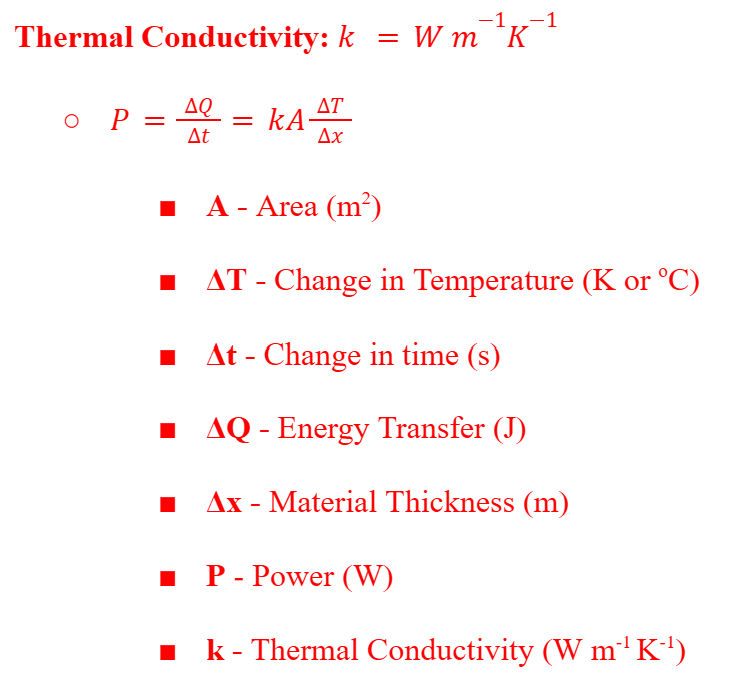
Thermal Conductivity
Stefan-Boltzmann Law

Wien’s Law

Apparent Brightness, Luminosity and Intensity

Apparent Brightness Equation

Power (Stars)

Net Power (Stars)

Emissivity
As emissivity decreases, the wavelength increases and the temperature decreases.
Intensity

Solar Constant

Albedo

Power reaching Earth

Average Incident Intensity

Average Intensity reaching Earth Formula

Average Intensity reaching Earth
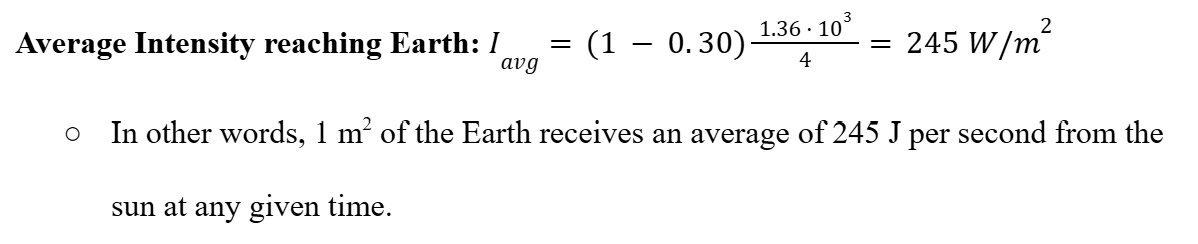
Intensity absorbed by Earth

Intensity reflected by Earth

Intensity radiated back into Space
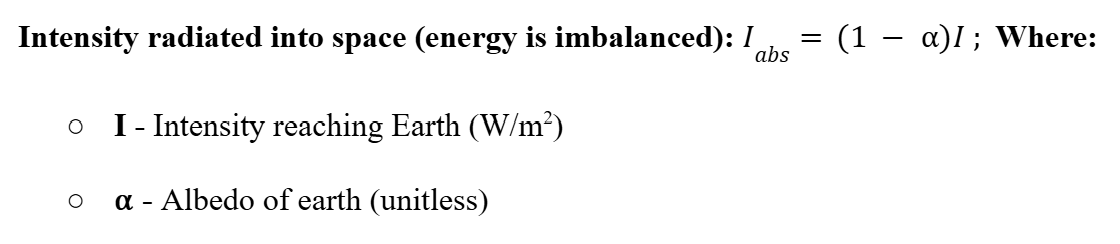
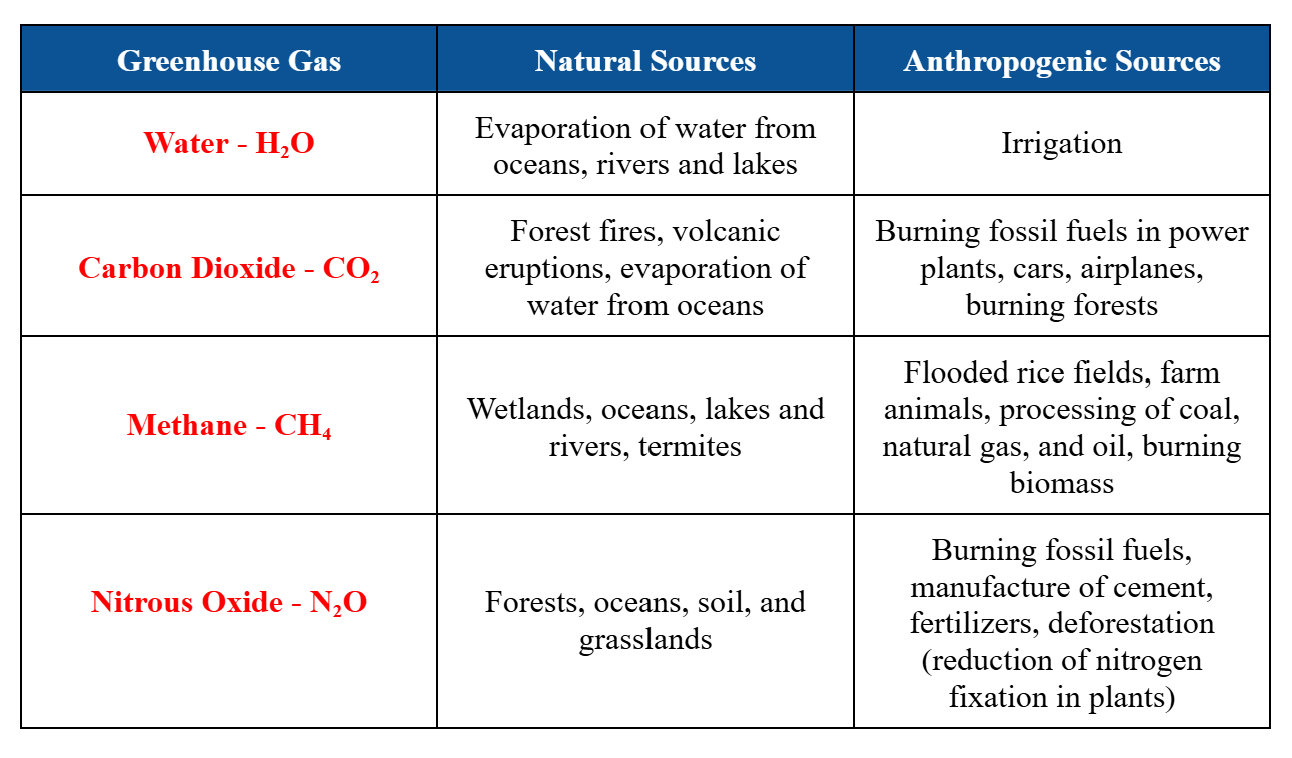
Common Greenhouse Gases
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
This refers to the additional warming caused by increased quantities of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The increase in gas concentrations is due to human activity and is closely related to the burning of fossil fuels.
Mechanism of Photon Absorption
Molecules have energy levels. The difference in energy between molecular energy levels is the energy of an infrared photon. These photons traveling through greenhouse gases are absorbed. The gas molecules that have absorbed the photons are now excited to higher energy levels.
The molecules, however, prefer to be in a low-energy state, so they immediately transition to a low-energy state by emitting the photons they absorbed. Not all photons are emitted to space; some are emitted towards the earth, thus warming the earth’s surface.
Energy absorbed by a Molecule
