Abeka 7th Grade Science Test 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
ovary
the part of the flower that fruit develops from
bulb
an underground structure made of thick, fleshly leaves surrounding a very short stem
compound leaf
a leaf that has more than one blade joined to a petiole
stolon
the creeping stem that grows along the surface of the ground in most grass plants
radicle
the part of the plant embryo that develops into the root system
plumule
the part of the plant embryo that develops into the shoot of the plant
sessile leaves
type of leaves attach directly to the stem
biennial
a plant that needs two growing seasons to complete its life cycle
angiosperms
the scientific name for plants that produce seeds covered by a flower
Christian Konrad Sprengel
German botanist known for discovering many complex details of plant reproduction
plant reproduction
primary purpose of flowers
sepals
leaf-like structures at the base of a flower's petals
transpiration
the term used for the main force that brings water up a plant's transport tubes, the loss of water from leaves
Queens Anne's lace
member of the parsley family that is also known as wild carrot
alternate leaf arrangement
what type of leaf arrangement does this branch have

seedling
the term for a young plant that is able to survive without its cotyledons
herbaceous
the type of plants have non-woody stems
photosynthesis
the food-making process of plants
anther
the part of the stamen that produces pollen grains
pollination
the transfer of pollen from the stamen to the top of the pistil
vegetative reproduction
plant reproduction that does not involve flowers, seeds or fruit
petals
the part of the flower that attracts pollinators
spores
tiny one-celled reproductive structures found on plants such as ferns
node
the place where the leaf attaches to the stem
pollen tube
tube that grows from a pollen grain through which a sperm cell travels to the egg cell?
pea family
the family that has fruits called legumes
grass family
the family that has fruits called grains
mint family
the family that has square and stout stems with flowers usually arranged in spikes
amaryllis family
the family that are monocots that have tepals and inferior ovaries and grow from bulbs, corns, or rhizomes
rose family
the family that has woody stems; fleshly fruits; flower parts in multiples of five; and cup-shaped blossoms with white, pink, or rose-colored petals
grass family
the family that is the most important group of plants
pea family
the family of plants that help return nitrogen to the soil
buttercup family
the family that is also called the crowfoot family because of their leaf shape that resembles a bird's foot
xylem
carries water and nutrients from the root hairs upward through the root system and the stem to the leaves
disk
what type of flowers found in the center of the composite flower head
osmosis
the process in which water and dissolved chemicals are absorbed through the cell membrane of the root hairs
cortex
the storage cells that surround a root's transport tubes
opposite
what type of leaf arrangement does this branch show
agent dispersal
animals, humans, or physical processes like wind and ocean currents scatter the seeds
bryophytes
plant without a vascular system
seed coat, endosperm, and embryo
the three main parts of a seed
primary growth
growth of a plant in length
root pressure
the upward force in the transport tubes produced by water entering the root hairs
mechanical dispersal
the ripened fruit bursts open, scattering the seeds
moisture, favorable temperature, oxygen
three main things seeds require to germinate
cotyledon
plant embryo structure designed for food aborption and storage
chloroplasts
chlorophyll -containing organelle where photosynthesis takes place in a plant cell
photosynthesis
process whereby a plant uses sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to manufacture glucose and give off oxygen
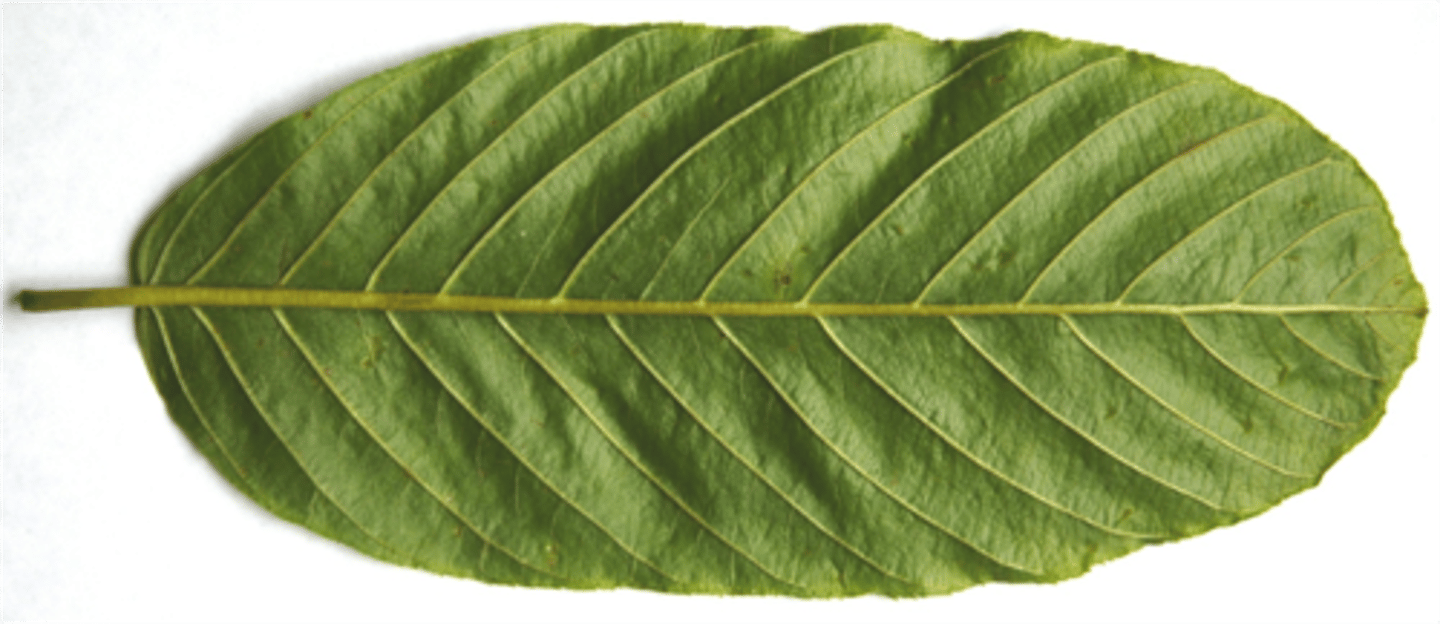
pinnate
What type of venation does this leaf illustrate?

lobed
margin that has extensions of itself that can be blunt or end in a sharp point
entire
margin that are smooth and unbroken
toothed
margins with either small, sharp teeth or large blunt teeth
Monocot
a plant whose seeds have only one cotyledons; generally have leaves with parallel veins, petals in multiples of three, and fibrous roots
dicots
a plant whose seeds have two cotyledons; generally have broad leaves with branching veins, petals in groups of four or five, and a large taproot with secondary rootlets