Fun. I - Epithelial Tissue
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What are the 4 major types of Tissues?
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Muscular
- Nervous
What are the 4 essential processes for generation of a Multicellular Organism?
- Proliferation
- Specialization
- Interaction
- Movement
Histogenesis
Development of Tissues
Histogenesis begins at ____.
gastrulation
Gastrulation
The process in which a gastrula develops from a blastula by the inward migration of cells
What are the 3 specialized layers of the Gastrula?
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
Ectoderm
Outermost Layer
- Neural Tissue
- Epidermis
Mesoderm
Middle Layer
- Connective Tissue
- Muscle
- Heart
Endoderm
Innermost Layer
- Lungs
- GI Tract
- Liver
- Pancreas
Epithelial Tissue
Sheets of cells covering all body surfaces/cavities
Connective Tissue
Collection of supporting cells and ECM that aid structure of other tissue
Tissue is basically a collection of ____ and ____.
cells/ECM
Muscle Tissue
Contractile cells that are responsible for movement
What are the 3 types of Muscle Tissue?
- Skeletal
- Cardiac
- Smooth
Skeletal Muscle
Striated and voluntary muscle attached to bone
Cardiac Muscle
Striated and involuntary muscle found in the wall of the Heart
Smooth Muscle
Non-Striated and involuntary muscle
Nervous Tissue
Receives, transmits, and integrates info to control and coordinate activities of the body
What are the 2 divisions of the Nervous System?
- CNS
- PNS
CNS
Central Nervous System
- Brain and Spinal Cord
PNS
Peripheral Nervous System
- Sensory and Motor Neurons
Light Microscopy
Any kind of microscope that uses visible light to observe specimens
Basic Steps of Tissue Preparation
(1) Fixation
(2) Dehydration
(3) Clearing
(4) Sectioning
(5) Staining
What are the 3 Stains used for Tissue Preparation?
- Hematoxylin (H)
- Eosin (E)
- Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS)
Hematoxylin (H)
Basic dye that stains basophilic structures blue/purple
Eosin (E)
Acidic dye that stains acidophilic structures red/pink
Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS)
Stains carbohydrates pink/red
The ____ is highly acidic, so it would be considered basophilic. This would require Hematoxylin for staining.
nucleus
Immunofluorescence
Use of antibodies tagged with fluorescent dye to identify the presence of a particular disease causing microbe
Basal Lamina
Thin extracellular layer that lies underneath epithelial cells and separates them from other tissues (typically connective tissue)
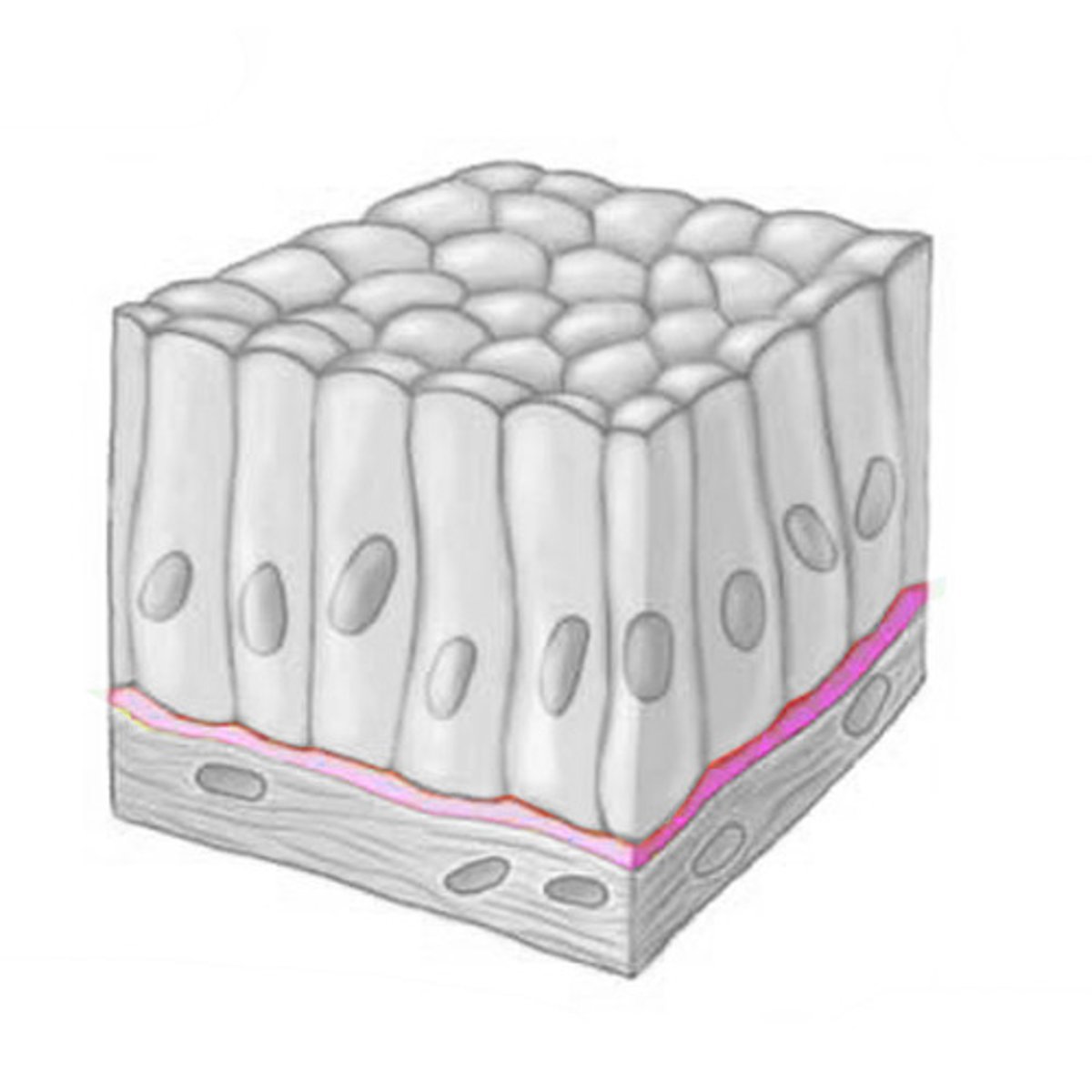
Cellular Junctions
Transmembrane proteins that bind cells together or to the ECM
Transmembrane Adhesion Proteins
Proteins that span the cellular membrane and link the cytoskeleton to extracellular structures
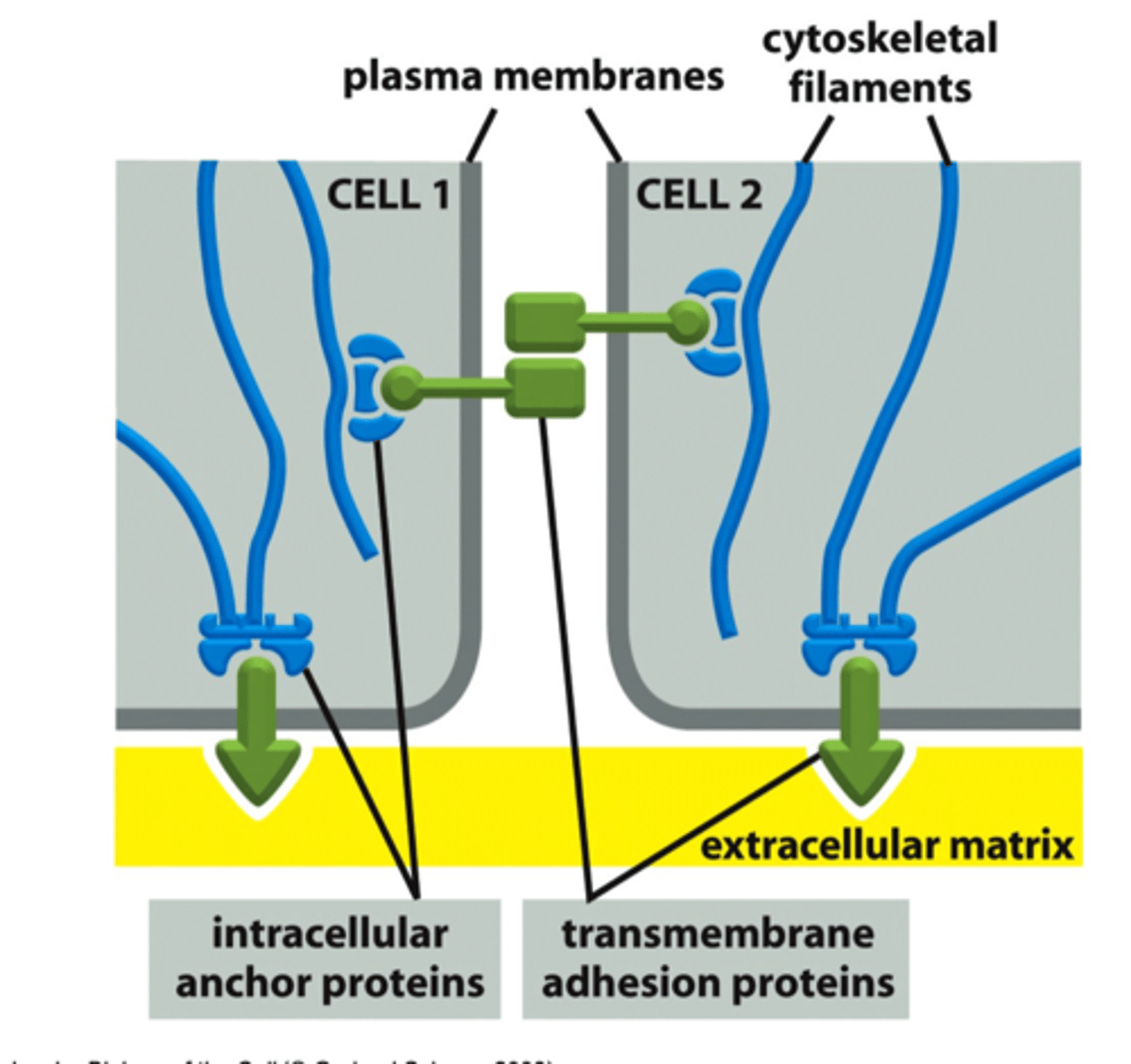
What are the 4 major Cell Adhesion Molecules?
- Cadherins
- Integrins
- Selectins
- Ig-Superfamily
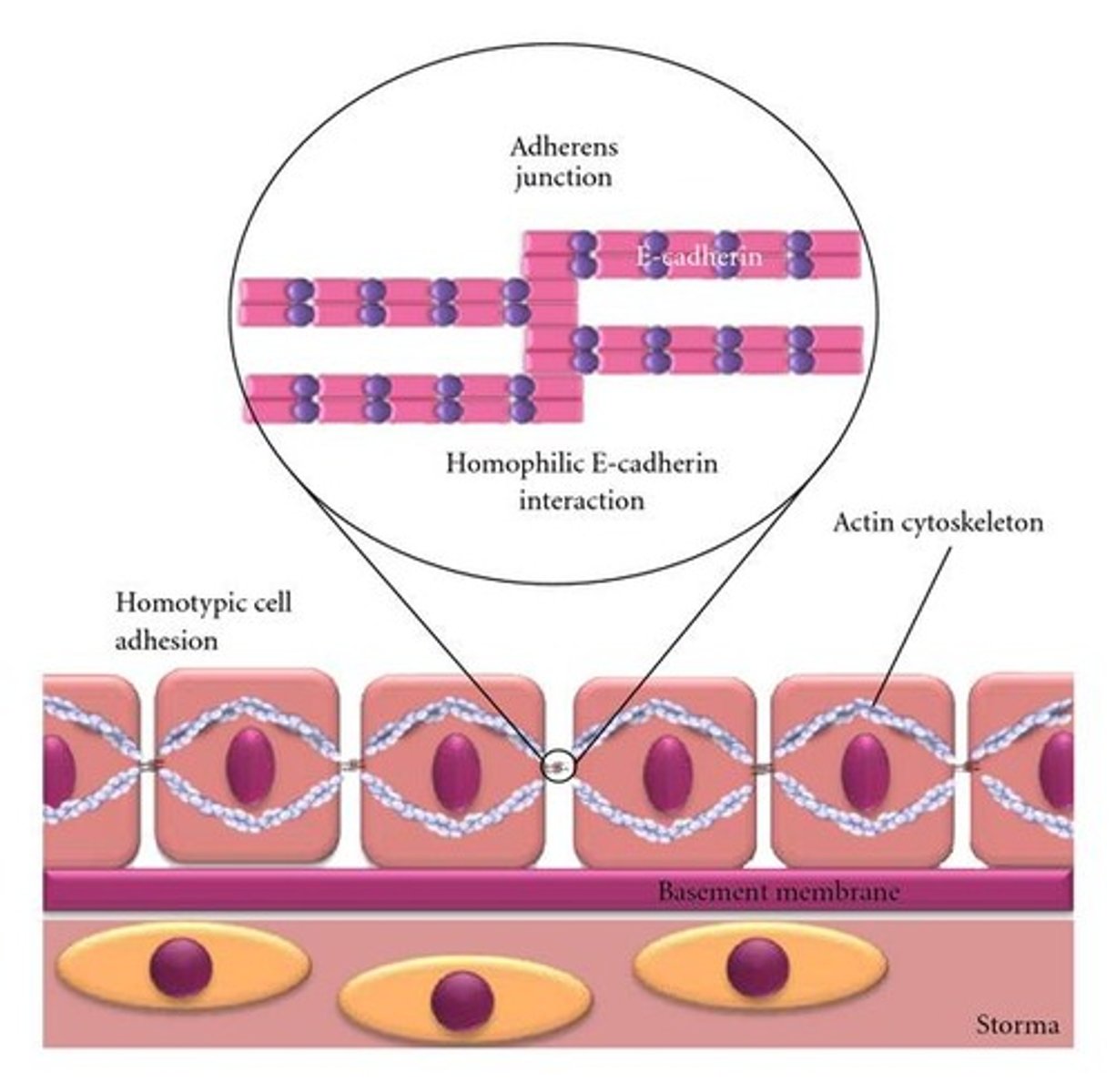
Cadherins
Calcium-Dependent glycoproteins that hold similar cells together
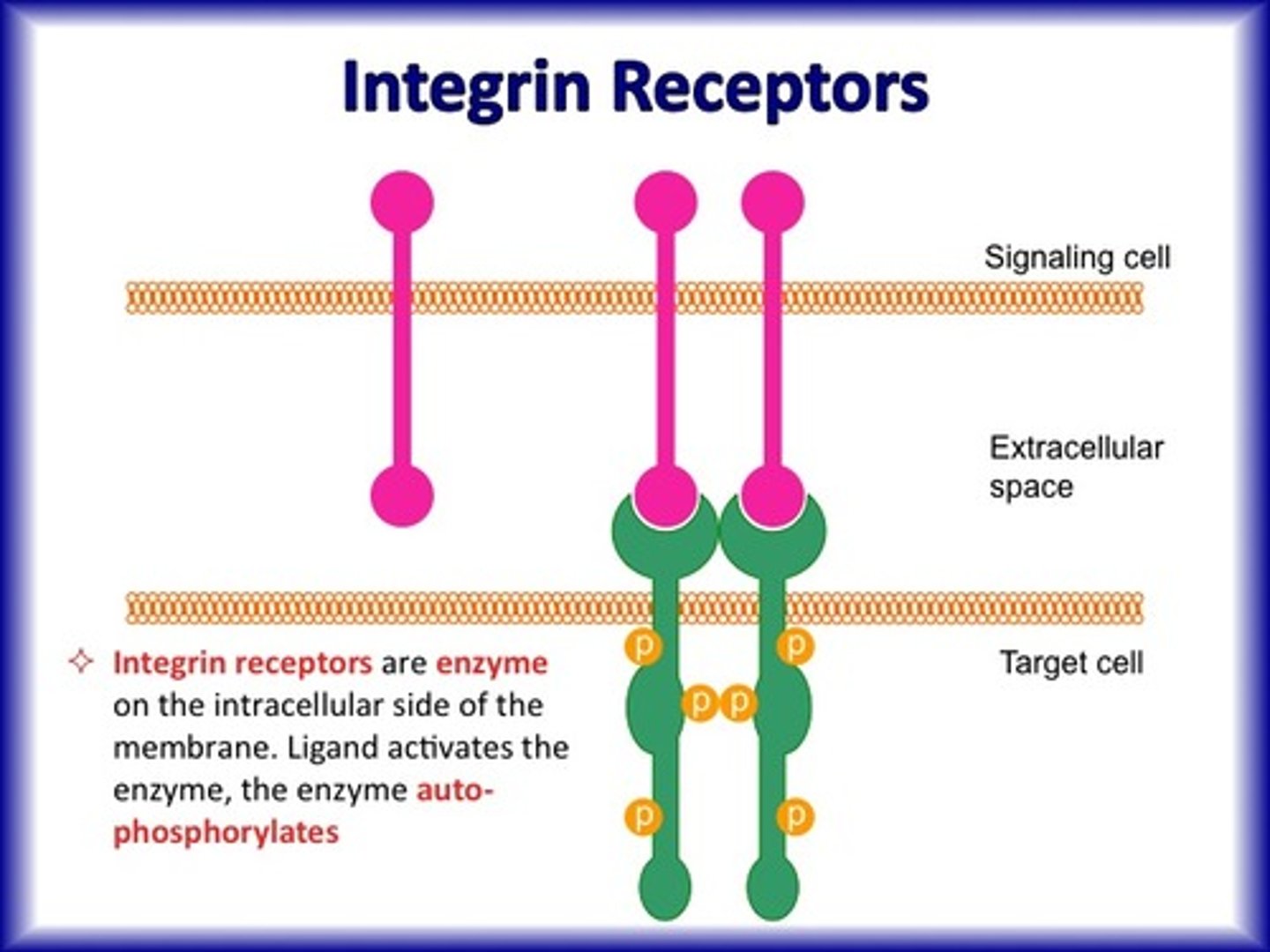
Integrins
Transmembrane protein that interconnects the ECM and cytoskeleton of a cell
Selectins
Transmembrane protein that binds carbohydrates on other cell surfaces
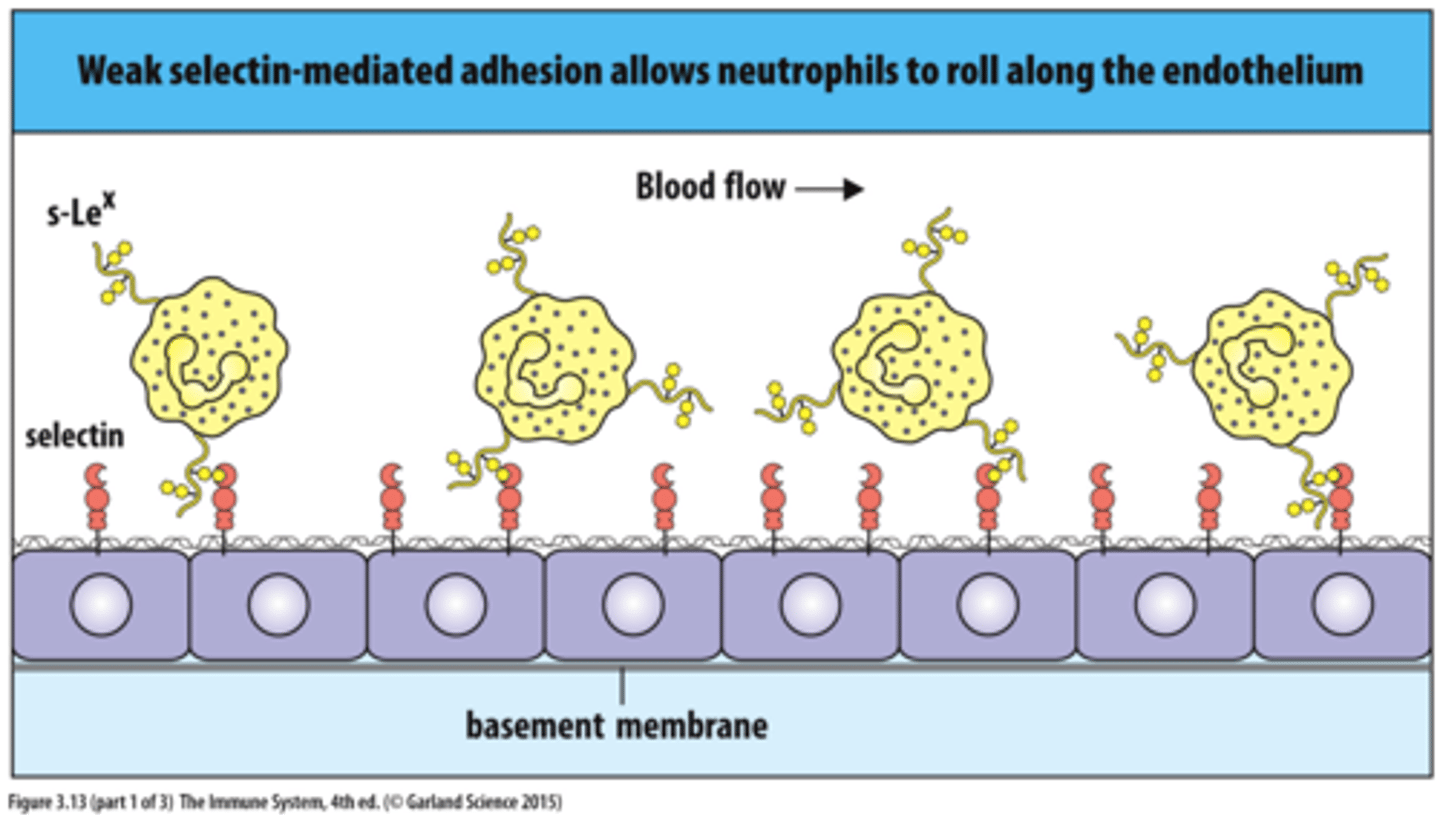
Selectins and Integrins play an important role in ____.
White Blood Cell Migration
White Blood Cell Migration
(1) Selectin-Dependent Adhesion and Rolling
(2) Adhesion and Emigration of WBC across barrier via Integrins
What are the 4 types of Junctions?
- Tight
- Anchoring
- Channel-Forming
- Cell-Matrix Anchoring
What are the 7 functions of the Epithelia?
- Protection: Epidermis
- Absorption: Digestive Tract
- Secretion: Glands
- Excretion: Kidneys
- Lubrication
- Sensory
- Reproduction: Sperm
The Epithelia is vascular (T/F)
False; Avascular
Cells are normally polarized. What does that mean?
Components of the cell are asymmetrically distributed, creating "poles"
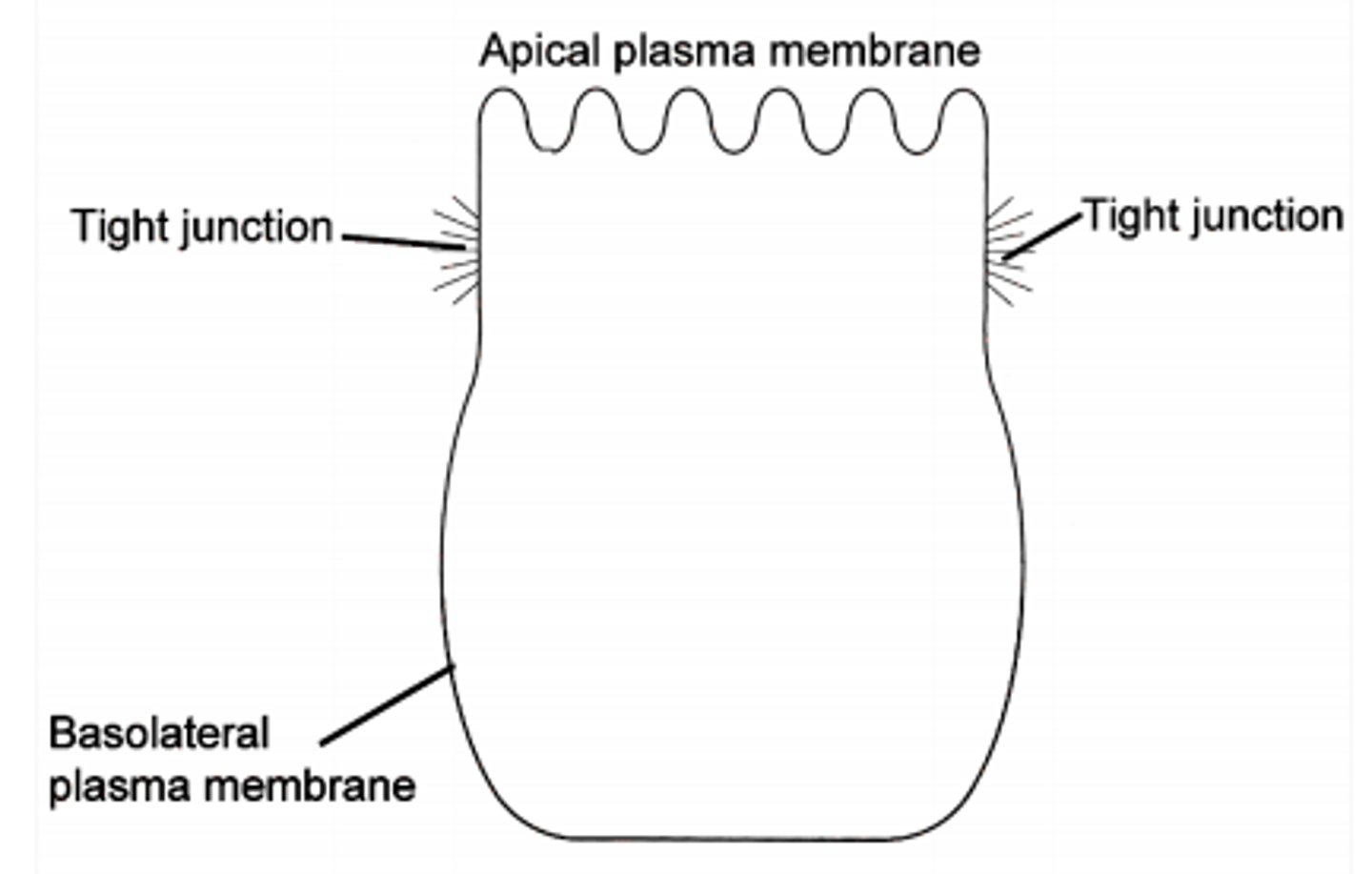
Apical Domain
The exposed free surface of a polarized epithelial cell. Typically have cilia/microvilli.
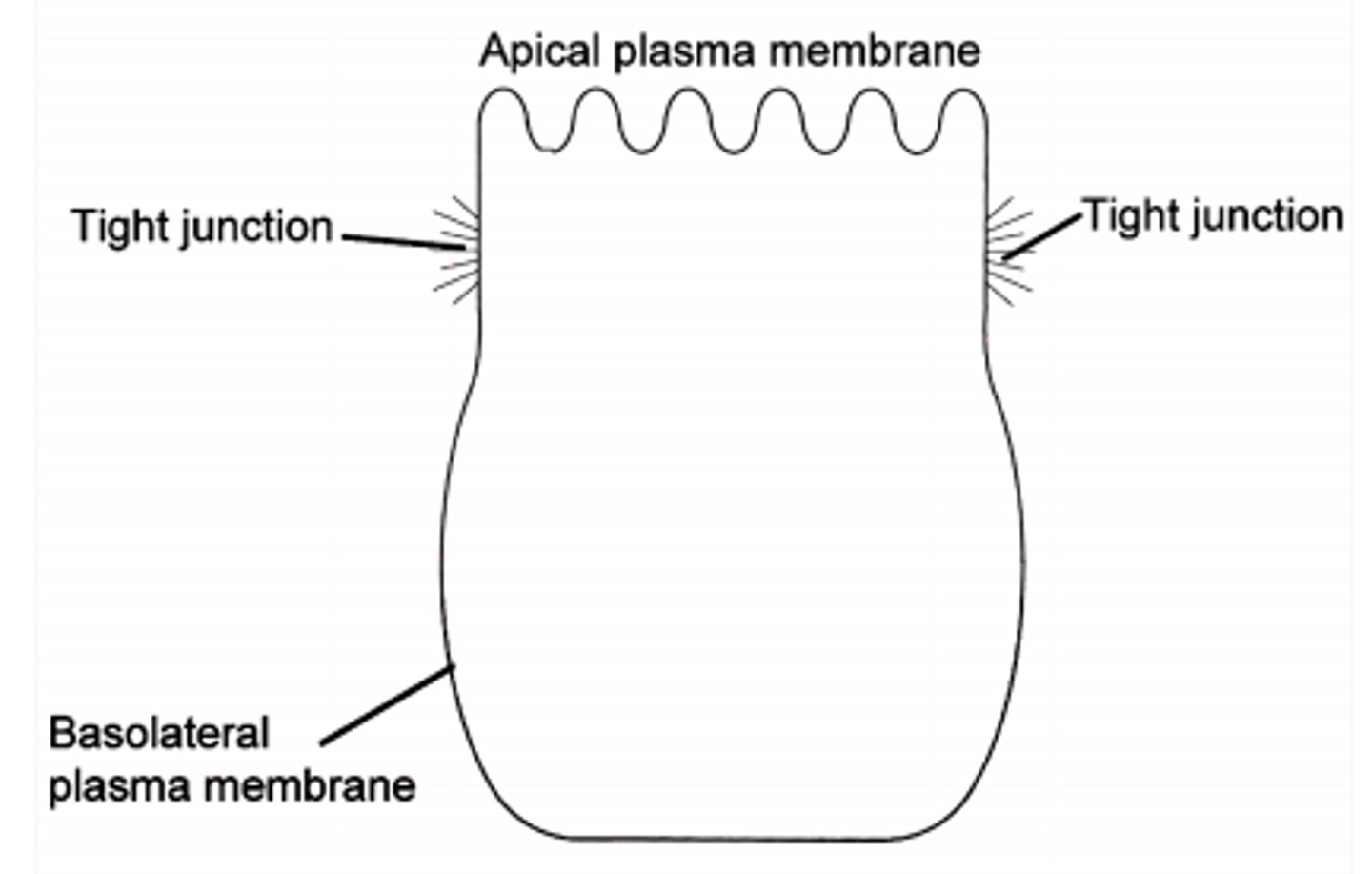
Basolateral Domain
The surface region of a polarized epithelial cell that is in contact with adjacent cells or the ECM
Functions of the Basal Lamina
- Binds Epithelia to the Connective Tissue
- Permits movement of nutrients into blood
- Filtration
What are the 2 major components of the Basal Lamina?
- Laminin
- Type IV Collagen
Laminin
Protein in the basement membrane to which integrins from cells attach
What is the difference in Basal Lamina and Basement Membrane?
The Basal Lamina is the protein portion of the Basement Membrane. The Basement Membrane also includes ECM.
2 Epithelial Layers can be fused to a Basal Lamina (T/F)
True; Used mainly for exchange and filtering like in the Lungs and Kidneys
Apical Modifications of Epithelia
- Microvilli
- Stereocilia (Stereovilli)
- Motile Cilia
Basolateral Modifications of Epithelia
Basal/Lateral Folds
What are the 5 Classes of Junctions?
- Tight Junctions
- Adherens
- Desmosomes
- Gap Junctions
- Hemidesmosomes
Tight Junctions
Transmembrane proteins that seal adjacent cells together
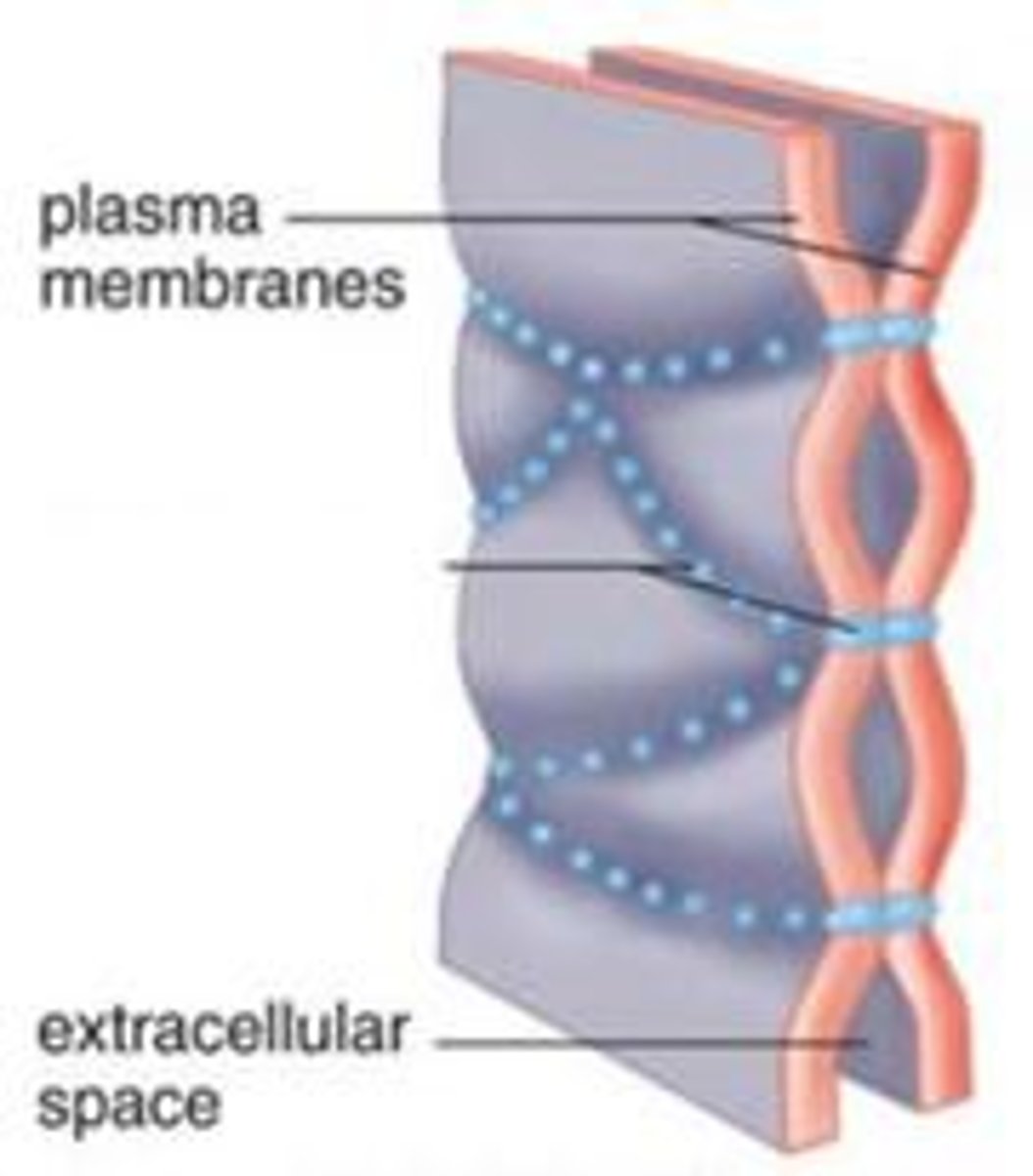
What are the 2 main Transmembrane Proteins that make up Tight Junctions?
- Occludin
- Claudin
Paracellular Transport
Transport of materials through the interstitial space without interactions with the cytoplasm or cell membrane
Occurs through Tight Junctions
Adherens
Joins intracellular actin-filaments between cells
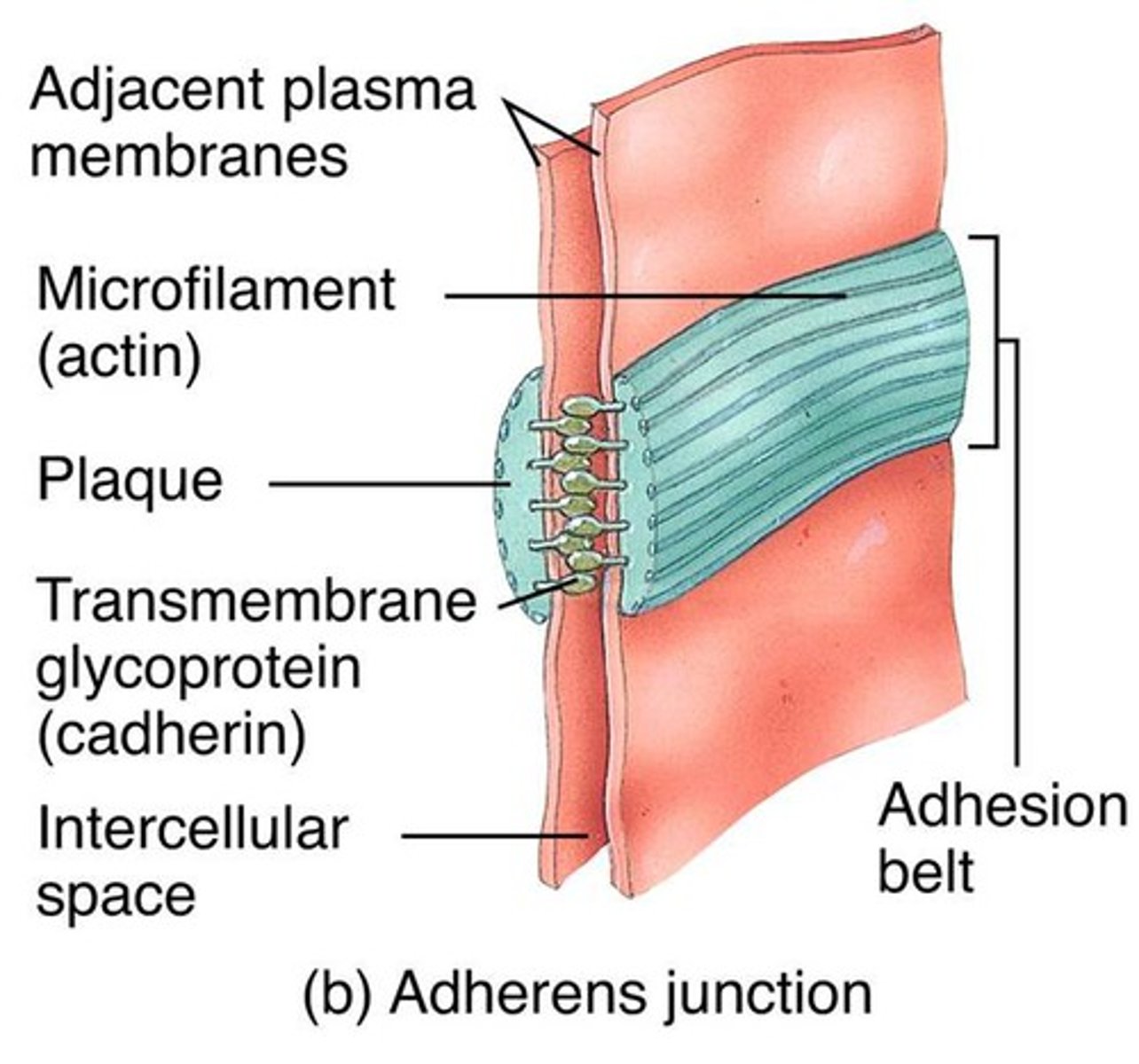
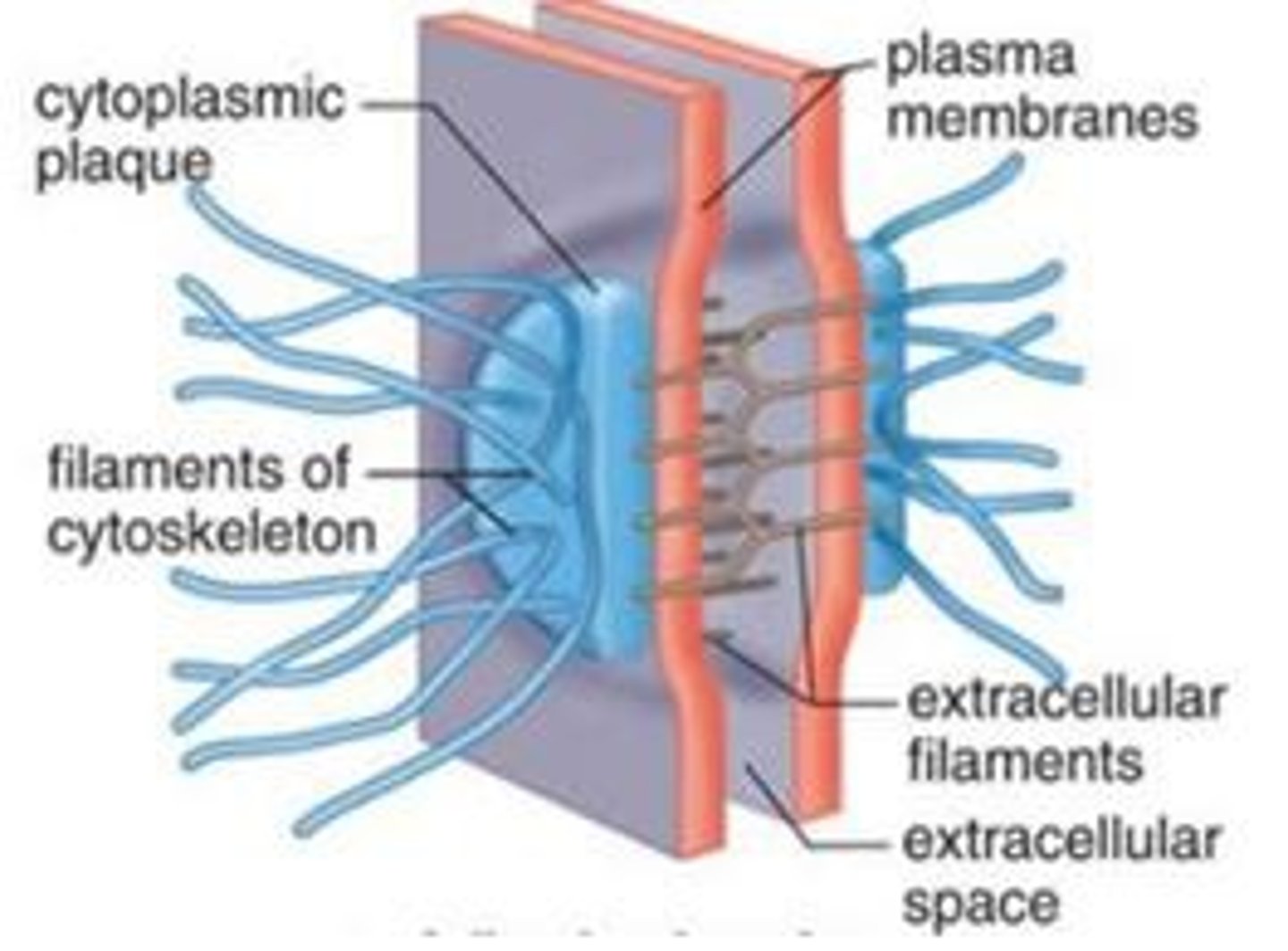
Desmosomes
Cell-Cell Anchoring junctions via intermediate filaments
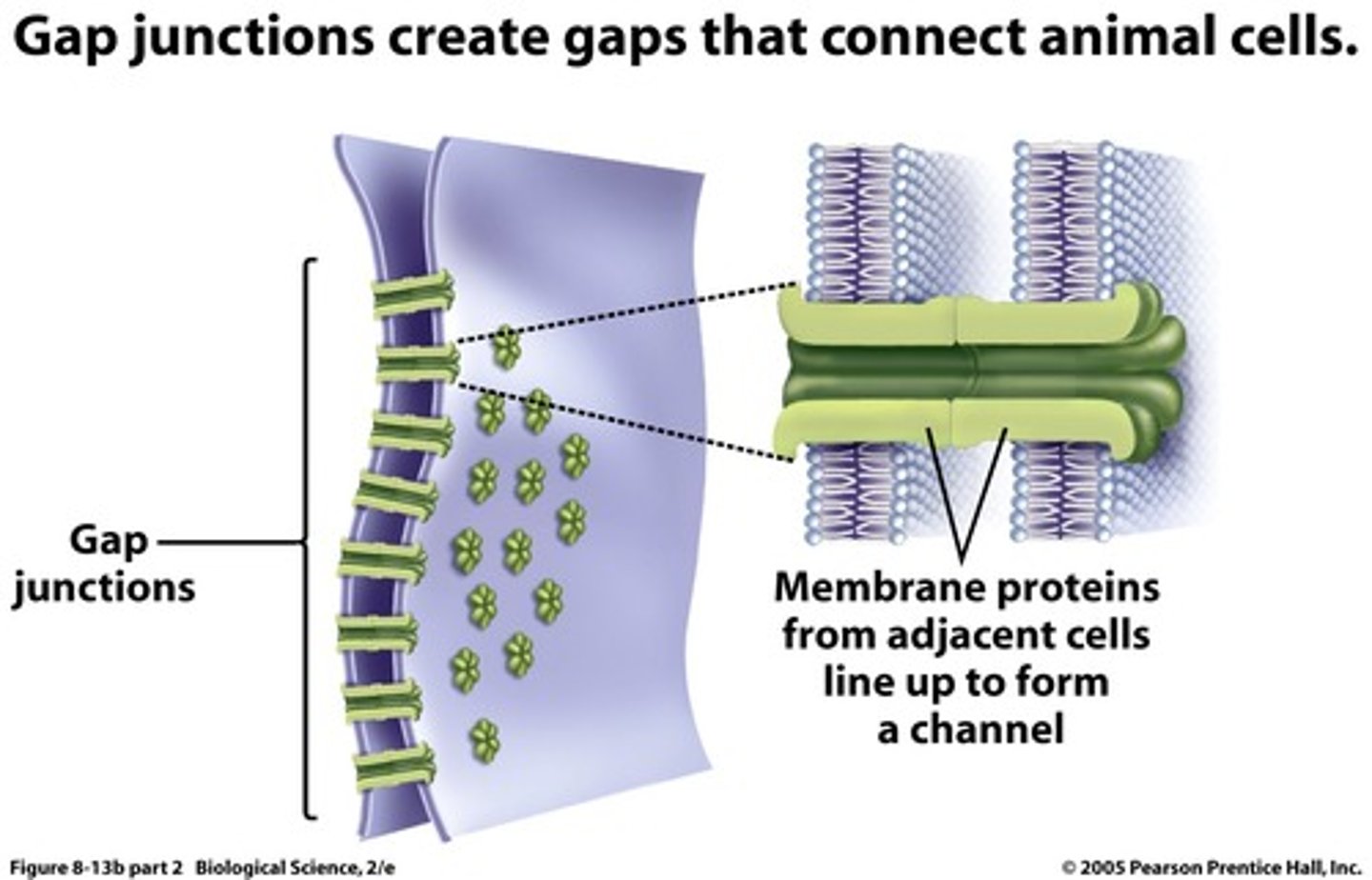
Gap Junctions
Provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent animal cells via connexins
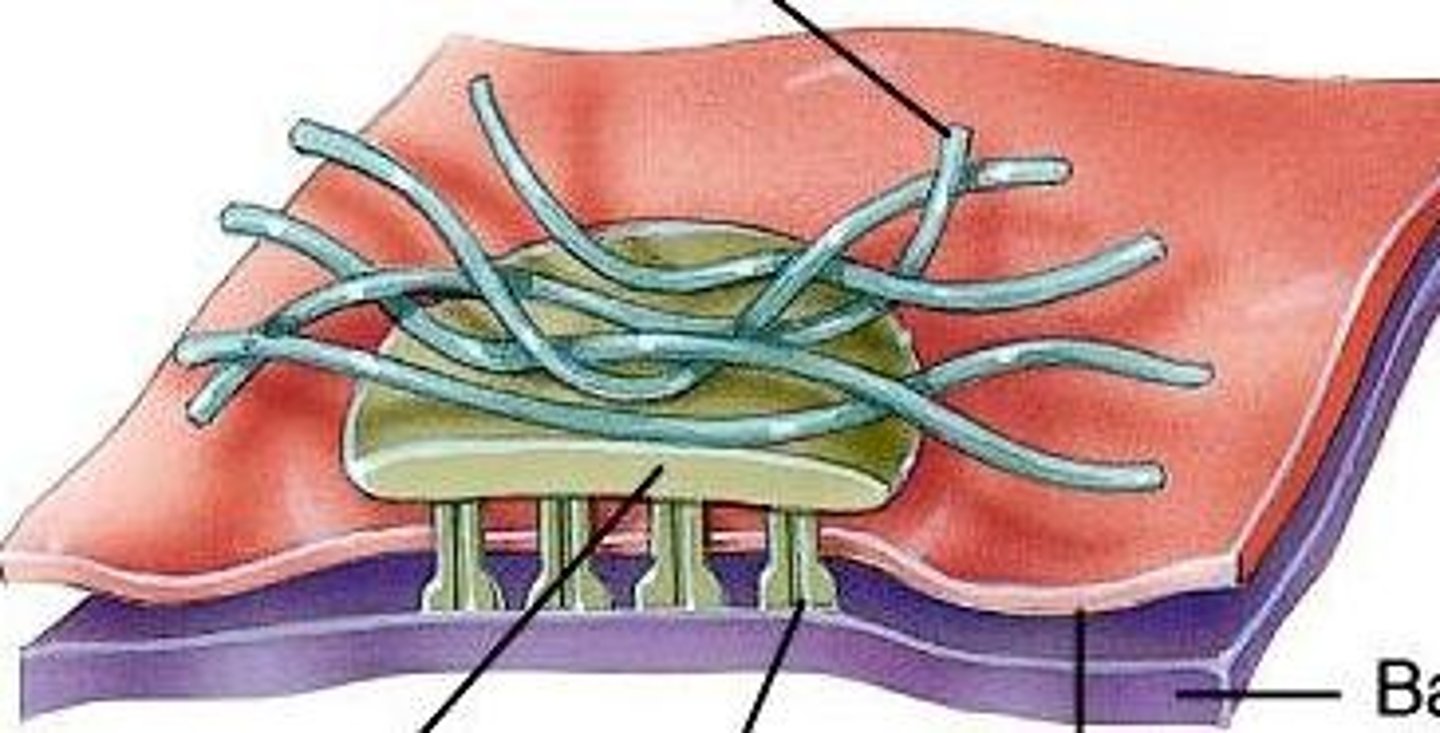
Hemidesmosomes
Attach epithelial cells to the basement membrane via intermediate filaments
Junctional Complex
Collective term for...
- Tight Junctions
- Adherens
- Desmosomes
Microvilli
Projections of actin-microfilaments that increase the cell's surface area
Stereocilia (Stereovilli)
Longer microvilli projections of actin-microfilaments that increase the cell's surface area
Limited to inner ear and male reproductive tract
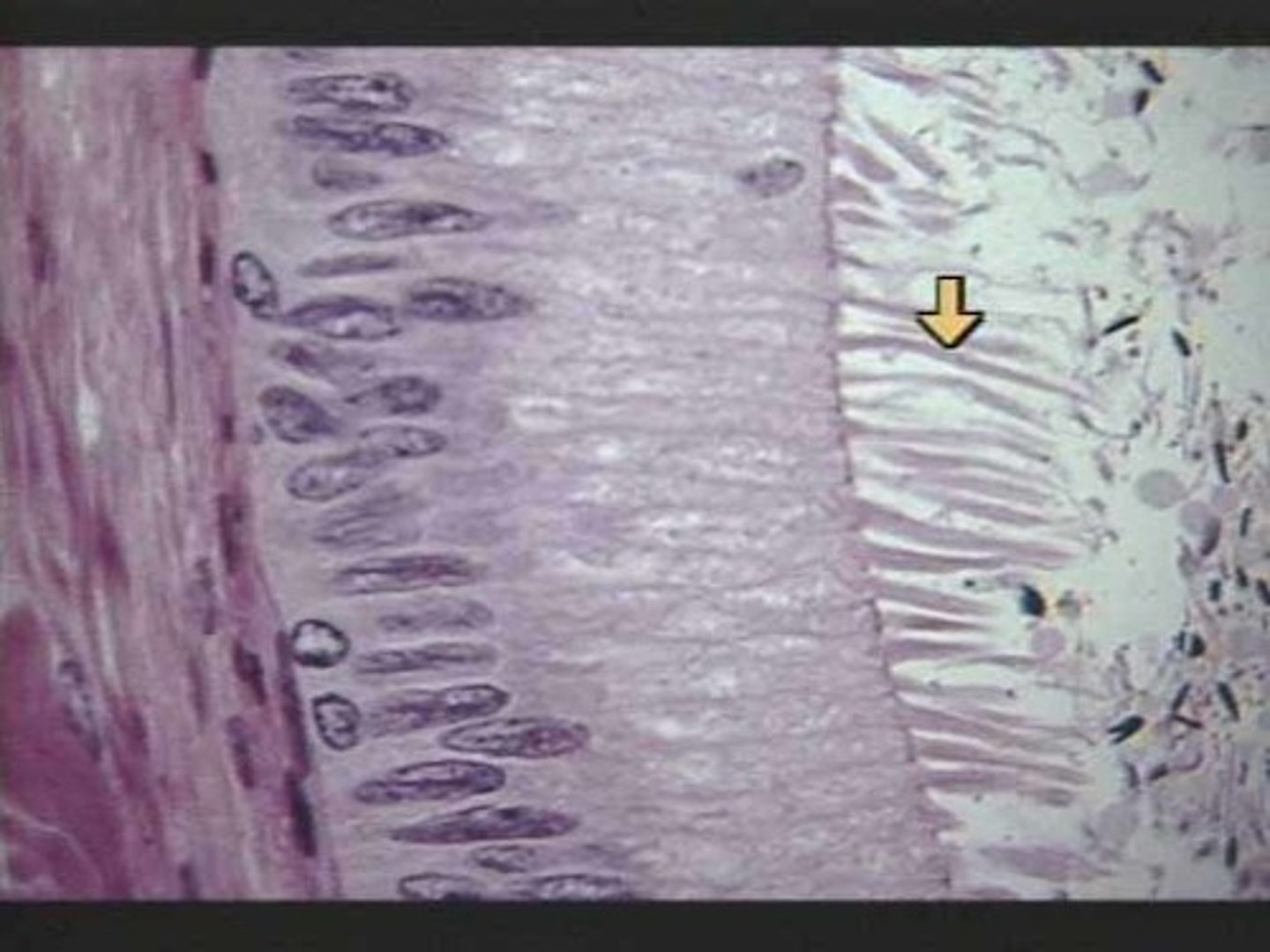
Motile Cilia
Projections of microtubules that "beat" to move fluid/cells
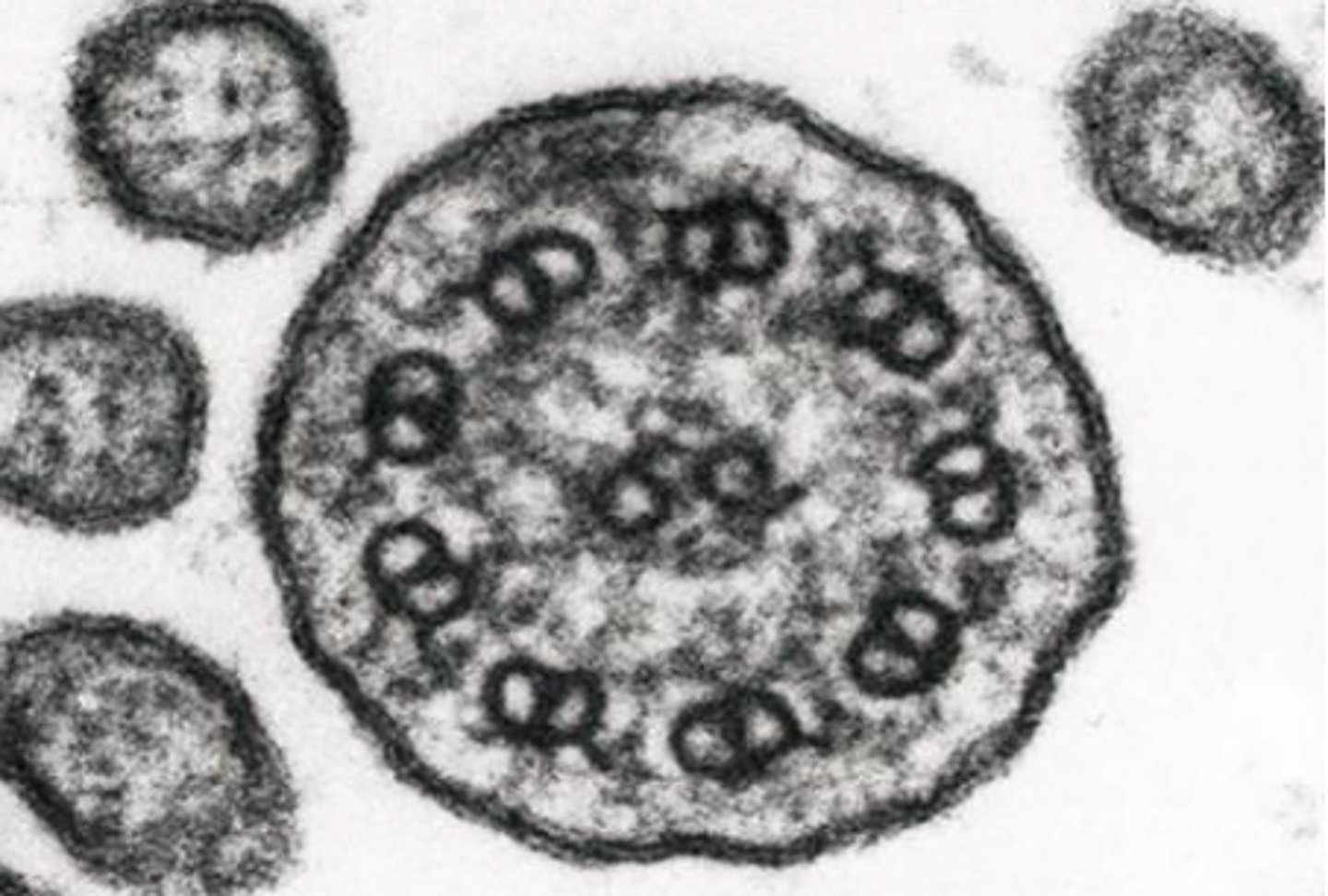
Motile Cilia are made up of ____.
axonemes
Axoneme
- Structure found in cilia and flagella that are responsible for motion
- Composed of two central microtubules surrounded by nine doublet microtubules (9 + 2 arrangement).
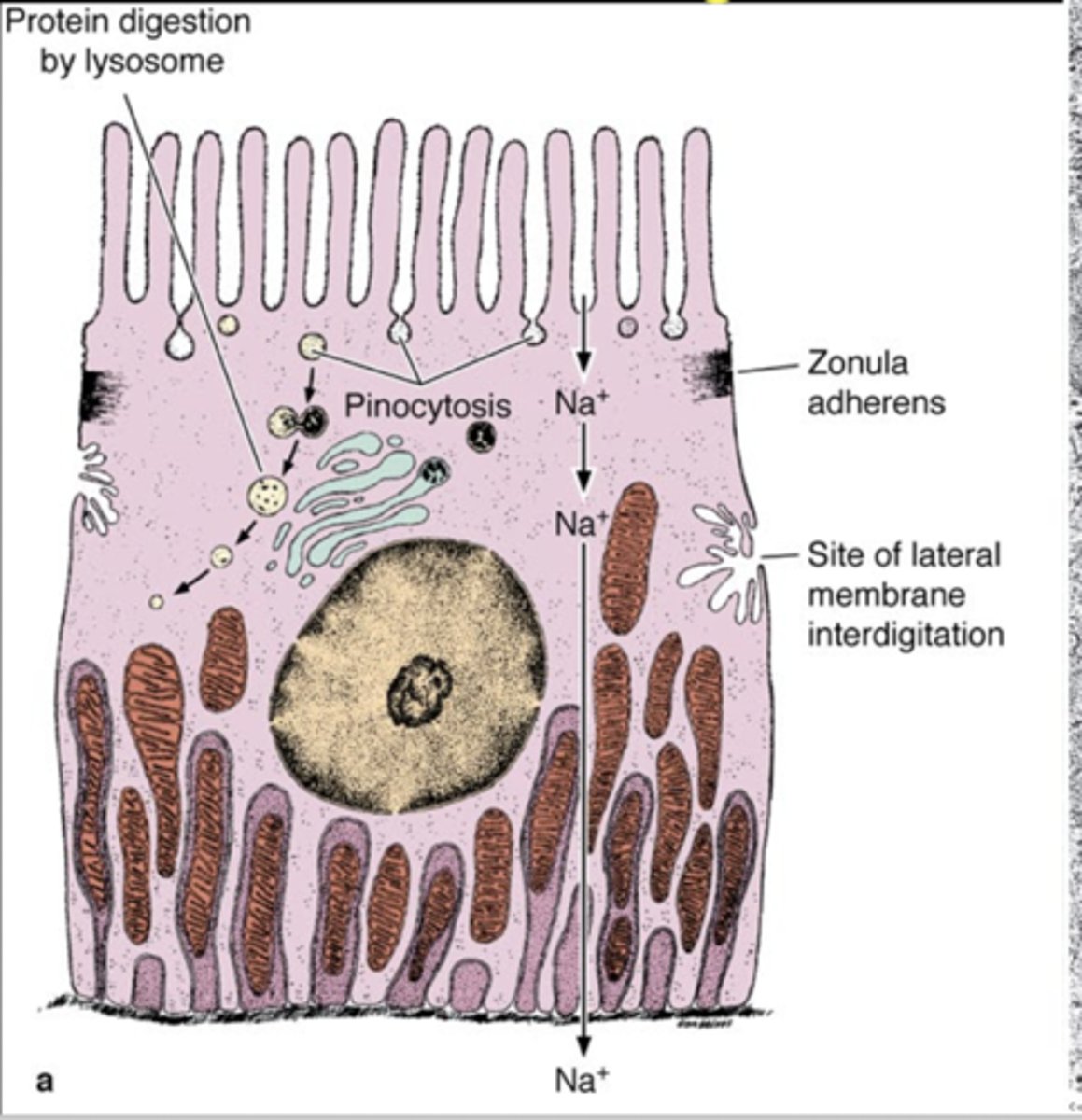
Basal/Lateral Folds
Increase surface area of basal/lateral regions
Epithelia shape is defined by the innermost layer (T/F)
False; Outermost
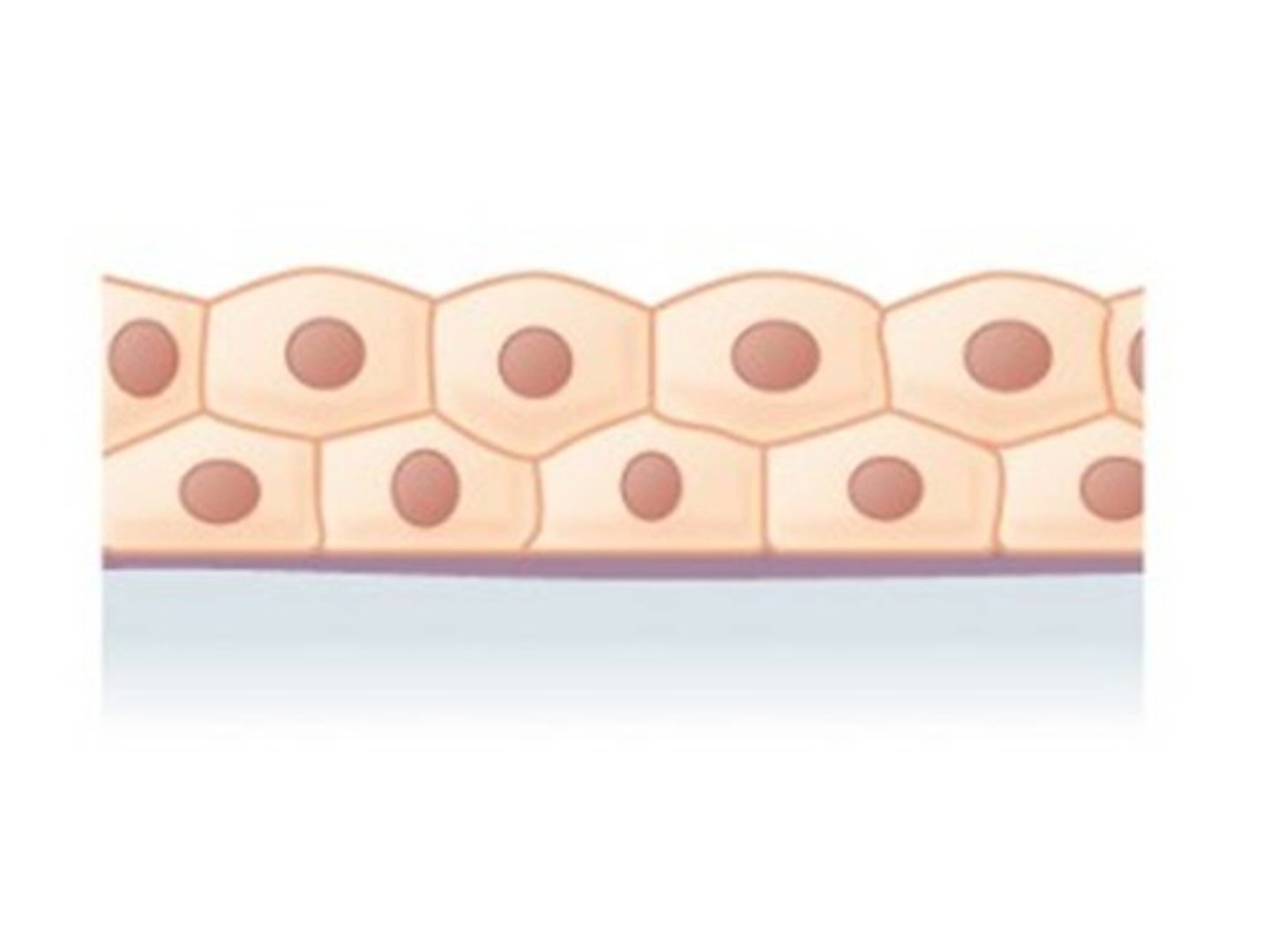
Simple Squamous Epithelia
Important for absorption and diffusion
- Blood Vessels
- Alveoli
- Kidneys
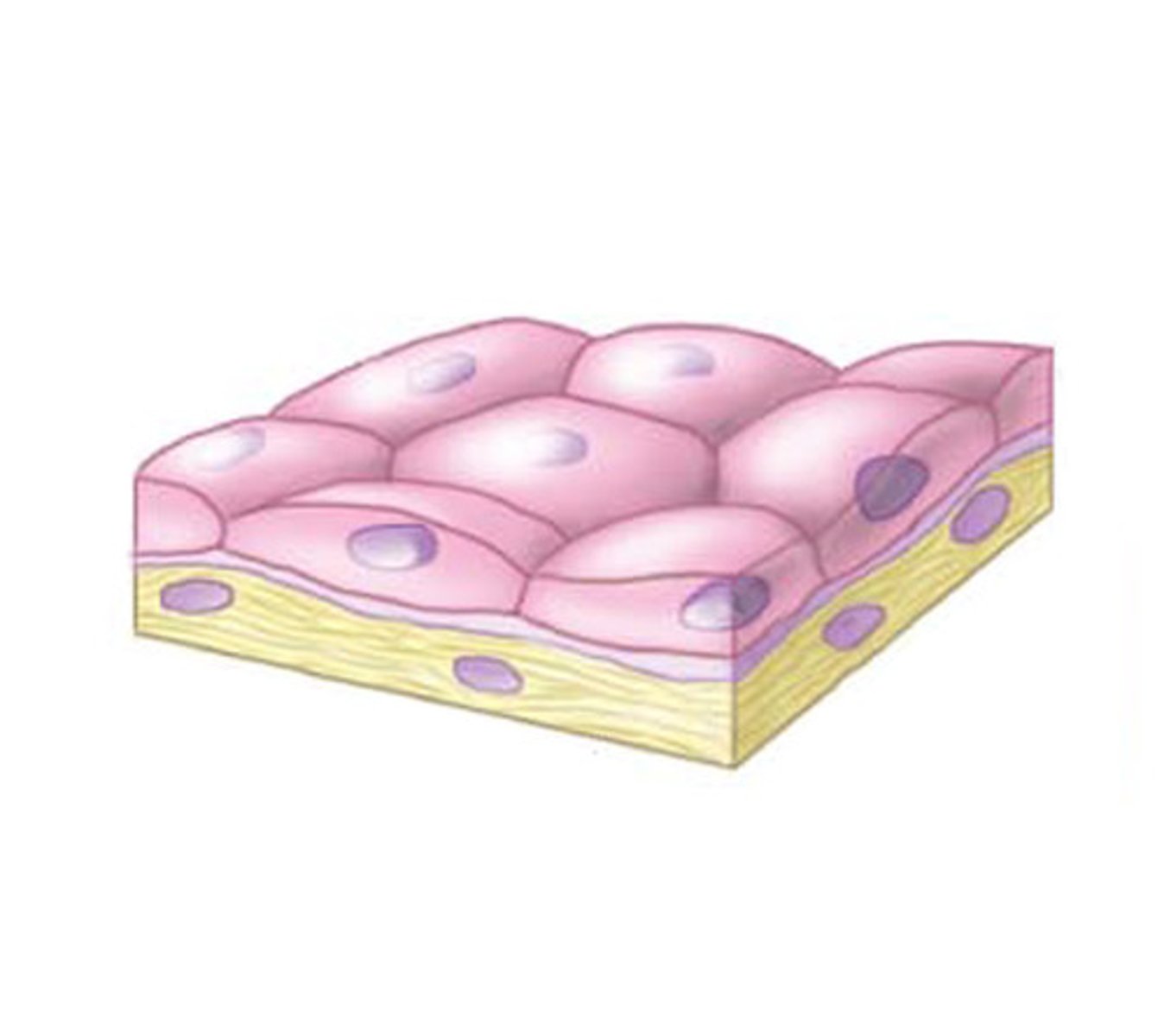
Simple Cuboidal Epithelia
Important for secretion and absorption
- Exocrine Ducts
- Kidneys
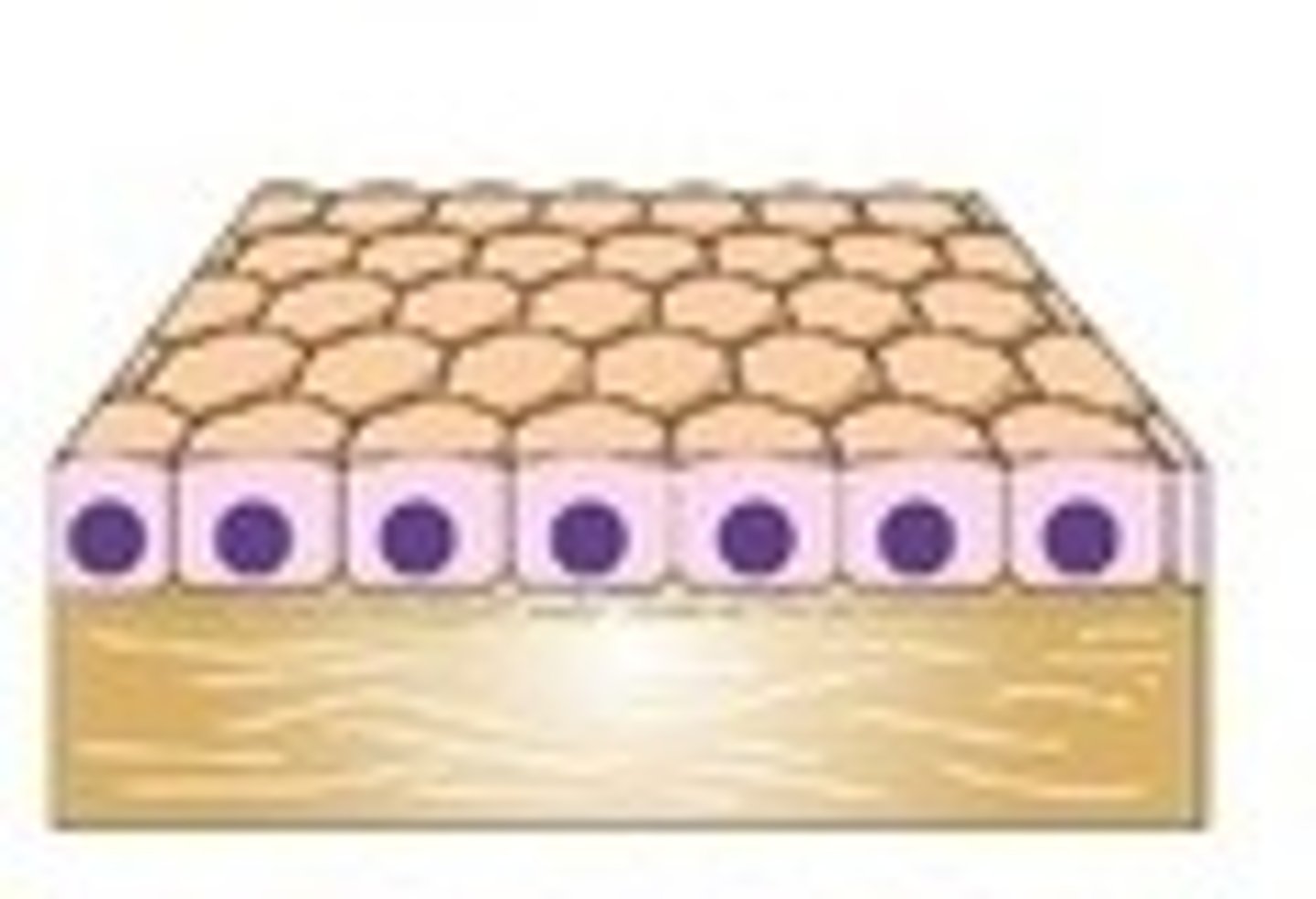
Simple Columnar Epithelia
Important for absorption and secretion
- GI Lining
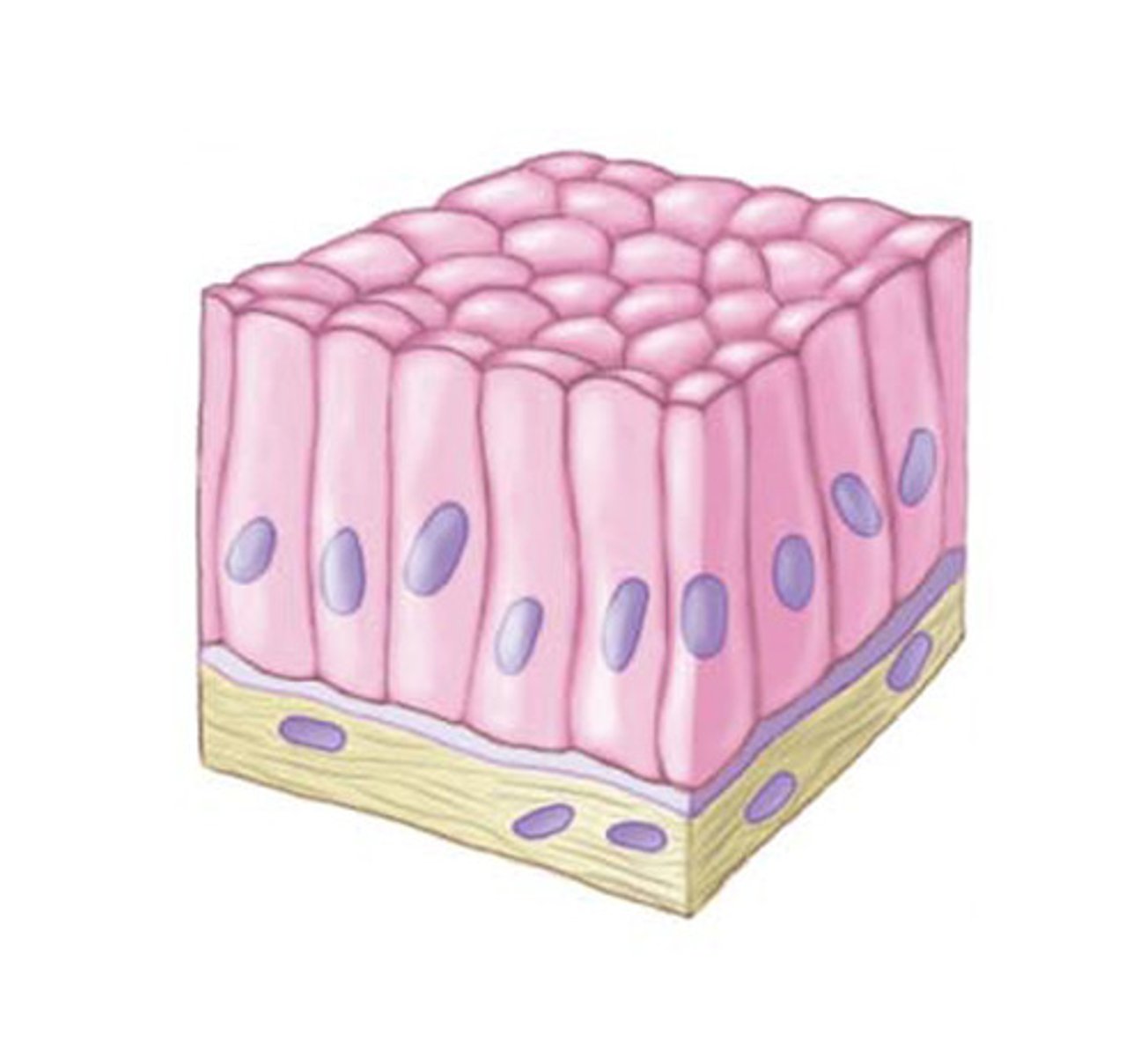
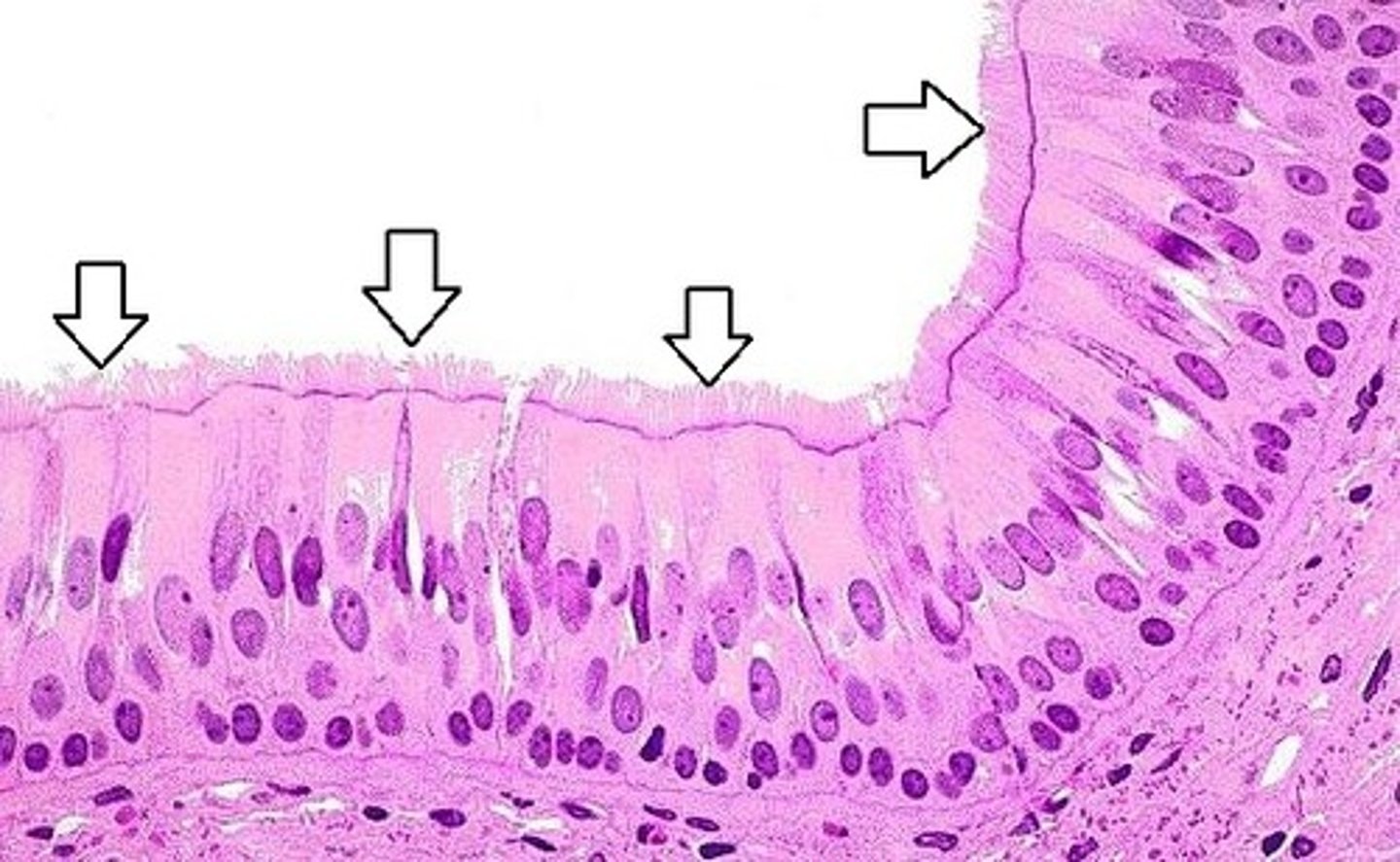
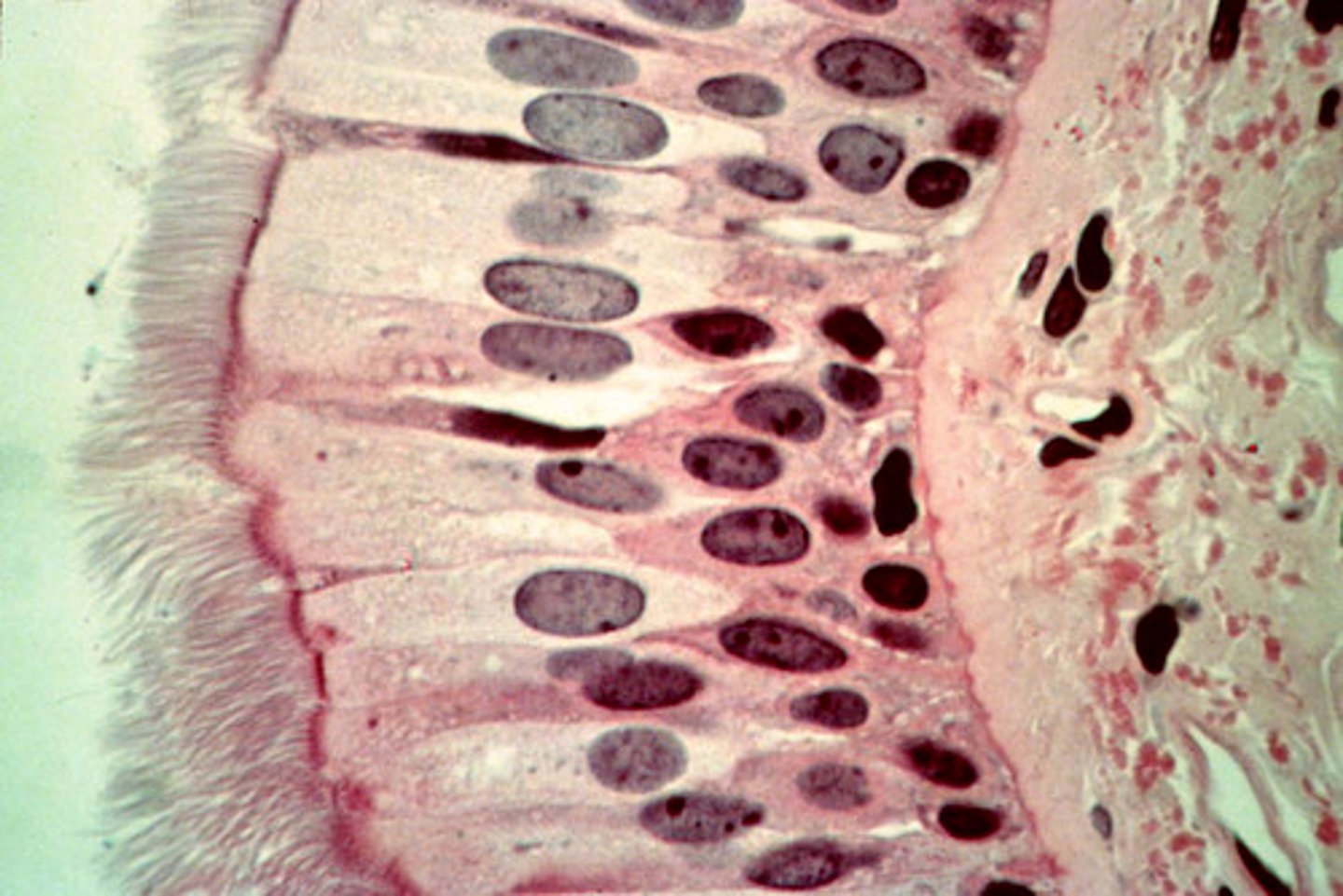
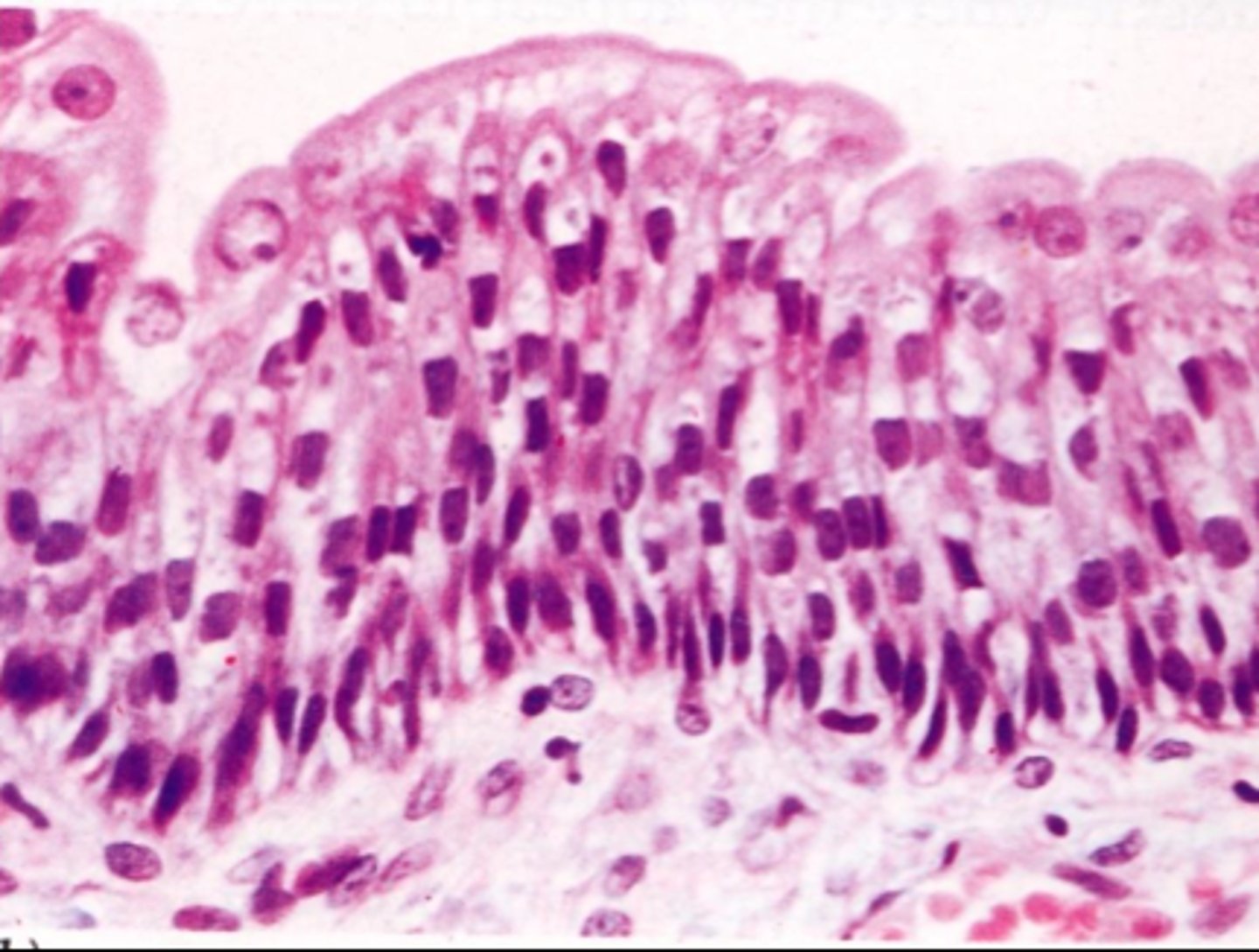
Pseudostratified Epithelia
Appear to have multiple layers due to difference in cell height, but are only 1 layer
- Trachea/Bronchioles
- Male Reproductive Tract
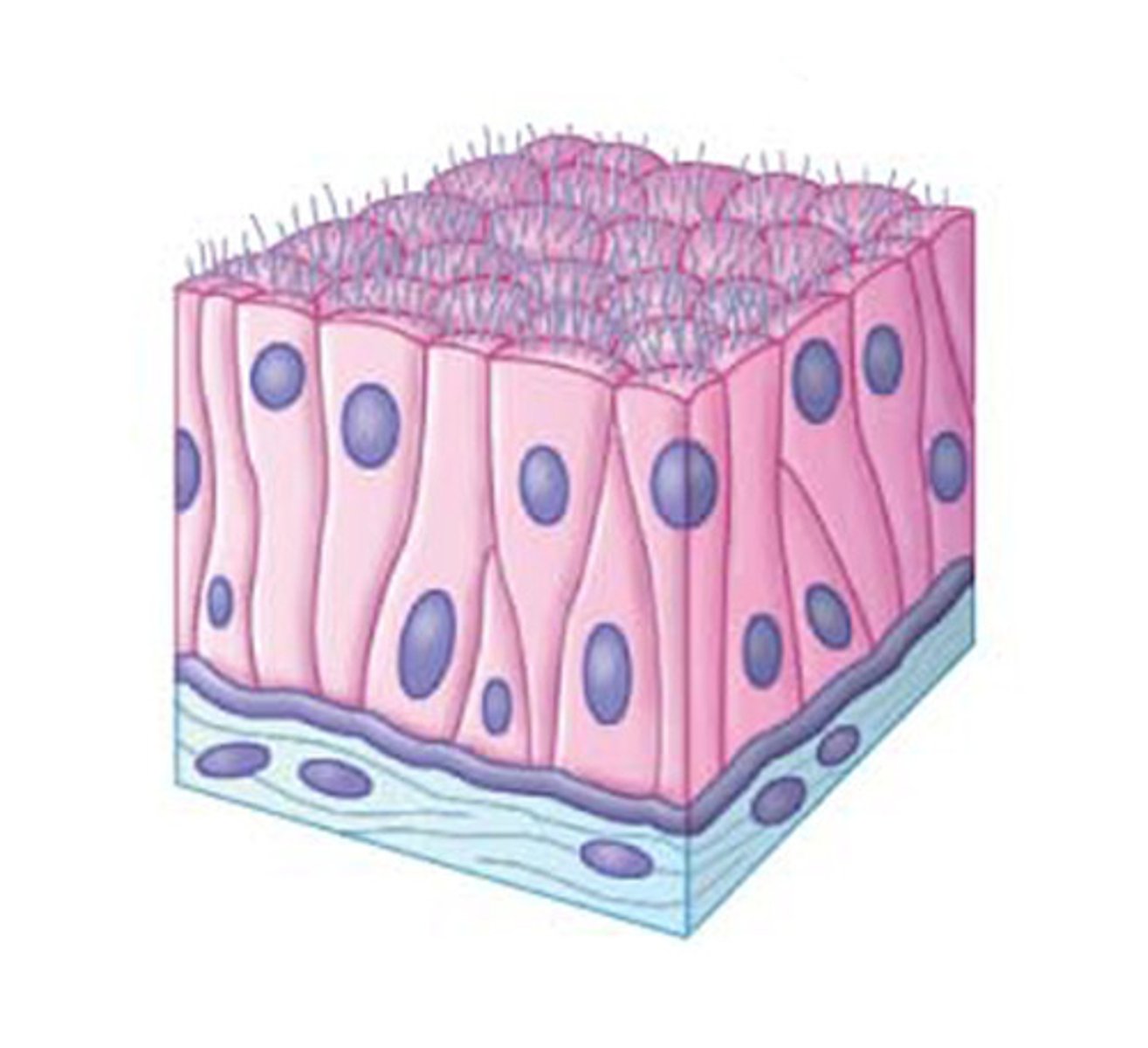
PCCE
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Epithelia
Important for protection against mechanical stress
- Skin
- Oral Cavity/Esophagus
- Vagina
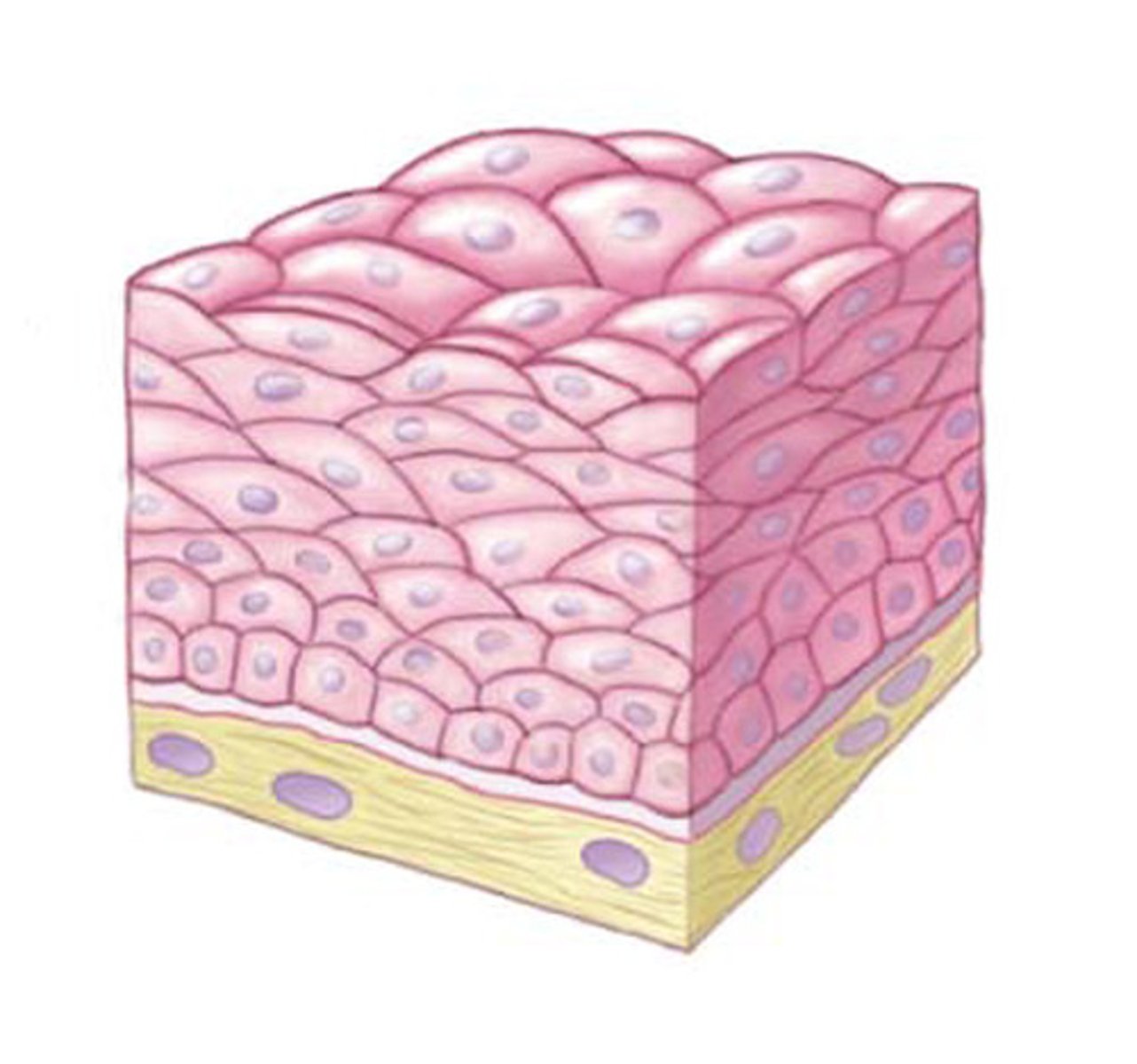
Stratified Squamous Epithelia can be ____ or ____.
keratinized/non-keratinized
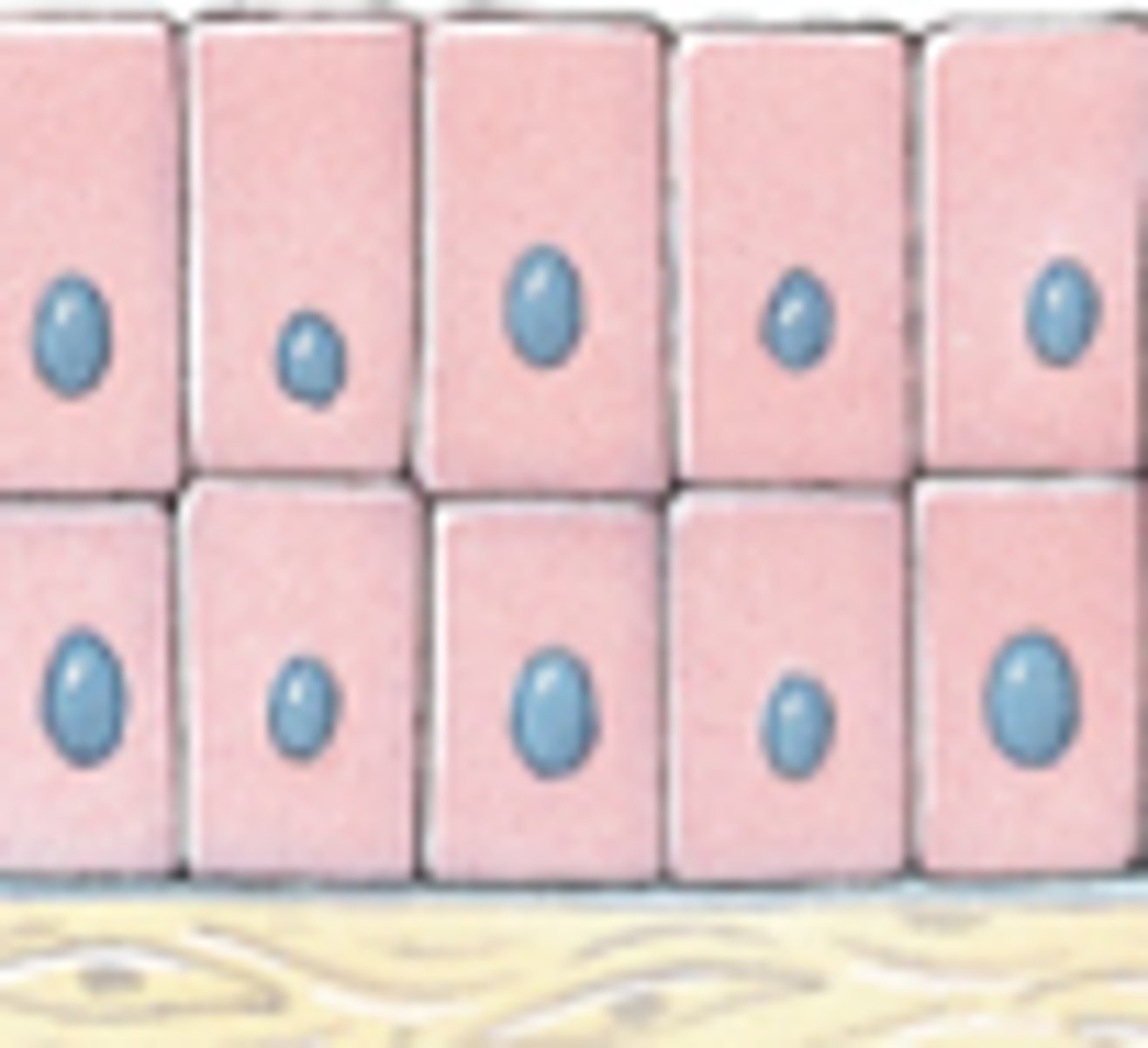
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelia
Important for secretion
- Sweat Ducts
- Mammary Ducts
Stratified Columnar Epithelia
Important for secretion
- Exocrine Glands

Transitional Epithelia
Cell Shape and Layering varies with stretching; Can appear squamous or cuboidal
Transitional Epithelia is found only in the ____.
urinary tract
What are the 2 types of Epithelial Glands?
- Exocrine
- Endocrine
What are the 2 portions of a Gland?
- Duct
- Secretory
Exocrine Gland Development
Invagination of Epithelial Cells
Endocrine Gland Development
(1) Invagination of Epithelial Cells
(2) Duct "disappears" and the secretory portion is isolated from surface layer
(3) Epithelial Cells become vascularized and secrete products into the blood
All glands are derived from and are lined with ____.
epithelia
Exocrine Glands are based on what 3 Characteristics?
- Structure
- Secretory Products
- Mechanism of Secretion
Exocrine Gland structure is typically either ____ or ____.
tubular/acinar
Tubular Exocrine Gland
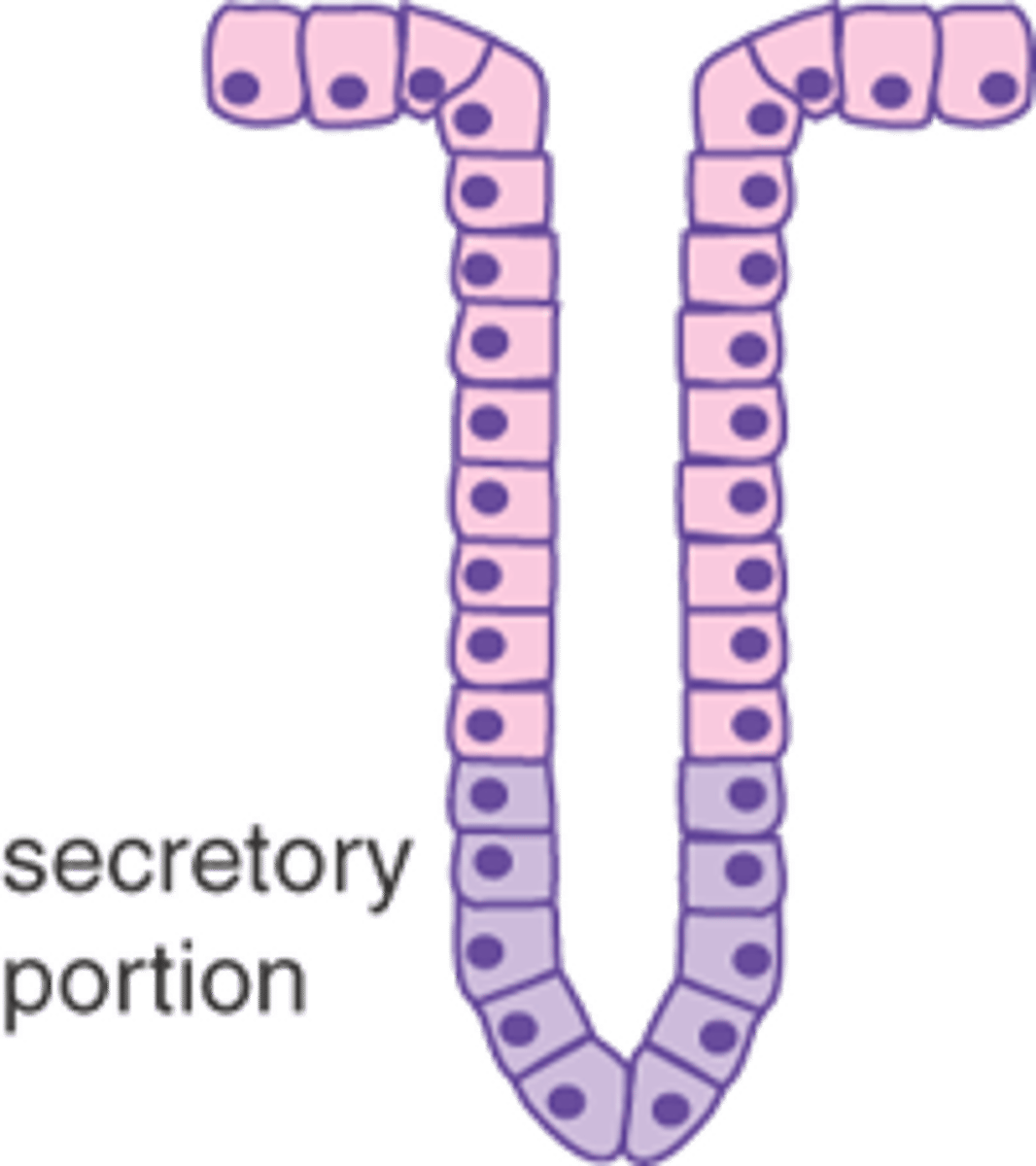
Acinar Exocrine Gland
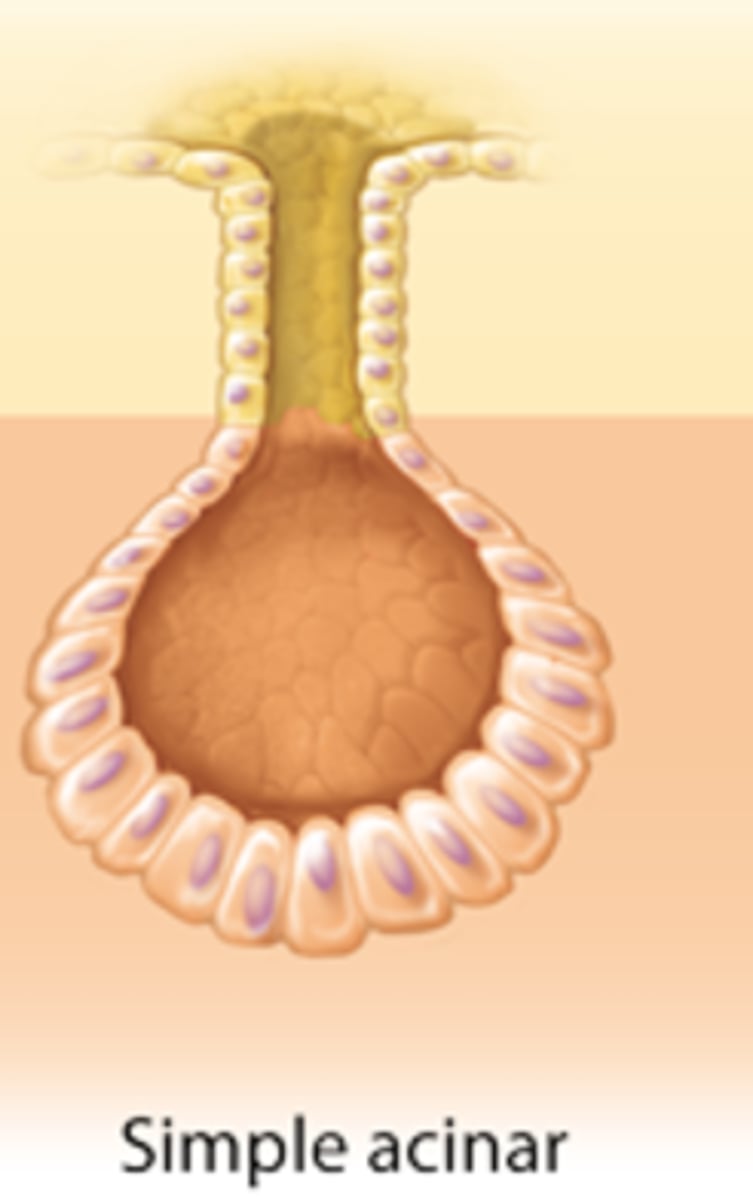
Exocrine Glands products can be considered ____ or ____.
serous/mucous
Epithelium Renewal
Occurs at different rates depending on the tissue
- Division occurs at the basal lamina
- Capable of rapid repair
Carcinoma
Malignant tumor that occurs in epithelial tissue
Adenocarcinoma
Malignant tumor that originates from glandular epithelial tissue
Collagen IX and XII are proteins important in basement membrane binding (T/F)
True