International Trade and Finance
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Why do countries trade?
Divergent opportunity costs, where countries can focus resources on G+S they have a comparative advantage on, such that they can increase production and GDP
When does a country have a comparative advantage over another country?
When they can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than any other country
How does international trade create gains for countries?
It’s Cheaper to buy than to produce
E.g. if the rest of the world buys UK chemicals, which is has a CA on, then countries can decrease their production of chemicals, move along their PPF, and be able to buy more chemicals for the same number of cars
Note: UK can now consume at any point along the trade line
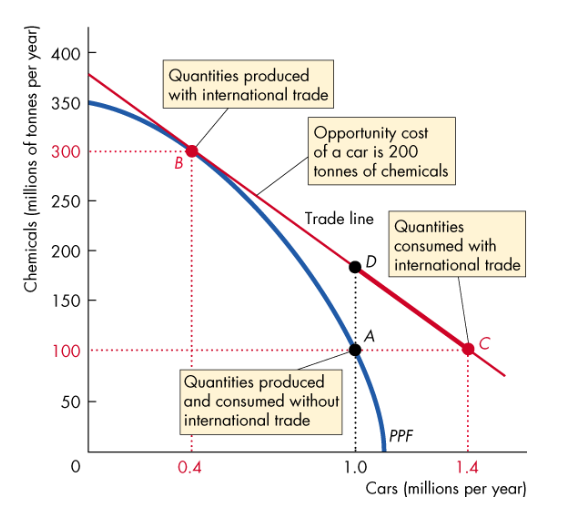
What are some other advantages of international trade?
Permits exploitation of economies of scale, supporting small countries who may not have a large enough domestic market
Increases choice, through the proliferation of differentiated products
Promotes competition by breaking down local monopolies
Leaning by doing decreases costs due to the large scale of production
Who are the winners and losers of international trade for an importing country
Price decreases after trade
Consumers gain as the pay less and buy more, increasing CS
Producers lose as the receive less, produce less and have a smaller PS
Consumers’ gain exceeds producers’ loss, so total surplus increases
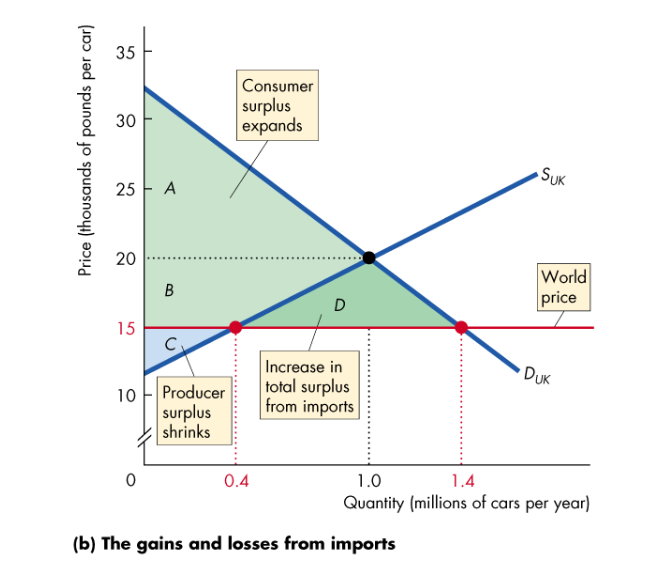
Who are the winners and losers of international trade for an exporting country?
Price increases after trade
Producers gain as they receive a higher price, produce more and receive a larger PS
Consumers lose as they pay more and buy less, decreasing CS
Gain in PS exceeds loss in CS, so total surplus increases
What is a tariff, and how does it work?
Tax imposed by the importing country when an imported good crosses int’l boundaries
By imposing a tariff, it increases producer surplus whilst decreasing consumer surplus, reducing imports but creating a DWL in the process
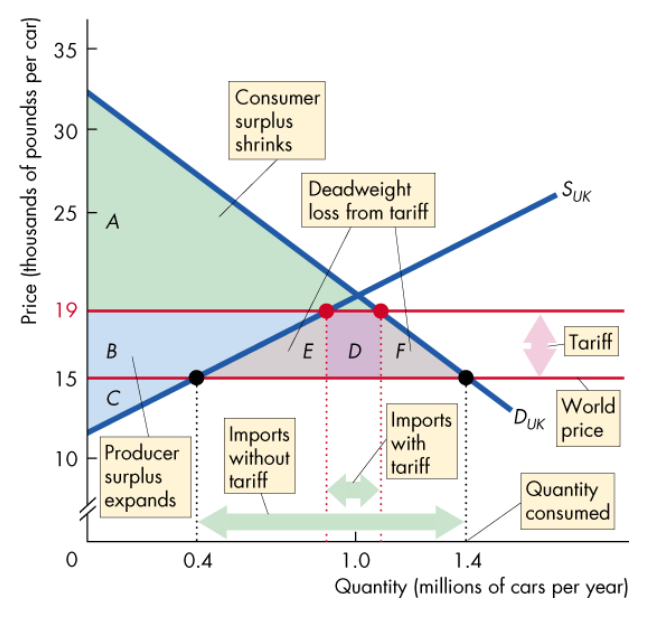
What is a quota, and how does it work?
It’s a limit of the quantity of a good that can be imported
By putting a limit on imports, it shifts the domestic supply curve right, meaning new equilibrium is at a higher quantity and lower price, increasing CS and decreasing PS, but imposing a DWL in the process
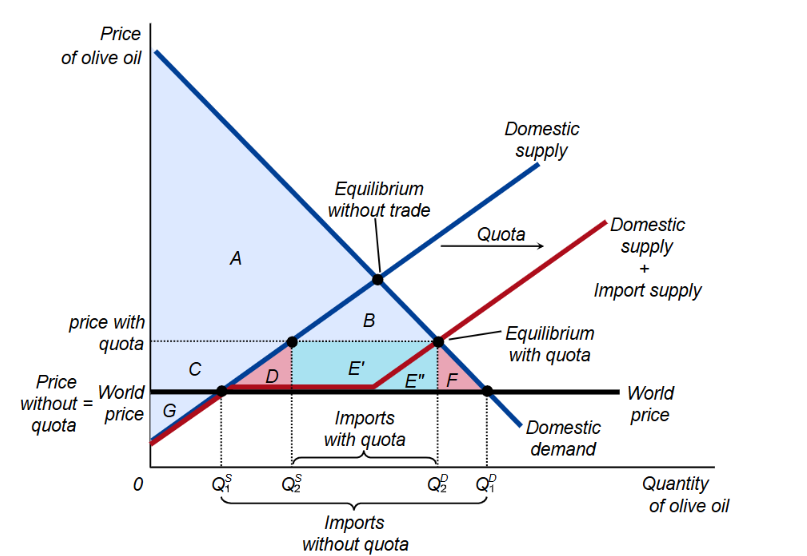
What are the arguments for protectionist policies?
National security argument
Infant-industry argument (e.g. post WW2 Japan)
Saves jobs
What are the arguments against protectionist policies?
Consumers pay higher prices
Resources moved from an efficient to inefficient use
Can’t export if we don’t import
Protection could invite retaliation
What is the Balance of Payments, Credit and Debit?
Balance of Payments = Record of a country’s transactions (Trading, borrowing and lending) with the rest of the world
Credit = Payments by foreigners
Debit = Payments to foreigners
What is a current account, and what does it include?
It records transactions in G+S
Includes:
Payments for imports
Receipts for exports
Net interest paid abroad
Net transfers
Current account balance = X - M + Net interest income + Net Transfers
When is the current account in deficit or surplus, and what must it do to rectify it?
Deficit when X - M < 0
Must borrow from foreigners or sell assets
Surplus when X - M > 0
Must make loans to foreigners or buy some of their assets
What does the capital account show, and what happens when a country is a net borrower/lender?
Capital account = S - I (Net capital outflow)
Net borrower (S<I):
Capital inflow needed: Purchase of domestic assets by foreigners
Net lender (S>I):
Capital outflow needed: UK purchases foreign assets
What is a key condition of the balance of payments, and what must be done in order to maintain this state?
BOP must always balance
Sum of current and capital accounts must always equal zero
Any difference needs to be compensated by a change in foreign currency reserve holdings
Countries with current account surplus acquire foreign assets
Countries with current account deficit sell assets
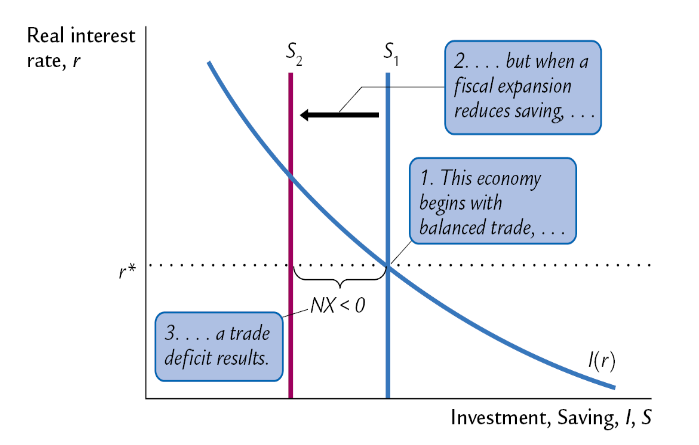
What happens to the investment and savings curves when an expansionary FP is pursued at home?
Starts with balanced trade, but a fiscal expansion reduces savings, resulting in a trade deficit occurring
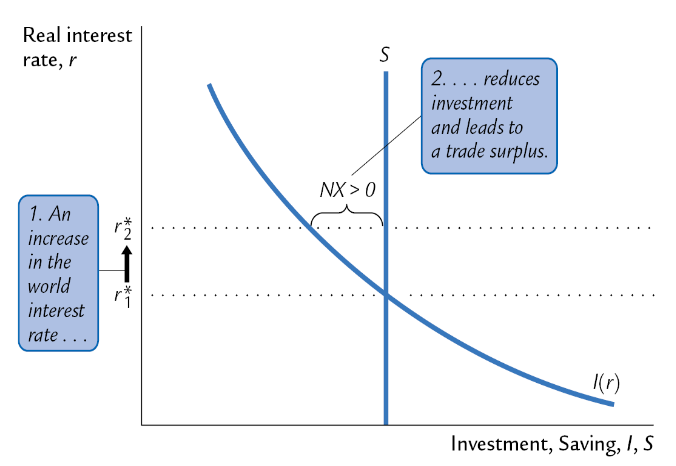
What happens when an expansionary FP is pursued abroad?
It leads to an increase in the world interest rate, reducing investment and leading to a trade surplus
What happens when the government decreases regulation?
Leads to an increase in investment demand, increasing interest rates and leading to a trade deficit
When is being a net borrower a problem or not?
Not a problem when borrowed funds are used for investments which boost national income
It is a problem when borrowed funds are used to finance consumption
What is an exchange rate?
The price of a foreign currency in terms of its domestic currency
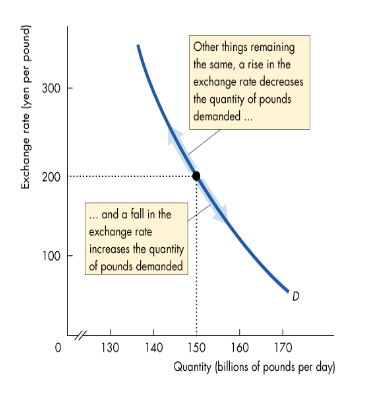
What determines the SR exchange rate?
The quantity of pounds demanded in the foreign exchange market
Higher the ER, the lower the quantity of £s demanded
Lower the ER, the higher the quantity of £s demanded
Explain the demand curve for pounds
Negatively sloped due to exports and expected profits
Moving down the vertical axis, the pound is worth fewer dollars, so it depreciates
Moving up the vertical axis, the pound is worth more dollars, so it appreciates
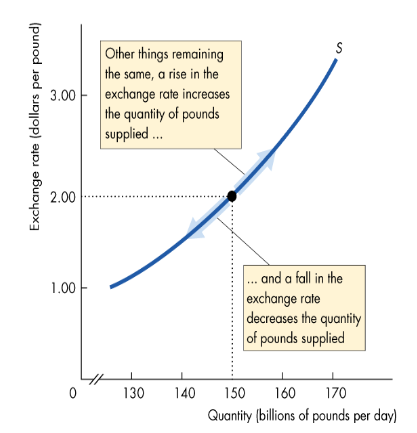
What determines the supply of foreign exchange?
Quantity of £s supplied depends on the exchange rate
The higher the ER, the larger the quantity of £s supplied
The lower the ER, the lower the quantity of £s supplied
Explain the supply curve for pounds
Positively sloped due to imports and the expected profits effect
Moving down the vertical scale, the pound is worth fewer dollars, so it depreciates
Moving up the vertical scale, the pound is worth more dollars, so it appreciates
Explain how foreign exchange market equilibrium is found
Occurs when the supply of pounds = demand of pounds
If exchange rate is too high, a surplus of pounds drives it down
If exchange rate is too low, a shortage of pounds drives it up
What causes a shift in the demand curve?
A change in the influence on the quantity of pounds that people plan to buy, other than exchange rate
Demand for pounds increases if:
World demand for UK exports increases
UK interest rate differential increases
Expected future exchange rate rises
Demand for pounds decreases if:
World demand for UK exports decreases
UK interest rate differential decreases
Expected future exchange rate falls
What causes a shift in the supply curve?
A change in any influence on the quantity of pounds that people plan to sell, other than the exchange rate
Supply of pounds increases if:
UK demand for imports increases
UK interest rate differential falls
Expected future exchange rate falls
Supply of pounds increases if:
UK demand for imports decreases
UK interest rate differential rises
Expected future exchange rate rises
What is the real exchange rate?
The rate at which a person can trade the G+S of one country for the G+S of another
Real ER = (Nominal ER x Domestic Price)/Foreign Price
Changes in RER change demand for imports and exports
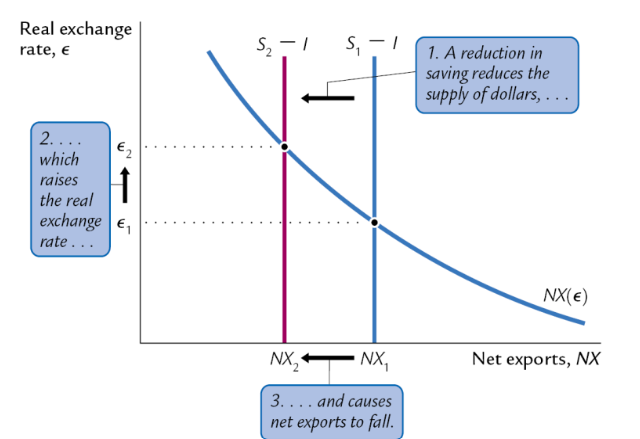
What’s the effect of a domestic expansionary FP on the RER?
A reduction in savings reduces supply of dollars, raising the real ER, causing net exports to fall
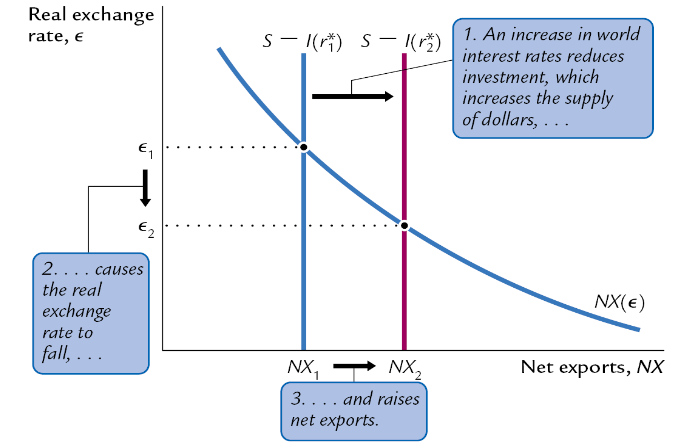
What’s the effect of a foreign expansionary FP on the RER?
An increase in world interest rates reduces investment, increasing the supply of dollars, which causes the RER to fall, raising net exports
What’s the effect of protectionist policies on the RER?
They raise the demand for net exports, raising the exchange rate, but leaving net exports unchanged
What factors determine the LR values of the exchange rate?
Determined by the relatives prices in 2 countries
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) occurs when 2 quantities of money can buy the same amount of G+S as one another
What happens when an ER is fixed?
The govt or CB maintains the rate by buying/selling its currency using foreign currency reserves. This shifts the supply curve and keeps the equilibrium at the desired rate
However, if the markets think the fixed value is unsustainable, they can force a revolution
What are some alternative exchange rate regimes?
Floating/Flexible
No intervention. ER adjusts so that supply = demand
Fixed/Pegged
CB/govt buys or sells reserves to fix the ER
Managed Float/Crawling Pegged
CB or govt intervenes only if the ER fluctuates too much