Core Practical 9: Determine the Ka for a weak acid
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Overview:

Procedure:

Reminder:
when using a burette, volumes should be recorded to 2 decimal places with the second figure being 0 or 5 only
titrations should always be repeated until concordant results are obtained
the Ka value is an indication of acid strength. The larger the value of the Ka, the stronger the acid
the Ka of a weak acid can be measured be titrating a known volume of the acid against sodium hydroxide using phenolpthalein as an indicator. A further equal volume of acid is then added, and the pH of the resulting solution is measured. Because effectively half of the acid has been titrated:
[Ha]=[A-] so [A-] and [HA] can be cancelled in the Ka expression
so Ka = [H+]
the pH value of the combined solutions can be converted to [H+] to give a Ka value
![<ul><li><p>when using a burette, volumes should be recorded to 2 decimal places with the second figure being 0 or 5 only </p></li><li><p>titrations should always be repeated until concordant results are obtained </p></li><li><p>the K<sub>a</sub> value is an indication of acid strength. The larger the value of the K<sub>a</sub>, the stronger the acid</p></li><li><p>the K<sub>a</sub> of a weak acid can be measured be titrating a known volume of the acid against sodium hydroxide using phenolpthalein as an indicator. A further equal volume of acid is then added, and the pH of the resulting solution is measured. Because effectively half of the acid has been titrated:</p></li><li><p>[Ha]=[A<sup>-</sup>] so [A<sup>-</sup>] and [HA] can be cancelled in the K<sub>a</sub> expression </p></li><li><p>so K<sub>a</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>]</p></li><li><p>the pH value of the combined solutions can be converted to [H<sup>+</sup>] to give a K<sub>a</sub> value</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4f20a92f-e119-4f87-b028-3f20f1ecf4f5.png)
Use the pH of your solution to calculate [H+]
10-4.66=[H+]
[H+]=2.19×10-5 moldm-3
Calculate the value Ka for the ethanoic acid
At half equivalence:
pH = pKa
4.66=pKa
Ka=2.19×10-5moldm-3
What are some sources of uncertainty in this experiment? What can you do to overcome them?
it is difficult to determine the end point of the titration
→ use white tile to see the colour change clearly
inaccuracies when reading burette volumes
→ ensure that you always read from the bottom of the meniscus
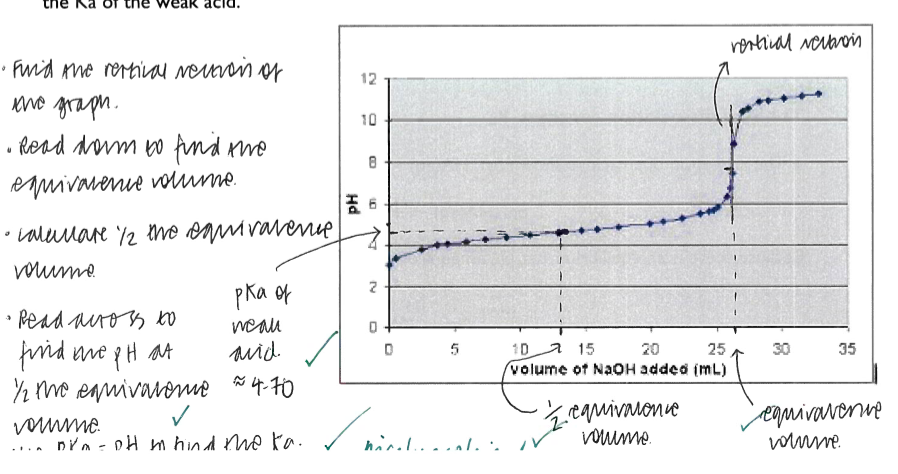
The following graph is obtained for the same reaction, measuring the pH after 1cm3 additions of the alkali. Show by annotation and explanation how this graph can also be used to determine the Ka of the weak acid.