South College AVL Lab Med: Glucose and Lipids - Lecture 8
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
CMP or BMP
Which lab panel do we need to order to obtain serum glucose?
74-106 mg/dL (OR 4.1-5.9 mmol/L)
What is a normal adult glucose level?
70-100 mg/dL (no cal x 8+ hours)
What is a normal fasting adult glucose level?
<50 and >450 mg/dL
<40 and >450 mg/dL
what are some critical glucose values for men? women?
food ingestion (insulin released), glucacon (increase glucose), stress (trauma, infection, burns, MI, strenuous exercise), acute pancreatitis (endocrine disorder), Cushing syndrome, pregnancy (gestational diabetes), meds (corticosteroids - cortisol causes hyperglycemia, IV fluids w/ dextrose, antidepressants, antipsychotics, diuretics, estrogens, statins)
What are some reasons as to why glucose would be elevated?
exercise/activity, hypopituitarism, Addison disease, extensive liver disease (liver not functioning properly), starvation, drugs (insulin but don't worry about specifics)
What are some reasons as to why glucose would be decreased?
glucometer (blood glucose monitoring or continuous glucose monitoring, home or clinic), venous blood sample sent to lab (clinic)
What are some ways in which we measure serum glucose levels?
capillary blood, interstitial fluid
what kind of blood does blood glucose monitoring use? continuous glucose monitoring?
increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, blurred vision, slow healing cuts/sores, fatigue
what are some symptoms of hyperglycemia/indications to measure glucose levels?
shaking/trembling, faster HR, extreme hunger, sweating, confusion/difficulty concentrating, dizziness
what are some symptoms of hypoglycemia/indications to measure glucose levels?
DM, annual physical, Cushing syndrome/Addison's disease, CKD, Chronic pancreatitis (Type 3c diabetes - aka pacreatogenic diabetes), hypothyroidism, pregnancy
What are some other indications that you should measure glucose levels, in general?
A1C >/= 6.5%
OR
fasting glucose >/= 126mg/dL (7 mmol/L) (fasting for at least 8 hours)
OR
2-hour plasma glucose >/= 200mg/dL (used in pregnancy)
OR
Pt with classic sx of hyperglycemia/hyperglycemic crisis and random plasma glucose of >/= 200 mg/dL
What is part of the Diabetes Diagnostic Criteria?
annual physical, diabetes suspicion, diabetic follow up (Med management)
When would you perform a fasting glucose?
fasting! (normal if meal was ingested in the past hour)
When is a glucose level of 130 concerning?
glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C)
blood test used to diagnose diabetes and monitor its treatment by measuring the amount of glucose bound to hemoglobin in the blood, avg blood glucose level
4-5.9%
5.7-6.4%
>/=6.5%
<7%
what is a normal HbA1C value?
prediabetic?
diabetic diagnosis?
diabetic control?
poorly controled diabetes, stress, cushing syndrome, splenectomy, steroids (constant use), pregnancy, acromegaly
What are some reasons as to why HbA1C would be elevated?
hemolytic anemia (not normal hemoglobin), chronic blood loss, chronic kidney failure
What are some reasons as to why HbA1C would be decreased?
hemoglobinopathies (quantity of HbA is affected, ex: sickle cell)
RBC lifespan is increased
Abnormally and chronically low levels of proteins (malnutrition)
ascorbic acid (falsely cause low levels)
what are some interfering factors of HbA1C?
increased risk of complications
what happens if your glucose is constantly above 6.4%
insulin C -peptide
byproduct of insulin synthesis into the body from the pancreas, used to distinguish between endogenous and exogenous insulin
CORRELATES W/ ENDOGENOUS INSULIN PRODUCED BY PANCREAS
islet beta cell function of the pancreas, determines severity of insulin deficiency (distinguishing between type 1 and type 2 DM)
what do we use insulin C-peptide to monitor?
determine pancreatic function (ability to produce own insulin) in insulin dependent diabetic patient
suspicion that an alleged type 2 diabetic patient is actually a type 1 diabetic (needs insulin instead of oral)
suspicion of insulinoma (pancreatic tumor)
surveillance of surgical pancreatectomy
what are some other uses of insulin C-peptide labs?
GAD65 autoantibodies (against glutamic acid decarboxylase enzyme produced in pancreatic beta cells; confirmatory)
what is the most important autoantibody lab needed in order to confirm a diagnosis of DM type 1?
insulin antibodies (IAA), islet cell autoantibodies (ICA), zinc transporter 8 autoantibodies (ZnT8), insulinoma-associated antigen-2 autoantibodies (IA2)
what are the other autoantibodies that can help confirm a diagnosis of DM type 1?
at least 2 and one needs to be GAD65
How many autoantibody labs need to be collected in order to diagnose DM type 1?
cholesterol and triglycerides
what are the two main lipids in the blood?
cholesterol
element of all animal cell membranes, forms the backbone of steroid hormones and bile acids
no - need to be transported
can lipids travel through the blood alone?
Lipoproteins
Posses a water-soluble outside and insoluble lipid core
Protein-and-lipid substances in the blood that carry fats and cholesterol; classified according to size, density, and chemical composition
apoproteins
specific to lipoprotein structure and "guide" it
triglycerides (makes less dense)
apoproteins (makes more dense)
what determines/contributes to the density of a lipoprotein?
chylomicron, VLDL, IDL, LDL (bad ~75%), HDL (~25%)
what is the order of lipoproteins from least to most dense?
chylomicrons or VLDLs (very bad to have high triglycerides)
How are most triglycerides transported?
cholesterol esters in LDLs and HDLs
How is most cholesterol transported?
cholesterol
causal in development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), the plaques in arterial walls contain large amounts of this
LDL cholesterol (deposits cholesterol into blood vessels from liver)
"BAD"
the higher level of this, the greater the risk of ASCVD
HDL cholesterol (takes cholesterol away from the blood vessels to the liver)
"GOOD"
the higher level of this, the lower the risk of ASCVD
lipoprotein
a subfraction of LDL
ASCVD (levels are largely genetically determined)
What do high lipoprotein levels pose as a risk for?
Hyperlipidemia
broad term for elevated lipids
Hypercholesterolemia
elevation of LDL-C
Hypertriglyceridemia
elevation of TGs
Mixed hyperlipidemia
elevated TG and LDL-C
Dyslipidemia
imbalance of lipids
total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL, HDL, VLDL (often non-HDL)
What does a fasting lipid panel typically contain?
some are calculated (can be affected by lab abnormalities)
all lab values are age dependent
What is important to note about some of the labs collected on a fasting lipid panel?
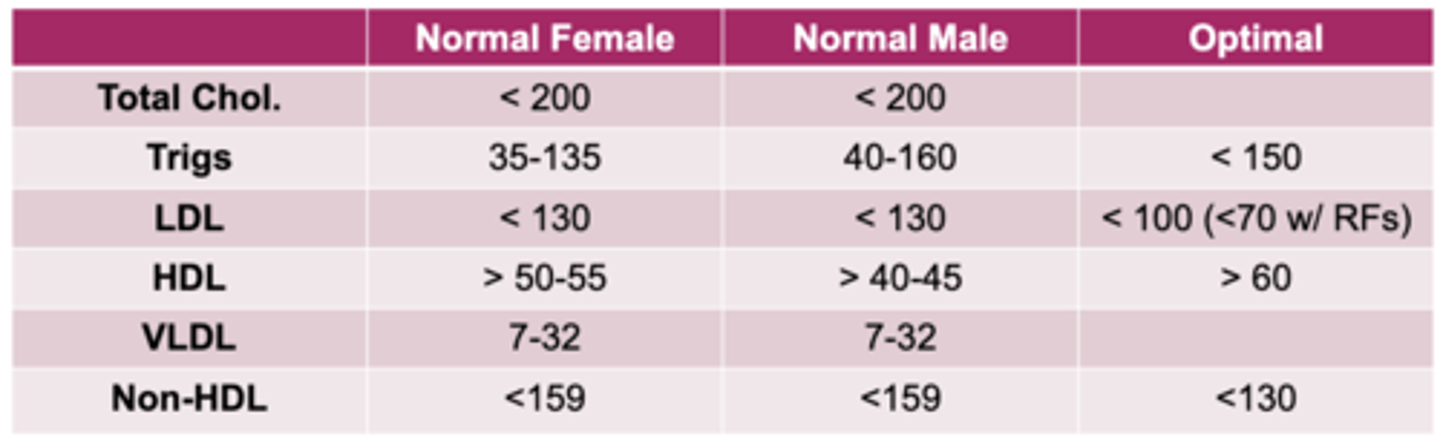
determine risk of coronary artery disease, evaluation for hyperlipidemia (NEED TO FAST 12-18 HOURS, only water consumed)
What is the purpose of obtaining a lipid profile/panel?
fluctuate (day to day by 15%, same day fluctuation 8%)
are lipid values stagnant or do they fluctuate?
pregnancy, postmenopausal, oophorectomy, drugs (steroids, OCP, beta-blockers, etc)
what are some causes of lipid values being elevated?
recumbent position, drugs (allopurinol (gout), bile salts)
what are some causes of lipid values being decreased?
<130 mg/dL (determines risk of coronary heart disease CHD risk, high triglycerides can make LDL calculations inaccurate)
what is an optimal LDL level?
>/=60mg/dL
<40 mg/dL
(smoking/EtOH can decrease HDLs)
Age and sex dependent
What HDL values is a negative risk factor for CHD? Positive risk factor for CHD?
VLDL (very low density lipoprotein)
carries triglycerides to adipose tissue; converts to LDL
total cholesterol = HDL + LDL + 20% triglycerides
what is the equation to calculate total cholecterol?
triglycerides
important for transferring energy from food into cells, transported mostly by VLDLs, storage source of energy
<150 mg/dL
>400 mg/dL
(Levels over 500 increase risk for pancreatitis)
(High TG levels can mask LDL levels)
normal values of triglycerides? critical value of triglicerides?
fatty meal ingestion, high starch consumption, alcohol, and pregnancy (no alcohol consumption 24 hours before test)
what can elevate triglyceride levels?
low risk: <4.9%, 10 year risk score
borderline: 5-is 7.4%, 10 year risk score
intermediate risk: 7.5-20%, 10 year risk score
high risk: >20%, 10 year risk score
What are the ASCVD Risk Score (ACC/AHA)?
MI and stroke
What can coronary heart disease lead to?