Kinematics
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sorry for the wrong answers :(. All fixed now! ||| texbook references: Mike Crundell, Geoff Goodwin - Cambridge International AS & A Level Physics student's book 3rd edition |||
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
What is displacement
distance moved in a particular direction
what is velocity
rate of change of displacement of an object
what is acceleration
rate of change of velocity on object
what does the gradient of a displacement - time graph give
velocity
what does the sign of the gradient of a displacement - time graph mean
direction of velocity
what does zero gradient mean on displacement - time graph mean
object is at rest
what does a constant gradient on a displacement - time graph mean
object is moving at constant velocity
what does a decreasing gradient on a displacement - time graph mean
object is decelerating
what does an increasing gradient of a displacement - time graph mean
object is accelerating
what does the gradient of a velocity - time graph give
acceleration
what does the area under a velocity - time graph give
displacement
what does zero gradient on a velocity - time graph give
no acceleration
what does a constant gradient mean on a velocity - time graph give
constant acceleration
what does a decreasing gradient of a velocity - time graph give
decreasing acceleration
what does an increasing gradient of a velocity - time graph give
increasing acceleration
what is the first step of finding the gradient of a curve
find the tangent
what is kinematics about
describing the motion of objects but not the cause
how do you find an area under the curve
using geometrical shapes to estimate the area
what is a scalar quantity
A physical quantity that has only magnitude
what is a vector quantity
A physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
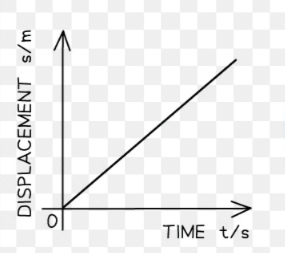
what is this graph showing?
constant velocity
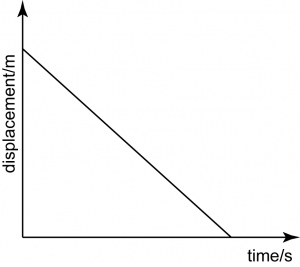
what is this graph showing
decreasing velocity
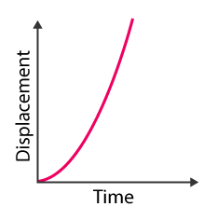
what is this graph showing
non-constant accelerating velocity
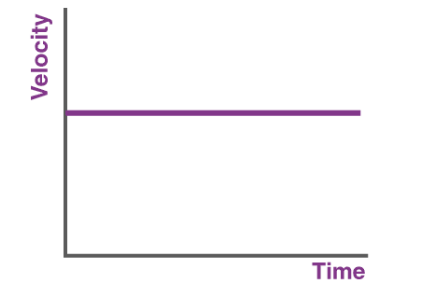
what is this graph showing
zero acceleration
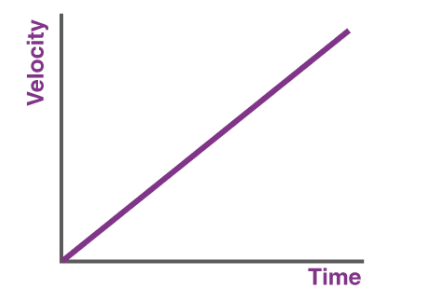
what is this graph showing
constant acceleration
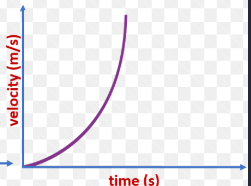
what is this graph showing
increasing acceleration
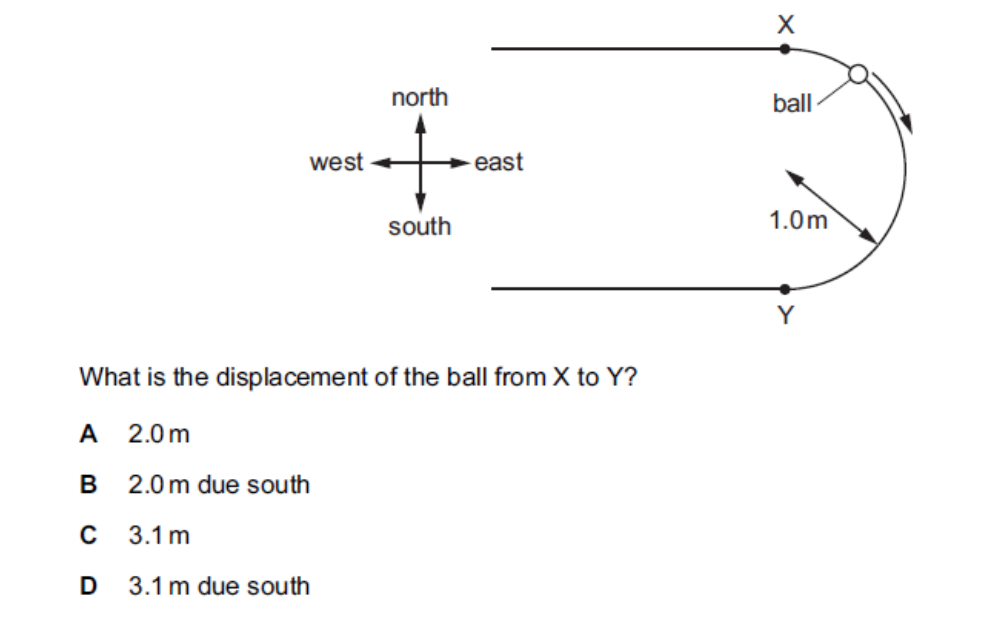
what is the answer
B
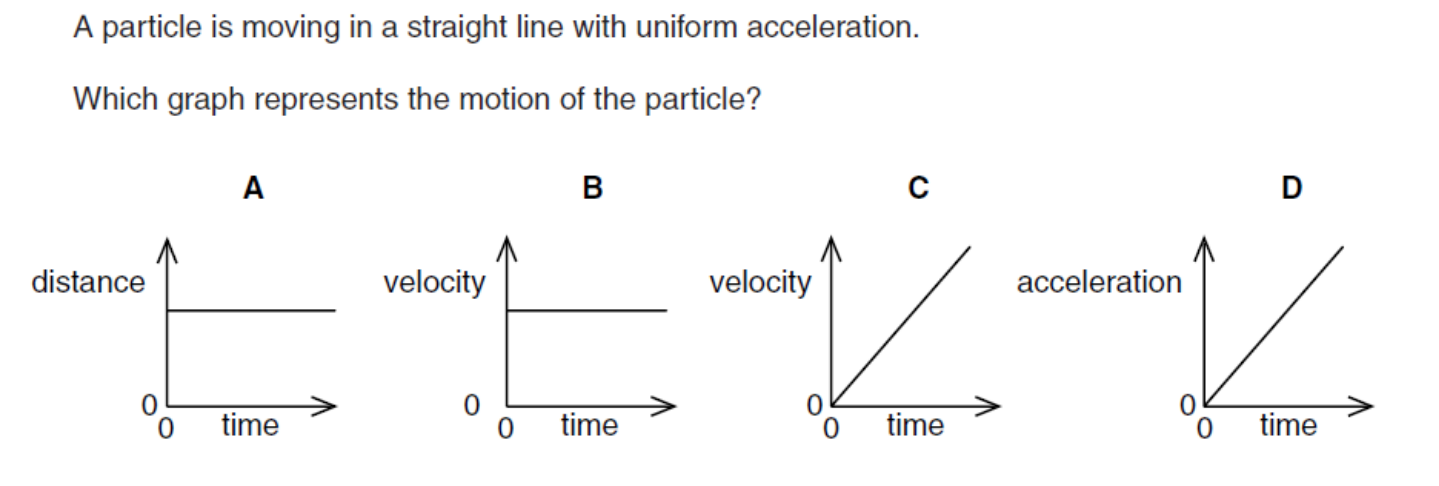
what is the answer
C
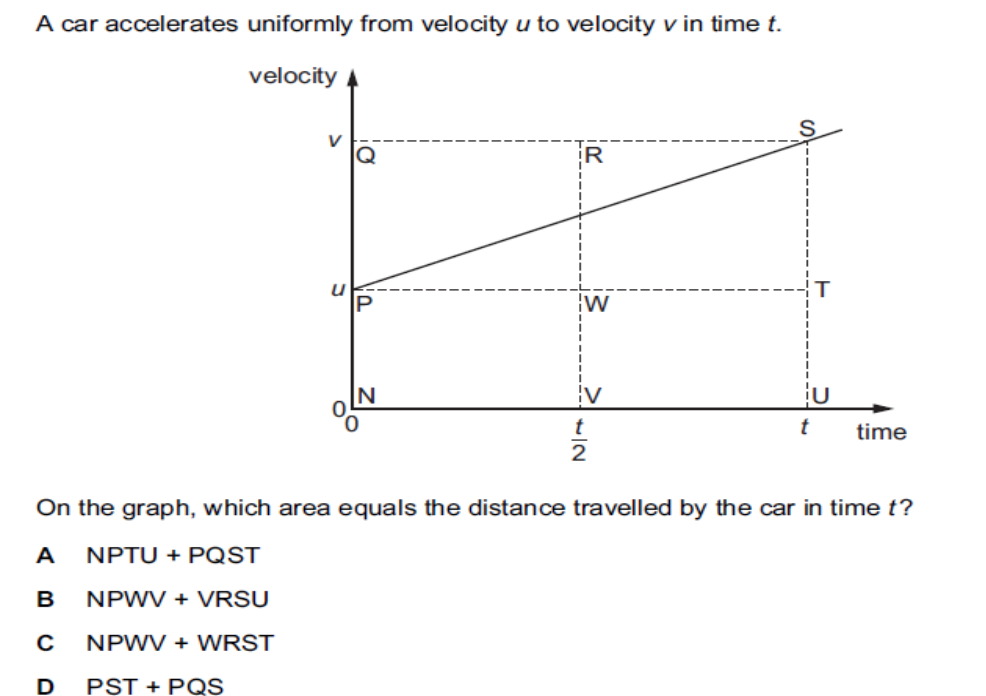
what is the answer
B
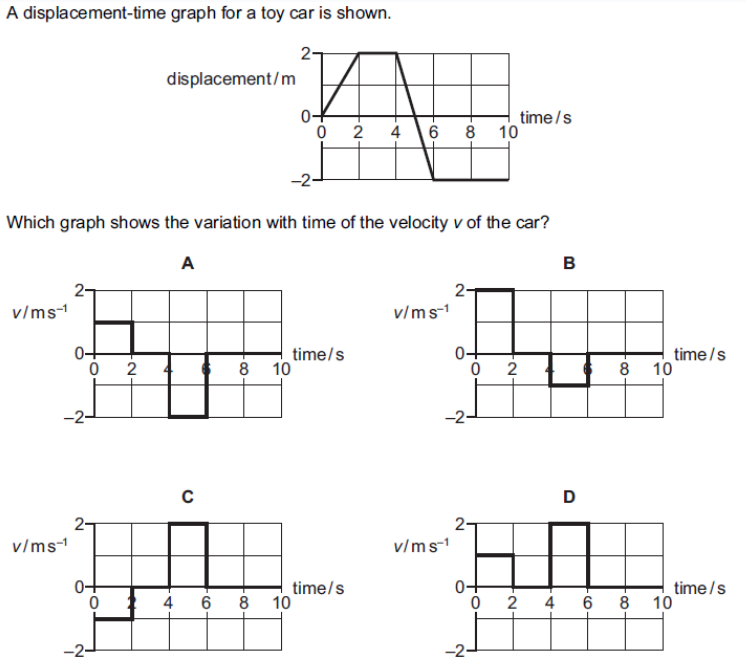
what is the answer
A
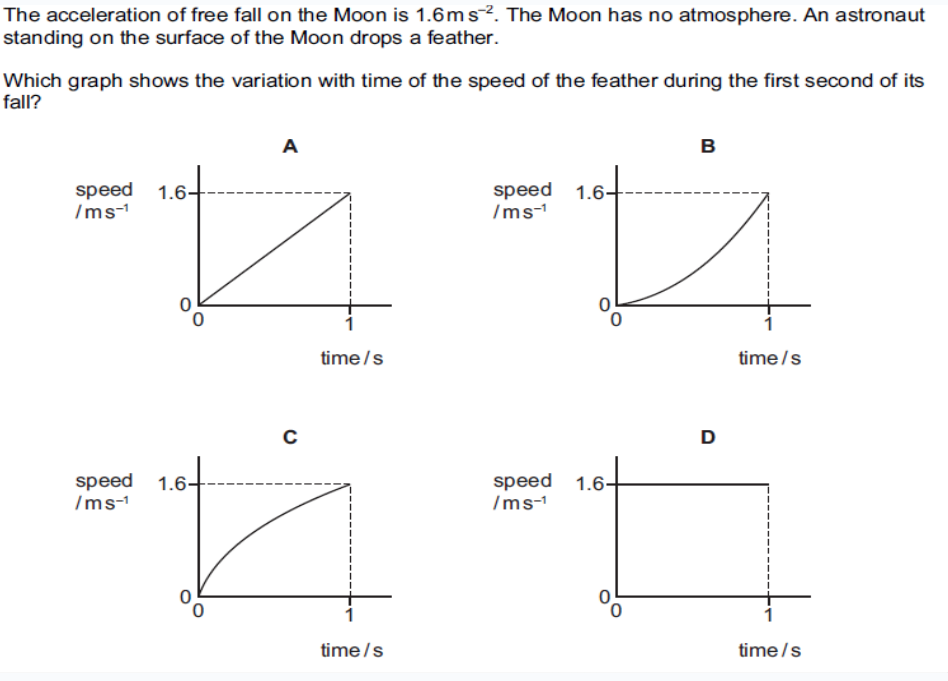
what is the answer
A
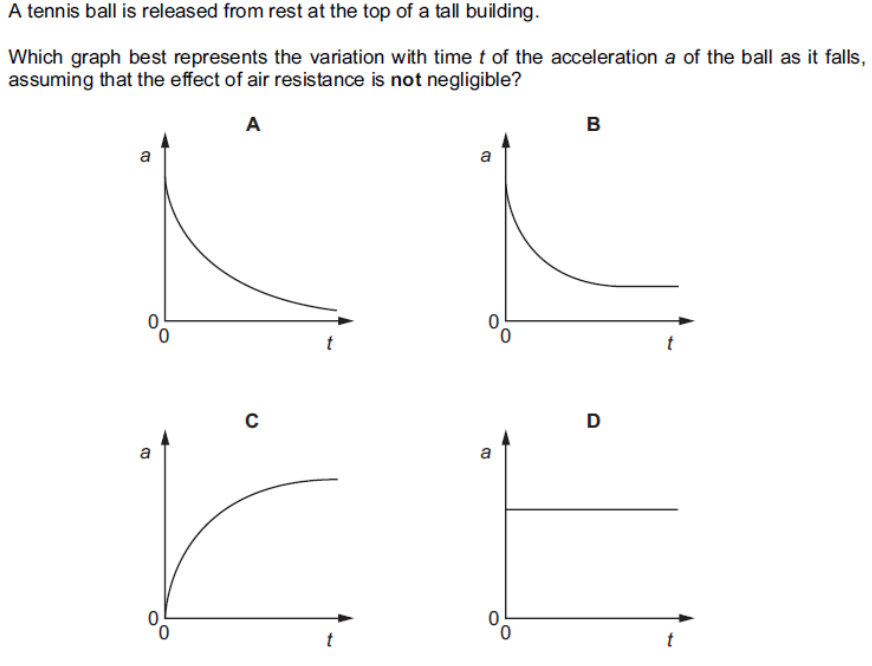
what is the answer
A
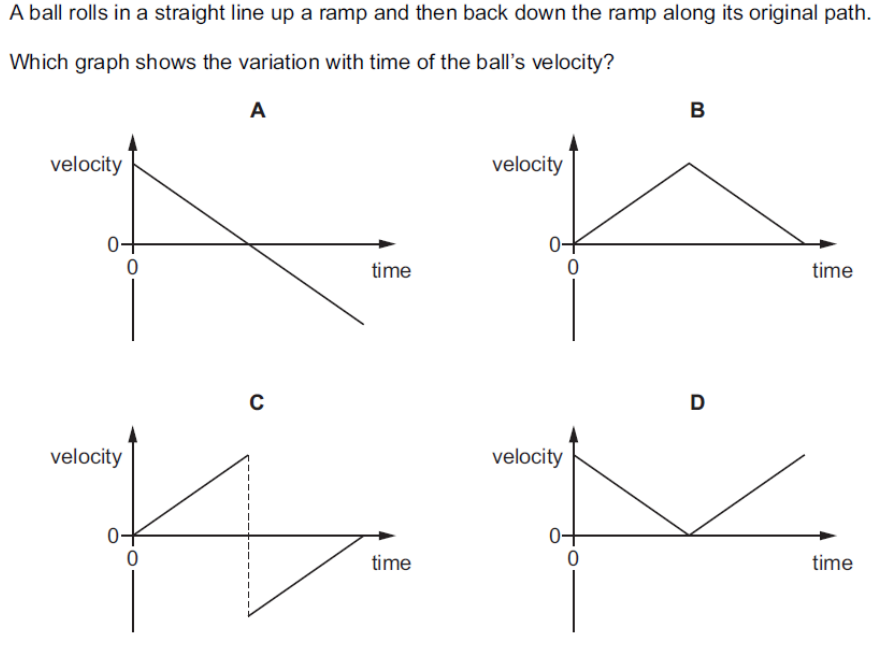
what is the answer
A
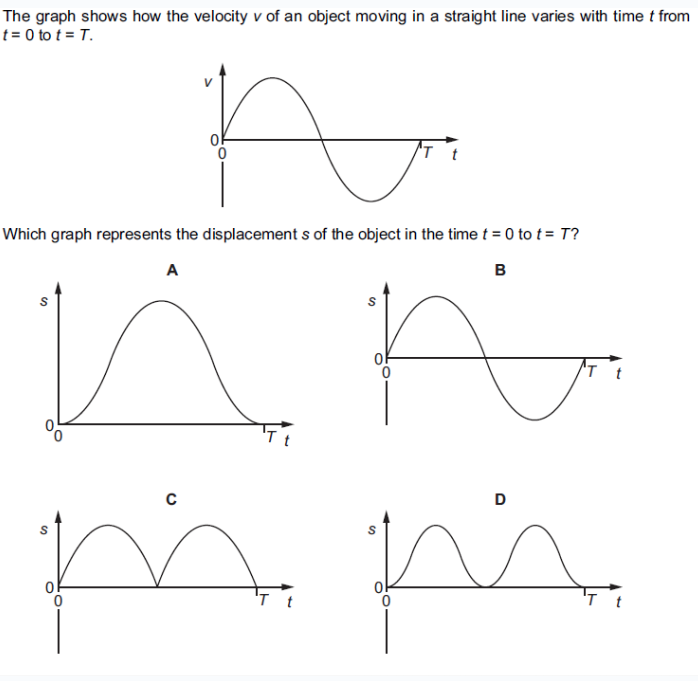
what is the answer
A
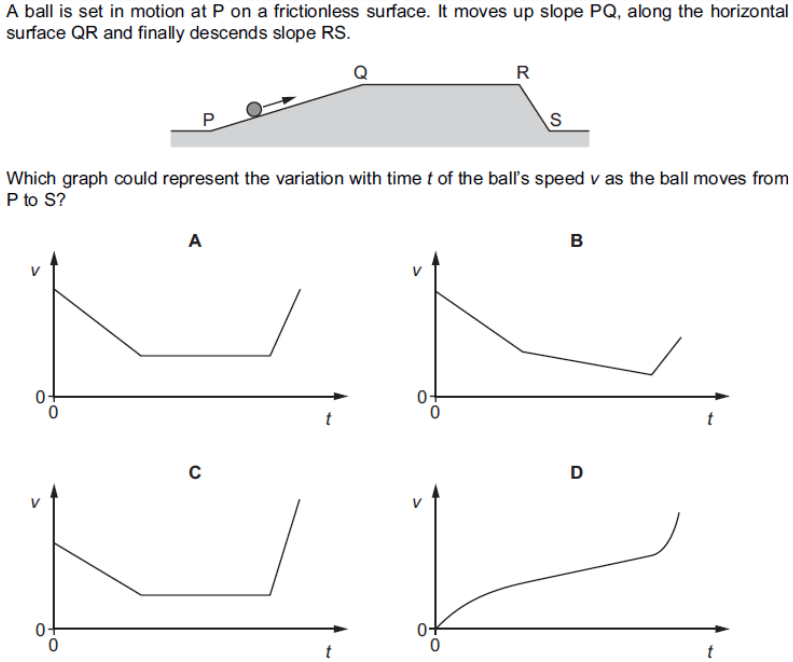
what is the answer
A
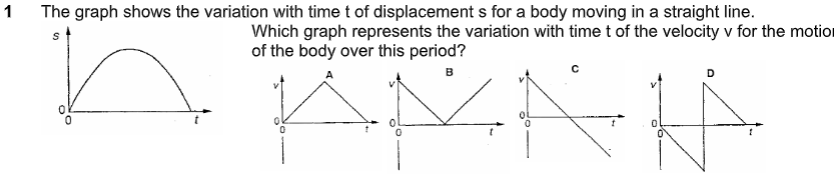
what is the answer
C

what is the answer
D

what is the answer
D
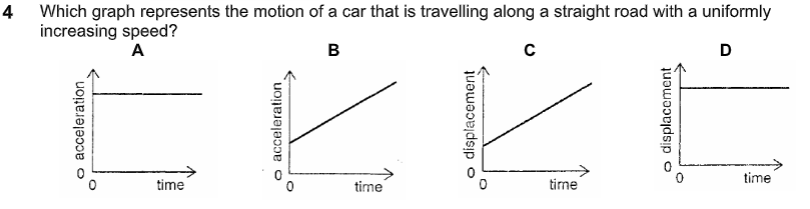
what is the answer
C

what is the answer
B

what is the answer
D
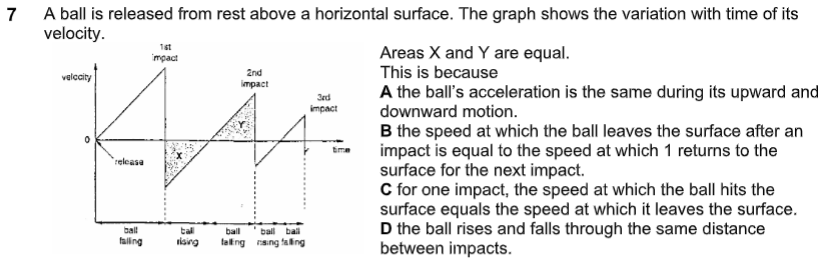
what is the answer
D
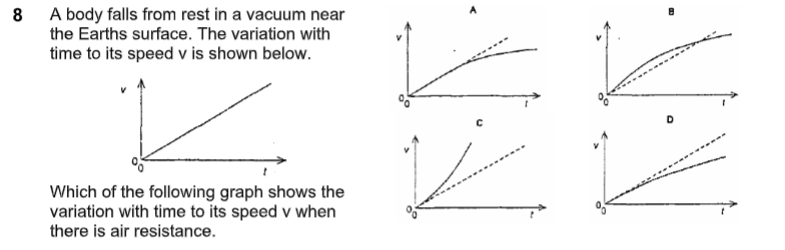
what is the answer
D
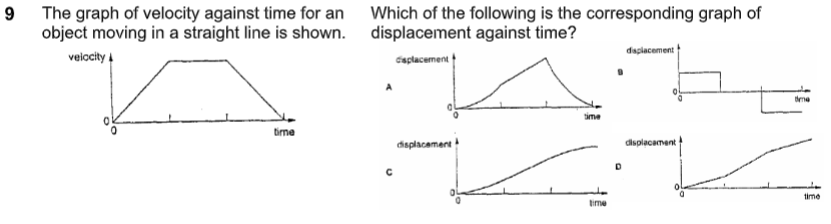
what is the answer
C

what is the answer
B
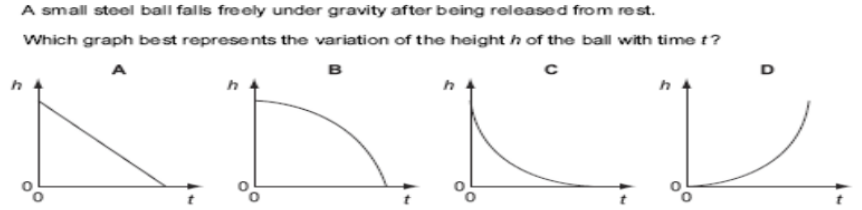
what is the answer
B
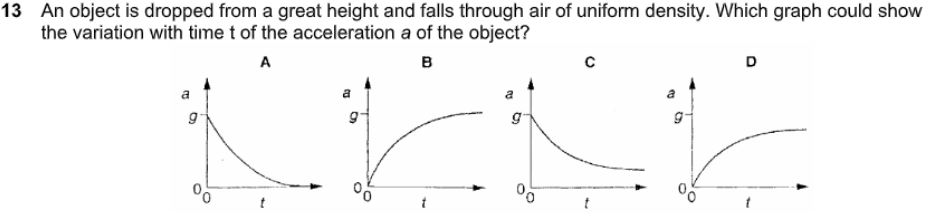
what is the answer
A
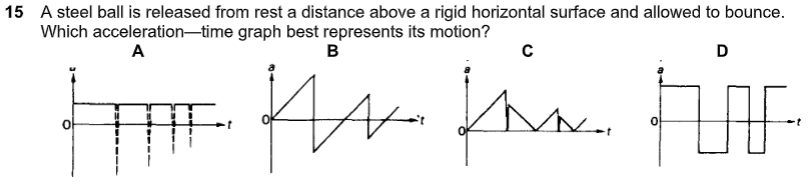
what is the answer
A
how do you calculate speed
distance / time
what is the unit for speed
ms ^-1
how do you define speed
distance moved along the path divided by the time taken
what is relative speed
speed of an object as observed from the perspective of another moving object
how do you calculate relative speed in the same direction
v1 - v2
how do you calculate relative speed in the opposite direction
velocity 1 + velocity 2
how do you calculate velocity
change of displacement / change of time
guess the average speed of: light
3.0 × 108
guess the average speed of: electron around nucleus
2.2 × 106
guess the average speed of: earth around sun
3.0 × 106
guess the average speed of: jet airliner
2.5 × 102
guess the average speed of: typical car speed (80km/h)
22
guess the average speed of: sprinter
1.0 × 101
guess the average speed of: walking speed
1.5
guess the average speed of: snail
1.0 × 10-3
what is quoted relative to a fixed referene
speed
how do you calculate average velocity
displacement / time
what is the average acceleration for: due to circular motion of electron around nucleus
9 × 1026
what is the average acceleration for: car crash
1 × 103
what is the average acceleration for: free fall on earth
9.81
what is the average acceleration for: family car
2
what is the average acceleration for: free fall on moon
1.6
what is the average acceleration for: an Equator, due to rotation of earth
3 × 10-2
what is the average acceleration for: due to circular motion of earth around sun
6 × 10-5
how does a displacement-time graph show constant velocity
displacement increases by equal amounts in equal times
how does the gradient of a displacement time graph indicate dierction
sign of the gradient
what is a parabola
the curve traced out by a particle subject to a constant force in one direction
what is air resistance
the forces that oppose the motion of an object as it passes through the air
what is the definition of acceleration of free fall
the same uniform acceleration with which all objects fall near the surface of the Earth, due to the Earth’s uniform gravitational field
what is gravitational field of earth
a region of space where a mass experiences a force
what is instantaneous velocity
the average velocity measured over a really short time interval
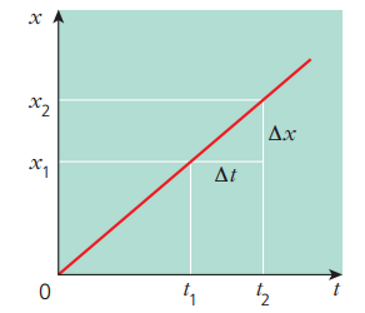
what kinematic equation is this graph showing?
x = vt
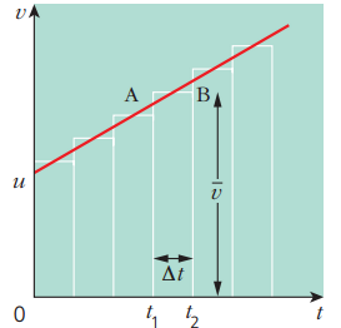
what kinematic equation is this graph showing?
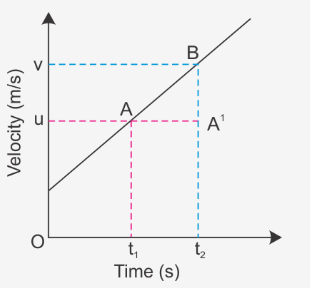
v = u + at
what kinematic equation is this graph showing?
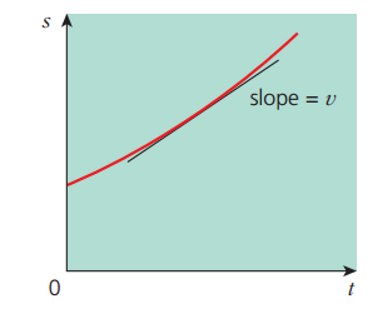
s = ut + 1/2 at²
what kinematic equation is this graph showing?
v² = u² + 2as
what is the symbol for acceleration of free fall
g
how can free fall happen
must be in the absence of air resistance
if you are doing an experiment to find acceleration of free fall as an AS level student, what aparatus are you recommened as the best?
steel sphere, electromagnet, metre rule, camera, stroboscope, stopwatch
do heavier bodies fall faster than light ones?
no
do heavy and light bodies fall at the same acceleration?
yes
what is this statement related to: displacement travelled is proportional to time squared
free fall
what is the formula for a particle projected with initial velocity at an angle to the horizontal from a point on level ground
R = (u² sin 2 (angle)) / g
what is R in the equation for a particle projected with initial velocity at an angle to the horizontal from a point on level groun
distance from the point of projection to the point at which the particle reaches the ground again
what is the best way to calculate projectile motion
looking at vertical and horizontal motion independently
how many forces are acting on a object if it is falling through free fall
one
how does acceleration due to gravity decrease when you fall
decreases as you go further away from the surface of the earth
during terminal velocity, what becomes significant
air resistance
if an object is speeding up, what happens to the air resistance
it increases
if you throw an object and air resistance is present, what happens to the object
falls more steeply that it rised
what is the effect on horizontal velocity at low speeds with air resistance
drag is proportional to velocity
what is the effect on horizontal velocity at high speeds with air resistance
drag becomes related to velocity squared
what happens when air resistance is affecting vertical motion upward
gravity and friction both act downward; object slowing down until rest