Cartilage
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cartilage
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Cartilage
type of connective tissue
found on the surface of bones at joints. different forms found on the nose, larynx, and outer ear.
Matrix, its features- what are the things that set it apart?
is made up of chondrin (protein-carbohydrate complex)
contains many collagen fibres embedded in the chondrin
the size and arrangement of these fibres gives the different types of cartilage different properties
is firm, meaning it can operate as support but maintains flexibility
Microscopic structure of catilage
chondroblasts
chondrocytes
lacunae
mature cartilage cells
chondrocytes
chondroblasts
an immature cartilage cell
produces the matrix +
surrounds itself with the matrix.
Lacunae
chondroblasts become trapped in the matrix
this space is called the lacunae
Features of cartilage
avascular
a lot of intercellular material
diffusion occurs to transport nutrients + molecules
perichondrium
perichondrium
fibrous membrane that covers the external surface of the cartilage- contains blood vessels.
How are nutrients transported ? Why?
there are no blood vessels
nutrients are transported through the matrix using diffusion
slow process (due to a lot of intercellular material/ matrix)
what is the result of the transport of nutrients through the matrix?
diffusion rate is slow=
metabolism and cell division is slow.
resulting in a long time taken to heal
Types of cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
Elastic cartilage
Fibro cartilage
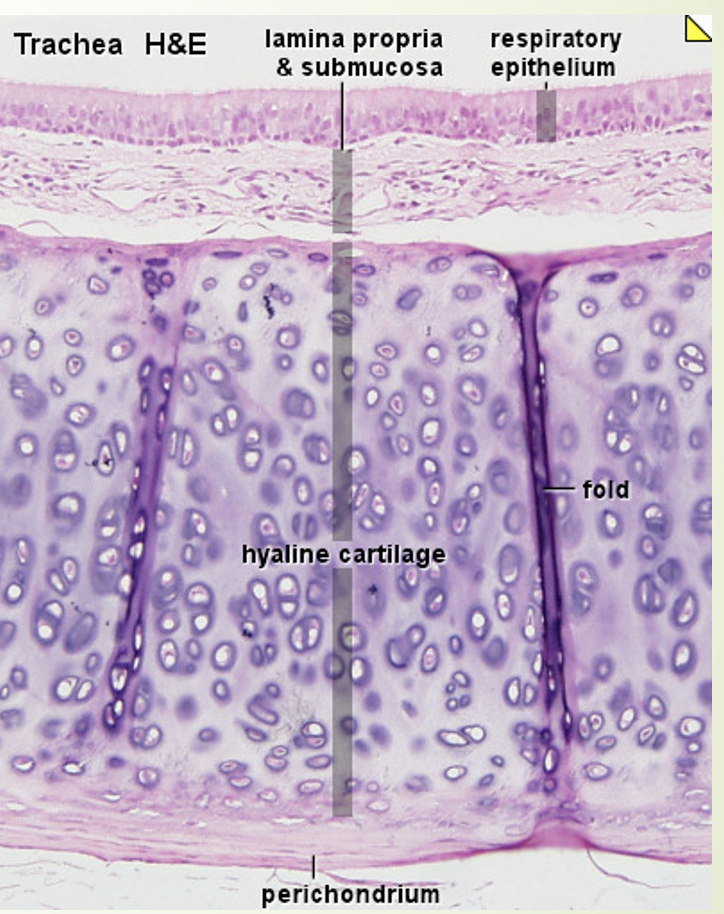
Hyaline Cartilage (features + where it is found)
thin collagen fibers closely packed together, in such a way that they are indistinguishable from one another.
looks like a smooth surface
very flexible
found in the rings of the trachea and bronchi
anywhere 2 bones meet to form moveable joint
Elastic Cartilage (features + where it is found)
consists of elastic and collagen fibres
not as closely packed together like hyaline cartilage
provides:
flexible, elastic support
Found in external ear and epiglottis provides:
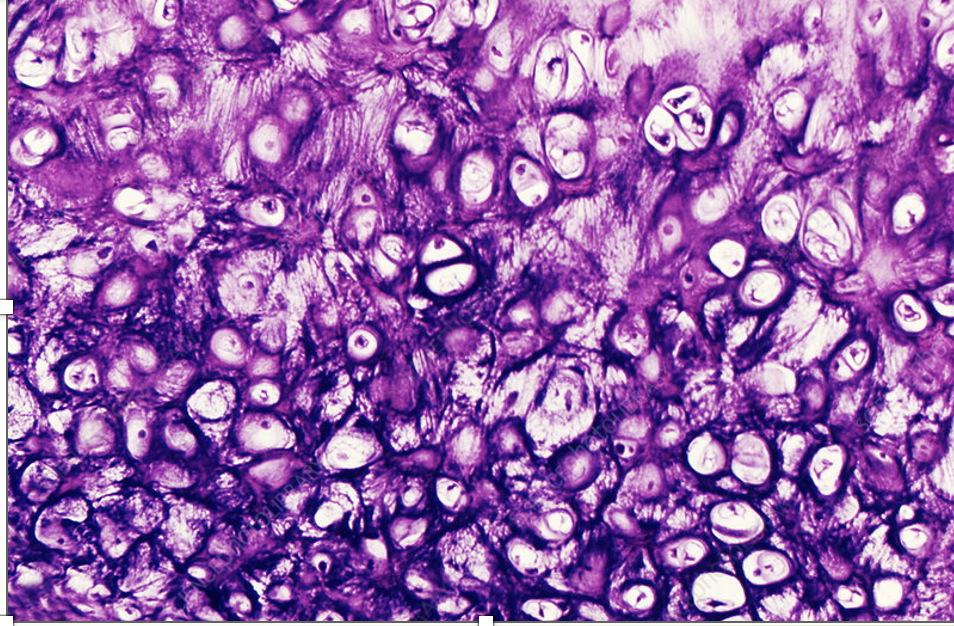
Fibrocartilage (features and where it’s found)
thick collagen fibres
not as densely packed like hyaline cartilage
allows for compression
provides cushioning for regions where the weight of body is being supported/ withstanding pressure
found:
intervertebral discs in spinal column
meniscus of knee joint
tissues that join the 2 sides of the pelvis