gram+ active agents
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
gram+ bacteria suscepibility
cell wall synthesis inhibitors
beta lactams e.g. penicillin and cephalosporins
glycopeptides e.g. vancomycin and teicoplanin
protein synthesis inhibitors
clindamycin, linezolid, fusidic acid
nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors
rifampicin
cell wall synthesis inhibitors
glycopeptides
vancomycin/teicoplanin - staphylococci (MRSA), clostridium difficile
beta lactams
penicillin
benzylpenicillin - streptococci, diphtheria
flucloxacillin - staphylococcus
ampicillin/amoxicillin - streptococcus pneumonia, enterococcus
cephalosporins - ceftazidime - streptococcus pneumonia, enterococcus
carbapenems - imipenem, ertapenem, meropenem - streptococcus, staphylococcus
peptidoglycan synthesis
building of cross linked chains is catalyzed by specific enzymes - transpeptidases which are also referred to as penicillin binding proteins PBP’s
reasons for different spectra of activity
these features and processes are also present in gram- (e.g. cell wall, cell membrane, transcription, translation)
different composition and/or location of target in gram- and gram+ (e.g. cell wall, cell membrane)
gram- have additional outer membrane that may impede entry of some agents
the periplasm, in gram- contains hydrolytic enzymes
porins present in some bacteria may actively remove agents preventing them from reaching target
beta lactams
defined by the presence of a beta lactam ring
four main types: penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, monobactams
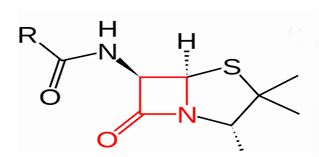
cell wall synthesis inhibitor beta lactam
agents that disrupt peptidoglycan. act by inhibiting enzyme transpeptidase (PBP)
transpeptidase (PBP) bunds to a beta lactams as they appear similar to the peptide bond the enzyme usually binds to
beta lactam then inactivating the enzyme, which prevents cross linking in the peptidoglycan wall
weakening the cell wall
the cell lysis = cell death (bactericidal)
penicillins
narrow spectrum
penicillin G - IM, IV admin
penicillin V - oral admin
broad spectrum
amoxicillin/ampicillin
extended spectrum
piperacillin
anti-staphylococcal penicillins
flucloxacillin
first generation penicillin
penicillin G (also called benzylpenicillin, benzathine penicillin) - IM/IV admin
penicillin V (also called phenoxymethylpenicillin) - gastric acid resistant, oral admin
first gen penicillin highly active against
gram positive cocci (except penicillinase producing staphylococci, penicillin- resistant pneumococci, enterococci and oxacillin-resistant staphylococci)
gram positive rods such as listeria
gram negatives (limited use)
most anaerobes (with certain important exceptions, including Bacteroides, C. difficile)
first gen penicillin therapeutic uses
endocarditis cause by susceptible bacteria (some streptococci)
meningitis cause by susceptible bacteria (L. monocytogenes, used alone or with an aminoglycoside)
pneumonia cause by susceptible bacteria
cellulitis (e.g. streptococcus pyogenes)
not useful for infections caused by staphylococci as majority are not susceptible due to penicillinase production
group A strep infections
syphilis (treponema pallidum)
anti staphylococcal penicillins
activity
active against penicillinase-producing staphylococci
not active against MRSA
not active against enterococci, listeria
examples - flucloxacillin (oral or IV), cloxacillin, dicloxacillin, nafcillin)
therapeutic uses
endocarditis cause by staphylococci
bloodstream infection cause by staphylococci
septic arthritis caused by S. aureus
broad spectrum penicillins with b-lactamases inhibitor
retain good gram+ activity but also expanded activity against gram-
co-amoxiclav (amoxicillin and clavulanic acid), (IV and PO)
pip - Taz (piperacillin and tazobactam) (IV only)
clavulanic acid and tazobactam inhibits b-lactamases so that amoxicillin and piperacillin remains active
therapeutic uses - provide cover gram+ in treatment of infections with mixed aetiologies e.g. enterococci in abdominal infection, staphylococci in pneumonia
cephalosporins
bactericidal antibiotics. same mechanism as penicillin. generally broad spectrum
1st generation
good gram positive activity but some gram negative
orally active e.g. cephalexin
used in treatment of respiratory and urinary infections
2nd generation
retain gram positive activity but also exhibit gram negative activity
oral and IV e.g. cefuroxime used for respiratory infections, complicated UTI and surgical prophylaxis
3rd generation
good gram negative activity, less staphylococcal activity, have some streptococcal activity
most IV e.g. ceftriaxone (IV), cefotaxime (IV)
carbapenems
very broad spectrum (gram+ and gram-)
similar to other beta lactams - binds to transpeptidase enzyme (or PBP) which inhibits cell wall synthesis
dissimilar to other beta lactams - have aa modified ring in their structure. they are less effected by resistance mechanisms of bacteria
imipenem, meropenem, eratpenem
monobactams
no active against gram positive and anaerobes
Aztreonam is the only antibiotic in this class
cell wall synthesis inhibitors glycopeptides
agents that disrupt peptidoglycan, binds to the peptide chain e.g. vancomycin, teicoplanin
unlike B-lactams, do not inhibit the enzyme transpeptidase (PBP)
glycopeptides bind to the peptide side chains of NAM sugars
binding to the peptides prevents the PBP from linking with the chains, then preventing cross-linking
weakening the cell wall
cell lysis = cell death
glycopeptide activity
narrow spectrum, gram positive only
used for treatment of MRSA (IV only) and C. difficle (oral only)
bactericidal
gram negative outer membrane prevents entry of glycopeptides, hence gram- intrinsically resistant
glycopeptide therapeutic uses
staphylococcal infections resistant to penicillin e.g. MRSA infections
susceptible enterococci (e.g. bloodstream infections)
viridians streptococci
severe C. difficile infection
nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors
inhibit folate synthesis → trimethoprim (combined with sulfamethoxazole = co-trimoxazole) → staphylococcus, saprophyticus
inhibit DNA gyrase → flouroquinones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, ofloxacin) → streptococcus, staphylococcus, bacillus
bind to RNA polymerase → rifamycin (rifampicin) → staphylococcus (endocarditis)
break DNA strands → nitroimidazoles (metronidazole) → clostridium difficile
rifampicin mode of action
binds to RNA polymerase and inhibits initiation of mRNA synthesis
rifampicin activity
bactericidal
spectrum:
gram+ ve (staphylococcus, enterococcus)
mycobacterium tuberculosis
gram- resistant due to decreased uptake of hydrophobic antibiotic
generally used in combination with other agent
PO or IV
rifampicin therapeutic uses
bone infections - as 2nd anti staphylococcal agent for osteomyelitis
tuberculosis - 1 agent in combined therapy
protein synthesis
fully functional protein synthesis is essential to bacterial cell survival and growth
protein synthesis (translation) is mediated by the bacterial ribosome which decode the information contained in mRNA to make proteins with the correct amino acid sequence
antibiotics that bind to the ribosome at various locations can disrupt this process
protein synthesis inhibitors
macrolides → clarithromycin, erythromycin, azithromycin → streptococcus pneumonia, S. aureus
lincosamide → clindamycin → clostridium spp., streptococcus spp., staphylococcus spp. (including penicillin resistance)
tetracyclines → tetracyclines, doxycycline → broad spectrum S. aureus, S. pneumonia, S. pyogenes
fusidane → fusidic acid → staphylococcus, enterococcus
antimicrobials
narrow spec gram+
linezolid
clindamycin
fusidic acid
broad spec gram-
erythromycin
clarithromycin
azithromycin
linezolid mode of action
oxazolidinone: inhibits protein synthesis by binding to 50S subunit of the prokaryotic ribosome, preventing formation of the initiation complex
linezolid activity
S. aureus (including MRSA)
S. epidermidis
enterococcus (including VRE)
streptococcus
bacteriostatic against most susceptible bacteria
bactericidal against some streptococcus
IV or oral formulation
linezolid therapeutic uses
MRSA, VRE bloodstream infection reserved for antibiotic resistant infections
macrolides mode of action
bind to 50S ribosomal subunit and prevent translocation along mRNA
macrolides activity
some gram positives: staphylococcus (not MRSA), streptococcus, NOT enterococcus
some gram negatives: legionella spp., H. influenza, NOT Enterobacteriaceae
some anaerobes
some others: H. pylori, C. trachomatis
bacteriostatic mainly but bactericidal at higher concentrations
IV and oral admin
many drug drug interactions
fusidic acid mode of action
binds to a bacterial elongation factor and prevents peptide chain elongation at the ribosome
fusidic acid activity
staphylococcus (e.g. s. aureus, S. epidermidis)
enterococcus (nut not VRE)
bacteriostatic
administer as: IV, oral, topical, ophthalmic (most common)
fusidic acid therapeutic uses
staphylococcal infections including MRSA (e.g. staphylococcal impetigo)
as 2nd anti staphylococcal agent for osteomyelitis
used in combination to reduce development of resistance
daptomycin mode of action
lipopeptide: lipophilic tail inserts directly into gram+ cell membrane (aerobes and anaerobes), causing rapid membrane depolarization and potassium efflux, followed by DNA, RNA and protein synthesis resulting in cell death
daptomycin activity
gram positive cocci: MSSA, MRSA, staph. epidermidis, streptococcus pneumonia, viridians streptococcus, group A strep, enterococcus faecium and faecalis
no activity against gram-
concentration dependent bactericidal activity
calcium dependent activity (needed for insertion of lipophilic tail)
IV admin only
daptomycin therapeutic uses
skin and soft tissue
S. aureus/MRSA bacteremia and right sided endocarditis
usually reserved for antibiotic resistant infections