Unit 1 Life: Vocabulary Part 3: Chemistry of Life
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
organic compound
A compound that contains carbon
macromolecule/biomolecule
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
monomer
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers bonded together.
carbohydrate
macromolecule made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (CHO); major source of energy for the human body
monosaccharide
simple sugar molecule; monomer of carbohydrates; glucose, fructose
disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis; sucrose (table sugar)
polysaccharide
A polymer of a carbohydrate; thousands of simple sugars (monomers) formed by dehydration synthesis;
lipid
macromolecule made mostly from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (CHO); includes fats, oils, and waxes
fatty acid
a monomer of lipids
glycerol
Combines with fatty acids to make lipids.
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
nucleic acid
macromolecule containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus atoms (CHONP)
protein
macromolecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms (CHON); needed by the body for growth and repair
amino acid
monomer of protein
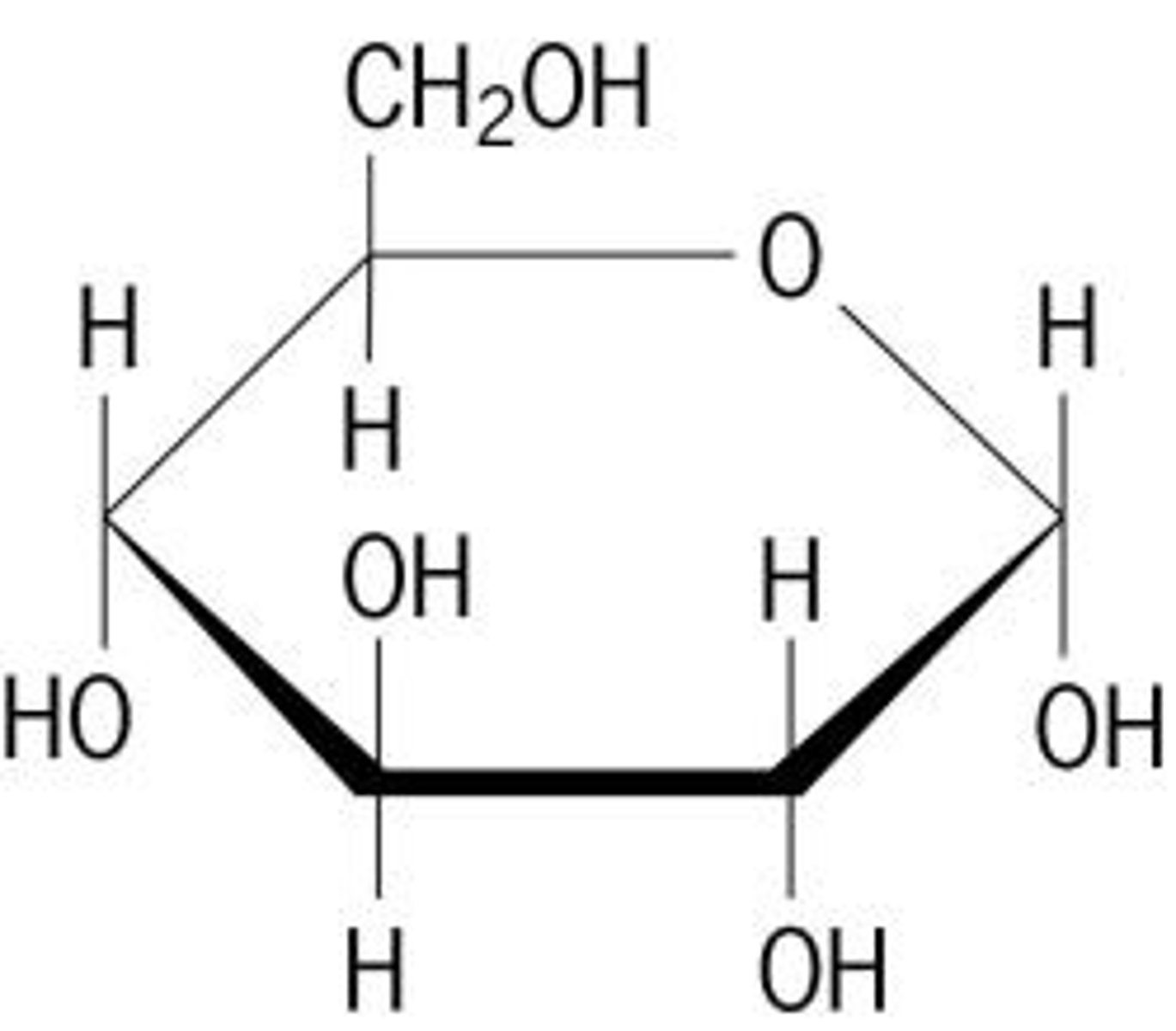
Which macromolecule is this? How do you know?
This is a simple sugar (a carbohydrate). It has a carbon ring.
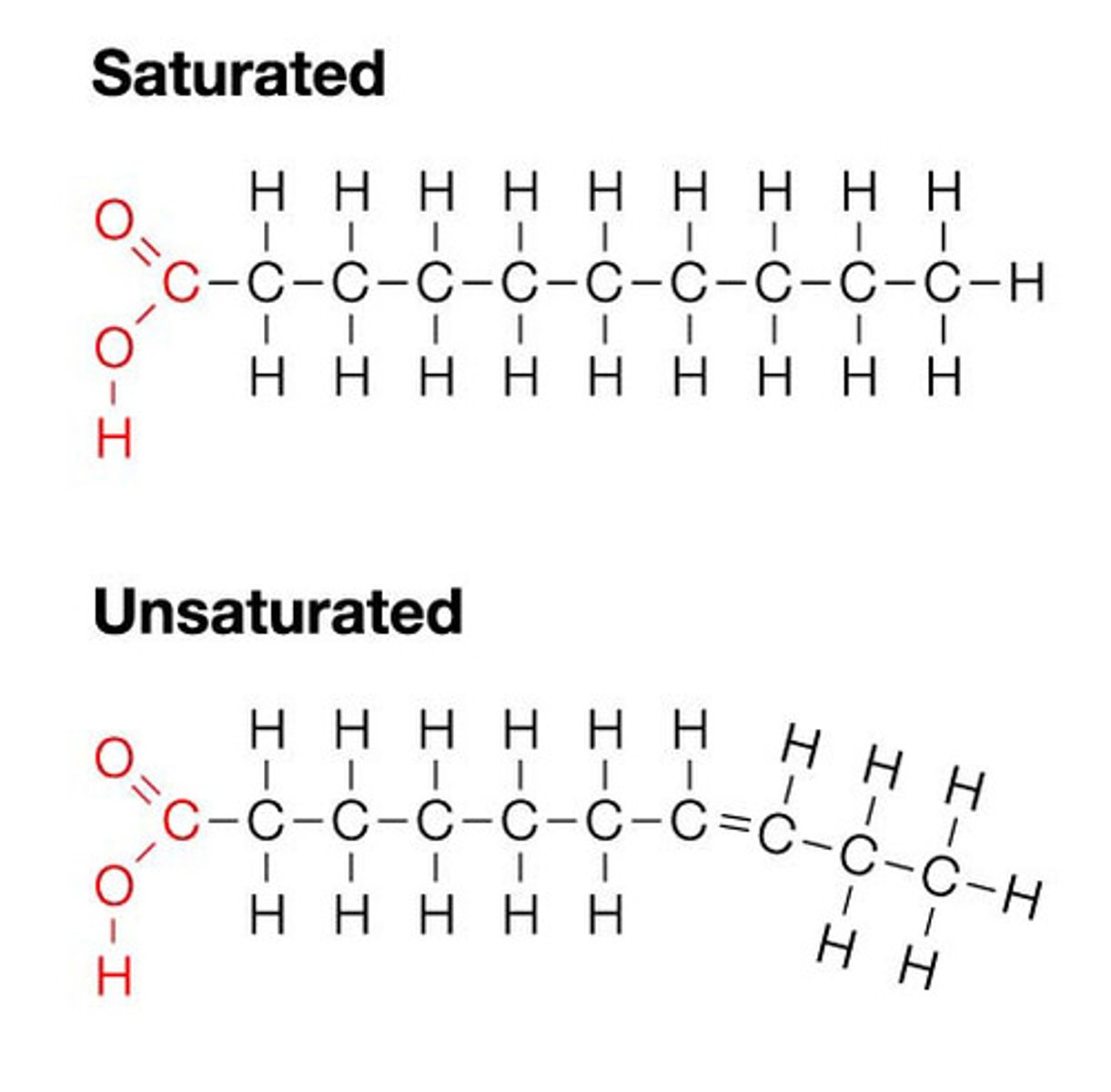
Which macromolecule is this? How do you know?
This is a lipid. It has two glycerols and two fatty acid chains. A fatty acid can be saturated or unsaturated.
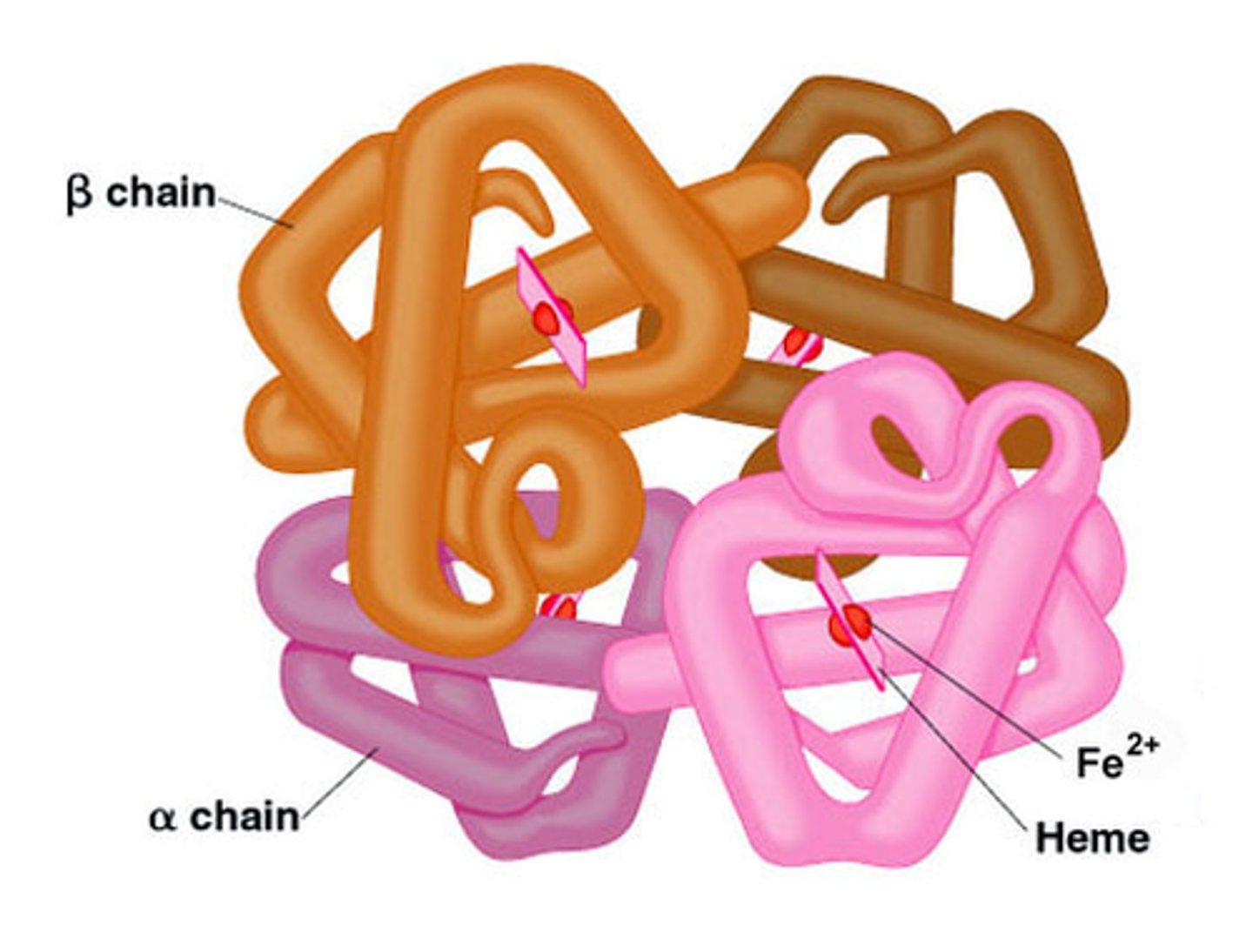
Which macromolecule is this? How do you know?
This is a protein. Proteins are often depicted as "ribbons" to show their primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures.
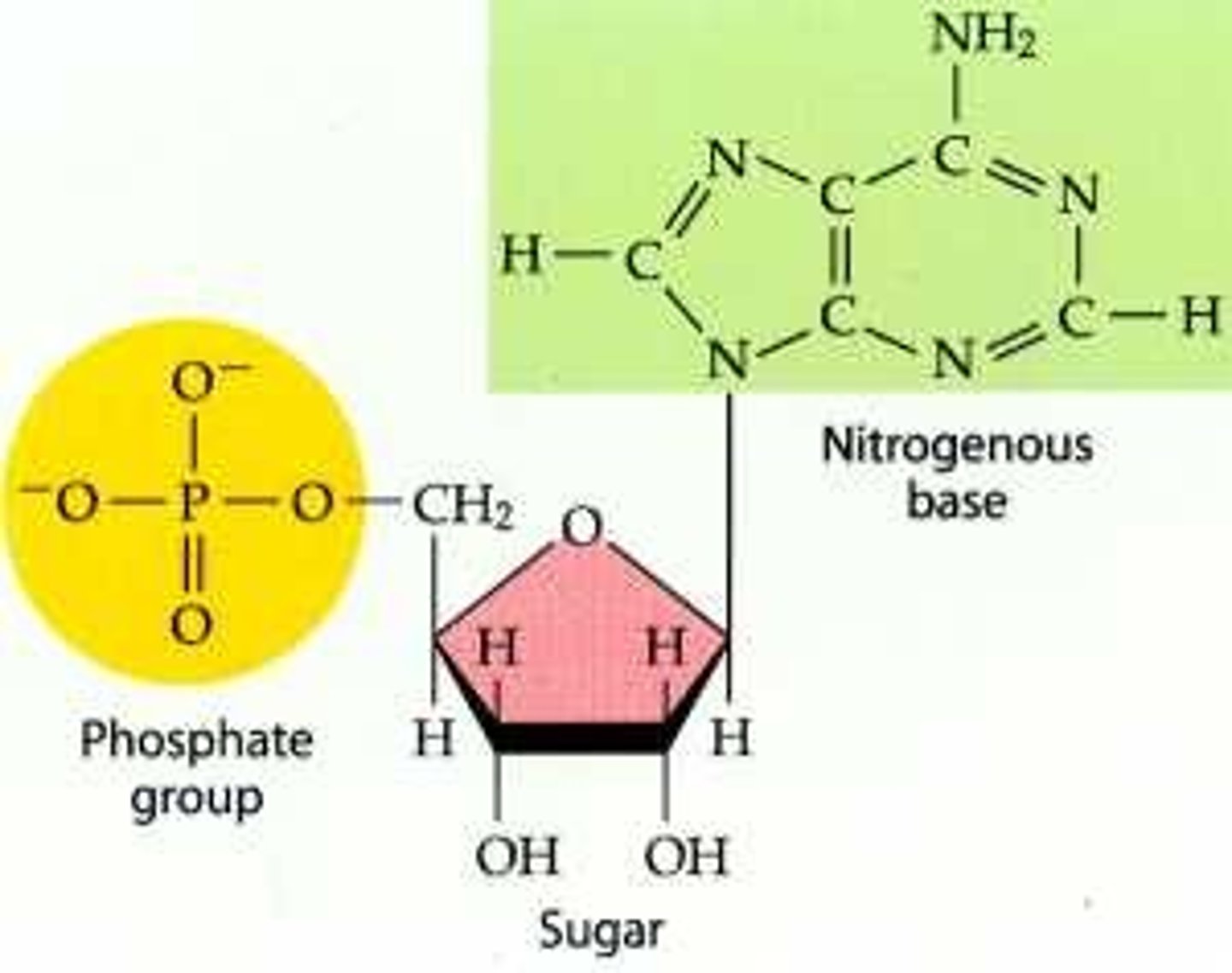
Which macromolecule is this? How do you know?
This is a nucleic acid. It is made up of a simple sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base.
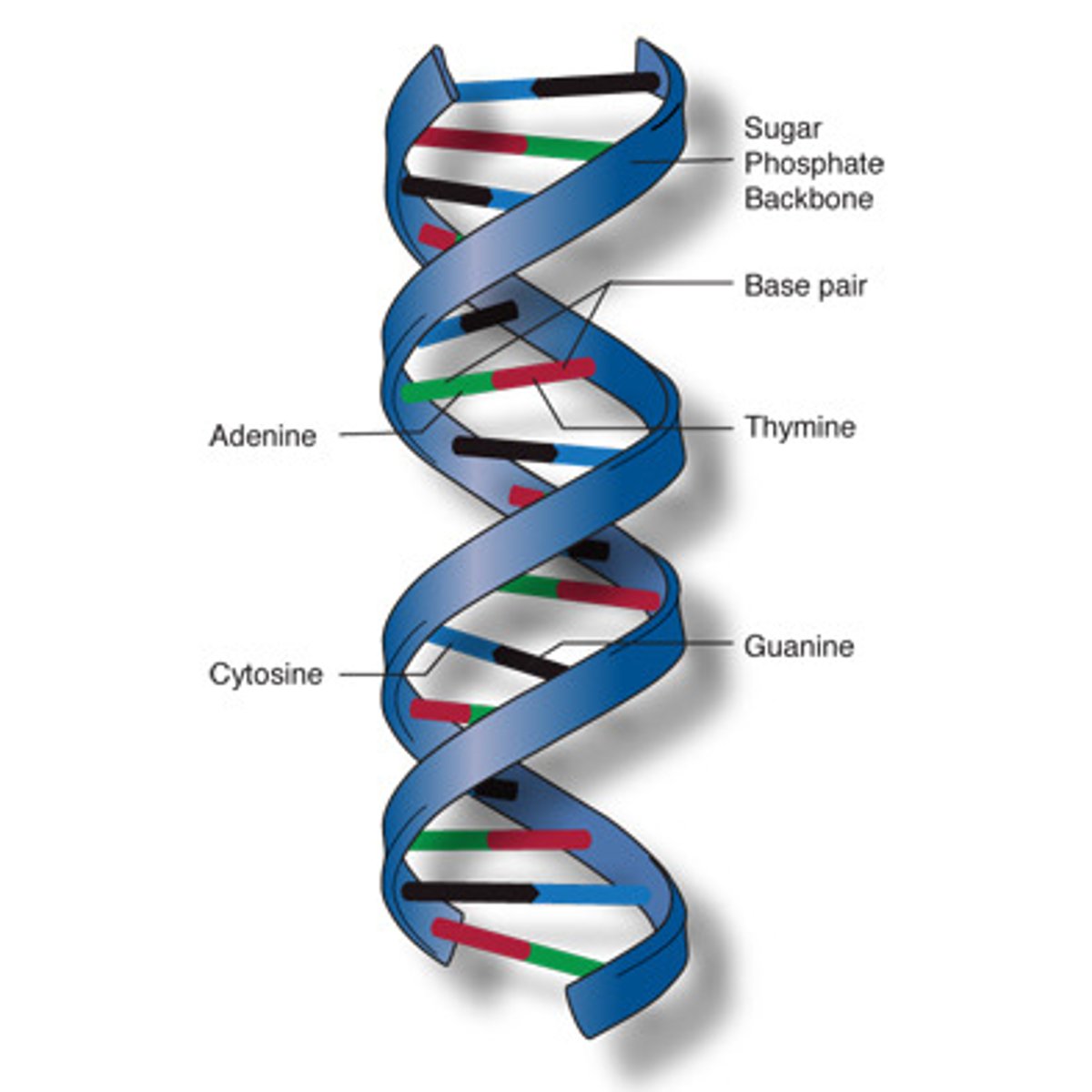
Which macromolecule is this? How do you know?
This is a nucleic acid (DNA).
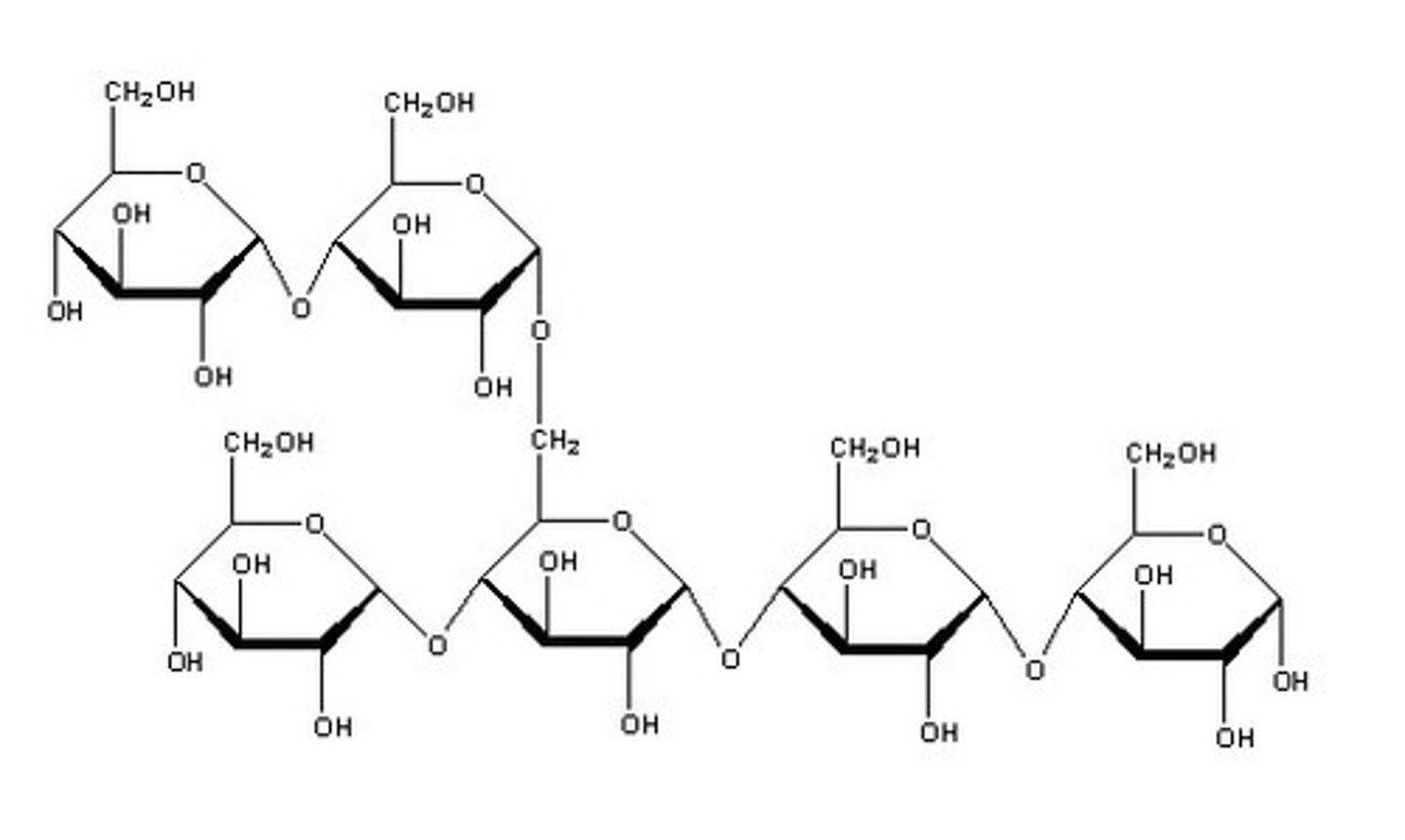
Which macromolecule is this? How do you know?
This is starch, which is a carbohydrate. Starch is a polymer made up of many monosaccharides bonded together.
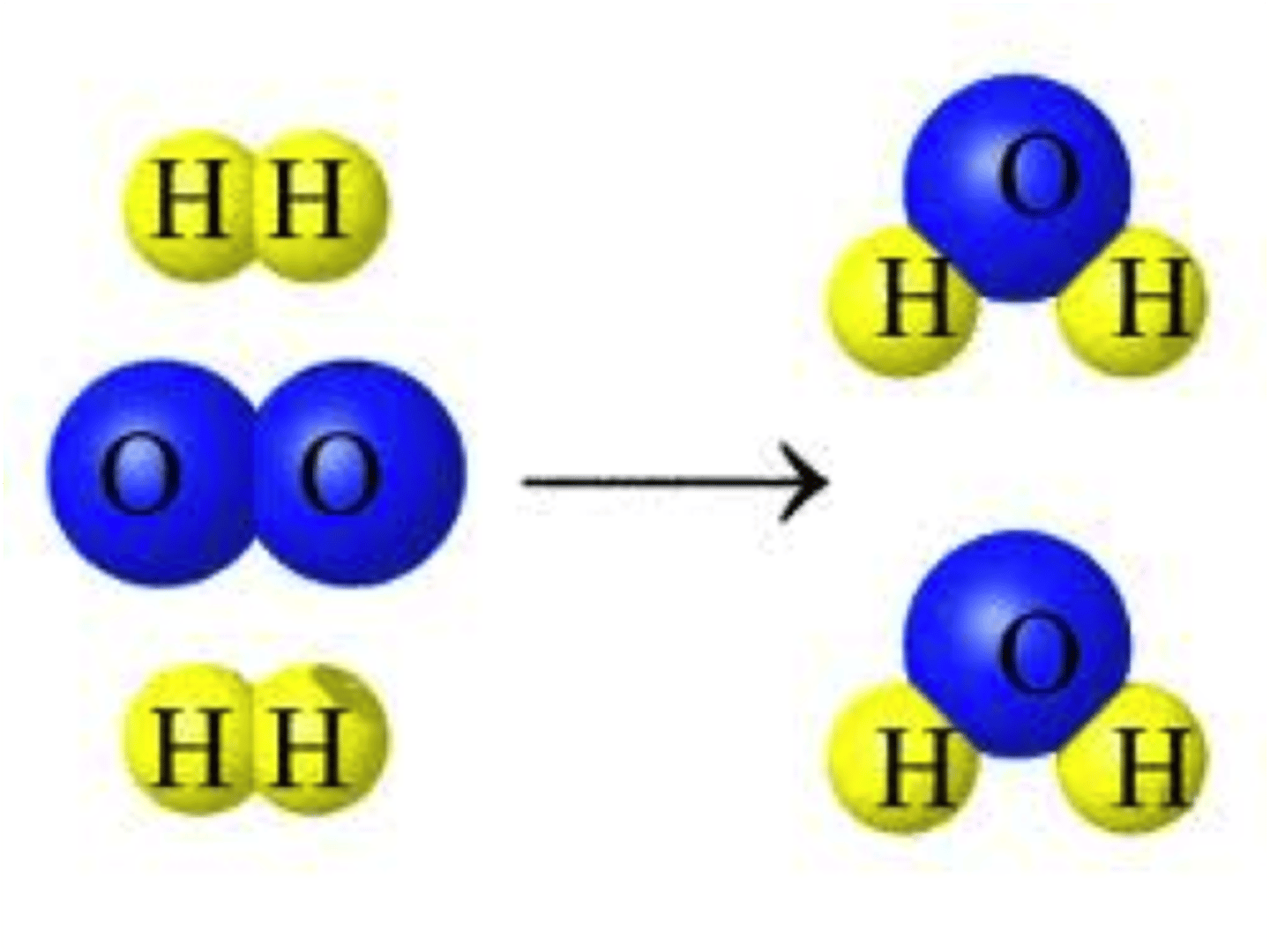
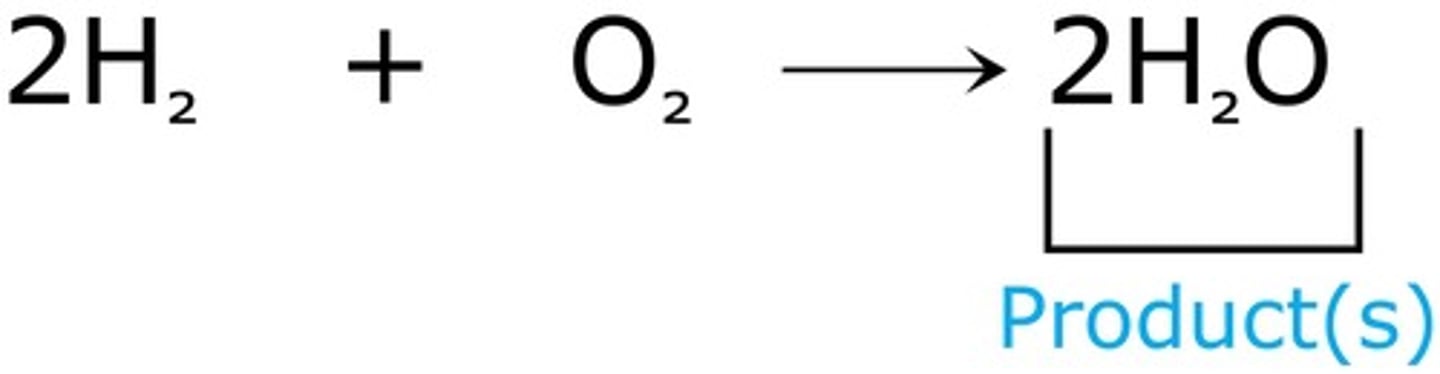
chemical reaction
process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals when bonds are broken and/or formed
reactant(s)
a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction.
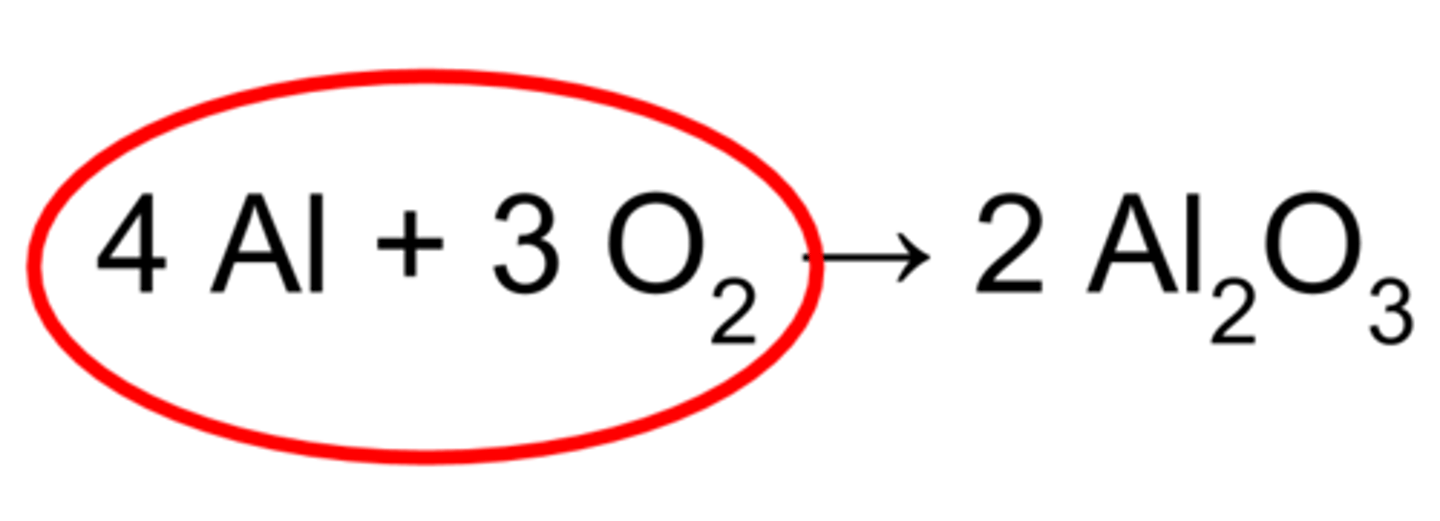
product(s)
the substances that are formed by the chemical change during a reaction
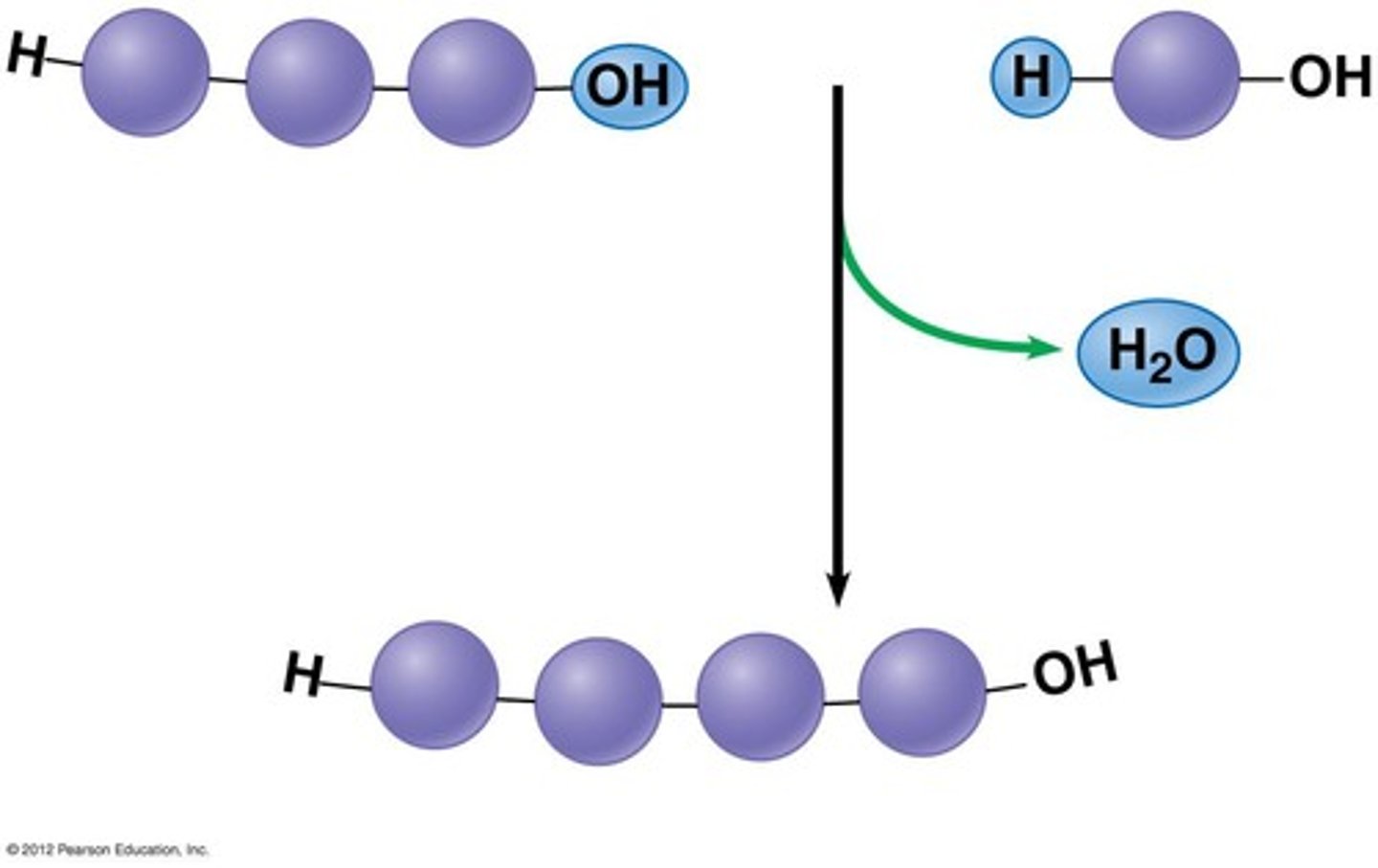
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules are bonded together with the removal of a water molecule.
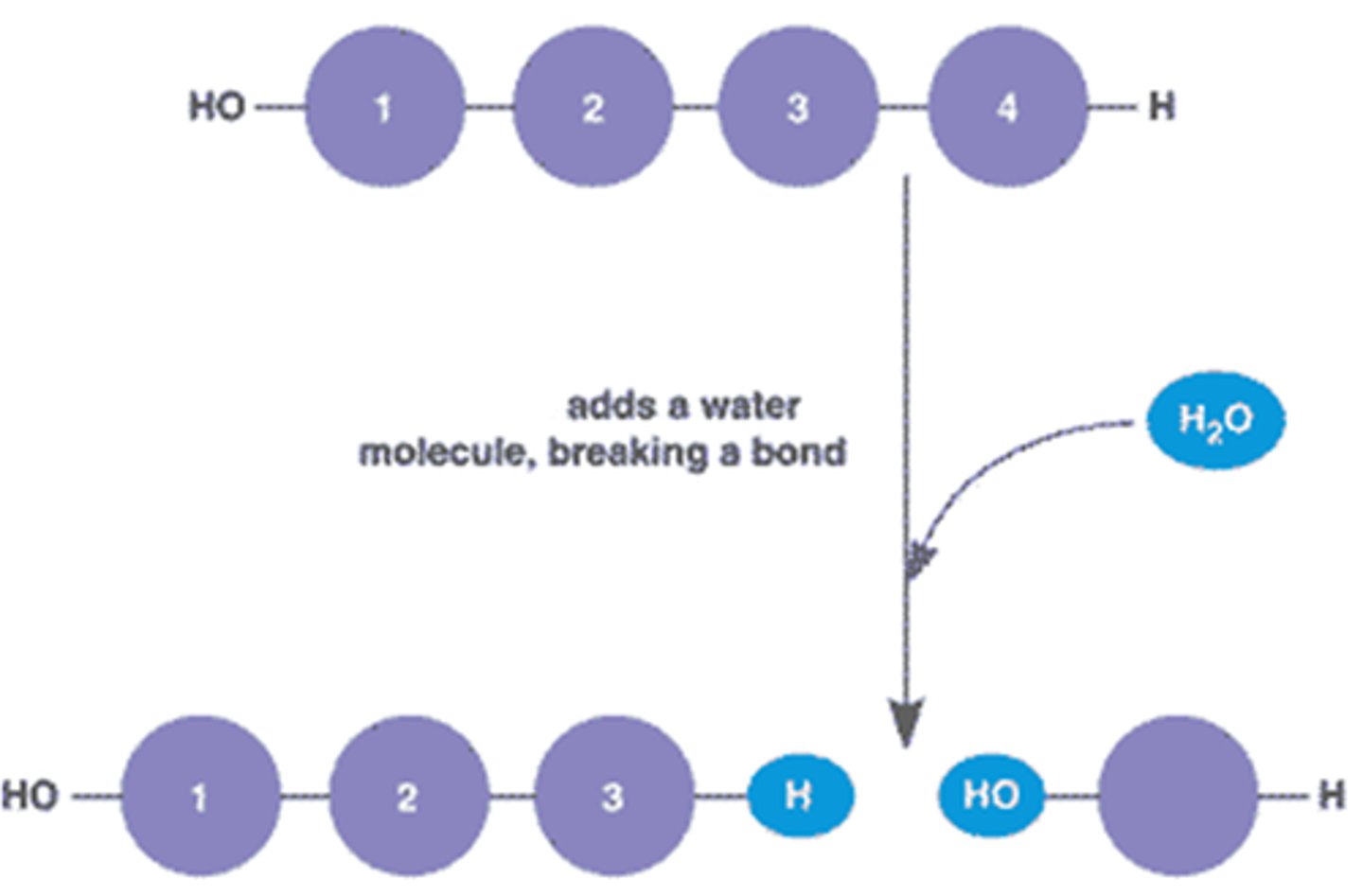
hydrolysis
A chemical reaction in which a molecule is broken apart by the chemical addition of a water molecule.
enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing