L12 - water and plant cells
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
no water = no -
plant
0 water potential indicates -
pure water
ecological aspect: water dictates - of plants
distribution
physiological aspects: water status is key for - and -
growth, photosynthesis
production of 1 gram of organic matter requires the absorption of - grams of water
500
water molecules are highly - due to - bonds
cohesive, hydrogen
water molecules minimize - with air, resulting in -
interaction, surface tension
water molecules are more strongly attracted to each other than to - phases, so the most stable configuration is to minimize - of the - interface
gas, surface area, air-water
energy required to increase surface area of the interface is known as -
surface tension
water molecules can form hydrogen bonds to molecules in some solid surfaces allowing for -
adhesion
contact angle is the angle from the - through the liquid to the -
solid surface, gas-liquid interface
contact angle quantifies the degree to which water is attracted to the - vs -
solid phase, itself
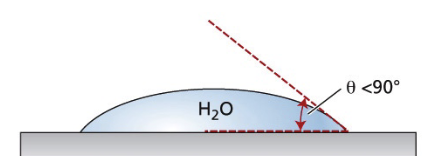
what type of surface?
hydrophilic
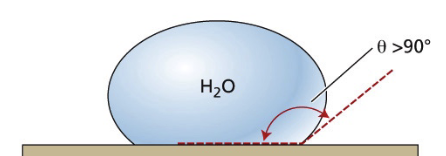
what type of surface?
hydrophobic
are primary or lignified cell walls more wettable? why?
cohesion, adhesion and surface tension give rise to -
capillarity
adhesion and surface tension pull water up the tube until the - is balanced by the - of water
upward force, weight
tensile strength = - per unit area that a - that can withstand before breaking
maximum force, continuous column of water
Cohesion between water molecules results in high - and -
latent heat of vaporization, tensile strength
osmosis is the diffusion of fluid through a semi-permeable membrane from a solution with a - solute concentration to a solution with a - solute concentration until there is an - concentration of fluid
low, higher, equal
transpiration stream is the flow of water from - to -
root, leaves
water moves from soil into root cells because it is more - inside roots
hypertonic
water flow mechanisms through membranes are driven by osmosis
diffusion across the - membrane
bulk flow through - proteins with water permeable pore
semi-permeable, aquaporin
compared to pure water, plant - has - free energy due to its solutes but plant cell wall will provide - and ultimately limit -
cytoplasm, low, counter-pressure, water uptake
compared to solution with high salt/sugar concentration, the plant cytoplasm has relatively - free energy due to its limited amount of -
high, solutes
in a hypotonic solution, water will - the cell
for plants, the plant cell wall will provide - and ultimately limit -
the animal cell will -
enter, counter-pressure, water uptake, lyse
in a hypertonic solution, water will - the cell
exit
plasmolysis means the shrinkage or contraction of the - away from the wall of a living plant or bacterial cell, caused by - of water through osmosis
protoplasm, loss
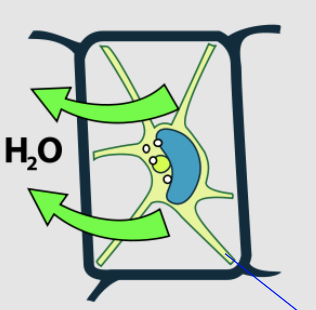
what type of solution is this plant cell in?
what state is this plant cell in?
what is the blue line pointing to (bottom right of cell)?
hypertonic, plasmolyzed, point of contact with cell wall at plasmodesmata
what type of solution is this plant cell in?
what state is this plant cell in?
isotonic, flaccid
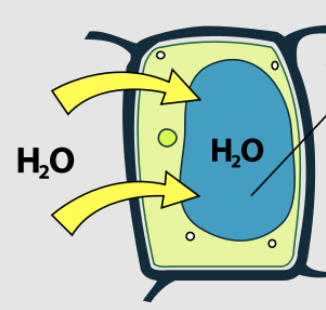
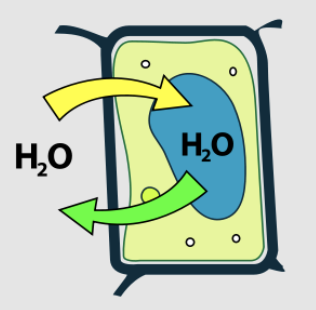
what type of solution is this plant cell in?
what state is this plant cell in?
what is the black line pointing to?
hypotonic, turgid, vacuole
protoplasm means the -, excluding the -
living cell, cell wall
turgor pressure is the force within the cell exerted by the - that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall, a turgid plant cell needs to be in a - environment
vacuole, hypotonic
water potential quantifies the tendency of water to move from one area to another due to - (four things)
osmosis, gravity, pressure, capillary action
water potential is the -
chemical potential to perform work/volume 1 mole of water
water potential equation
Ψw = Ψs + Ψp + (Ψg)
Ψs
solute component or osmotic potential
Ψp
pressure component or pressure potential
Ψg
gravity component, can be ignored at cell level
Ψw of a cell can be determined by defining a state when Ψp is - as Ψw = Ψs
zero
water will leave the cell when the water potential is - outside than inside the cell
lower
there is no net flow of water when water potential is the - outside and inside the cell
same
water will enter the cell when the water potential is - outside than inside the cell, until the cell wall provides a counter pressure that - the difference in water potential
higher, balances