Biology Reading Notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/266
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
267 Terms
1
New cards
Fact of Biology
division of living forms into different species
2
New cards
North-Western European Town
each bird species has distinctive body size, shape, plumage colouration, song, feeding and nesting habits
3
New cards
Sexually reproducing animals and plants can do what, within a geographical location?
can nearly always be readily assigned to distinct groups
4
New cards
Reproductive Isolation
- lack of interbreeding; criteria for defining different species
- different species that coexist in the same area but do not interbreed
- different species that coexist in the same area but do not interbreed
5
New cards
What would happen if there were no barriers to interbreeding between members of different species?
Diversity of life would not exist
- something approaching a continuum of forms
- something approaching a continuum of forms
6
New cards
What happens when interbreeding happens?
highly variable offspring are produced
7
New cards
How are species prevented from interbreeding? (5)
- difference in habitats
- difference in time of breeding (plants have flowering)
- species with overlapping flowering times will be unable to interbreed
- in animals, the use of different breeding sites
- small features (prevent mating): not the right smell/sound/display
- behavioural barriers: plants of chemicals for detecting pollen from wrong species
- sperm from wrong species unsuccessful in fertilizing eggs of female
- difference in time of breeding (plants have flowering)
- species with overlapping flowering times will be unable to interbreed
- in animals, the use of different breeding sites
- small features (prevent mating): not the right smell/sound/display
- behavioural barriers: plants of chemicals for detecting pollen from wrong species
- sperm from wrong species unsuccessful in fertilizing eggs of female
8
New cards
Small Features (Barriers to Interbreeding)
prevent successful mating; don't produce the right smell, sound, display
9
New cards
Behavioural Barriers (Barriers to Interbreeding) examples:
- plants have chemicals that detect pollen from wrong species and reject it
- if mating takes place, sperm from wrong species will be unsuccessful in fertilizing the eggs
- if mating takes place, sperm from wrong species will be unsuccessful in fertilizing the eggs
10
New cards
Do some different species occasionally mate? If so, give an example.
Yes, especially if there is no option within own species. Example are dogs, coyotes, jackals. First generation hybrids don't develop
11
New cards
Problems of Hybrids (3)
- first generation fail to develop
- survive at lower frequency than non-hybirds
- are often sterile, don't produce offspring
- survive at lower frequency than non-hybirds
- are often sterile, don't produce offspring
12
New cards
What two things of hybrids isolates two species?
complete inviability and complete sterility
13
New cards
What did Darwin point out in Ch 9 of The Origin of Species? (according to interbreeding) (advantage/disadvantage)
it is most unlikely that the inviability or infertility of hybrids are a direct produce of natural selection
- no advantage of producing inviable/sterile offspring
- advantage to avoid mating w other species if hybrid offspring are inviable/sterile
- no advantage of producing inviable/sterile offspring
- advantage to avoid mating w other species if hybrid offspring are inviable/sterile
14
New cards
What are most barriers to interbreeding between species by-products of?
evolutionary changes that occurred after pop. became isolated from e/o, geographically and ecologically separated
15
New cards
Example of barriers to interbreeding through evolutionary change after population is isolated geographically and ecologically
Galapagos Finches. If some migrate to another island, both species on the islands will evolve independently from e/o. Through mutation, natural selection, genetic drift, genetic composition of two species will diverge. Changes are promoted by differences in environments.
16
New cards
Geographical Variation & Example
pops. of same species that differ because of geographical location
Example: humans; diff race and features
Example: humans; diff race and features
17
New cards
Does the amount of migration vary between organisms? Examples?
Yes, snails have low migration rates. Birds are highly mobile.
18
New cards
What happens when migrant individuals migrate? What do they contribute?
they can interbreed with the new members of the population and they contribute their genetic makeup to the population
19
New cards
What is migration?
homogenizing force, opposing tendency for local pops. to diverge genetically by selection or genetic drift
20
New cards
What causes populations of species to diverge more or less from e/o?
depends on the amount of migration and evolutionary forces promoting differences between local pops.
21
New cards
What does strong selection do in terms of migration? What is an example?
Strong selection can cause adjacent populations to differ.
Example: metal-tolerant plants have evolved on the polluted land surrounding mines. Absence of metals, plants grow poorly.
Example: metal-tolerant plants have evolved on the polluted land surrounding mines. Absence of metals, plants grow poorly.
22
New cards
Why do gradual geographical changes in traits arise? Example?
because migration blurs the differences caused by selection that varies geographically; changes in environmental conditions
Example: mammals living in northern hemisphere have larger body size; body size changes reflecting SA to V in climates where heat loss is a problem
Northern populations have shorter ears and limbs than southern populations
Example: mammals living in northern hemisphere have larger body size; body size changes reflecting SA to V in climates where heat loss is a problem
Northern populations have shorter ears and limbs than southern populations
23
New cards
Selection Responses
- differences btw geographically separate populations of same species do not require different types of selection
- same selection can lead to different responses
- same selection can lead to different responses
24
New cards
Malaria (selection responses)
- areas subject w malaria infections have diff genetic mutations that resistant malaria
- diff mutations can cause resistance by chance in diff places
- differences btw pops. of same species can also evolve if there is no selection, result of genetic drift
- in species, there are genetic differences among diff pop. for variants in DNA or protein sequence that have no effect on visible traits
- diff mutations can cause resistance by chance in diff places
- differences btw pops. of same species can also evolve if there is no selection, result of genetic drift
- in species, there are genetic differences among diff pop. for variants in DNA or protein sequence that have no effect on visible traits
25
New cards
Example of human populations that are have genetic differences but no effect on visible traits. (hint: Britain)
In Britain, depending on where you live, there is a difference in frequencies of individuals with blood types
- O is frequent in North Wales and Scotland then south
- B blood is frequent in India than from native Americans
- O is frequent in North Wales and Scotland then south
- B blood is frequent in India than from native Americans
26
New cards
Are there barriers to interbreeding with humans?
No, there are visible differences but no biological barriers
27
New cards
Species with Extreme Species Range (intermediate interbreeding)
- pops on extreme end of range can be considered as different species
- but they are connected by set of intergrading populations at opposite ends of range that have diverged sm that they cannot interbreed
- if intermediates became extinct, they would constitute different species
- but they are connected by set of intergrading populations at opposite ends of range that have diverged sm that they cannot interbreed
- if intermediates became extinct, they would constitute different species
28
New cards
Theory of Evolution (reproductive isolation/barriers to interbreeding)
must be intermediated stages in development of reproductive isolation
29
New cards
Example of intermediate stages in evolution btw geographically separated populations. (hint: flies) (5)
- flies in Columbia look similar to ones in North and central America
- DNA sequences differ
- flies from Columbia will mate with flies from America
- F1 females are fertile, males with mothers not from Columbia are sterile
- therefore, Columbian flies are distinct based of geographic isolation
- DNA sequences differ
- flies from Columbia will mate with flies from America
- F1 females are fertile, males with mothers not from Columbia are sterile
- therefore, Columbian flies are distinct based of geographic isolation
30
New cards
What could be the answer to failure to interbreed based off geographic variation/
product of adaptations to different environments
31
New cards
Floral Characteristics of Mimulus Species
- grow in mountains in North-Western USA
- unusually M. Cardinals is pollinated by hummingbirds rather than bees
- its flowers differ in characteristics that promote pollination by hummingbirds
- unusually M. Cardinals is pollinated by hummingbirds rather than bees
- its flowers differ in characteristics that promote pollination by hummingbirds
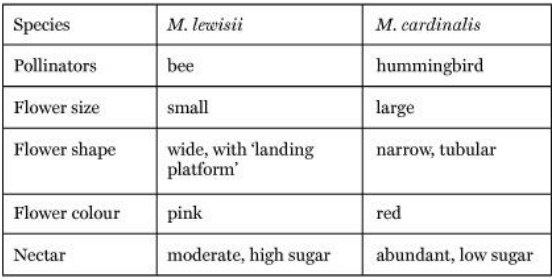
32
New cards
Fertilization of monkey flowers
- hybrids of species are healthy and fertile
- in nature, they do not interbreed
- bees and hummingbirds would go to respective flower
- in nature, they do not interbreed
- bees and hummingbirds would go to respective flower
33
New cards
How did pollinators (bees and hummingbirds) react to second-generation hybrids with a range of combinations from parents in the wild?
- color red attracted hummingbirds
- high nectar value increased hummingbird visits
- large flowers bees visited
- high nectar value increased hummingbird visits
- large flowers bees visited
34
New cards
Intermediation Forms of Monkey Flowers
- intermediate forms btw flower species had intermediated probabilities of being pollinated by bees vs.
hummingbirds
- intermediate degrees of isolation from parent species
- changes by NS as HB pollution evolved leads to both flower species becoming reproductively isolated
hummingbirds
- intermediate degrees of isolation from parent species
- changes by NS as HB pollution evolved leads to both flower species becoming reproductively isolated
35
New cards
What must be favoured by selection or have little effect on fitness so that it can spread by genetic drift?
alteration in the genetic composition of one population
36
New cards
If a variant is spreading in a population, will it have harmful effects when combined with genes form a diff population? Is the variant spreading because it is advantageous or disadvantageous?
- it will not have impeded by harmful effects
- the variant is advantageous because its spreading and adapting the population to its local environment
- the variant is advantageous because its spreading and adapting the population to its local environment
37
New cards
Is there selection to maintain compatibility of mating behaviour between individuals from geographically or ecologically separated populations?
No!
38
New cards
Is there selection to maintain interactions that allow normal development between genes that differ in diff pops.?
No!
39
New cards
Summarized Theory of Interbreeding
the ability to interbreed degenerates over time
- not subject to selection to maintain them
- not subject to selection to maintain them
40
New cards
What do genetic analysis' of interspecies crosses show?
show that diff species contain diff sets of genes which are dysfunctional when tgt in hybrids
41
New cards
Example of Genetic Analysis with Flies (4)
- hybrid females are fertile, males are sterile
- testing fertility of male offspring, study the genetic basis of hybrid male sterility
- hybrid sterility is produced by interactions btw diff genes from the two species
- 15 differed genes are different between the species that affect sterility of hybrid males
- testing fertility of male offspring, study the genetic basis of hybrid male sterility
- hybrid sterility is produced by interactions btw diff genes from the two species
- 15 differed genes are different between the species that affect sterility of hybrid males
42
New cards
What occurred in the Fish Species in Lake Victoria? (3)
- 500 fish species in 14,600 years
- due to behavioural trains and colouration differences
- no diffjerenentaion in DNA sequences
- due to behavioural trains and colouration differences
- no diffjerenentaion in DNA sequences
43
New cards
What is said to happen when two related populations are completely isolated from e/o by many barriers to interbreeding?
their evolutionary fates will forever be independent of one other and they will diverge over time
44
New cards
What is one cause of divergence of related populations that do not interbreed?
Natural Selection
45
New cards
Examples of species that interbreed and do not interbreed? Therefore....
Example 1) Flies have similar boy structures apart from male genitalia and they are the same species but do not interbreed
Example 2) Pipistrel bat divided into two species that do not interbreed in a nature and differ in calls and DNA sequence
Therefore, there are marked differences between populations of same species with no barriers to interbreeding
Example 2) Pipistrel bat divided into two species that do not interbreed in a nature and differ in calls and DNA sequence
Therefore, there are marked differences between populations of same species with no barriers to interbreeding
46
New cards
What is the interbreeding aspect within asexual reproduction?
- interbreeding is meaningless
47
New cards
What can we conclude from the previous examples in Ch 6?
- there is no relationship btw observable characteristics and strength of reproductive isolation btw pair of pop.
- no relationship btw extent of differences btw species related to time since they became reproductively isolated
- no relationship btw extent of differences btw species related to time since they became reproductively isolated
48
New cards
Reproductive Isolation in terms of Fossil Records
- lineages that show little or no change for years followed by abrupt new forms
- unable to tell if evolutionary change implies new species or involves lineage, evolving in response to environmental changes
- unable to tell if evolutionary change implies new species or involves lineage, evolving in response to environmental changes
49
New cards
Do traits change once species have had time to adapt to stable environment?
No, they do not change greatly.
50
New cards
How do biologists make inferences about a relationship of two species? What do they study?
they use into from their DNA sequences
- see differences in same genes in diff species
- they study time since species separated
divergence in morphological characteristics
- see differences in same genes in diff species
- they study time since species separated
divergence in morphological characteristics
51
New cards
What changes are rare in DNA? Why?
changes due to insertions and deletions are rare In genes that code for proteins
- major effect on sequence of AA in protein, make it non-functional
- major effect on sequence of AA in protein, make it non-functional
52
New cards
In closely related species, what are most changes in the coding sequences of genes involved in?
they're involved in single changes to individual letters of the DNA sequence
53
New cards
What can we see when comparing the number of differing letters in DNA sequence of same gene btw diff organisms?
we can quantify their level of divergence
54
New cards
What can we see once we know the genetic code?
which differences alter the protein sequence corresponding to the gene in question (replacement changes) and which do not (silent changes)
55
New cards
What do studies of sequence divergence show, relative to humans vs. other animals?
- shows the number of differences from human sequence compared to other species
- how we are closely related to chimpanzees b/c our sequences differ slightly
- patterns of relationships revealed by sequence comparisons are in agreement w what is expected from the times at which major groups of animals and plants appear in the fossil record
- how we are closely related to chimpanzees b/c our sequences differ slightly
- patterns of relationships revealed by sequence comparisons are in agreement w what is expected from the times at which major groups of animals and plants appear in the fossil record
56
New cards
What can we infer from this table?
- silent changes are more common then replacement changes
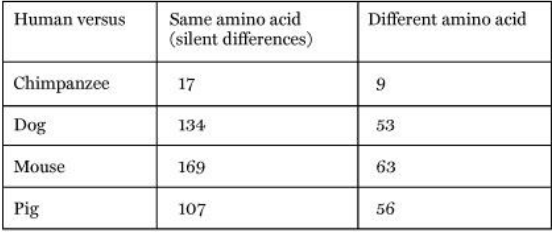
57
New cards
What will a small effect caused by a mutation result in?
result in selection eliminating the mutation from the population
58
New cards
What do most mutations that change protein sequence never contribute to?
they never contribute to evolutionary differences in gene sequences that accumulate btw species
59
New cards
What is molecular adaptation in terms of mutations?
evidence that some amino acid sequence evolution is driven by selection acting on favourable mutations so that molecular adaptation occurs
60
New cards
What is the effect of silent changes to gene sequences?
they have little to no effect on biological functions
61
New cards
How does a mutation spread if it does not confer any advantage to carrier?
random changed in frequencies of alternative variants (GD) take place in finite populations
62
New cards
Drosophilia Melanogaster Example Population (9)
- adults must contribute two descendants
- some have bright red, some have dull red
- if there is average number of offspring = no selection on eye colour, neutral in effect
- genes from nest generation will be random
- frequency mutant gene will not be the same
- continual fluctuations over generations
- all members will have gene for bright eyes or lost is all
- small population = genetic drift is fast
- large population = genetic drift is slow
- some have bright red, some have dull red
- if there is average number of offspring = no selection on eye colour, neutral in effect
- genes from nest generation will be random
- frequency mutant gene will not be the same
- continual fluctuations over generations
- all members will have gene for bright eyes or lost is all
- small population = genetic drift is fast
- large population = genetic drift is slow
63
New cards
What is the first effect of genetic drift?
- when new variant is drifting to loss or fixation, the character affected by the gene is variable within pop.
- input of new neutral variants by mutation & changes in frequencies by drift determines variability in the population
- examining DNA sequences of same gene from diff individuals reveals variability at silent sites
- input of new neutral variants by mutation & changes in frequencies by drift determines variability in the population
- examining DNA sequences of same gene from diff individuals reveals variability at silent sites
64
New cards
What is the second effect of genetic drift?
- selectively neutral variant that is initially rare has a change to spread in whole population and replace alternative variants, although it has great chance in being lost
65
New cards
What does genetic drift lead to? What does its rate relate to?
- leads to evolutionary divergence btw isolated pops. w/o selection promoting changes; slow process
- rate relates to when mutations rise and rate which genetic drift leads to replacement of gene by new one
- rate relates to when mutations rise and rate which genetic drift leads to replacement of gene by new one
66
New cards
What does the rate of DNA sequence divergence btw pair of species depend on?
it depends on the rate of mutation per DNA letter
- frequency where a letter in parent is mutant in the copy that is passed to an offspring
- frequency where a letter in parent is mutant in the copy that is passed to an offspring
67
New cards
If not selection is acting, what effects the number of mutational differences btw a pair of species?
- the rate at which mutations appear in the sequence
- the amount of time since species' last CA
- the amount of time since species' last CA
68
New cards
Why does a large population have more new mutations per generation?
because there are more individuals in which a mutation may occur
69
New cards
Is genetic drift faster in small populations or large populations? Why?
Small Populations because in fewer generations you can either eliminate the mutation or everyone can have it
70
New cards
The mutation rate determines the....
the rate of divergence
71
New cards
What is the molecular clock principle?
- neutral changes accumulate in a gene as time goes on
- at a rate that depends on the gene's mutation rate
- sequence changes in genes are likely to take place in clock-like fashion than changes in traits subject to selection
- at a rate that depends on the gene's mutation rate
- sequence changes in genes are likely to take place in clock-like fashion than changes in traits subject to selection
72
New cards
What do the rates of morphological changes depend on?
- environmental changes
- variable rates
- reversals of direction can occur
- variable rates
- reversals of direction can occur
73
New cards
What is the use of molecular clocks?
- biologists use it to date divergence btw species when there is not fossil evidence
- also applied to the amino acid sequence of proteins
- also applied to the amino acid sequence of proteins
74
New cards
Why are molecular clocks not precise?
rates of molecular evolution change over time within the same lineage and btw lineages
75
New cards
How do we calibrate clocks?
sequences from closest species whose divergence dates are known
76
New cards
Why are molecular clocks slow?
b/c the rate pf neutral sequence evolution depends on mutation rate, since the rate of which single letters in DNA change by mutation is low
77
New cards
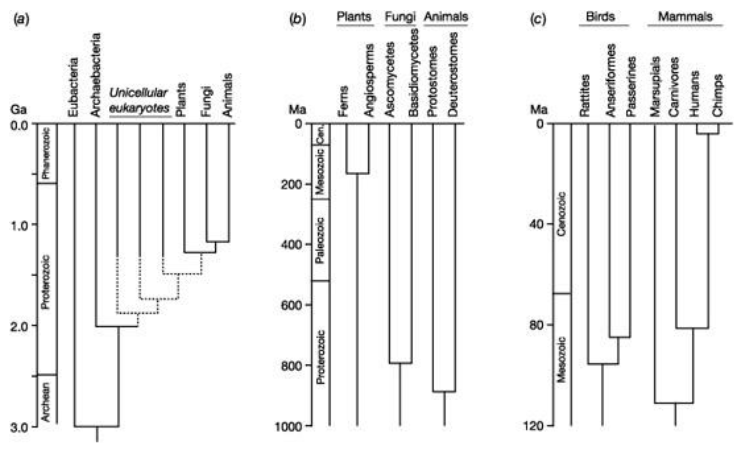
What do each of these trees show?
- all graphs hips estimated divergence dates between groups
a) all organsims
b) mulitcellular organisms
c) birds and mammal groups
a) all organsims
b) mulitcellular organisms
c) birds and mammal groups
78
New cards
Which evolves more slowly: protein sequences or silent DNA differences? What is the slower one useful for? What do scientists use it to do? (4)
protein sequences; useful for comparing species that diverged a long time ago
- btw species multiple changes occurred at some sites in DNA sequecences so its hard to keep track of mutations
- scientists who reconstruct the times of divergence between major groups use data from slow evolving molecules
- allows them to reconstruct the genealogical tree of life
- btw species multiple changes occurred at some sites in DNA sequecences so its hard to keep track of mutations
- scientists who reconstruct the times of divergence between major groups use data from slow evolving molecules
- allows them to reconstruct the genealogical tree of life
79
New cards
How do Complex Adaptations Evolve?
by working towards better and better designs, improving the quality of the adaptations to better adapt to the situation
80
New cards
Tinkering
tinkering with an organism with minor changes that allow them to better survive and reproduce
81
New cards
Can adavtagneous treats spread through a population over a short time period, even if they're initially rare?
Yes!
82
New cards
Can a succession of small changes to a structure that already works be improved?
Yes, and it can produce large evolutionary changes bc of it
83
New cards
Complex Adaptation of Proteins: Chance of AA on a particular site?
- proteins are complex structures whose parts interact to function properly
- chance of correct AA in right site is 1/20
- proteins start as short chains that cause rxns to go faster and improved as they involved
- stepwise changes of changing sequence and each changing the sequence or adding to its length could improve a protein
- chance of correct AA in right site is 1/20
- proteins start as short chains that cause rxns to go faster and improved as they involved
- stepwise changes of changing sequence and each changing the sequence or adding to its length could improve a protein
84
New cards
Proof of Protein's having small amount of Amino Acids
- typical enzyme has small amount of amino acids that interact with chemical that is being changed by the enzyme
- rest supports structure of part involved
- protein soles relies on small set of amino acids, so new function can evolve by small number of changed to sequence of protein
- rest supports structure of part involved
- protein soles relies on small set of amino acids, so new function can evolve by small number of changed to sequence of protein
85
New cards
Summary of Protein Complex Adaptations
- functioning part of protein depends on small amount of amino acids so new function can evolve by small number of changes to sequence of protein
86
New cards
How is it possible for pathways of successive enzyme reactions to evolve? Such as those which make chemicals that organisms need? (4)
- useful chemicals were present in environment of early organisms
- an organism that could change chemical into useful would benefit, so enzyme could evolve to catalyze that change
- useful chemical will be synthesized from related one
- short biosynthetic pathway will be favoured
- an organism that could change chemical into useful would benefit, so enzyme could evolve to catalyze that change
- useful chemical will be synthesized from related one
- short biosynthetic pathway will be favoured
87
New cards
We should find evidence of *blank* if complex adaptations really evolve in steps?
intermediate stages
88
New cards
What are the two sources of evidence of intermediate stages?
1) existence of intermediates in fossil recourse
2) present day species that show I-stages btw simple and advanced states
2) present day species that show I-stages btw simple and advanced states
89
New cards
1) First Source of Evidence of Intermediate Stages: Intermediate Stages of Molluscs, Anthropoids, and Vertebrates
- appeared 500 million yea ago
- no fossil record of ancestors
- DNA sequence suggests they were separate lineages before Cambrian era
- they were soft-bodied and didn't fossilize
- no fossil record of ancestors
- DNA sequence suggests they were separate lineages before Cambrian era
- they were soft-bodied and didn't fossilize
90
New cards
2) Second Source of Evidence for Intermediate Stages:
Flight and how it's beneficial? What animals have this ability?
Flight and how it's beneficial? What animals have this ability?
- first bat species have same limbs as modern bats
- flying squirrels can glide
- flying lemurs, sugar-gliders, gliding species of lizards, snakes, frogs
- reduces risk of being caught by predators
- gliding could evolve by gradual modification
- increase in area of skin and modifications for forelimbs will be advantageous
- flying squirrels can glide
- flying lemurs, sugar-gliders, gliding species of lizards, snakes, frogs
- reduces risk of being caught by predators
- gliding could evolve by gradual modification
- increase in area of skin and modifications for forelimbs will be advantageous
91
New cards
2) Second Source of Evidence for Intermediate Stages:
Eyes
Eyes
- all vertebrates have same design of eye but w variations
- series of intermediates btw light-sensitive receptors and various complex devices that produce images can be seen in groups of animals
- protein rhodopsin started with ability to detect light to producing sharp images
- series of intermediates btw light-sensitive receptors and various complex devices that produce images can be seen in groups of animals
- protein rhodopsin started with ability to detect light to producing sharp images
92
New cards
What is rhodopsin?
- allow animals to be capable of detecting and responding to light by receptors composed of light-sensitive protein rhodopsin
- found in animals eyes and bacteria
- detect light, and eventually improves to produce sharp image
- found in animals eyes and bacteria
- detect light, and eventually improves to produce sharp image
93
New cards
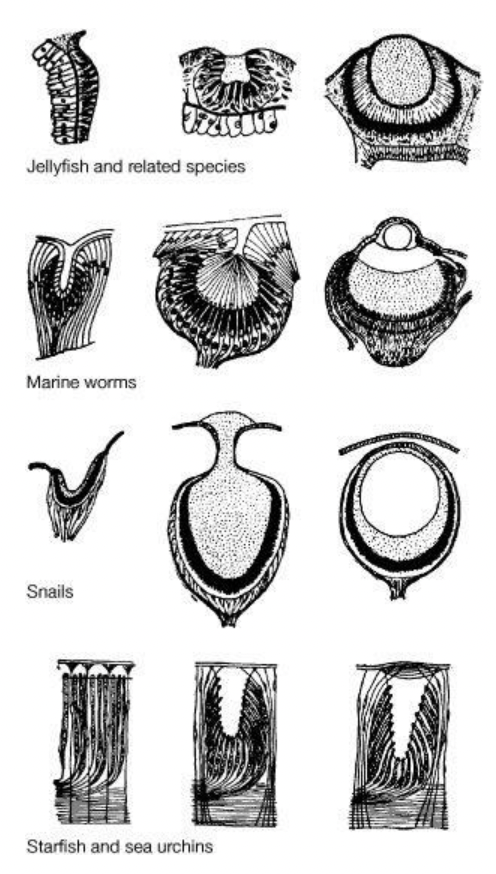
- left to right; shows more advanced types of eyes
94
New cards
Mortality
- high for young individuals
- declines as they become older and larger
- increases after adulthood
- adult death rate increases with age
- declines as they become older and larger
- increases after adulthood
- adult death rate increases with age
95
New cards
Mortality in Mice
- high mortality rates than compared to humans
96
New cards
Mortality in Bacteria
- they do not senesce
-they break down damaged parts and replace them
-they break down damaged parts and replace them
97
New cards
Rates of aging in species are because of...
- the difference effective of repair processes
- extent to which these are maintained with advancing age
- extent to which these are maintained with advancing age
98
New cards
When does selection favour fitness?
- selection favours survival and reproduction early rather than late in life
99
New cards
What are the two ways NS works to cause ageing?
1) keeping early-acting mutations rare in populations, allowing ones with effects late in life to become common
- alzhemiers
2) variants that have beneficial effects early in life will be more likely to spread through pop. that those whose good effects come in old age
example: flies by breeding only from old individuals
- evolve slower aging but reduce reproductive success early
- alzhemiers
2) variants that have beneficial effects early in life will be more likely to spread through pop. that those whose good effects come in old age
example: flies by breeding only from old individuals
- evolve slower aging but reduce reproductive success early
100
New cards
What does the Theory of Aging predict?
species w low external cause death rates should evolve low rats of aging and longer life spans compared to species w high external death rates
- smaller animals tend to age faster and reproduce earlier than large ones
- result of predation of small animals
- smaller animals tend to age faster and reproduce earlier than large ones
- result of predation of small animals