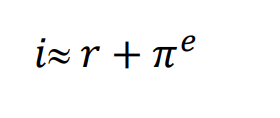Lesson 1B: The meaning of Interest rates
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Types of Interest Rates: Nominal Interest Rate
– The stated rate, not adjusted for expected inflation.
Types of Interest Rates: Real Interest Rate
The nominal rate adjusted for the expected inflation rate — reflects actual purchasing power gained.
How can we compare cash payments ( cash flows) of different amounts and with different timings?
Present value
Present Value
– A dollar paid to you one year from now is less valuable than a dollar paid to you today
– In other words, future cash flows are discounted in order to see what they are worth today, i.e. their present value
Simple Loan
Assume simple interest rate of i=10%
–One-year simple loan: Loan $100 today and require $110 repayment in one year
– The $100 today and the $110 next year are equivalent if discounting the future with 10% is appropriate
Present Value Formula:
i = appropriate discount rate PV = today’s present value CF = future cash flow or payment n years from now , then
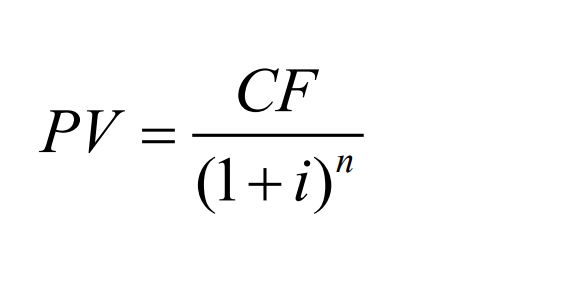
Four types of Credit Market Instruments:
Simple Loan, Fixed Payment Loan, Coupon Bond, Discount Bond.
Simple loan
–One payment at the maturity date
Fixed Payment Loan
–Multiple fixed payments at pre-specified dates
Coupon bond
– A bond that pays fixed amounts (the coupons) at fixed dates, plus a final payment (the face value) at maturity
Discount bond
– A bond that pays zero coupons, only a final payment at maturity – “Discount” since price typically less than face value
Yield to Maturity
Interest rate that equates the present value of all cash flow payments received from a debt instrument with its value today.
• It is the return an investor actually earns if they buy the debt instrument at today’s market price and hold it to maturity.
Yield to Maturity Formula
PV = amount borrowed (market price if loan is traded)
CF = cash flow in one year
n = number of years from today
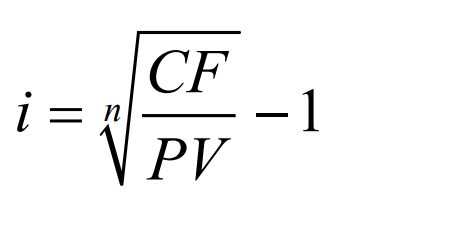
Yield to Maturity Formula on a Fixed Payment Loan
LV = loan value (market price if loan is traded)
FP = fixed yearly payment
N = number of years until maturity
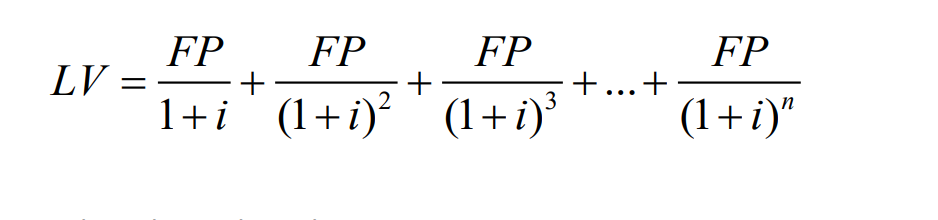
Coupon Bond Formula
P = market price of coupon bond
C = yearly coupon payment
F = face value of the bond (also known as par value)
n = years to maturi
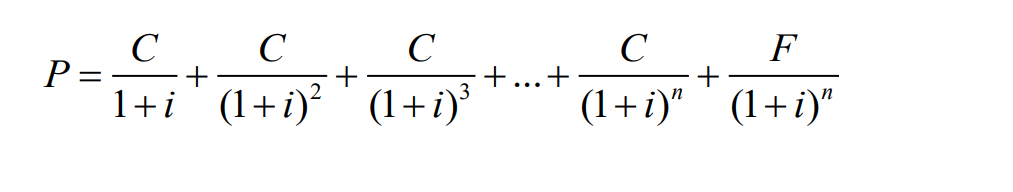
Consol
a bond without a maturity date. It never repays the principal, but pays fixed coupon payments forever
Interest Rate Risk
The risk level associated with an asset’s return that results from interest-rate changes
• Prices and returns for long-term bonds are more volatile than those for shorter-term bonds
• There is no interest-rate risk (over the holding period) in case the time to maturity matches the holding period
How to measure the real interest rate?
Before it was subtract the level of inflation, now we use adjust for expectred inflation
Fischer Equation approximation
i = nominal interest rate r = real interest rate πe = expected inflation rate