eye diseases patho
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
anatomy of eyes
•Sclera
•Cornea
•Choroid
•Ciliary body
•Iris
•Pupil
•Retina, which contains rods and cones
•Optic nerve
Aqueous humor
watery liquid in anterior chamber
Vitreous humor
clear, gelatinous material in posterior chamber
Conjunctiva:
fragile membrane that covers the inner surface of the eyelid and the exposed surface of the eye
Lacrimal glands
keep surface moist
Tears drain on the inner side through two lacrimal ducts
Blinking
•cleans the eye by sweeping the fluid
Sensory Conditions Associated with Aging: Eyes
•Changes:
•Less tear production
•Structural deteriorations
•Cornea becomes less sensitive
•Pupils decrease in size/react more slowly
•Lens becomes yellowed, less flexible, slightly cloudy
•Fat pads decrease
•Eye muscles weaken
•Presbyopia
•Intolerance to glare/difficulty adapting to darkness
•Inability to distinguish color
aging eyes treatment
•Glasses/contact lenses
•Keeping a red light on in darkened rooms
Refraction
•Controls clarity of vision regardless of distance
•Refraction errors affect 1/3 of persons aged 40+ years
•Advanced age increases risk for all 4 refractive disorders
•4 refractive errors
•Occur when bending of light rays by the cornea and lens does not focus image correctly on the retina
•Myopia, Hyperopia, Astigmatism, Presbyopia
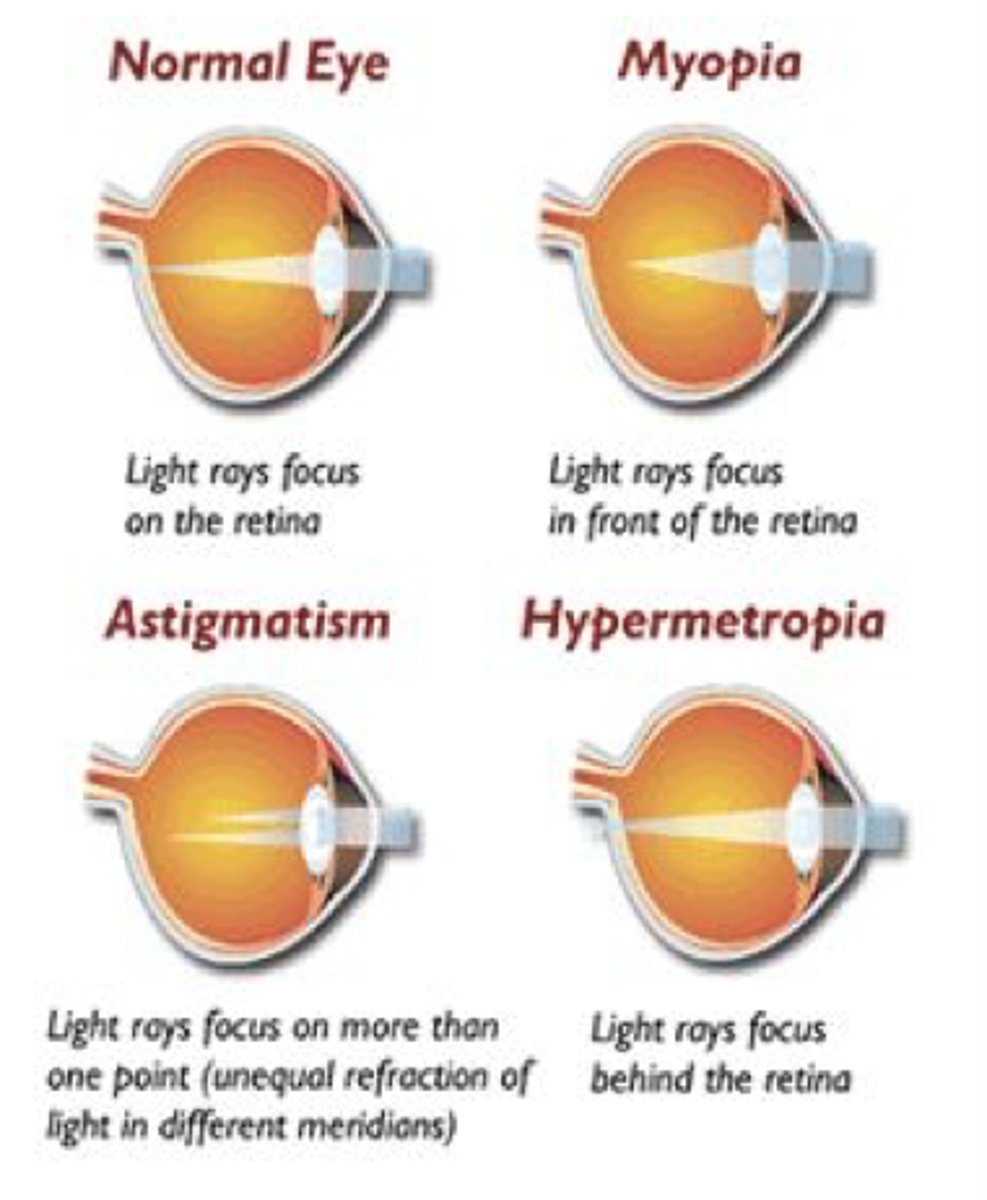
•Myopia (Nearsightedness)
•Corrective lenses such as glasses or contact lenses
•Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
•Convex corrective lenses in eyeglasses or contact lenses
Astigmatism
a condition in which the eye does not focus properly because of uneven curvatures of the cornea •Eyeglasses, contact lenses, or orthokeratology
•Presbyopia
•"Reading glasses" or magnification
Corneal Abrasion
•Epidemiology
•Contact lens wearers present more frequently
•2 types of abrasions
•Superficial
•Deep
Pathophysiology Corneal Abrasion
•Disruption of the cornea resulting from a physical or chemical trauma
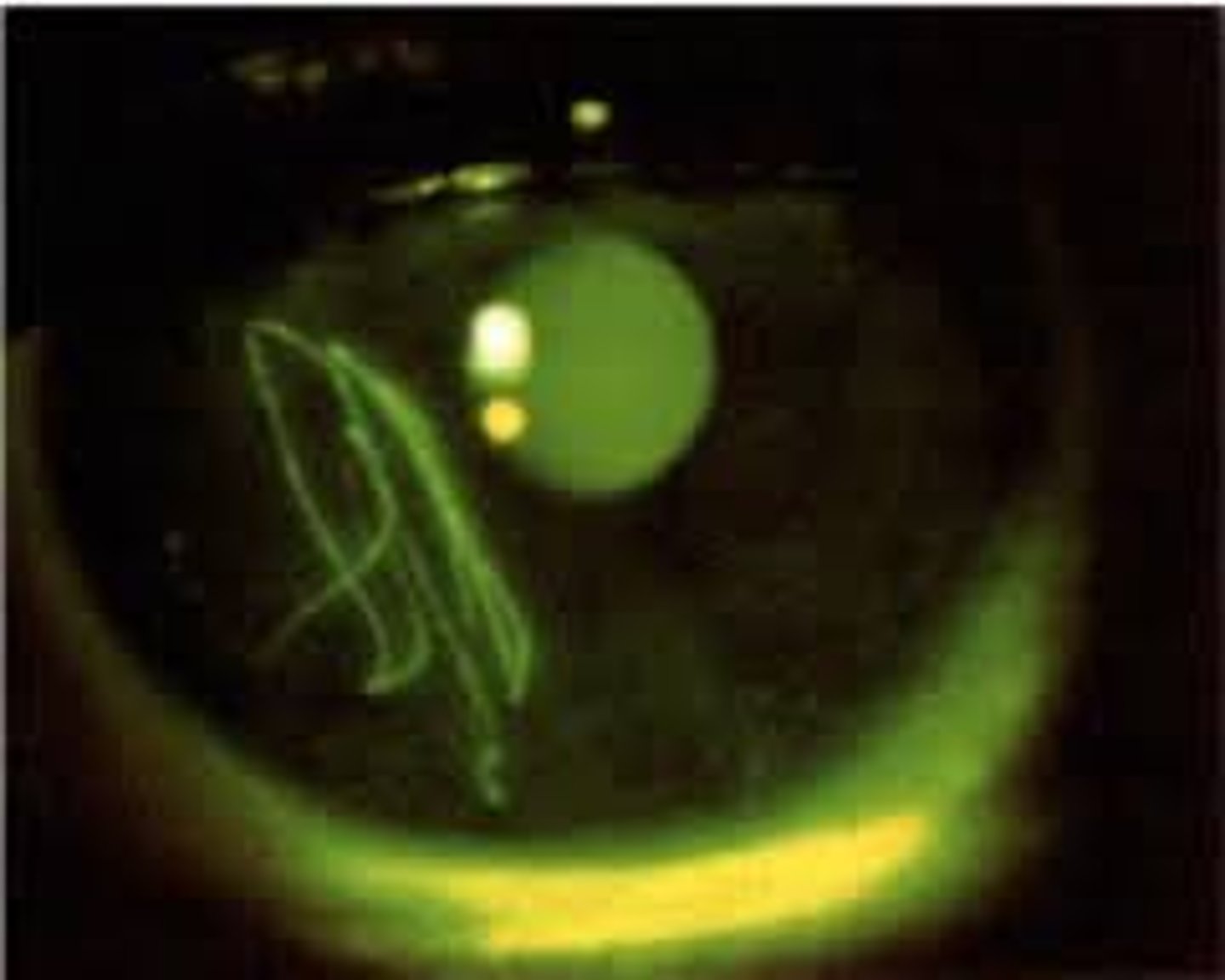
Corneal Abrasion •Clinical manifestations
•Traumatic corneal abrasion
•Foreign bodies
•Contact lenses
•Spontaneous defects
Corneal Abrasion •Management includes comprehensive exam
•Visual acuity test, anesthetizing eye, corneal staining, and visualization under a Wood lamp/black light
Cataracts
•Opacity of clouding of the lens of the eye
Cataracts epidemiology
•Affect 22 million Americans aged 40+ years
Most reimbursed Medicare Procedure
Cataracts Risk Factors
•Exposure to UV light
•Advanced age
•Family history
• DM, HTN
•Obesity
• Smoking, alcohol abuse, and many other chronic diseases
Cataracts •Pathophysiology
•Affects the lens which is made up of water and protein in a unique pattern to keep the lens clear.
•Alteration in the lens proteins occurs as a person ages; protein clumps together and makes the lens unclear
•Gradual lens clouding secondary to chemical change
•Can also be do to blunt trauma
Cataracts Clinical Manifestations
•Opaqueness
•Affects central vision (What you see straight ahead)
•Decreased visual acuity
•Blurred or distorted vision
•Unable to distinguish colors
•Progresses to diplopia, absent red reflex, white pupil, and can lead to blindness
•Halos around lights
•No pain or eye redness
cataracts diagnosis
•History
•Exam
cataracts treatment
•Surgery (removal of the cataract or a lens transplant)
•Managing/eliminating contributing factors
Glaucoma
•Group of eye conditions that lead to damage to the optic nerve
•Results in decreased blood flow to the optic nerve
•Open-angle
•Angle-closure
Glaucoma Epidemiology
•Anyone can develop glaucoma
•2.2 million Americans have been diagnosed
•Another 2 million people have the disease without knowing
Glaucoma Pathophysiology
•IOP increases due to pressure changes in the aqueous Chamber
•Increased pressure leads to ischemia, lack of oxygen and cell death
•Damage to the optic nerve occurs and results in vision loss beginning with peripheral vision
Glaucoma risk factors
•Family Hx
•African American decent
•Trauma
Glaucoma Diagnosis
•History
•Exam
•Primary open Angle Glaucoma
•Gradual loss of vision in both eyes
•Headaches, mild eye pain, decreased accommodation, halos around lights
•IOP > 21 mm Hg
•Acute angle glaucoma
•Eye pain
•Sudden onset
•Emergency
glaucoma treatment
• focuses on decreasing intraocular pressure and varies based on type
•Best prevention is regular eye exams
•Medications
•Laser surgery
•Drainage Implants
Macular Degeneration Epidemiology
•Most common age-related disease
•Gradually destroys sharp, central vision
Macular Degeneration Risk Factors
•Family history
•Female
•Caucasian decent
•Smoking,
•Increased UV light exposure (natural or artificial)
•High-fat diet,
•Decreased carotenoid intake
•Cardiovascular disease, hypertension, high cholesterol
•Obesity
Macular Degeneration Pathophysiology Dry
•Dry macular degeneration
•Dry form can turn into wet macular degeneration
•3 Phases
•Early
•Intermediate
•Advanced
Macular Degeneration Pathophysiology Wet
•Wet macular degeneration ( Develops after having dry)
•Damage to the macula occurs rapidly
Macular Degeneration Clinical Manifestations Dry
•Dry macular degeneration:
•Gradual blurring of central vision
•Difficulty recognizing faces
•Difficulty seeing in low light
Macular Degeneration Clinical Manifestations Wet
•Wet macular degeneration
•Distortion of straight lines
•Quick loss of central vision
•Dark spot in central vision
•Known as advanced macular degeneration
Macular Degeneration Diagnosis
•History
Exam
Macular Degeneration treatment Dry
none, but Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 formula may slow progression
Macular Degeneration treatment Wet
•Wet: laser surgery, photodynamic therapy, antiangiogenics /antivascular endothelial growth factor therapy