Biology: Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover vocabulary related to asexual and sexual reproduction, including terms relevant to meiosis and chromosomal abnormalities.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Asexual Reproduction
A type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes, resulting in genetically identical offspring.
Sexual Reproduction
A type of reproduction involving the fusion of two gametes (sperm and egg) to form a zygote, leading to genetic variation.
Gamete
A haploid reproductive cell (sperm or egg) that contains half the number of chromosomes of a somatic cell.
Fertilization (Syngamy)
The fusion of two haploid gametes to form a diploid zygote.
Meiosis
A specialized type of cell division reducing the chromosome number by half, producing four haploid gametes.
Homologous Chromosomes
A pair of chromosomes in a diploid cell.
Diploid (2n)
A cell containing two compete sets of chromosomes; one from each parent
Haploid (n)
A cell or organism that has a single set of unpaired chromosomes.
Germ Line Cells
Specialized diploid cells in sexually reproducing organisms that undergo meiosis to produce gametes.
Somatic Cells
Any living organism's cell other than reproductive cells.
Meiosis I
The first division of meiosis, during which homologous chromosomes separate.
Meiosis II
The second division of meiosis, where sister chromatids separate.
Prophase I
The first stage of Meiosis I characterized by chromosome condensation and crossing over.
Synapsis
The pairing of homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis.
Crossing Over (Recombination)
The exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids during prophase I of meiosis.
Chiasmata (singular: Chiasma)
Points of contact between homologous chromosomes where crossing over occurs.
Metaphase I
Stage of Meiosis I where homologous pairs align at the metaphase plate.
Anaphase I
Stage of Meiosis I where homologous chromosomes separate to opposite poles.
Telophase I
Final stage of Meiosis I where chromosomes arrive at the poles and the cell divides.
Prophase II
First stage of Meiosis II where chromosomes condense again.
Metaphase II
Stage of Meiosis II where chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
Anaphase II
Stage of Meiosis II where sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
Telophase II
Final stage of Meiosis II where four haploid daughter cells are formed.
Independent Assortment
The random orientation of homologous chromosome pairs during Metaphase I of meiosis.
Spermatogenesis
The process of sperm formation through meiosis in males.
Oogenesis
The process of egg formation through meiosis in females.
Chromosome Variation
Differences in structure or number of chromosomes within or between species.
Karyotype
A visual representation of an individual's complete set of chromosomes arranged in homologous pairs.
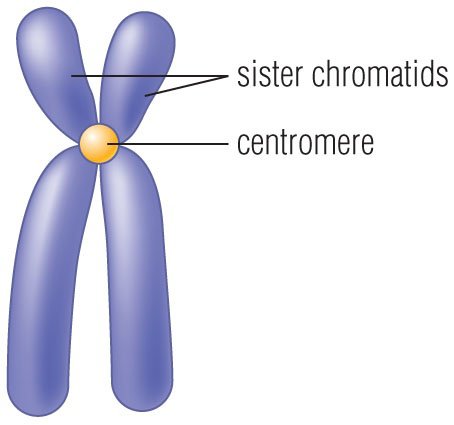
Centromere
The constricted region of a chromosome where sister chromatids are joined.
Metacentric
A chromosome with the centromere located in the middle, resulting in equal length arms.

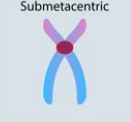
Submetacentric
A chromosome with off-center centromere, resulting in one shorter arm and one longer arm.
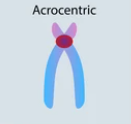
Acrocentric
A chromosome with the centromere near one end, resulting in very short and very long arms.
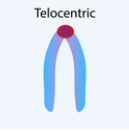
Telocentric
A chromosome with the centromere located at one end.
p arm
The short arm of a chromosome.
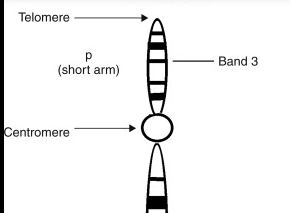
q arm
The long arm of a chromosome.
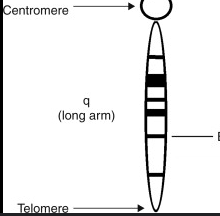
Chromosome Banding
Staining techniques revealing patterns of dark and light bands on chromosomes for identification.
Nondisjunction
The failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during meiosis.
Aneuploidy
A condition with an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, either an extra or a missing chromosome.
Monosomy (2n-1)
A type of aneuploidy with one copy of a particular chromosome instead of two.
Example: Cri-du-chat syndrome - missing chromosome 5
Trisomy (2n+1)
A type of aneuploidy with three copies of a particular chromosome instead of two.
Example: Edwards syndrome - 3 copies of chromosome 18
Deletion
A chromosomal abnormality where a segment of DNA is lost from a chromosome.
Duplication
A chromosomal abnormality where a segment of DNA is repeated, resulting in multiple gene copies.
Inversion
A chromosomal abnormality where a segment of a chromosome is reversed end-to-end.
Translocation
A chromosomal abnormality where a segment of DNA is transferred to a different chromosome, potentially leading to gene fusion or disruption.