Mechanical vent -Chapter 11: Hemodynamic Monitoring & Chapter 12: Methods to Improve Ventilation in Patient-Ventilator Management
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Which of the following describes the filling pressure of the ventricle at the end of ventricular diastole?
Preload
Which measurement is typically used to indicate right ventricular preload?
Right ventricular end-diastolic pressure (RVEDP)
Which of the following can be used to estimate the contractility of the ventricles?
Ejection fraction
Calculate the ejection fraction of a female patient with a stroke volume of 40 mL and an end-diastolic volume of 125 mL.
0.32
Which of the following is an indication of left ventricular afterload?
Systemic vascular resistance
What is the most determining factor for preload?
Venous return
Which of the following will cause an increase in systemic vascular resistance?
Increase left ventricular afterload
Which of the following is the main component of a hemodynamic monitoring system?
Strain gauge transducer
Which of the following is the function of the transducer in the invasive vascular monitoring system?
Convert the fluid pressure to an electrical signal
Which of the following statements is true concerning the insertion of a radial arterial line?
1. The catheter tip must face upstream.
2. The catheter tip must face downstream.
3. The transducer must be higher than the catheter tip.
4. The transducer must be level with the catheter tip
1,4
While checking an indwelling central venous pressure (CVP) catheter the respiratory therapist observes that the transducer is at the epistatic line. The respiratory therapist should do which of the following at this time?
Accept the CVP reading obtained
While attempting to draw blood from an indwelling arterial catheter, the respiratory therapist notices a dampened waveform and has difficulty withdrawing blood for sampling. What should the respiratory therapist's immediate action be?
Remove the catheter.
The respiratory therapist preparing to insert an arterial line in the right radial artery performs an Allen test. The result of the Allen test is 20 seconds. The respiratory therapist should do which of the following
Perform an Allen test on the left hand.
Which of the following is not a common complication of systemic artery catheterization?
Phlebitis
Which of the following measurements can be used to estimate right ventricular preload?
Central venous pressure
Confirmation of placement of a central venous pressure catheter is done with which of the following?
Chest radiograph
Which of the following can cause a low pulmonary artery occlusion pressure?
Hypovolemia
Which of the following are vessels that often require a surgical cut down when used for pulmonary artery catheter access
1. Femoral vein
2. Subclavian vein
3. Internal jugular vein
4.. Antecubital vein
2,4
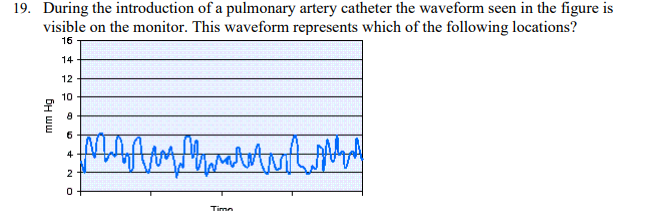
During the introduction of a pulmonary artery catheter the waveform seen in the figure is visible on the monitor. This waveform represents which of the following locations?
Right atrium
During the insertion of a pulmonary artery catheter, the balloon needs to be inflated with air when it enters which of the following?
Intrathoracic vessel
Which of the following include the most appropriate insertion sites for a pulmonary catheter in a patient with phlebitis?
1. Internal jugular vein
2. Subclavian vein
3. Antecubital vein
4. Femoral vein
1,2
Which of the following can occur with excessive pulmonary artery catheter movement?
Catheter knotting
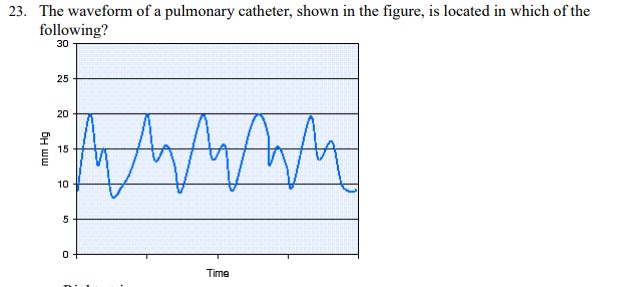
The waveform of a pulmonary catheter, shown in the figure, is located in which of the following?
Pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery catheter must be wedged in which of the following locations?
Zone 3
Which of the following is the range for the time a pulmonary artery catheter should be inflated?
15-30 seconds
Calculate the arterial oxygen content for a patient with the following arterial blood gas measurements: Hgb = 9 g%, arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) = 96%, arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) = 97 mm Hg.
11.9 vol%
Calculate the arterial oxygen content for a patient with the following arterial blood gas measurements: Hgb = 17 g%, arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) = 93%, arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) = 64 mm Hg.
21.4 vol%
A patient with an oxygen consumption of 340 mL/min, arterial oxygen content of 17.3 vol%, and mixed venous oxygen content of 12.8 vol% has a cardiac output of which of the following?
7.6 mL/min
Calculate cardiac output using the Fick principle for the following values:
Oxygen consumption 280 mL/min
Arterial oxygen content 19.5 vol%
Mixed venous oxygen content 12 vol%
3.9 L/min
A patient with the hemodynamic values below has a cardiac output of which of the following? Oxygen consumption 380 mL/min Arterial oxygen content 23.2 vol% Mixed venous oxygen content 10.3 vol%
2.9 mL/min
Calculate the cardiac index using the following data:
Cardiac output = 4.6 L/min
Body surface area = 1.2 m
Cardiac index (CI) = cardiac output (C.O.)/body surface area (BSA) Cardiac index (CI) = 4.6/1.2 Cardiac index (CI) =
3.8 L/min/m2
Calculate a 90-kg patient's cardiac index with the following measurements:
cardiac output 3.8 L/min,
body surface area 3 m2 .
1.3 L/min/m2
Calculate the cardiac index for a patient with the following data: heart rate = 80 beats/min,
stroke volume = 55 mL,
and body surface area = 2.8 m2 .
1.6 L/min/m2
Calculate the stroke index using the following data:
cardiac output = 3.7 L/min,
heart rate = 90 beats/min,
and body surface area = 1.7 m2
24 mL/m2
Calculate the stroke volume (SV) and the stroke volume index (SI) using the following information:
cardiac output = 4.5 L/min,
heart rate = 110 beats/min,
and body surface area = 1.3 m2 .
SV = 41 mL; SI = 31.5 mL/m2
If the heart rate is 80 beats per minute, how long is one beat?
1.3 second
Calculate the left ventricular stroke work index for a patient with a body surface area of 1.1 m2 , blood pressure 105/68 mm Hg, heart rate 86 beats per minute, and cardiac output of 4.3 L/min
49.6 g-m/m2
The hemodynamic values for a patient in the cardiovascular care unit are: blood pressure (BP) 96/60 mm Hg, pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) 29 mm Hg, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) 14 mm Hg, stroke volume (SV) 50 mL. The patient has a body surface area of 1.6 m2 . Calculate the patient's left ventricular stroke work Index (LVSWI)
LVSWI = [(MAP x SV) x 0.0136]/BSA
30.6 g-m/m2
Calculate the right ventricular stroke work (RVSW) given the following patient data: pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) = 35/25 mm Hg, cardiac output (C.O.) = 3.6 L/min, heart rate (HR) = 107 beats per minute, and body surface area (BSA) is 1.6 m2
12.7 g-m/m2
Calculate the right ventricular stroke work (RVSW) for a patient with the following measurements: pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) 50/32 mm Hg, cardiac output (C.O.) 4.0 L/min, heart rate (HR) 127/min, and body surface area (BSA) 1.72 m2 .
16 g-m/m2
The following hemodynamic measurements were obtained from a patient in the intensive care unit: pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) = 67/25 mm Hg, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) = 18 mm Hg, blood pressure (BP) = 100/50 mm Hg, central venous pressure (CVP) = 17 mm Hg, cardiac output (C.O.) = 5.7 L/min, and heart rate (HR) = 75 beats/min. Calculate this patient's pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR)
253 dyne x sec x cm x 5
Calculate the pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) given the following measurements obtained during a hemodynamic study: pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) = 40/22 mm Hg, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) = 12 mm Hg, blood pressure (BP) = 156/80 mm Hg, central venous pressure (CVP) = 19 mm Hg, cardiac output (C.O.) = 4.8 L/min, and heart rate (HR) = 68 beats/min.
267 dyne sec cm -5
The following hemodynamic measurements were obtained from a patient in the intensive care unit: pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) = 67/25 mm Hg, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) = 18 mm Hg, blood pressure (BP) = 100/50 mm Hg, central venous pressure (CVP) = 17 mm Hg, cardiac output (C.O.) = 5.7 L/min, and heart rate (HR) = 75 beats/min. Calculate this patient's systemic vascular resistance (SVR).
698 dyne sec cm5
Calculate the systemic vascular resistance (SVR) given the following measurements obtained during a hemodynamic study: pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) = 40/22 mm Hg, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) = 12 mm Hg, blood pressure (BP) = 156/80 mm Hg, central venous pressure (CVP) = 19 mm Hg, cardiac output (C.O.) = 4.8 L/min, and heart rate (HR) = 68 beats/min.
1438 dyne sec cm5
A patient with a mitral valve stenosis is most likely to have which of the following pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) values?
20 mm Hg
Which of the following is the hemodynamic measurement that is indicative of a patient with right heart failure?
Central venous pressure (CVP) = 16 mm Hg
Which of the following disorders can cause an increase in systemic vascular resistance?
Hypervolemia
Which of the following hemodynamic parameter that is not within normal limits?
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) = 18 mm Hg
A high cardiac output can cause which of the following complications with a pulmonary artery catheter?
Catheter whip
Advancing a pulmonary artery catheter into a smaller artery may cause which of the following complications?
Pulmonary infarction
During the inspiratory phase of spontaneous breathing, what happens to the pulmonary artery (PA) waveform?
The PA waveform trend decreases.
An intubated patient with no known history of congestive heart failure is in the ICU. The patient is comatose and currently receiving mechanical ventilation via volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation (VC-CMV), set rate 12 breaths/min, set tidal volume (VT) 400 mL, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 18 cm H2O, fractional inspired oxygen (FIO2) 0.35, and the patient is not assisting. Hemodynamic measurements show the following: central venous pressure (CVP) 5 mm Hg, pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) 33/20 mm Hg, and pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) 16 mm Hg. Arterial blood gas (ABG) results are: pH 7.43, arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) 38 mm Hg, arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) 90 mm Hg. The physician asks for recommendations to improve this patient's hemodynamics. The most appropriate recommendation for this patient is which of the following?
Decrease the PEEP incrementally and recheck hemodynamic measurements.
A patient in the ICU has a chest X-ray that shows bilateral infiltrates and has the following hemodynamic measurements: central venous pressure (CVP) 5 mm Hg, pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) 24/13 mm Hg, and pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) 21 mm Hg. These findings are consistent with which of the following?
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
A patient in the ICU has a chest X-ray that shows bilateral infiltrates and has the following hemodynamic measurements: central venous pressure (CVP) 3 mm Hg, pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) 21/10 mm Hg, and pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) 8 mm Hg. These findings are consistent with which of the following?
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Ventricular contractility can be estimated by which of the following?
Ejection fraction
Which of the following can cause an elevated right arterial pressure?
Cardiac tamponade
During mechanical ventilation of a patient with COPD, the PaCO2 = 58 mm Hg and the minute ventilation = 5.5 L/min. The desired PaCO2 for this patient is 45 mm Hg. To what should the minute ventilation be changed?
7.1 L/min
A patient with CHF is being mechanically ventilated. The patient's current PaCO2 = 28 mm Hg, and the ventilator set rate is 16 per minute. The desired PaCO2 for this patient is 40 mm Hg. To what should the set rate be changed?
11/min
A patient with pneumonia and underlying COPD is being mechanically ventilated in the VC-CMV mode with VT 650 mL. The resulting PaCO2 is 62 mm Hg. What change should be made to the VT to obtain a desired PaCO2 of 50 mm Hg for this patient?
800 mL
The average tidal volume range in an individual with no pulmonary problems is which of the following?
6-8 mL/kg IBW
A male patient (76-kg IBW) with no history of pulmonary disease is brought to the emergency department for treatment of a drug overdose. He is intubated and placed on mechanical ventilation with VC-CMV, f = 12/min, VT = 450 mL. The resulting arterial blood gas values are: pH 7.32, PaCO2 53 mm Hg, and HCO3 25 mEq/L. The most appropriate action to correct the acid-base disturbance is which of the following?
Increase VT to 595 mL
A female patient (59-kg IBW) with no history of pulmonary disease is being invasively ventilated with VC-CMV, f = 12/min, VT = 470 mL, PEEP = 5 cm H2O, FIO2 = 0.5. ABG results with these settings are: pH 7.31, PaCO2 54 mm Hg, PaO2 92 mm Hg, SaO2 90%, HCO3 24 mEq/L. The most appropriate action for the respiratory therapist to take is which of the following?
Increase f to 16/min
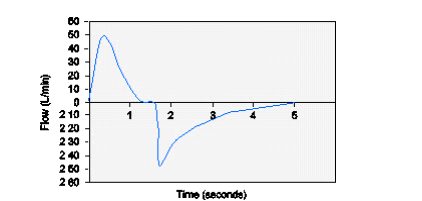
A male patient (74-kg IBW) is being ventilated with PC-CMV, f = 12/min, PIP = 20 cm H2O, TI = 1.5 seconds; the resulting flow-time scalar is shown below. The patient's measured VT is 435 mL. ABG results on these settings are: pH 7.32, PaCO2 54 mm Hg, HCO3 25 mEq/L. The most appropriate action to take is which of the following?
Increase PIP to 27 cm H2O
A 28-year-old female (55-kg IBW) is being mechanically ventilated with VC-CMV, f = 14/min, VT = 700 mL. The patient has no history of pulmonary disease. The resulting ABG values are: pH 7.55, PaCO2 27 mm Hg, HCO3 23 mEq/L. The most appropriate action to take is which of the following?
Decrease VT to 440 mL
A male patient (83-kg IBW) is intubated and ventilated with PC-CMV, f = 12/min, set PIP = 28 cm H2O, resulting in a VT of 430 mL. The ABG results on this setting are: pH 7.35, PaCO2 45 mm Hg, and HCO3 23 mEq/L. Forty-eight hours later on the same settings, the ABG results are: pH 7.54, PaCO2 27 mm Hg, and HCO3 21 mEq/L with an exhaled VT of 800 mL. The most appropriate action at this time is which of the following?
Decrease PIP to 19 cm H2O
A patient with an IBW of 68 kg is intubated and being mechanically ventilated with VC-CMV, f = 12/min, and VT = 470 mL. The patient has a combined respiratory rate of 25/min. The ABG results are: pH 7.56, PaCO2 26 mm Hg, and HCO3 22 mEq/L. The most appropriate action is to do which of the following?
Change the mode to VC-IMV.
Which of the following can cause metabolic acidosis?
Overdose with salicylate
Which of the following can cause metabolic alkalosis?
Potassium deficiency
If respiratory acidosis persists after alveolar ventilation of a patient has been increased, which of the following could be the cause?
Pulmonary embolism
A 59-kg IBW female patient is being mechanically ventilated in the CMV mode, f = 12/min, VT = 400 mL, PEEP = 5 cm H2O, FIO2 = 0.5. The ABG results on these settings show a respiratory acidosis and severe hypoxemia. The respiratory therapist increases the set VT and increases the PEEP to 12 cm H2O. The resulting ABGs show improved oxygenation, but the patient still has a respiratory acidosis. The respiratory acidosis may be due to which of the following?
Increased dead space
A patient diagnosed with sepsis who is being mechanically ventilated has a combined minute ventilation of 25 L/min with a PaCO2 of 38 mm Hg. The reason for these findings is most likely which of the following?
1. Increased CO2
2. Decreased CO2
3. Increased VD/VT
4. Decreased VD/VT
1,3
In which of the following situations might iatrogenic hyperventilation be considered?
Acute neurological deterioration with increased intracranial pressure
Permissive hypercapnia could benefit patients with which of the following?
Acute lung injury
A 45-year-old female (58-kg IBW) with a past medical history of asthma arrives at the emergency department short of breath, anxious, diaphoretic, and unable to perform a peak expiratory flow measurement. She also has a combined acidosis. Breath sounds reveal the patient is not moving much air. The patient is intubated, stabilized, and transported to the ICU. The ventilator settings are: PC-CMV, f = 12/min, PIP = 30 cm H2O, FIO2 = 0.6, and PEEP = 3 cm H2O. The patient is sedated and paralyzed; the resulting ABGs are: pH 7.17, PaCO2 69.3 mm Hg, PaO2 90 mm Hg, and HCO3 21 mEq/L after continuous bronchodilator therapy. The respiratory rate is increased to 20/min, and the next ABG results are: pH 7.26, PaCO2 58 mm Hg, PaO2 96 mm Hg, and HCO3 22 mEq/L. The respiratory therapist should suggest which of the following at this time?
Continue with current therapy
At what point during deep suctioning should negative pressure be applied?
After 1-cm withdrawal from the point of resistance
A suction catheter long enough to reach a mainstem bronchus should be what length?
56 cm (22 inches)
What size suction catheter is appropriate for use in a patient with a 7-mm ET tube
10 Fr
Advantages of closed suctioning include which of the following?
1. No need to prehyperoxygenate.
2. No need to posthyperoxygenate.
3. Decreased risk of infection for caregiver.
4. No loss of PEEP during the procedure
3,4
During a closed suctioning procedure, the patient's heart rate changes from 95 to 58 beats/min. The respiratory therapist should take what immediate action?
Stop the procedure and use the ventilator to hyperoxygenate the patient with 100% oxygen
Which of the following is an advantage of using a vibrating mesh nebulizer when administering aerosols to mechanically ventilated patients?
Devices produce smaller aerosol particles than pMDIs and SVNs without the addition of gas into the ventilator circuit
When using an SVN or pMDI with NIV, where in the NIV circuit should the device be placed to obtain the greatest aerosol deposition?
Between the leak port and the face mask
Which of the following ventilator graphics could be used to assess the response to bronchodilator therapy for a patient receiving mechanical ventilation with VC-CMV?
1. Pressure-time scalar
2. Flow-time scalar
3. Pressure-volume loop
4. Volume-time scalar
1,2,4
A mechanically ventilated patient continues to have rhonchi after deep suctioning. The respiratory therapist should recommend which of the following?
Vest Airway Clearance System
A physician and a respiratory therapist are performing bedside bronchoscopy of an invasively ventilated patient. Fentanyl and midazolam were used for conscious sedation. After the bronchoscopy, the patient is not arousable. Which of the following should be done at this time?
Administer naloxone.
Which of the following is the normal ratio of dead space to tidal volume (VD/VT)?
0.2-0.4
What effect does positive-pressure ventilation have on fluid balance?
It increases plasma ADH levels
Which of the following suggests and increased dead space in a patient receiving mechangical ventilation?
a. An iccrease in EtCO2 and an decrease in the PaCO2-to-PetCO2 gradient
b. A decrease in EtCO2 and an decrease in the PaCO2-to-PetCO2 gradient
c. A decrease in EtCO2 and an increase in the PaCO2-to-PetCO2 gradient
d. An increase in EtCO2 and an increase in the PaCO2-to-PetCO2 gradient
A decrease in EtCO2 and an increase in the PaCO2-to-PetCO2 gradient
Normal Value for Systolic Arterial Blood pressure?
90-140 mm Hg
Normal Value for Diastolic Blood pressure?
60-90 mm Hg
Normal MAP?
70-100 mm Hg
Formula for pulse pressure?
Systolic - Diastolic
Formula for Stroke Volume?
CO / HR
Formula for Stroke index?
SV / BSA
Formula for Cardiac Index?
CO / BSA
Formula for MAP?
(Systolic + (2 x Diastolic)) / 3
Formula for mPAP?
(Pulmonary artery pressure + (2 x Pulmonary venous pressure)) / 3
Formula for Systemic Vascular Resistance?
[( MAP-CVP] / CO) x 80
Formula for Pulmonary Vascular Resistance?
[ (mPAP - PAOP) / CO ] x 80
Formua for Ca02?
(Hemoglobin x 1.34 x SaO2) + (PaO2 x 0.003)
Formula for Cv02?
(Hemoglobin x 1.34 x SvO2) + (PvO2 x 0.003)