Skeletal Dysplasias and Short Stature
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
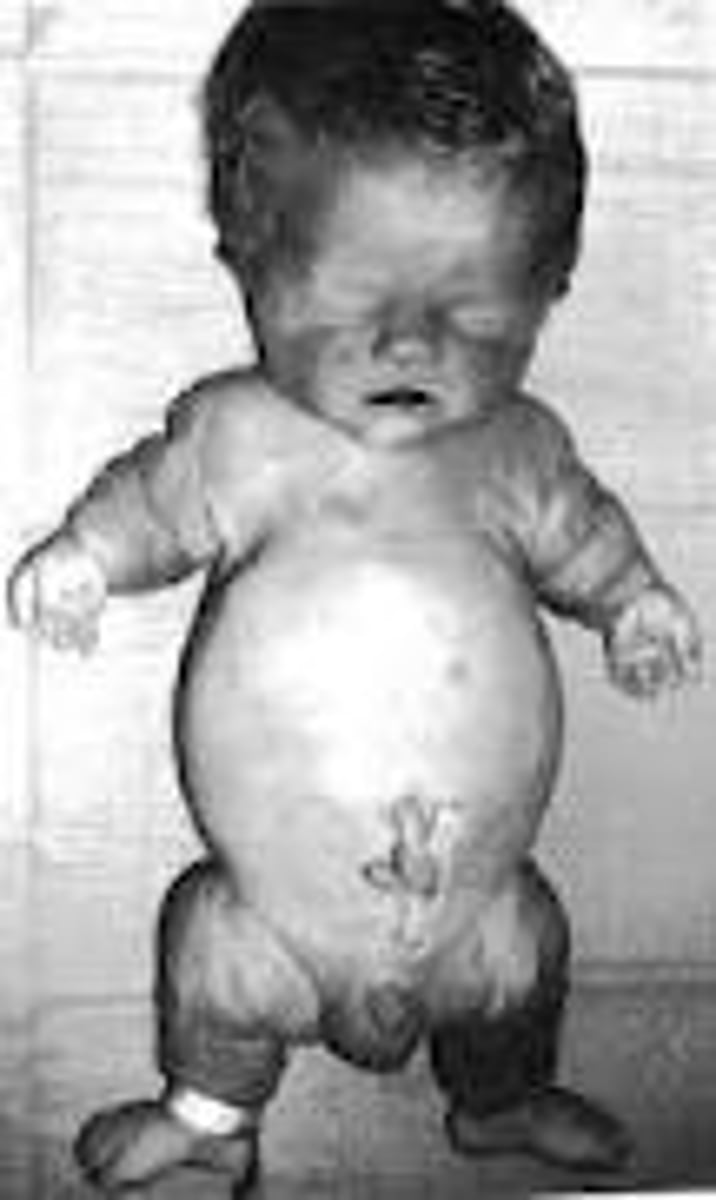
Thanatophoric dysplasia
the most common lethal skeletal dysplasia characterized by a cloverleaf skull with frontal bossing and hydrocephalus. Caused by mutations in FGFR3
SADDAN
Severe achondroplasia with developmental delay and acanthosis nigricans. Caused by heterozygosity for the K650M mutation in the FGFR3 gene
Achondroplasia most common mutation
Gly380Arg
Achondroplasia de novo rate
80%
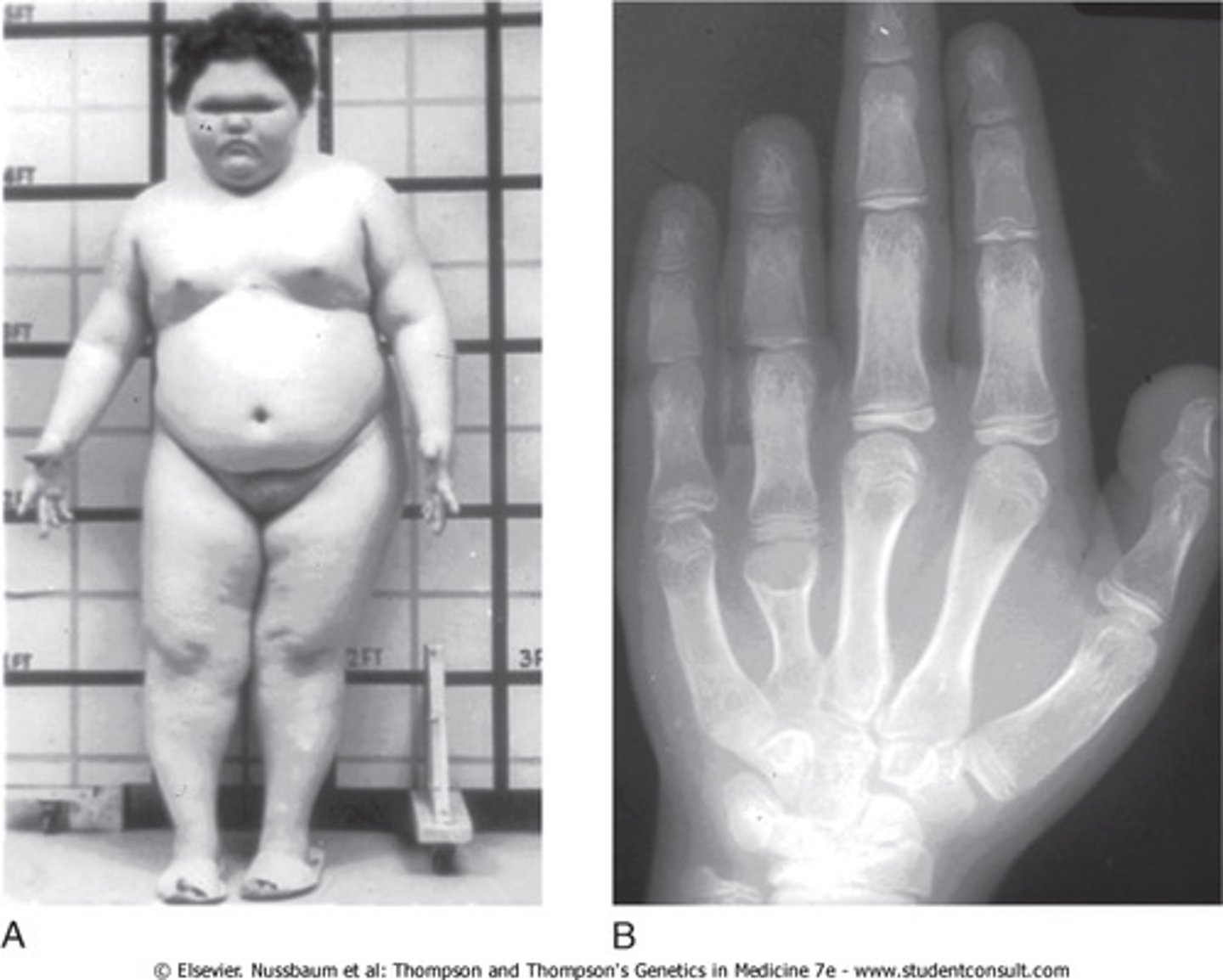
achondroplasia dwarfism type
Average height: 4'4" for males, 4'1" for females. shortened proximal limbs, average size trunk
achondroplasia dysmorphism
macrocephaly, prominent forehead, frontal bossing, foramen magnum stenosis, midface hypoplasia
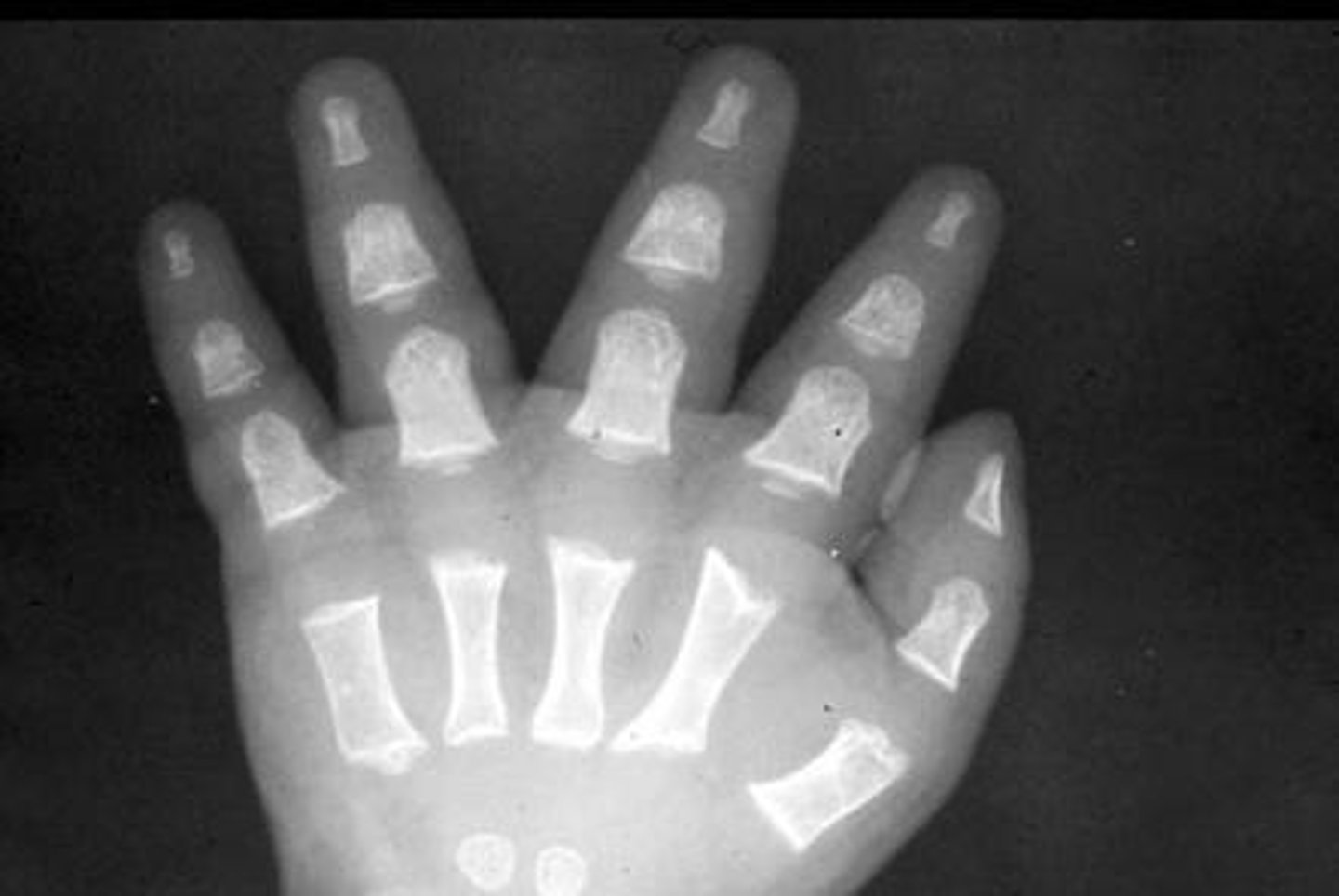
Trident hand
Hand finding associated with achondroplasia. A wide separation between the middle and ring finger, which gives the hand a 3-pronged appearance
Voxzogo
FDA approved CNP C-type Natriuretic Peptide, which bypasses FGFR3 in its pathway, increasing chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation in those with achondroplasia. Requirements: 5 years of age or older, open growth plates
achondroplasia complications
lordosis, kyphosis, apnea, obesity, spinal stenosis, joint pain, delayed motor milestones
achondroplasia prenatal ultrasound
frontal bossing, shortened long bones, sometimes increased NT. Usually not diagnosed until the 3rd trimester
FGFR3 gene function
Cell proliferation and differentiation, blood vessel formation, wound healing, ossification (cartilage --> bone)
Achondroplasia testing considerations
can be diagnosed on x-ray alone, 99% of all cases associated with Gly380Arg
hypochondroplasia mutation
TK1 region of FGFR3
most significant genes mutated in APA
FGFR2, FGFR3, RET
hypochondroplasia distinctive feature
although stature is increased over classic achondroplasia, ID/DD and CNS problems are more common in hypochondroplasia
osteogenesis imperfecta genetics
AD, defects in type 1 collagen (COL1A1, COL1A2)
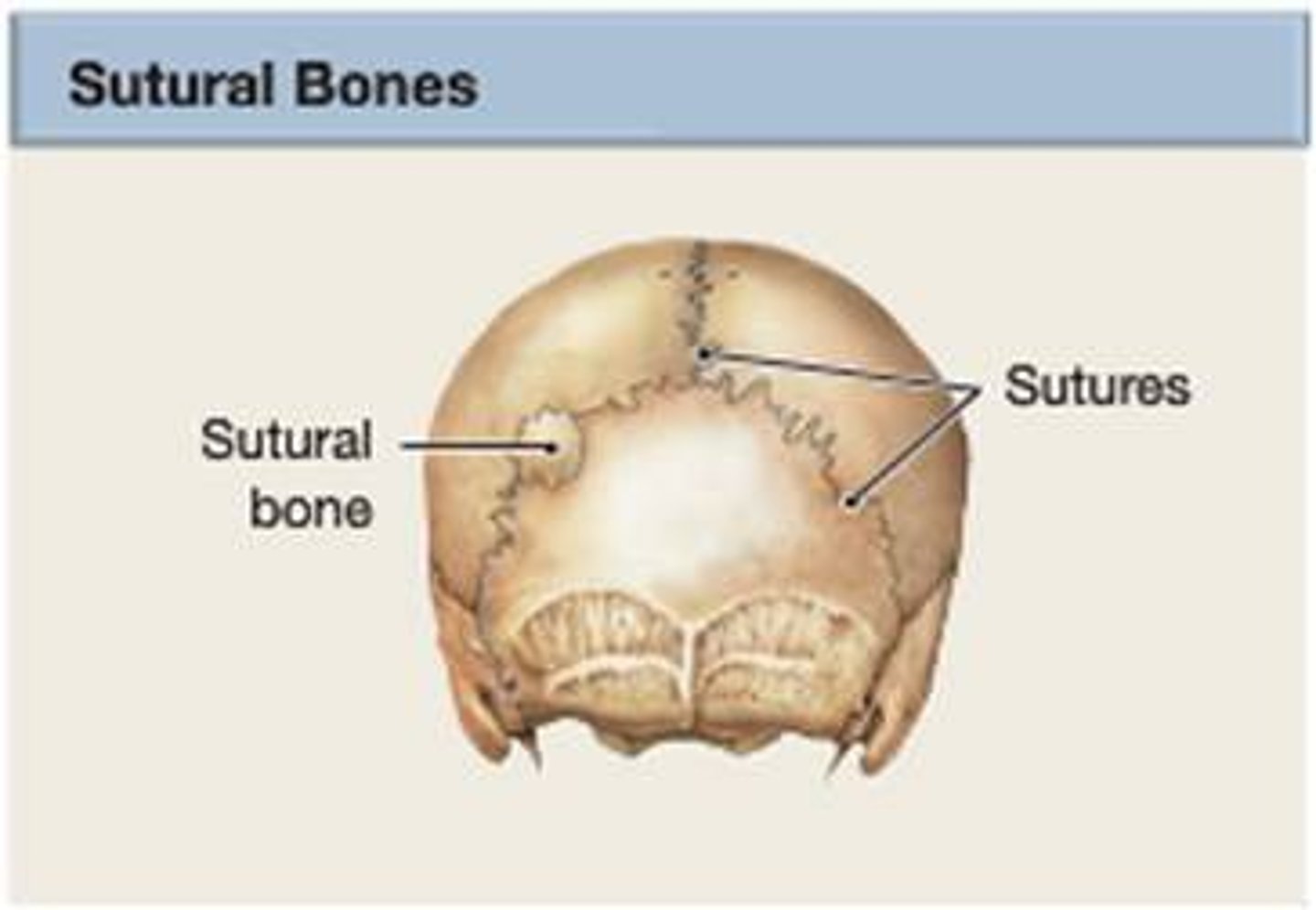
wormian bones
extra irregularly shaped bone pieces that occur within a suture in the cranium. Can occur in OI.
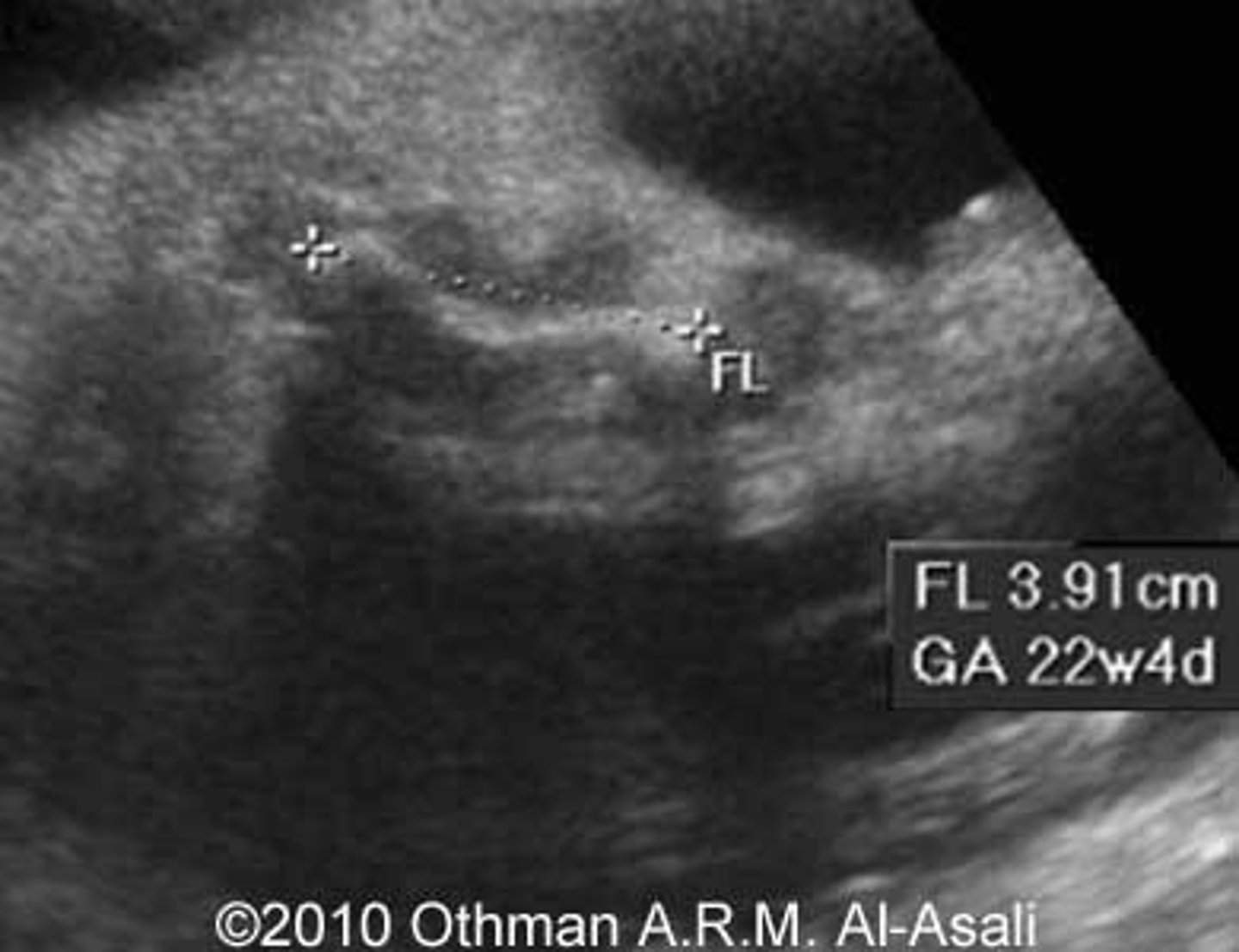
OI prenatal ultrasound
Shortened long bones, increased NT, evidence of fetal fractures and healing, growth restriction. All most likely only going to be seen in OI2
biphosphinates in OI
slow bone turnover by retaining more calcium in the bones during growth. Does not work for type 1. Side effect: hypocalcemia
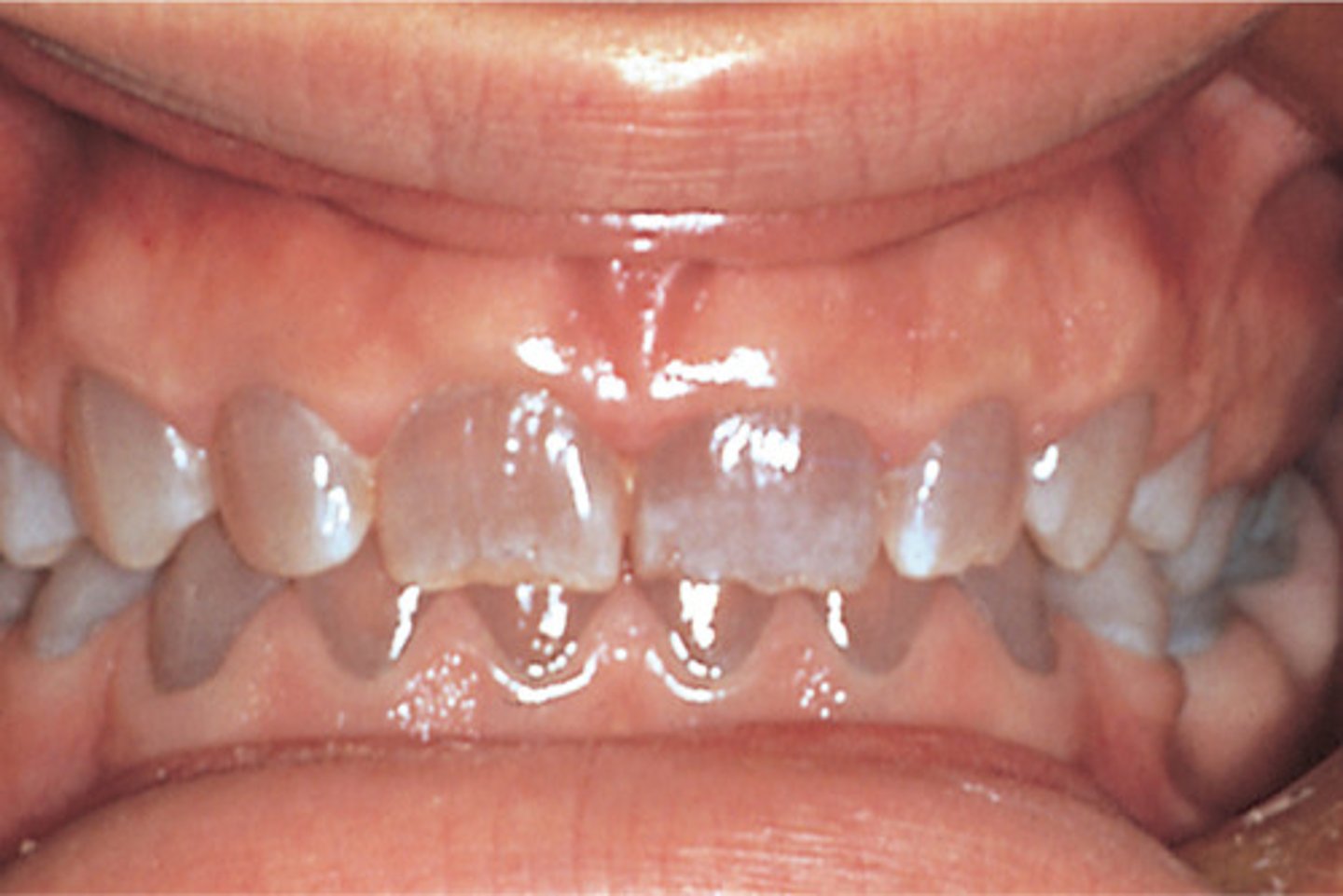
dentinogenesis imperfecta
Disorder of dentin formation in which the odontoblasts lay down an abnormal matrix. Associated with OI Type 2 & 4, and can occur as its own disorder associated with the DSPP gene
OI clinical features (all types)
recurrent fractures, relatively short stature, risk of hearing loss, leg bowing, possible wormian / sutural bones
OI Type 1 unique features
light blue sclera, triangular face, unresponsive to bicarbonate therapy
OI Type 2 unique features
congenital fractures, neonatal respiratory failure, dark blue sclera, bone deformities, IUGR, muscle weakness, barrel chest, dentinogenesis imperfecta
Basilar invagination
bones of spine intersect with brain, can occur in OI 3 & 4
telescope rod bone support
surgically implanted rod into long bones in those with OI. Can provide additional stability for walking without fractures, can grow with patient
Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia (SED) dwarfism type
short trunk / spine, average limbs
Diastrophic Dysplasia
AR at SLC26A2. Progressive skeletal features such as hip dysplasia and scoliosis (diastrophy = destroyed over time). Constant hitchhiker thumb, flat nasal bridge, prominent cheeks, cleft palate, cystic pinnae, cleft palate, abnormal cartilage in trachea, cervical spine instability, cervical scoliosis / kyphosis, contractures, subluxations, clubfeet, sandal gap, arthritis, short stature
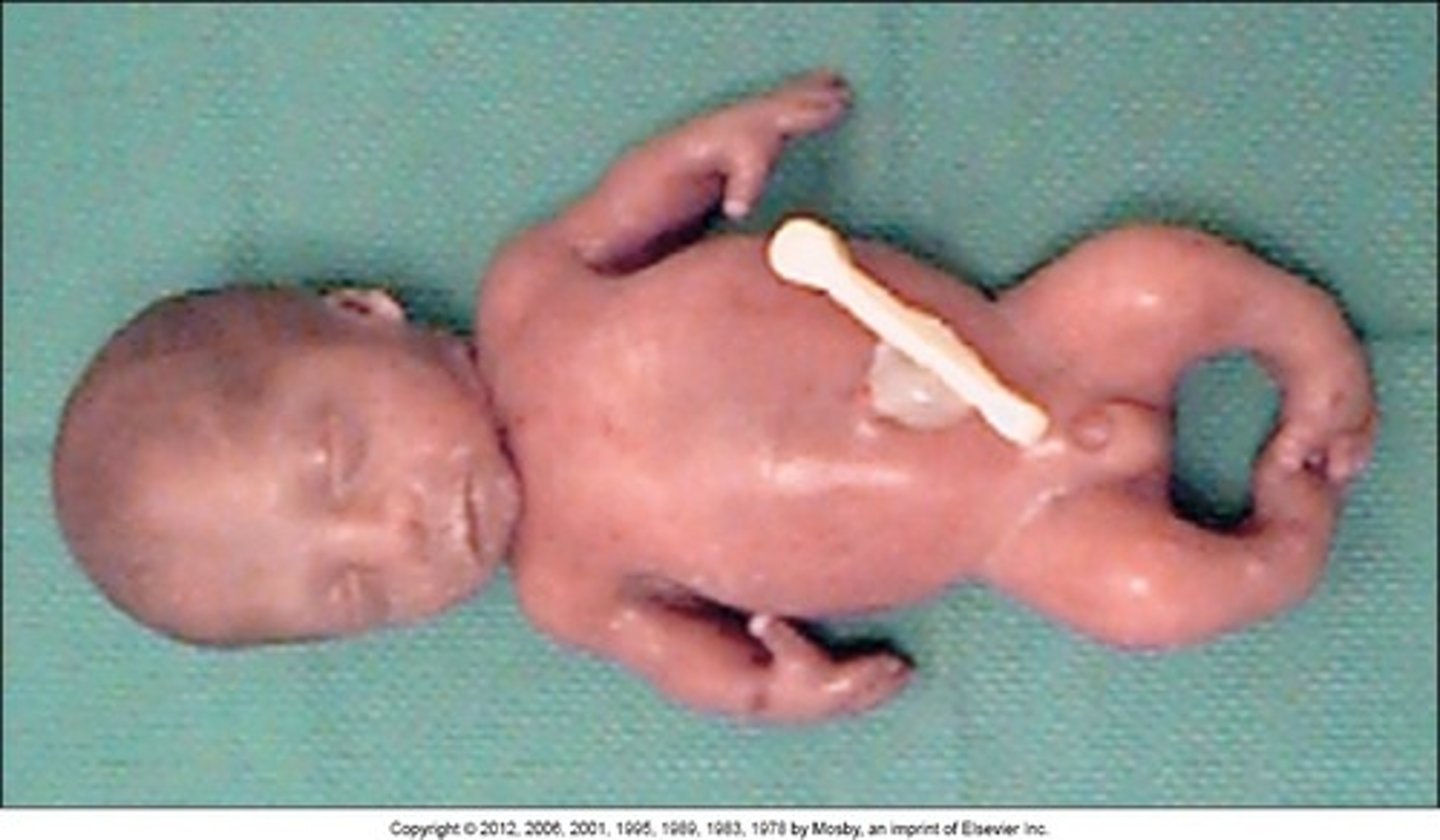
Campomelic Dysplasia
AD (de novo) at SOX9. Campomelic = bent limbs. Bowing of the legs, dislocated hips, small lungs and chest, undervirilization of XY infants, Pierre Robin Sequence, prominent eyes, flat face, large head, congenital heart defects, laryngotracheomalacia, 11 pairs of ribs instead of 12. Death typically occurs in early infancy due to trouble breathing.
11 pairs of ribs
highly associated with campomelic dysplasia. Remember: musicals are campy and your favorite musical is about [sox]9/11[ribs]
hitchhiker placement of thumb
highly associated with diastrophic dysplasia. Remember: if you hitchhike you'll be destroyed over time
Cleidocranial dysplasia
AD at CBFA. Hypertelorism, failed /delayed closure of the anterior fontanelle / cranial sutures, hypoplasia or aplasia of the clavicles, short stature, supernumerary teeth, dental anomalies, skeletal anomalies, smooshed together shoulders (could touch elbows together behind the back)
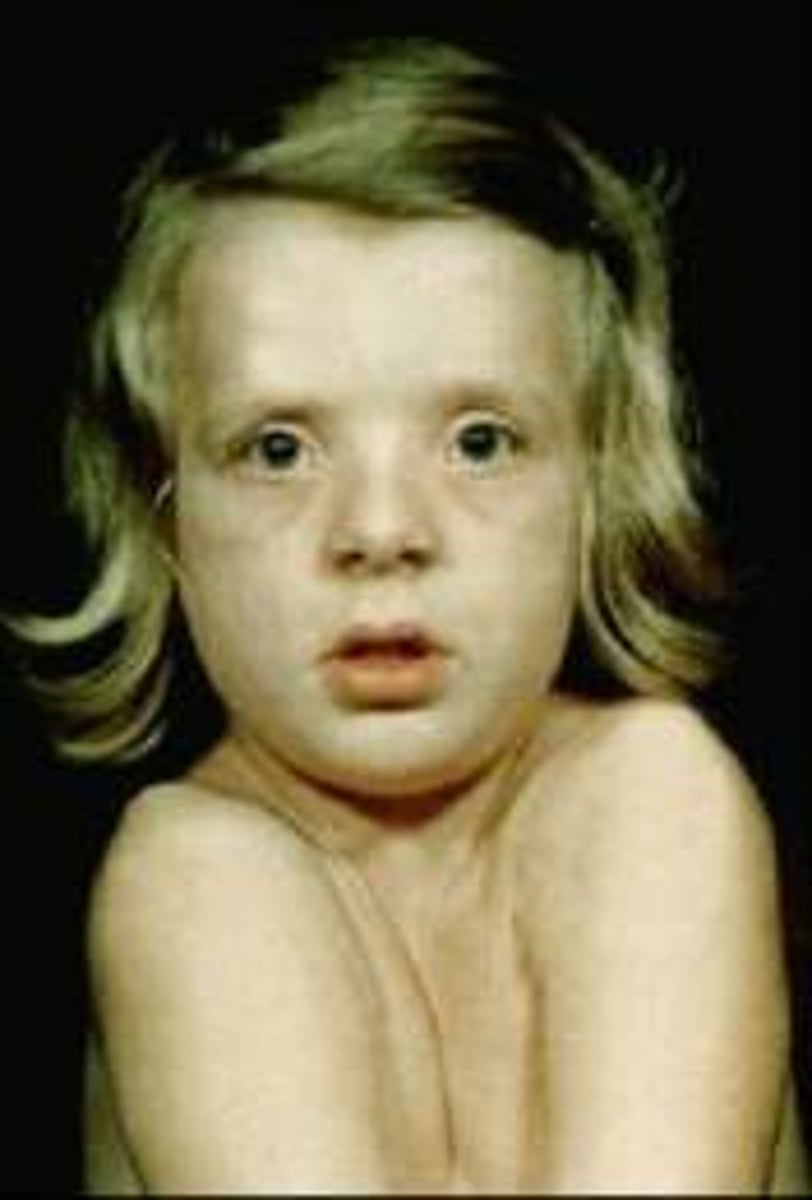
Cartilage-hair hypoplasia
AR at RMRP, an untranslated mitochondrial processing gene. Features: short stature, fine and sparse blond hair, defective T-cell immunity (cannot receive live vaccines), severe combined immunodeficiency, anemia, Hirchsprung, aganglionic megacolon, increased risk of basal cell carcinoma + non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia
AD at COL2A1. Short trunk, average trunk, pectus carinatum, flattened vertebrae resulting in scoliosis / lordosis / kyphosis, decreased joint mobility, conductive hearing loss, myopia, retinal detachment. Gives short & stiff Marfan vibes.
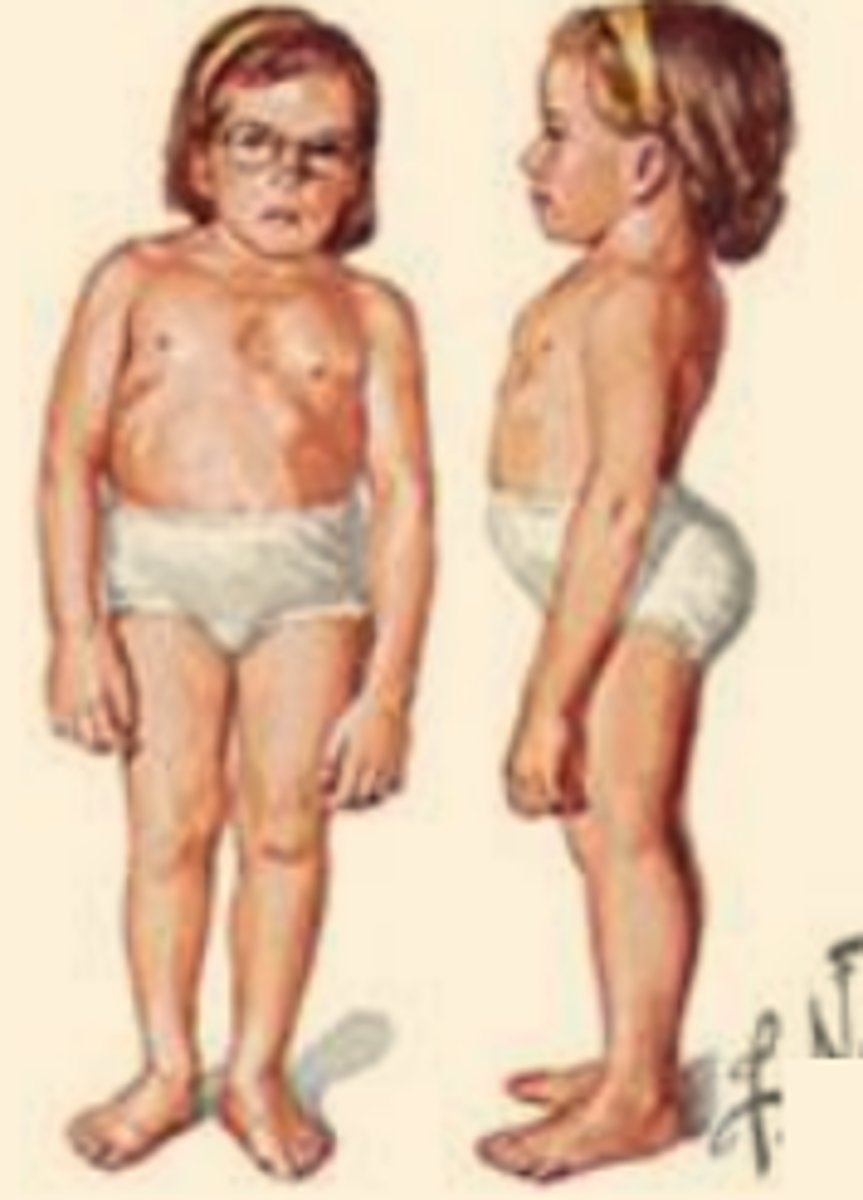
Robinow
AR at ROR2, AD at FZD2, WNT5A, DVL1, and DVL3. Shortened long bones, brachydactyly, wedge-shaped hemivertibrae resutling in kyphoscoliosis, fused / missing ribs, short stature, "fetal facies", overgrowth of gums, crowded teeth
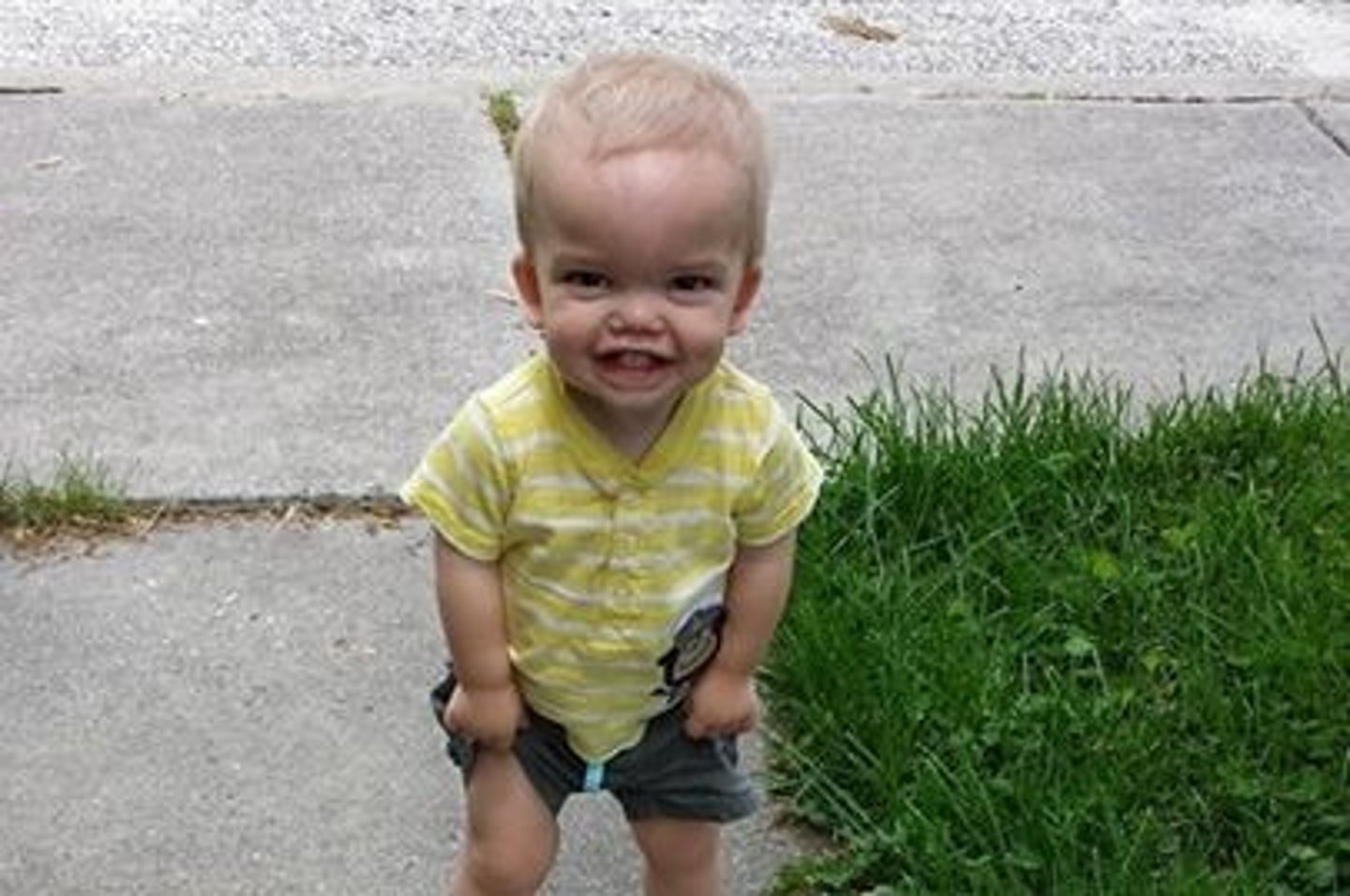
mulibrey nanism
AR at TRIM37. MUscle-LIver-BRain-EY Nanism (Dwarfism). Growth restriction, short-broad neck, misshapen sternum, small thorax, square shoulders, enlarged liver, and yellowish dots in the ocular fundi. Individuals with Mulibrey nanism have also been reported to have intellectual disability, tumors, and infertility. Almost all cases are in Finnish population
Johanson-Blizzard
AR at UBR1. Malabsorption of fats and other nutrients due to pancreatic insufficiency, failure to thrive, short stature, small "beak-shaped" nose, varying degrees of intellectual disability, sparse light hair, aplasia cutis. Pancreatic features / failure to thrive give the vibe of CF. Remember: Blizzard "Beak" like the Disney park Blizzard Beach
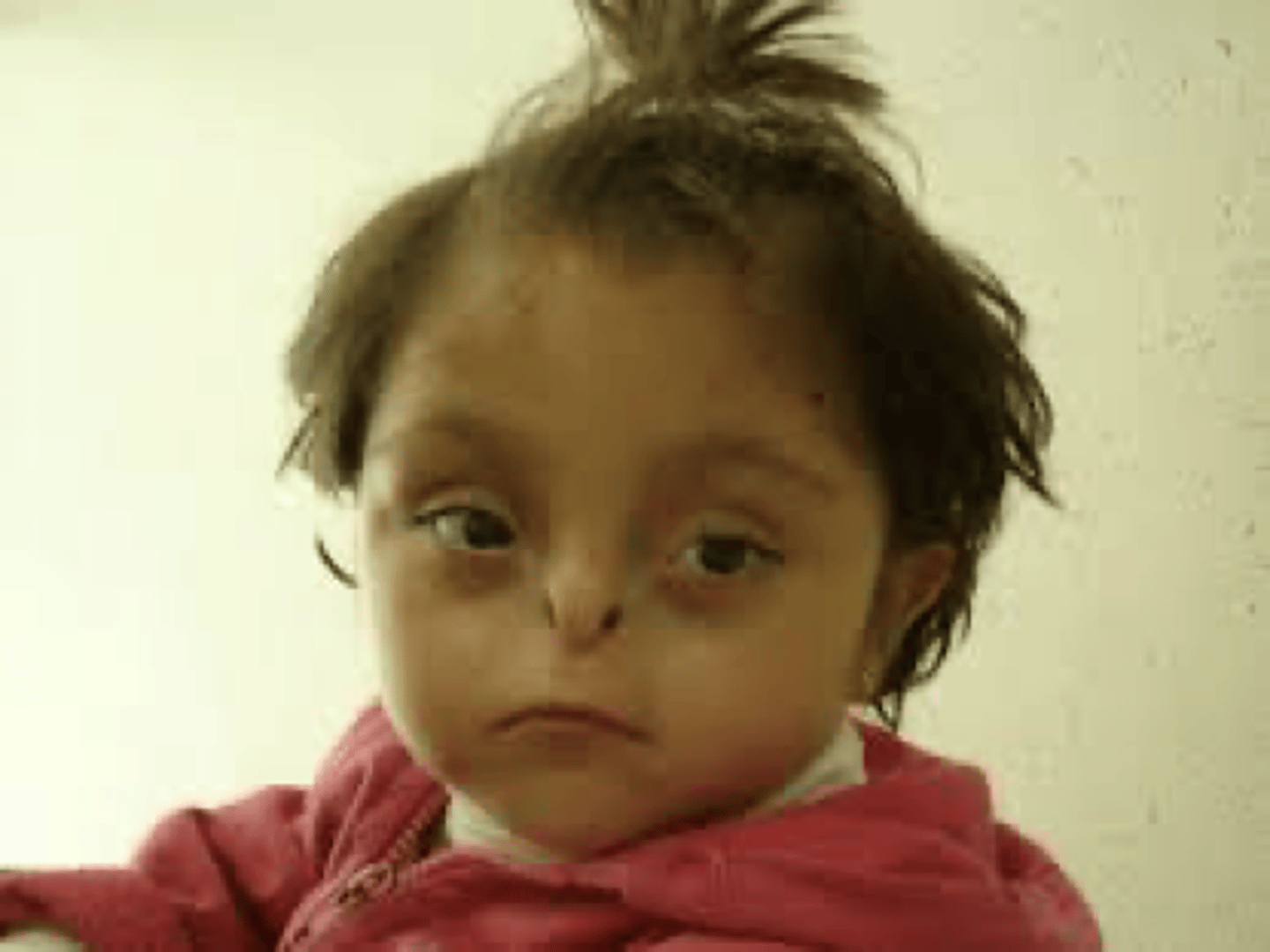
Seckel Syndrome
AR at ATR. Primordial dwarfism, microcephaly, IUGR, ID/DD, sloping forehead, beak-like nose, micrognathia, hip dysplasia, radial dyslocation, *bird head dwarfism*

Hallermann-Streiff Syndrome
AD, unknown genes. Distinctive craniofacial malformations (brachycephaly, prominent forehead, hypoplastic mandible, high arched palate, pinched / tapering nose), sparse hair, eye abnormalities, dental defects, scalp and nasal atrophy, proportionate short stature, ongenital cataracts, corneal stromal opacities, microphthalmia, glaucoma, retinal detachments, delayed tooth eruption, enamel hypoplasia, absent permanent teeth (hypodontia or partial adontia), abnormal tooth development resulting in short roots and early loss of teeth, and/or improper alignment of teeth.
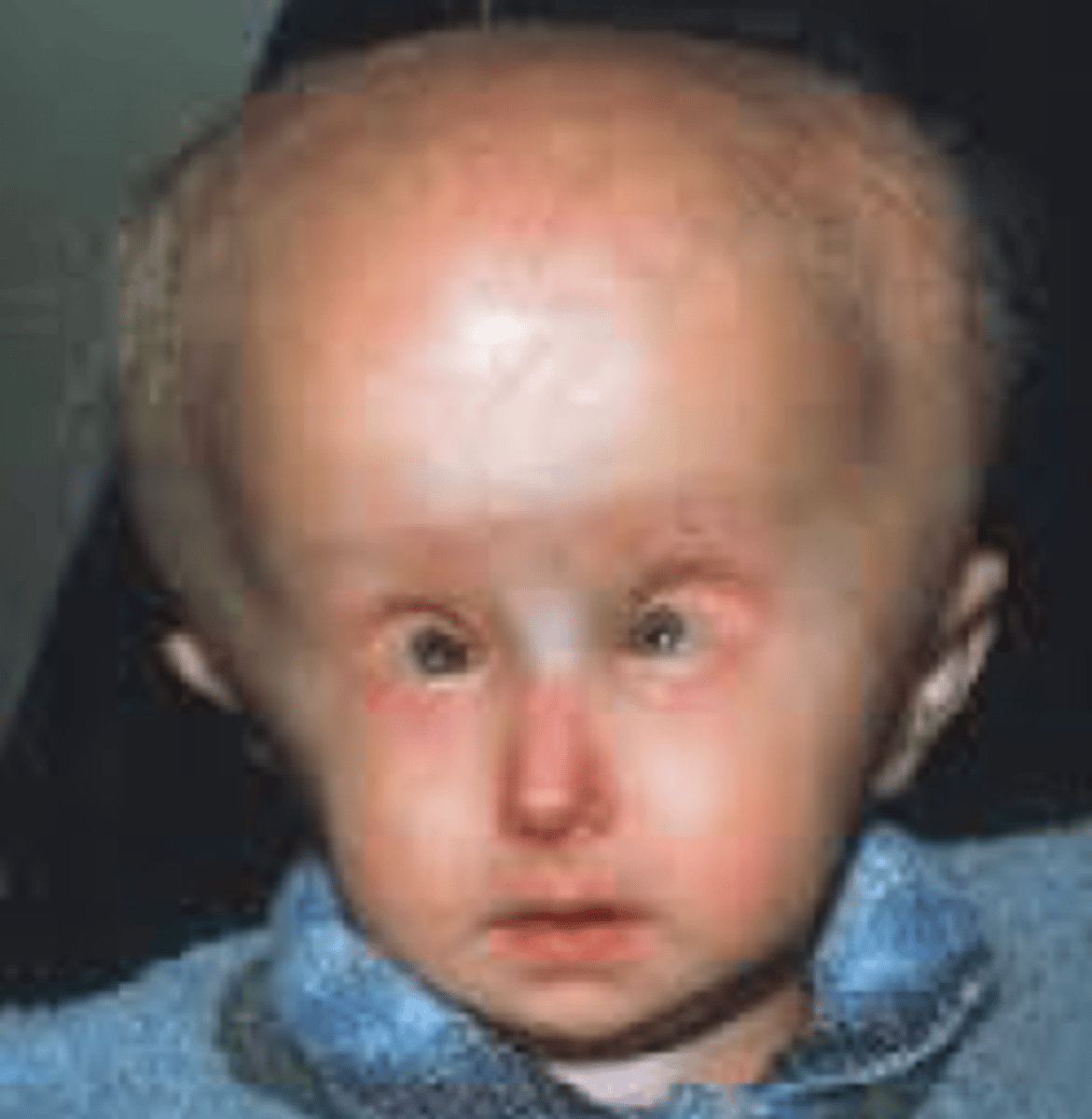
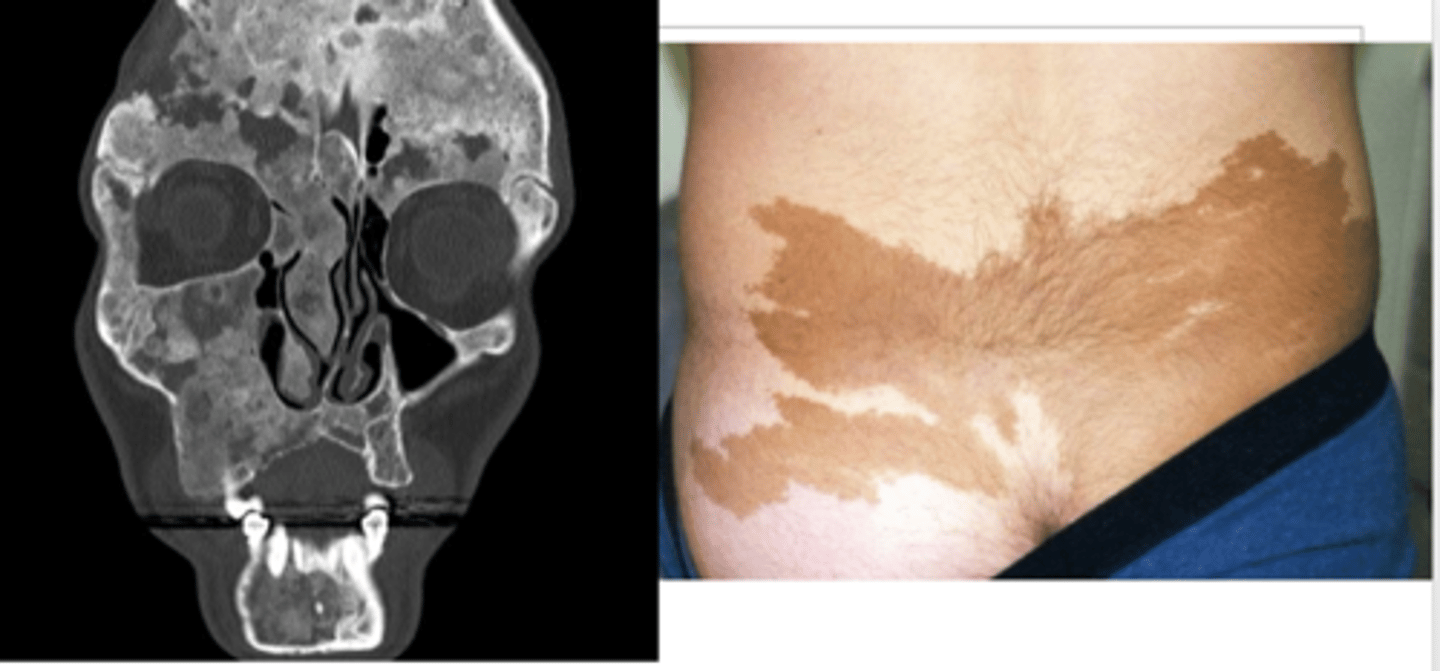
fibrous bone dysplasia
An uncommon bone disorder in which scar-like (fibrous) tissue develops in place of normal bone. Associated with McCune Albright
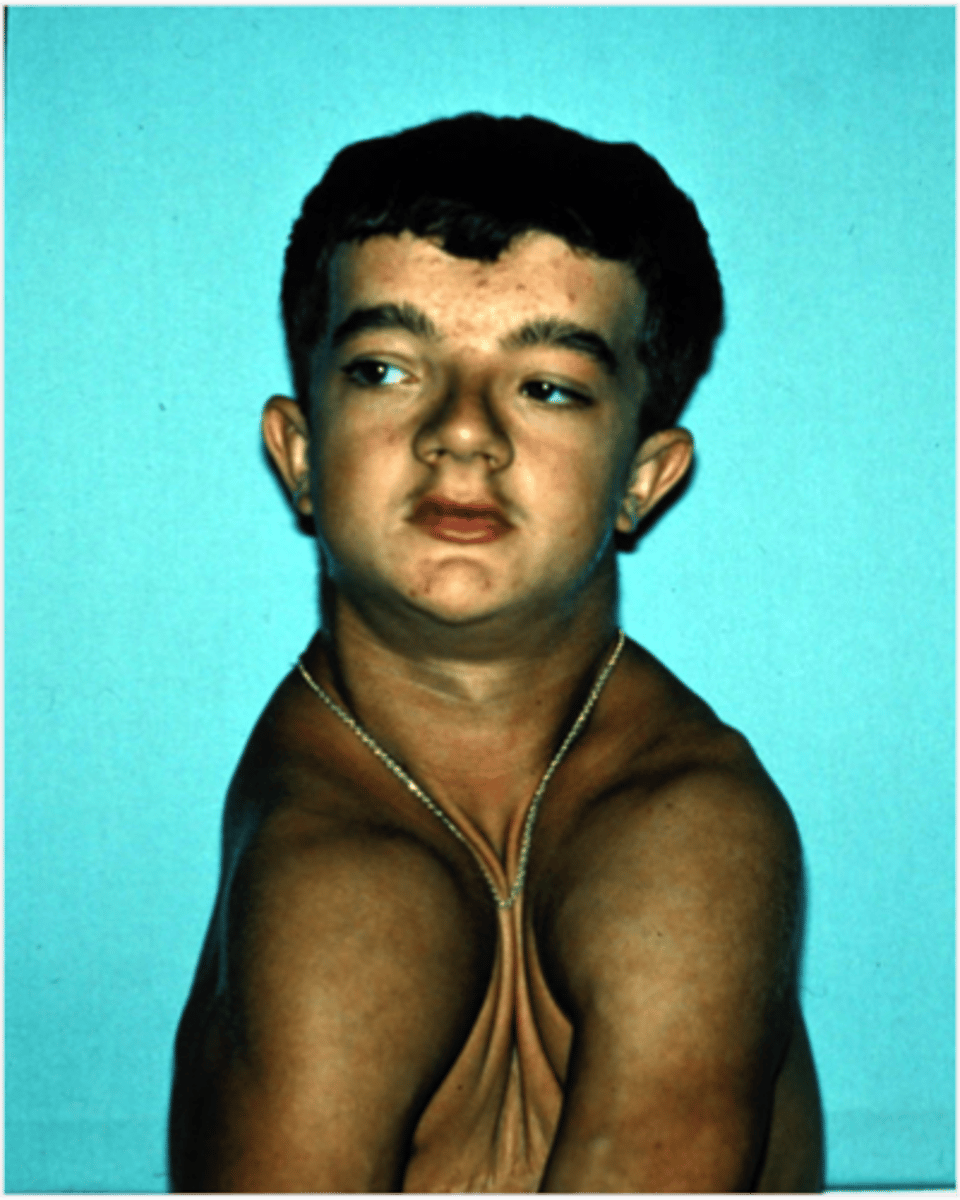
delayed closure of the cranial sutures
Buzzword for Cleidocranial dysplasia
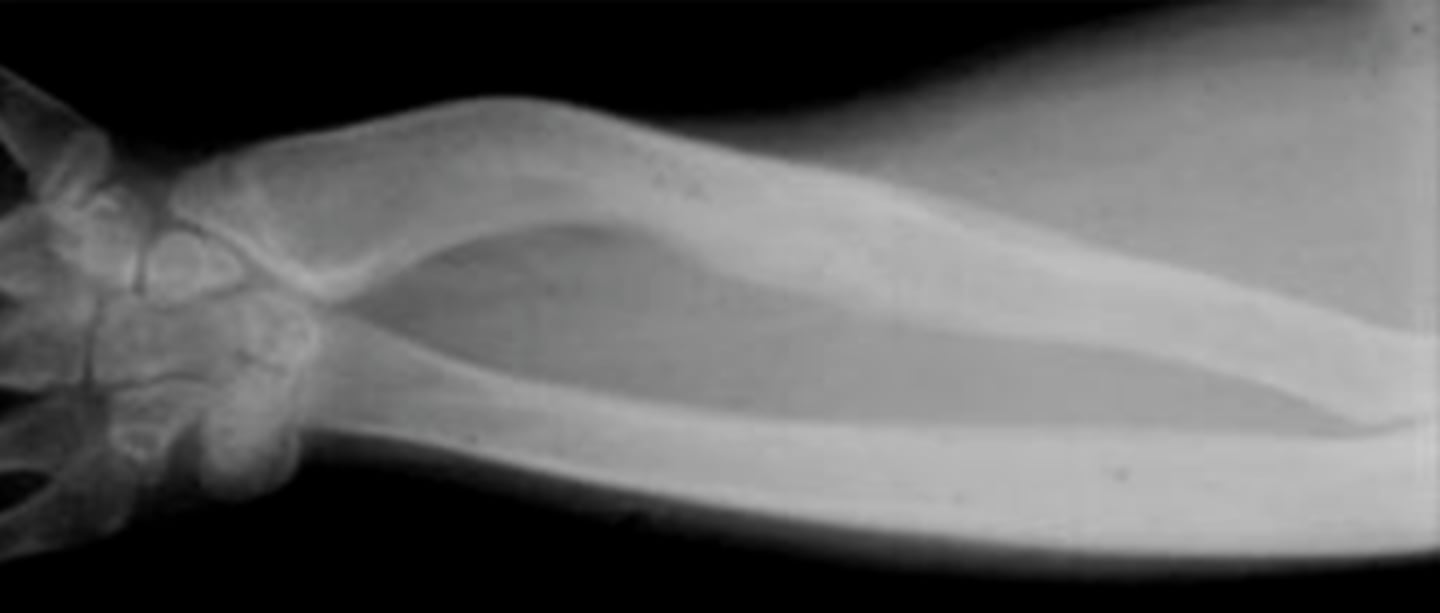
Madelung deformity
Shortened distal radius with abnormal ulnar tilt of its distal articular surface. Think of Leri Weill Dyschondrogenesis
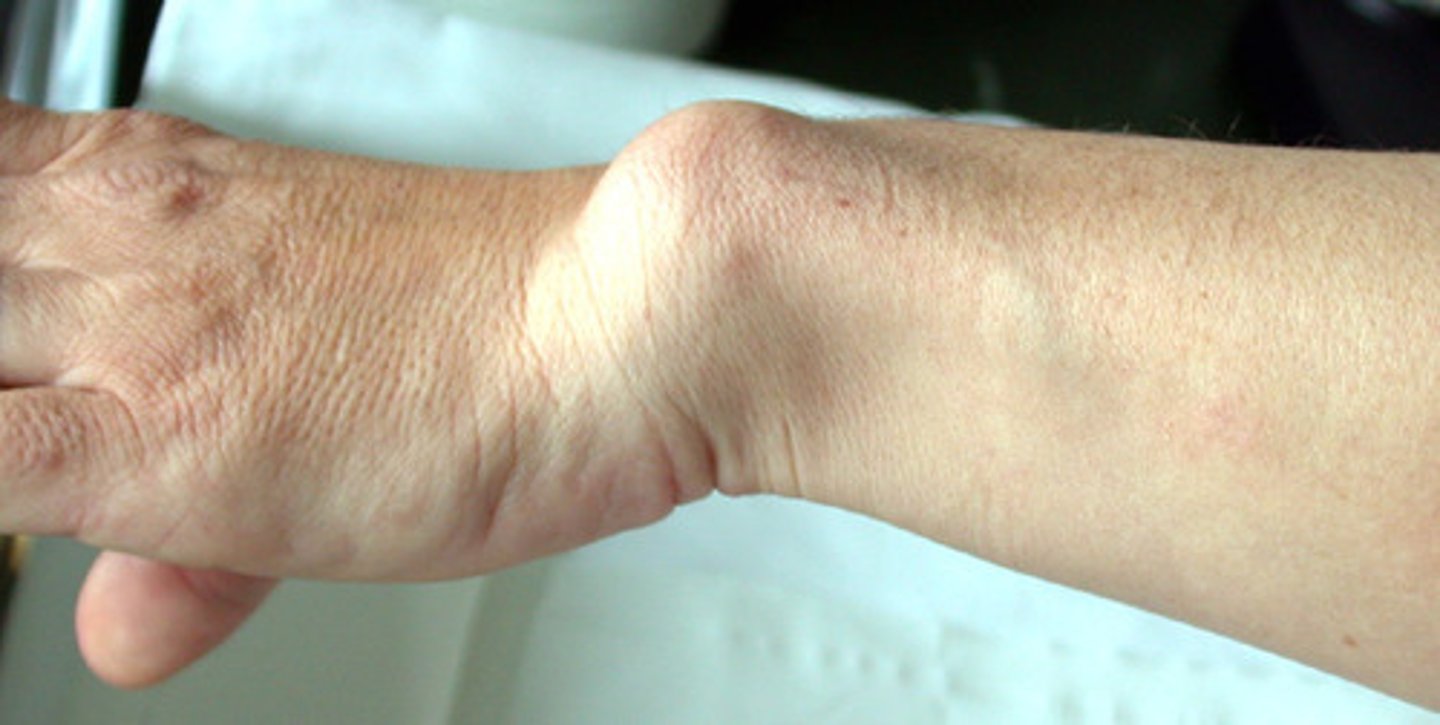
Leri Weill Dyschondrogenesis
pseudoautosomal at SHOX (X chromosome, pseudoautosomal region). Mesomelia (resultant short stature). Most people with the condition also have an abnormality of the wrist and forearm bones called Madelung deformity, which may cause pain and limit wrist movement.
Meier-Gorlin Syndrome
AR at ORC1, ORC4, ORC6, CDT1, and CDC6. Primary dwarfism which begins with IUGR, microcephaly, *absent kneecaps*, underdevelop of sex organs / secondary sex characteristics
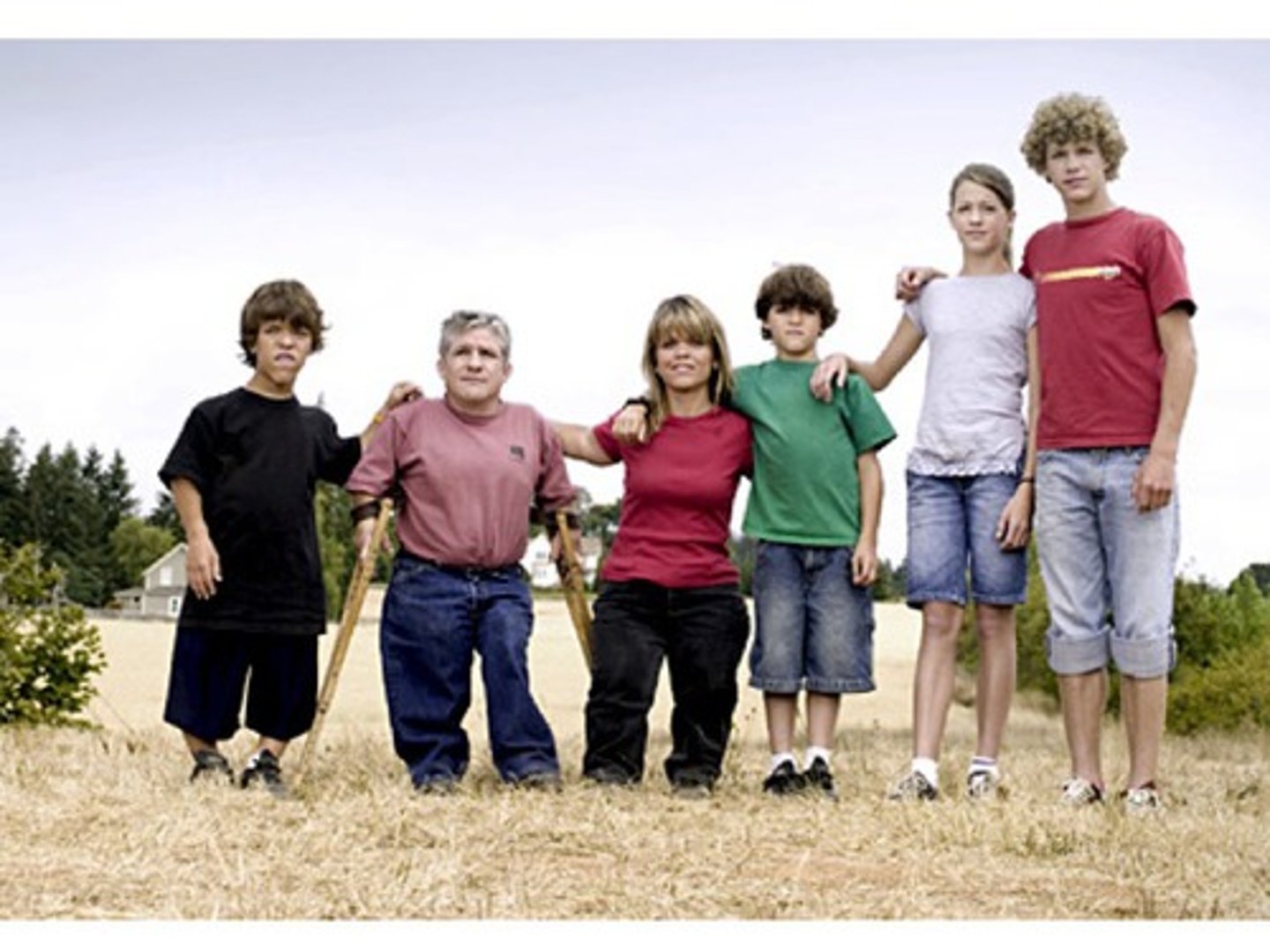

bird-head dwarfism
think of Seckel Syndrome (even though there are definitely other beak-nosed skeletal dysplasias)
Geleophysic Dysplasia
AR at ADAMTSL2. Geleophysic literally means "good natured", named after the good natured facial appearance of affected individuals. Think of this syndrome when you see short stature, contractures, and "good natured" facial appearance
Albright hereditary osteodystrophy
AD / imprinted at GNAS1. Pseudohypoparathyroidism Type 1 (body does not respond to parathyroid hormone). Results in brachydactyly, hypogonadism, choroid plexus calcification, full / round face, short stature.