Chemistry Final
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
**Why are no two emission spectra for different elements ever the same?
** Because each element has a unique arrangement of electrons and energy levels
**Why does each salt have its own distinctive flame test color?
** Because different metal ions have unique electron transitions that emit characteristic wavelengths of light when excited.
**Molarity of the acid in each trial
** (Molarity of NaOH × Volume of NaOH) ÷ Volume of acid.
**Average molarity of the acid
** (Trial 1 molarity + Trial 2 molarity) ÷ 2.
**Relative average deviation
** (|Trial 1 − Avg| + |Trial 2 − Avg|) ÷ 2 ÷ Avg × 100%.
**What sorts of transitions give rise to emissions in the ultraviolet and infrared regions?
** UV: transitions ending at n=1; IR: transitions ending at higher n levels such as n=3 or more.
**How can you tell whether a chemical reaction has taken place when Cu(NO₃)₂ is added to Zn?
** A visible reaction like bubbling or solid formation occurs; Zn(s) + Cu(NO₃)₂(aq) → Zn(NO₃)₂(aq) + Cu(s).
**Energy of photon for electron transition from n=6 to n=3 in hydrogen
** ΔE = 2.18 × 10⁻¹⁸ × [(1/n₁²) − (1/n₂²)] J.
**Limiting reactant between Al and KOH
** Convert grams to moles and compare mole ratios from balanced equation.
**Mass of alum produced from aluminum
** Moles of Al × molar mass of alum (474.39 g/mol).
**Percent yield from actual and theoretical yield
** (Actual yield ÷ Theoretical yield) × 100%.
**What is the purpose of an ice-water bath in the alum experiment?
** To cool the solution and promote alum crystal formation.
**Purpose of washing alum crystals with cold ethanol-water mixture?
** To remove impurities without dissolving alum.
**What happens when a hydrate cools on a lab bench instead of a desiccator?
** It reabsorbs moisture from the air
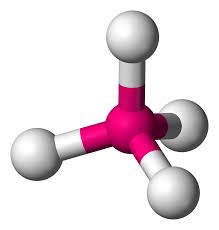
**Geometry around central atom in model a?
** Tetrahedral.
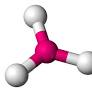
**Geometry around central atom in model
** Trigonal planar.
**Mass of water driven off from a hydrate sample
** Mass of hydrate − Mass of anhydrous residue.
**Percent water in hydrate
** (Mass of water ÷ Mass of hydrate) × 100%.
**Why determine heat capacity of a calorimeter?
** To account for the heat absorbed by the calorimeter so total heat is accurate.
**Density of an unknown liquid from pipetted volume and mass
** Density = (Mass of beaker + liquid − Mass of empty beaker) ÷ Volume.
**Will heat released increase if 100.0 mL acid and base used instead of 50.0?
** Yes
**Volume in graduated cylinder (image)
** Read from image to correct number of significant figures.
**Beer’s Law equation and definitions
** A = εbc; A = absorbance
**How to determine molar absorptivity from Beer’s Law plot?
** From the slope of absorbance vs. concentration graph.
**Label volumes in three beakers to correct sig figs (image)
** Based on each beaker’s precision (e.g.
exothermic reaction
A chemical reaction that releases heat to its surroundings, resulting in an increase in temperature.
endothermic
reaction A chemical reaction that absorbs heat from its surroundings, resulting in a decrease in temperature.
Boyle’s Law
The principle that states the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume when temperature is held constant.
Beer’s Law
A principle that relates the absorption of light to the properties of the material through which the light is traveling.
Gas Law
A set of laws that describe the behavior of gases, including relationships between pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles.