Geology Exam II
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Sedimentary Rocks
Formed from the transported, deposited and lithified weathering products of rocks and biological material
Covers 75% of earths surface
Sediments
Weathered and transported products (solid and dissolved) of other rocks as well as biological materials
Erosion
General term for the processes by which rock is broken down and the products moved
Includes weathering and transport
Weathering
The breaking down of rocks
Transport
Moving of products
Includes gravity, wind, ice, and liquid water
Deposition
The process of sediment accumulation that occurs when transport of solids or dissolved species ceases
Lithification
Process of turning deposited sediments into stone through compaction, cemnetation, precipitation and/or recrystallization
Physical Weathering
The breaking of rocks with physical means including wind/water abrasions, root wedging, freeze/thaw and thermal expansion
Chemical Weathering
Breaking of rocks by chemical means including disolution, oxidation/reduction and hydrolysis
Impact/Abrasion
Things knocking rocks together and breaking them apart
Root Wedging
Roots growing into cracks of rocks and eventually splitting them apart
Freeze / Thaw
Water seeping into cracks of rocks then freezing and expanding making bigger cracks in rock
Thermal Expansion
When flakes are spalled off from heat. Heat makes outside of rock more mallable but inside is cold so it breaks off
How Physical and Chemical Weathering Work Together
Physical breaks up rocks, making more surface area for chemical weathering to attack!
Water and Temperture
Most important factor in controlling rate of chemical weathering
Transportation By Glaciers
Ice melts so material the glacier was carrying is deposited
Transportation By Gravity
It falls. Like duh.
Transportation By Wind
It blows things making it move
Transportation By Water
When it evaporates the dissolved load is deposited
When it slows down the solid load is deposited
Name for Pebble (or larger) sized grains
Breccia (angular)
Conglomerate (Rounded)
Name for Sand sized grains
Sand stone
Name for Silt sized grains
Silt stone
Name for Clay sized grains
Shale (Or clay stone)
Depositional Enviorment
Physical, biological and chemical conditions (that is, the enviorment) at the time sediments are deposited
Sedimentary Facies
A distinctive group of characteristics within a sedimentary unit (including sedimentary structures, grain size, and rock type) that allow one to infer the depositional enviorment
Sedimentary Structures
Features in sedimentary rocks that reflect some aspect of the depositional enviorment
Metamorphism
Textural and compositional changes in ricks due to increased temperture and pressure
Metamorphic Rocks
Rocks changed by heat and/or pressure
Important Factors in metamorphism
Pressure (Confining or directional)
Temperture
Parent rock (protolith) composition
Fluids
time
Types of Metamorphism
Mountain Belt
Contact
Subduction Zone
Foliation
Parallel orientation of platy minerals (like micas) or elongated grains in some metamorphic rocks
Usually breaks parallel to this orientation
Contact Metamorphism
Metamorphism caused by magmatic intrusions. Intrusions bring in a lot of heat to relatively shallow, cool, depths and also give off fluids. The rocks in contact witht he intrusion are changed ( = Metamorphosed)
Shock Metamorphism
Results from extreme, short-lived, high pressures
Mountain Belt Metamorphism
increases in both heat and pressure
Subduction Zone Metamorphism
Low Temperature and high pressure
Principles of stratigraphy
Putting things in order / Relative timeline
Original Horizontality and Lateral Continuity
Sedimentary rocks are originally laid down in horizontal (or almost horizontal) layers
Layers continue laterally until they run into a discontinuity, grade into something else or pinch out
Superposition
Oldest layers on bottom and younger layers get piled on top
Only requirement is to find which side is “up” and which is “down”
Cross-Cutting Relationships
Features that cut across layers are younger than the layers they cut across
Includes Magmatic intrusions, faults and erosion
Faunal Succession
Way to tell time using fossils since creatures lived at different times
Fossil organisms succede one another in a definite order.
Relative Datitng
Placing events/rock units/organisms in a chronological sequence, using principles of stratigraphy
Catastrophism
If the geologic column accumulated over biblical timescales, forces of tremendous violence and magnitude that surpass anything experienced in nature are predicted/required
Uniformitarianism
Theory that changes in Earth’s crust were the result of continouis and uniform processes
Absolute Dating
Estimating an age for an event, rock unit, and/or organism’s range in years
Calculation for absolute age
Time = Total / Rate
Isotope
atoms of the same element (that is, same # of protons) but with different numbers of neutrons
Half life
Time it takes for half of a radioactive isotope to decay
Radiometric Dating
Way to tell age on decay of radioactive material
The Percentage of radioactive atoms that decay during a half life is always the same (50%)
Stress
The force that causes rocks to deform (confining - pressure)
Can be tensional, compressional and shear stress
Strain
The deformational response to stress
Can be…
Elastic Deformation
Brittle Deformation
Ductile Deformation
Pressure
Type of stress where the force is equal in all directions
Compression
Type of stress where it is pushed together

Tension
Type of stress where it is pulled apaet
Shear
Type of stress where it is pulled in 2 directions on different sides

Elastic
When deformation happens due to strain but strain and deformation will go away when the stress is removed
Ex. Tennis Ball
Brittle
Permanent breakage
Ex. Disposable Fork
Ductile
Permanent bending or flowing
Ex. Clay Ball
Favored at higher temps, slower deformation rates, softer minerals with planes of weakness and higher pressure
Factors that affect whether a rock will break or bend
Temperature
Time / Deformation Rate
Composition
Confining Pressure
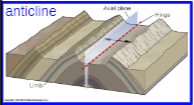
Hinge
Position on fold where curvature is greatest
Axial plane
plane that contains hinges in successive layers
Limb
Sides of the fold with lower curvature
Anticline
Fold where limbs are inclined (dip) away from the hinge
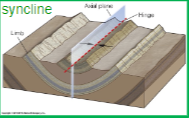
Syncline
Fold where limbs are inclined (dip) toward the hinge
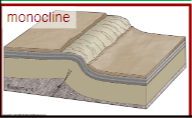
Monocline
Fold where one incline between two levels, like a carpet draped over a step
Basins
Fold with a center towards which rock layers are inclined (dip)
Looks like a bowl
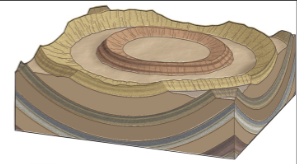
Dome
Fold with a center away from which rock layers are inclined (dip)
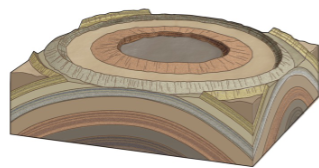
Plunging antilcline & syncline
Its a anticline or syncline but the hinge goes down towards earth
Anticlines “close” in the direction of plunge
Synclines “open” in the direction of plunge
Fracture
General term for when there is a break in a rock
Joint
A fracture across which little or no movement has occured (e.g. cooling joints - Devil’s Tower, expansion - Yosemite)

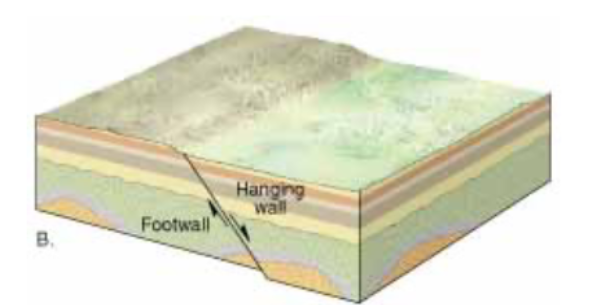
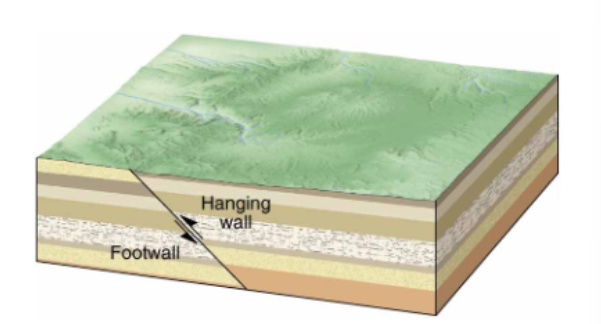
Hanging Wall
Overhead
Foot Wall
Under Foot
Fault - Normal
A fracture across which significant movement has occured
A fault in which the hanging wall moves down, relative to the foot wall
Fault - Strike Slip
One piece goes forward while the other either stays or go backwards
Can be Right lateral or Left Lateral
Fault - Reverse
A fault in which the hanging wall moves up, relative to the footwall
Earthquakes
Vibrations of the earth caused by the rupture and sudden movement of rocks that have been strained beyond their yield points
Elastic Rebound
The mechanism for earthquake generation
Rock strength and friction fault prevents movement
elastic deformation in fault blocks
force of friction (and/or rock strength) exceedes; Fault ruptures
Rocks rebound or spring back to their deformation state
Epicenter
The point on earths surface that lies vertically above the focus
Focus
Center of energy release and site of first movement on a fault
Seismic Waves
They are produced by earthquakes thgat propagate radially from the surface.
The types are…
Body Waves
Surface Waves
Body Waves
They travel through the earths interior. There are 2 types
Primary - Compressional, travel through all states of matter, the fastest
Secondary - Shear, can only go through solids
Surface Waves
Seismic waves that travel on the surface of the earth
Do the most damage
Seisometers
Produce a record of the arrival and size of seismic waves
Seismograph
The record produced by a seisometer
Mercalli Scale
Scale based on the damage of an earthquake. Ranges from 1 to 12.