APUSH chapter 1+2 vocab
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From textbook, class, and google. Take with a grain of salt.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Maize
A cereal plant that yields large grains, farmed in rows like corn
Base of Inca and Aztec farming
Hernán Cortéz
Led army of 600 men + non Aztec natives and marched on Tenochtitlán. Conquered Aztec empire
Columbian exchange
Global movement of plants, animals, + diseases around the world
Epidemics
Widespread and fast occurrence of disease in a community at a specific time.
Small pox
disease from the eastern hemisphere transmitted to communities in western hemisphere who had no immunities
Encomienda system
System that demanding labor and goods from natives by the Spanish.
Crown —> land grants to colonists —> colonists demand tribute in exchange for protection and christian instruction
Corn
Important crop grown by Natives. Provided easy food and fuel for fires.
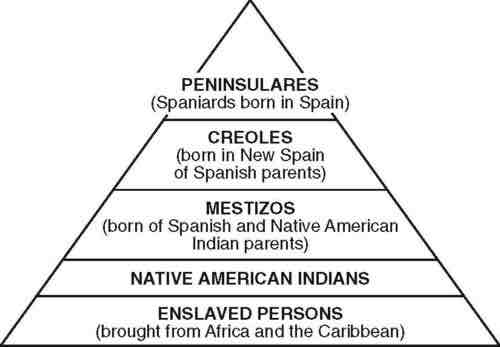
Casta system
Hierarchal ordering of racial groups based on how much Spanish blood they had. Power flowed from the top
Chattel slavery
Ownership of human beings as property
Neo-Europes
Colonies where Colonists tried to replicate or get very close to the social structures and economies of Europe
Mercantilism
Economic relationship between imperial country and its colonies to benefit the imperial country by creating favorable balance of trade
Atlantic slave trade
enslaving and trading of people from Africa, then shipping them primarily to the new world.
Potatoes
A super food, nutrient dense and good carbs.
Fed a ton of people in Europe and America
Semi Sedentary societies
Central fields and villages that were occupied seasonally
Mississippian culture
Native American culture in the Mississippi River Basin and the Southeast.
Characterized by mound-building, maize agriculture, distinctive pottery styles.
Complex chiefdoms
Eastern woodlands
Culture area of Native Americans
Atlantic ocean west to Great Plains and Great Lakes to Gulf of Mexico
Semisedentary, agriculture based on maize, beans, and squash
Mostly chiefdoms
Algonquian
Native American language family widespread in the eastern woodlands, great lakes, + subarctic regions.
NOT THE ALGONQUINS
Iroquois confederacy
Powerful group of Natives in the East of the U.S. made up of five nations: Mohawk, Seneca, Cayuga, Onondoga, + Oneida
Great lakes
Five big interconnected freshwater lakes
Ontario, Erie, Huron, Michigan, Superior
In era b4 long distance land travel, they were center of continents transportation system
Great plains
broad plateau region from central Texas to Canada
Primarily grasslands that support grazing but not agriculture
Rocky mountains
Mountain range spanning 3k miles
Natives fishes, gathered roots and berries, and hunted elk, deer and bighorn sheep.
Silver mining boomed in the Rockies in the 19th century.
Great basin
Arid region.
All its water drains or evaporates in the basin.
Resource scarce
Thinly populated by hunter/gather societies
Comanche
Native American tribe of equestrian nomads in the Great Plains
Sioux
Broad alliance or Native Americans who spoke three related languages /w in the Siouan language family.
Anasazi
“Ancient Outsiders” that originated in the four corners regions.
Sedentary people
Ancestors or the Pueblo Indian
Pueblos
Tribe located in the Southwest who lived in adobe housing and were canal builders.
Animist
Spiritual beliefs centering around the natural world.
Cahokia
1100 AD
Mississippian settlement home to as many as 25k Natives.
Better compared to European towns than other Native settlements.
Green corn ceremony
Ceremony held when the corn ripened in late July.
A time ir community building, rekindling friendships, restoring balance, giving praise and thanks to god.
Matriarchy
Political arrangement where a community is ruled by women
Christianity
Religion holding the belief that Jesus Christ was divine.
For centuries the Roman Catholic Church was the unifying institution in Western Europe
Christianity Europe —> Americas
Crusades
Series of military expeditions in the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries by Western European Christians to regain control of the Holy Lands from the Muslims
Protestant Reformation
Reform movement beginning /w Martin Luthers critique of the Roman Catholic Church in 1517
Began a divide between Protestants and Catholics
Plantation system
Form of estate agriculture using slave labor pioneered by Italian merchants and crusading knights in 12Th century
Primogeniture
Legal principle the oldest son inherits all family property or land
Caravel
Small vessel /w a high deck and three triangle sails
Allowed European sailors to explore easier and more reliably.
Joint-stock companies
Short term partnership between multiple investors to fund a commercial enterprise.
Safe way to invest money
If went bad only the money u invested could be taken. They would not come for ur property or belongings
Tenochtitlan
Capital of the Aztec empire
Conquered by Cortes in 1521
Population was 150,000 before Spanish Conquest
Aztecs
Native American empire in present day Mexico.
Maintained control by trade and tribute.
Had advanced mathematics and writing
Human sacrifices for religious ceremonies
Pizzaro
Francis Pizzaro conquered the Incas
Killed Atahualpa —> claimed his empire
Incas
Advanced South American civilization that occupied present day Peru.
Developed sophisticated agricultural techniques (terrace farming)
Bartolome De Las Casas
A colonist/slave owner turned preacher who argued that the Spanish King should protect Native populations.
His writings persuaded King Charles V to make the “New Laws of the Indies for the Good Treatment and Preservation of the Indians”
New France
Region controlled by France by the Great Lakes to at furthest Mississippi.
Excelled in fur trade
Quebec
Founded in 1608 by Samuel de Champlain
A fur trading post
Fur trade
Trade with Natives that gave the french access to mink, otter, and beaver furs.
French provided manufactured goods
Luxury pelts were desirable
Beaver dominated the trade because it had soft “underfur” ghat matted into a dense mass. Used by European hat makers to make felt super strong and pliable that even broad brimmed hats held their shape.
—> beavers almost went extinct
Hurons
Iroquoius speaking, traded beaver furs to the french for manufactured goods like kettles and guns.
First focus of french catholic missionary activity.
Initially welcomed the french “Black Robes” but grew skeptical when their religion did not stop disease and drought.
Missionaries
spread gospel of the catholic church throughout south/central America + Mexico.
Drove a lot of European emigration to the US
Indentured servants
A very poor person obligated to a fixed term of unpaid labor. Drove majority of workforce for the Americas
Mississippi
Settled by the french
French founded New Orleans at the mouth of the Mississippi river
Louisiana
Robert de La Salle traveled down to the Gulf of mexico and named the area Louisiana after Louis XIV
New netherland
Colony founded by the West India Company
Banking
Dominated by the Dutch
New Amsterdam
Capital of New Netherlands on Manhattan Island.
Algonquian
A language family
Attacked New Netherland in retaliation and almost wiped them out, but the Dutch attacked back much harder
West India Company
Founded by the Dutch government to create the colony of New Netherland. Oversaw New Netherland until it abandoned it
Iroquois/Haudenosaunee
Capitalized on their strategic location in central New York to trade /w both Dutch and French. Got guns and goods from the Dutch
Terrorized their neighbors.
Waged war against the Hurons, Neutrals, Eries, and Suquehannocks.
Beaver wars.
Beaver Wars
conquest of the Iroquois against other Native settlements.
Wiped out the Hurons.
Dominated Native groups from New England to the Carolinas and to Quebec.
Dramatically altered the map of northeastern North America.
Jamestown
A swampy peninsula named Jamestown to honor the king.
Many people died because they lacked fresh water and refused to plant crops.
Virginia company
Was granted all the land from north carolina to southern new York in 1606.
Named the region Virginia after the “Virgin Queen”
A joint stock company
Virginia
land from north carolina to southern new York in 1606.
Named the region Virginia after the “Virgin Queen”
first successful colony of the Brits
House of Burgesses
Government in colonial Virginia made up of an assembly of representatives elected by the colony’s inhabitants.
Indian War of 1622
War sparked by influx of migrants to Virginia.
Opechancanough (Powhatan’s successor) waged war on the Englishmen and killed almost a third of their population. English called them savages and declared war.
Took control of indian lands and made them slaves
—> virginia became a royal colony
Royal Colony
In the english system, a colony chartered by the crown. Colony’s governor was appointed by the crown and served according to the instructions of the board of trade.
Maryland
A colony that became a refuge to catholics who fled England because King Charles 1 gave land to Lord Baltimore (a catholic)
Lord Baltimore
Cecilius Calvert, Lord Baltimore. A Catholic aristocrat who made Maryland a sanctuary for Catholics. Promoted growth in Maryland by importing artisans and giving land to wealthy migrants.
Persuaded assembly to grant the Tolerance Act
Maryland Act of Toleration
1649, Granted all christians the right to follow their beliefs and hold church services.
Land owned in its entirety, without feudal dues or landlord obligations. Freeholders had legal right to improve, transfer, or sell their lands.
Headright system
System of land distribution (50 acres) to anyone who paid the passage of a new arrival.
Large plants amassed huge landholdings as they imported large numbers of servants and slaves
Gentry
High social class, in england represents those just below nobility.
Tobacco
A plant native to the Americas.
Medicine and stimulant
Cash crop for Virginia colonists