1.2 The Market
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Demand -
amount of a product/service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a set price in a given period of time.
Total revenue -
Total revenue - Price x Quantity
Demand curve-
Why are businesses interested in knowing what the demand curve for their product/service looks like?
Demands curves are useful as they can help businesses to predict:
The change in demand in response to a change in price - this allows the business to plan stock levels, staffing etc.
The resulting change in revenue - this helps the business to decide whether or not a price change is a good idea or not.
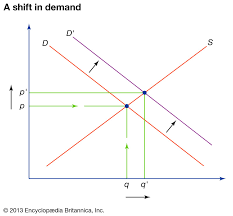
What does a demand and supply graph look like?
Substitutes -
goods that provide similar benefits that consumers could use as alternatives, e.g. a train ticket or a bus ticket.
Complementary goods -
goods that are consumed together, e.g. a cinema ticket and popcorn.
Normal goods -
goods for which demand rises as incomes rise and vice versa
Inferior goods -
goods for which demand falls as incomes rise and vice versa, e.g. own brand baked beans.
There are lots of other factors (not price) that affect the level of demand for a product or service
changes in related goods
o changes in consumer incomes
o fashions, tastes and preferences
o advertising and branding
o demographics (changes in the population)
o external shocks
o seasonality
Supply -
the amount of a good that producers are willing and able to supply at a given price in a given time period
Supply curve -
shows the relationship between the price of the product and the quantity supplied
Supply diagram
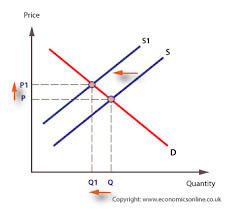
There are factors (other than price) that affect the amount of a good producers are willing and able to supply
o changes in the costs of production (e.g. raw materials, wages)
o introduction of new technology (as it can affect efficiency)
o indirect taxes (taxes on goods and services e.g. VAT or tariffs)
o government subsidies (grants from government to incentive firms to supply)
o external shocks (e.g. a fire at a supplier's factory)
Market -
where buyers and sellers interact to buy and sell goods and services
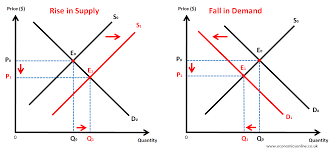
Equilibrium price -
the price where demand and supply are equal (also known as the market clearing price)
Surplus -
this is where supply is higher than demand as the price is too high (also known as excess supply)
Shortage -
this is where demand is higher than supply as the price is too low (also known as excess demand)
Market equilibrium
Equilibrium exists when the price is at a level where the amount consumers want to buy (demand) is the same as the amount producers want to supply. This is where the demand and supply curves intersect (cross)
Price elasticity of demand
- measures how much demand changes in response to a change in price
PED=

Price elastic demand
- When a change in price leads to a more than proportionate change in quantity demanded. These goods have a PED of <-1.
Price inelastic demand -
When a change in price leads to a less than proportionate change in quantity demanded. These goods have a PED between 0 and -1
Factors affecting PED

What does the units in PED mean?
PED <-1 = elastic e.g. confectionary
PED between 0 and -1 = inelastic, e.g. petrol
PED IN SUMMARY
PED | Change in price | Effect on revenue | Why? |
Price elastic (<-1) | Increase in price | Fall in revenue | Because a small increase in price -> large fall in quantity demanded |
| Decrease in price | Rise in revenue | Because a small cut in price -> large increase in quantity demand |
Price inelastic (between 0 and -1) | Increase in price | Rise in revenue | Because an increase in price -> small fall in demand |
| Decrease in price | Fall in revenue | Because a price cut -> small increase in demand |
Pros and Cons of PED
PED data is useful because….
It can help managers with:
| PED is of limited use because….
|
Income elasticity of demand -
measures how much demand changes in response to a change in income
Income elastic demand
- When a change in income leads to a more than proportionate change in quantity demanded. These goods have a YED >1 or less than -1
Income inelastic demand
- When a change in income leads to a less than proportionate change in quantity demanded. These goods have a YED between -1 and 1.
Normal goods -
goods for which demand rises as incomes rise and vice versa. These goods have a positive YED.
Inferior goods -
goods for which demand falls as incomes rise and vice versa, e.g. own brand baked beans. These goods have a negative YED.
The SIZE of the YED co-efficient tells us how much demand is likely to change in response to a change in income.
Income elastic | A change in income leads to a bigger % change in demand | YED is: >1 (if the good is normal) <-1 (if the good is inferior) |
Income inelastic | A change in income leads to a smaller % change in demand | YED is: Between 0 and 1 (if the good is normal) Between 0 and -1 (if the good is inferior) |
Unitary Income Elasticity
Occasionally, a change in income leads to an equal % change in demand. E.g, incomes rise 2%, and quantity demanded rises 2%. In this case, the YED coefficient would 1 (+or - depending on if the good is normal or inferior).
What factors affect YED?
Whether the good is normal or inferior. This determines the sign of the YED coefficient. | Whether the good is a necessity or a luxury. Necessities are normally quite income inelastic whereas luxuries tend to be more income elastic. | The price of the good in relation to consumers incomes. E.g. if consumers incomes went down they would probably by almost the same number of pencils, whereas the number of houses bought could fall quite a lot. |
Pros and Cons of YED Data
YED data is useful because….
It can help with sales forecasting and associated planning (e.g. production, stock, workforce) as businesses can predict how demand might change in response to forecast changes in consumer incomes.
It can help with product portfolio management. Consumer incomes change over the business cycle. When the economy is booming most incomes rise and during a recession incomes generally fall. Businesses can help to maintain a more stable cash flow over the cycle if they have quite income inelastic products in their portfolio, and/or a mix of normal and inferior goods.
| YED is of limited use because….
|
YED formula

Unincorporated
sole trader and partnership owner is the business and no legal differences, owner has unlimited liability for business actions
Incorporated
Private limited company and public Limited company. There is a legal difference between the business and the owners, owners have limited liability.
Soul trader is when there’s one owner of the business. Advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages, owner keeps all profits, owner has total control, quick and easy to set up.
Disadvantages, not legal distinction between businesses and owners, might pay more tax
Partnership is when a business is owned by more than one person
Advantages, simple way to set up a business, business can benefit from the work of more than one owner, easier to risk finance
Disadvantages profits must be shared, no legal distribution, may pay more tax
Lifestyle business
Set up an order to fit in with personal choices, and those of their family work. Life balance will be important and their prime objective is to be profit, satisfying, rather than profit maximisation.
Private limited company
LTD, shareholders often by Me and friends, sell shares, privately, shareholders are often directors
Pros and cons of an LTD
Pros, shareholders have limited liability, raise capital, three shares, owners control, who buys shares, tax advantages
Cons, more complex to set up, some loss of control, unable to sell shells to the public, which means it’s harder to raise finance
Public Limited company PLT
that is legally allowed to offer its shares for sale to the public. They don't have to offer shares to the public if they choose not to, but the option is there if and when needed.
Social enterprise
Business with the primary social objective, E.g. co-op run by members, shareholders involved in decision-making
Community interest company
CIS, design for social enterprises, limitations on the dividends, easier to find shareholders
Advantages and disadvantages for franchising to the franchisee
Advantages, established product, lower risk, predictable, set up, costs, exclusive area contract
Disadvantages, lack of independence, cost of buying, profits are shared with franchiser, have to buy equipment from franchiser
Advantages and disadvantages of franchising to the franchiser
Advantages, fast method of growing business, risk shared with franchisee, franchisee is most likely to be motivated
Disadvantages, profit shared, with franchisee, less control, can they effectively manage growth?
Advantages and disadvantages of a plc
Advantages, raise large amount of capital, easier to sell shares, risk shared between shareholders
Disadvantages, loss of control, risk of short termism
Cost plus pricing, advantages and disadvantages
Advantages, simple and cheap, every product sold is a profit
Disadvantages, ignores market conditions, difficult to establish costs
Competitive pricing, advantages and disadvantages
Advantages, involves close attention, selling price should be in line with rivals, prevent dangerous price wars
Disadvantages, price may not provide enough profit margin, main problem is that the business needs another way to attract customers
Psychological pricing, advantages and disadvantages
Advantages, can a draw attention to the product, increase sales
Disadvantages, may lead to an inaccurate perception of value, may harm the brand reputation
Predatory pricing
It’s illegal in the UK and considered anti-competitive. It must not be confused with competitive pricing which is legal.
Price skimming Advantages disadvantages
Advantages, quick returns, high profit margins, can add to product, exclusivity, and image
Disadvantages, may have to drop prices quite fast, high price may put some people off
Penetration, pricing, advantages and disadvantages
Advantages, sale should be high to start with, can lead to economies of scale
Disadvantages, low price may affect brands image, low price may not work/be effective