Superpowers 1
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
A superpower
a nation which is able to project its influence and be dominant on a global scale
Uni polar world
world means there is only one superpower
bipolar
world exists when there are two superpowers
multipolar
world means there are multiple superpowers
historical superpowers
The USA and USSR became superpowers after World War II.
Before this, the superpowers were the British Empire and the USA
USA - uni polar
Currently the USA is the only superpower therefore the world is uni-polar
The USA is also referred to as a hyperpower or hegemon meaning that it is dominant in all aspects of power
Emerging super powers
The EU is a group of nations which qualifies as an emerging superpower
Brazil
Russia
India
China
Factors affecting super power status
Physical size and geographical position
Economic power
Demographics
Military strength
Physical resouces
Resources
Access to resources such as minerals and metals
Control of resources
These can be sold and exported which supports economic growth
Discovery of oil and gas in the Middle East has given OPEC countries economic power
size and geographical position
This links to resources, the larger a country the more resources it may have
Russia has significant reserves of coal, oil and gas
The geographical position of a country impacts its links and influence over other countries
Economic factors
Influence on global economics through membership of International Governmental Organisations (IGOs) and trading blocs such as European Union (EU)
High levels of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
The USA has the highest global inflow of FDI at US$86 billion
it influences areas such as
Military strength
Ability to exploit resources
Cultural influence
Political strength
demographic factors
Populations with a large working age population supports economic growth
A large dependent population (e.g. ageing population of Japan) may have a negative impact on economic growth
Population size also impacts on the military strength of a country
Hard powers
Use economic and military power to try and force countries to behave in a certain way
Economic - trade deals, sanctions
Military - use of force, threats of force or military action, the forming of military alliances
soft power
Joseph Nye- to demonstrate effective foreign policy and maintance of power needs the use of both hard and soft powers
Mackinders heartland theory
In 1904 Halford Mackinder proposed the 'Heartland theory'
Based on the premise that most of the world's natural resources are to be found in Asia and Europe
The 'heartland' is an area bordered by mountains on three sides and the Arctic to the north
This makes it difficult to invade
Maintenance of power in the imperial era
In the early 20th century the world was multi polar
European powers dominated invading and taking power in many countries in Africa, Asia and America
This was an imperialist system which involved political, economic and/or cultural control
The UK exploited the population as a workforce and the resources of the countries
The system was maintained mainly through the use of hard power - military
indirect control post ww2
The role of the UK in WWI and WWII, together with the Great Depression led to the collapse of the UK as a superpower
The period after WWII saw the rise of the USA and USSR to form a bi-polar world
The result of this was the 'cold war'
Neo colonialism
An indirect mechanism of control
Used by Western nations to exert influence and control over ex-colonies
Tied aid which means that developing countries have to spend money on goods or services with the donor country
Uneven trade where countries are paid little for their resources
Rise of China
Political |
|
Economic |
|
Military |
|
Demographic |
|
Cultural |
|
facts about India
POLITICAL
Poor relations with some neighbours including China and Pakistan
Member of the G20 and UN
ECONOMIC
Attracts many TNCs and FDI- young growing population
Many people remain in poverty
MILITARY
Second largest armed force
A nuclear power
DEMOGRAPHIC
Largest population in the world
Large English speaking population
Russia key facts
POLITICAL
Reduced global influence
Invasion of Ukraine in 2022
ECONOMIC
9th largest GDP in the world
Decreasing influence over global financial decision making
Lack of investment by TNCs and FDIs
MILITARY
Fifth largest military force in the world
Wide scale corruption
Ageing weapons and vehicles
A nuclear power
DEMOGRAPHIC
Population is experiencing slow decline
development theory
Core- high income nations, skilled labour
Periphery- Middle income, industrialising
Semi- peripheries- low income, export labour and natural resources
Critism of worlds system theory
Too focussed on the economy
Insufficient focus on culture
modernised theory- Rostow 1960
Stage 1: Traditional society: economy based on bartering, subsidence farming and little investment
Stage 2: Pre-conditions for take off (transitional stage): surpluses are traded through improved infrastructure and shift to manufacturing
Stage 3: Take off: industrial and regional growth, investment and political change
Stage 4: Drive to maturity: growth is supported through technological innovation, diversification and investment
Stage 5 - High mass consumption: consumer orientated society, durable goods production, dominant service sector, higher disposable incomes
critismof rostows theory
The model is outdated and too simple
The model assumes all countries start at the same point (same resources, population, climate etc.)
Capital is needed to advance from Stage 1
Dependency theory- Frank 1960
Persistent poverty in developing countries is the result of their dependency on developed countries
There is an unequal relationship between the developed and developing countries
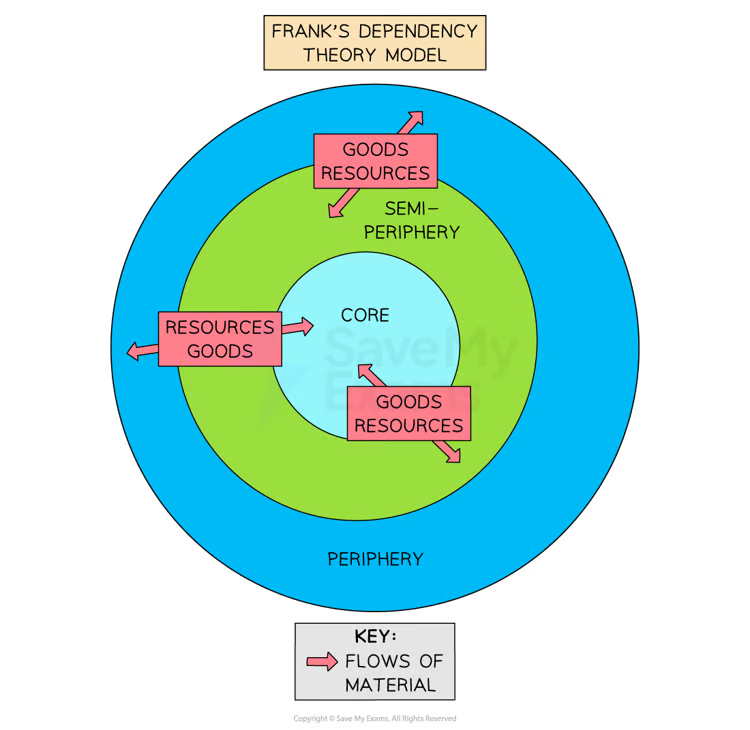
criticism of the dependency theory
Developed countries have lost their power to control developing countries
Countries are emerging and becoming more developed semi-peripheral countries, such as Mexico and India
The global system is now controlled by TNCs and the World Trade Organisation
Underdevelopment may be due to internal, not external, factors