15+16 Polymers
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Backbone Bond Type
Covalent Bods (Typically carbon-carbon), (directional)
Natural Polymers
derived from existing biological process(Cellulose, DNA), unlike plastics which are synthetic, semi-synthetic
Polymer Charactertistics
lightweight
low elastic modulus
low strength
low fracture toughness
good ductility
formable (easy to deform)
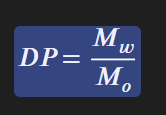
Degree of Polymerization
represents the average number of mer units in a chain
Higher DP means
higher melting point
higher stiffness
higher strength
Polymer Characteristics which influence mechanical properties
DP (degree of polymerization)
Linear vs Branches
Cross-linking and networking
Co-polymers
Side chains
more branching means
lower tensile strength (less intermolecular, dipole-dipole, forces)
increased ductility (less intermolecular, dipole-dipole, forces)
high-density polyethylene (HDPE)
low degree of short chain branching
Linear-low density polyethylene (LLDPE)
high degree of short-chain branching
Low-density polyethylene
high degree of short chain + long chain brainching
LLDPE vs LDPE
higher tensile strength
higher impact and puncture resistance
ca be less thick
crosslinked polymers
adjacent linear chain strongly joined together
non reversible chemical reaction
network polymers
3-dimensional networks (3 active covalent bonds)
Copolymers
polymer composed of two different per units with different combinations
random
block
alternating
graft polymer
stereoisomerism
atoms linked together in the same order (head to tail) but in different spatial arrangements (isotactic, syndiotactic, atactic)
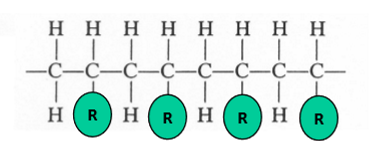
isotactic
side groups all on the same side
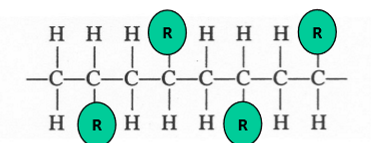
syndiotactic
side groups on alternating sides
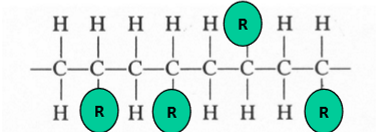
atactic
random distribution for side group locations
geometrical isomers
molecules that have the same molecular formula, but have a different arrangement of the atoms
when C=C are present, the chain can no longer rotate freely (locked)
long range order
atoms are arranged in a regular, repeating pattern over long distances
amorphous vs crystalline
Amorphous materials do not have long-range order, while crystalline materials do
polymers form crystalline structures when…
side chain groups form van der waals bonds with other side chain groups in the chain
crystal formation inhibiting properties
branches
extensive cross linking and networking
randomness in copolymers
bulky side groups
atacticity (random distribution of sidechain locations)
chemically complex mer structures
speed of formation (rapid cooling is less likely to result in organized crystallization)
increased % crystallinity means higher
strength
stiffness
density
resistance to softening (higher melting points)
chemical resistance
polymers are highly sensitive to
rate of deformation (strain rate)
temperature
environment (organic solvents and water)
as temperature increases in polymers
elastic modulus decreases (less stiff)
tensile strength decreases
ductility increases
decreasing the rate of deformation has the same effect as
increasing the temperature
thermoset
polymer decomposes/oxidizes/burns when heated
formed by cured viscous/soft liquid
typically stiffer, harder, and can be used at higher temperatures
thermoplastic
polymer melts when heated (without change in properties)
elastomers
can withstand large deformations and elastically return to original form
most are thermoset
lightly crosslinked
fabrication of thermosetting polymers
linear polymer with a low molecular weight is prepared (in liquid or malleable solid form)
Cured with addition of heat, catalysts, or pressure (generates irreversible crosslinked polymers or network polymers, preventing melting)
glass transition temperature
occurs when heating or cooling polymers in the amorphous/semicrystalline state
lower than glass melting temperature
stress relaxation
specimen is strained rapidly to a predetermined strain level, and the change in stress is measured overtime (under constant strain when measuring change in stress, opposite to viscoelastic testing)
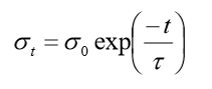
elastomers criteria
must not crystallize easily (amorphous)
chain bond rotations are relatively free (easy to uncoil)
limited amount of crosslinking (onset of plastic deformation is delayed)
above glass transition temperature
air entrainment
pores and air bubbles trapped inside while the polymers are viscous, then are cured
plasticizers
increased flexibility, ductility, and toughness
polymer additives
plasticizers and stabilizers
stabilizers
counteract deterioration of plastics (UV, oxidation, and heat protection)