Anticoagulant, Antiplatelet and Thrombolytic Therapies NOT DONE
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
How does a clot form?
vWF binds to GPIb → release ADP
ADP binds to P2Y12 receptor → increase Ca2+ → bind to GPIIb/IIIa → platelet plug
Ca2+ → increase PLA2 → acts on A.A (via COX-1)→ increased thromboxane A2
PDE3 blocks CAMP → incraesed Ca2+
How do ADP receptor inhibitors work? Name some
** anti-platelet
Prevents binding of ADP to P2Y12 receptor → prevents activation of GPIIb/IIIa
eg. Clopidogrel, Prasugrel, Ticagrelor (only reversible), Ticlopidine
How do COX inhibitors work? Name some
** anti-platelet
Irreversible cyclooxygenase inhibitor blocks synthesis of thromboxane A2
low doses inhibits COX-1: anti-thrombotic effects
higher doses inhibits COX-2 as well: anti-inflammatory effects
e.g. Aspirin
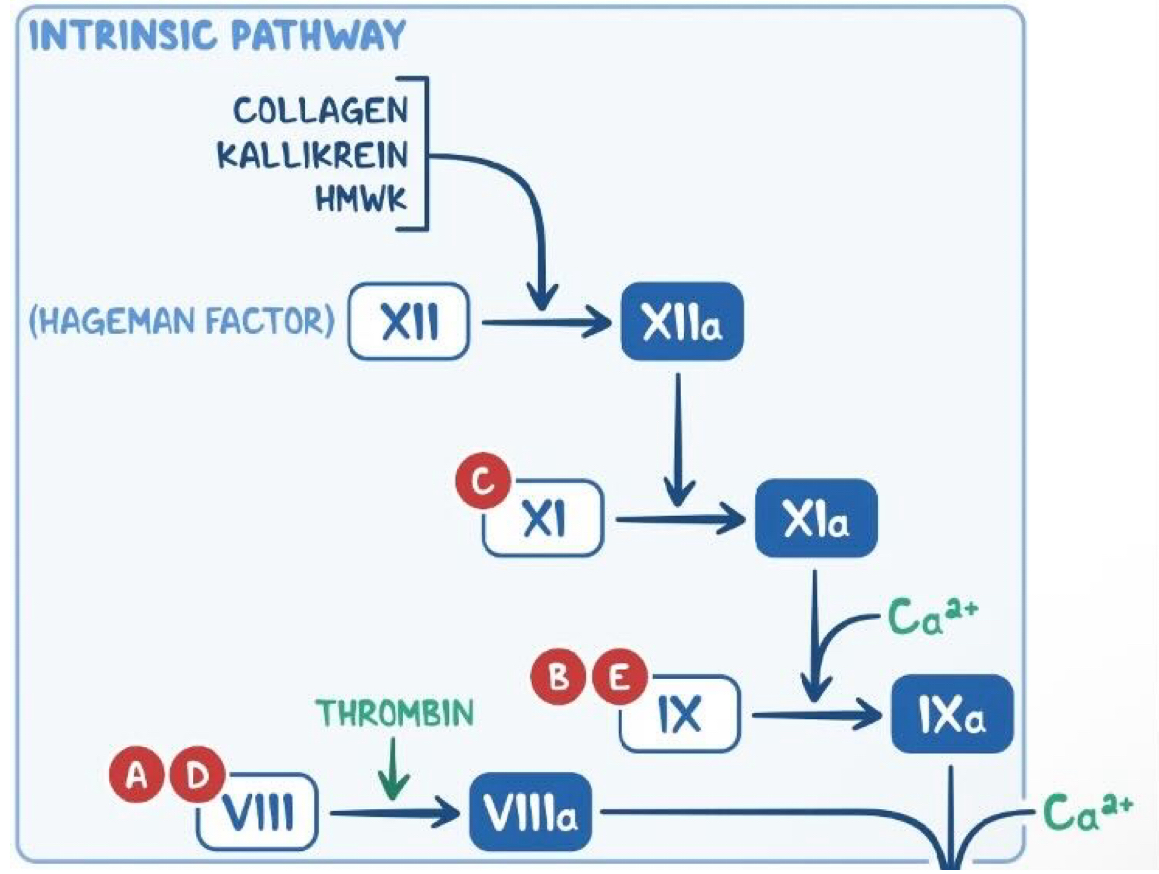
explain the intrinsic pathway
Factor XII (hageman factor) becomes activated after exposure to subendothelial collagen → XIIa
This causes the activation of Factor XI → XIa
Factor Xla + calcium activate factor IX → IXa
Factor IXa + Factor VIlla form a complex (with calcium) to activate Factor X
The common pathway then begins
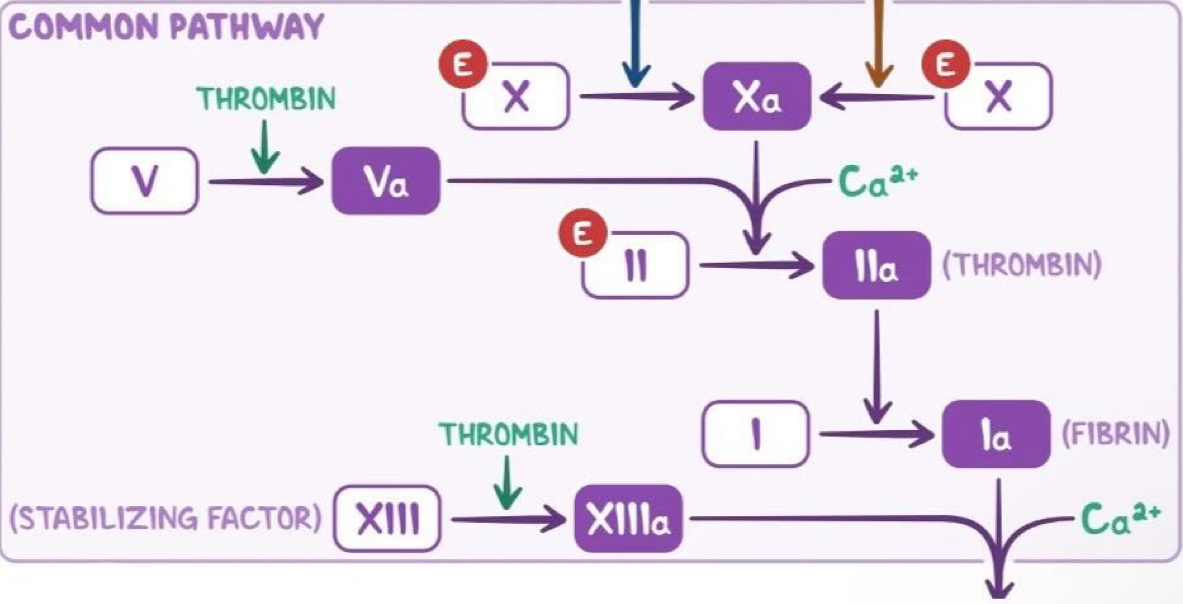
explain the common pathway
Factor V activated by thrombin → Va
Factor Xa, Va and calcium bind together to form a prothombinase complex.
This activates prothrombin into thrombin (factor II → IIa)
Thrombin cleaves fibrinogen to form fibrin (factor I → Ia)
** Factor XIlla is known as the stabilising factor
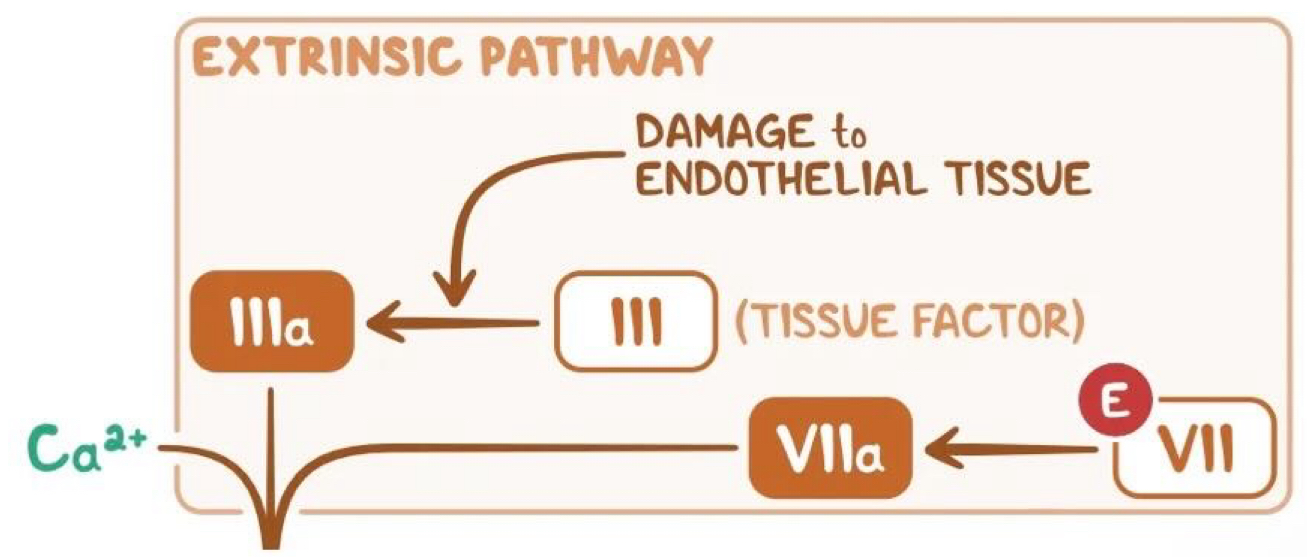
explain the extrinsic pathway
Tissue factor (secreted by endothelial cells after external damage ) comes into contact with Factor VII and activates it → factor VIIa
Factor VIla goes on to activate Factor X → Xa
The common pathway then begins
How do GPIIb/IIIa receptor inhibitors work? Name some
** anti-platelet
A monoclonal antibody that acts as a non-competitive inhibitor of GPIIb/IIIa
prevents binding of fibrinogen → prevents cross-linking and aggregation of platelets
eg. Abciximab (i.v)
Explain how Phosphodiesterase inhibitors and name some
** anti-platelet
** anti-platelet Increases CAMP levels in platelets which inhibits calcium release
** Has anti-platelet and vasodilatory effects
eg. Cilostazol, Dipyridamole
Explain how you can inhibit factor X and name some
** anticoagulant
Indirect inhibition of factor X: Heparin(administered parenterally)
Direct inhibition of factor X: direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs)
Name some direct thrombin inhibitors
** anticoagulant
Dabigatran (oral) (reversible)
Argatraban (IV)
Name a vitamin K antagonists and explain how it works
** anticoagulant
Inhibits Vitamin K epoxide reductase
Warfarin (oral)
How do we lyse clots?
Tissue plasminogen activator analogues
Promote conversion of plasminogen to plasmin → fibrinogen to fibrin
eg. Alteplase, Tenecteplase, Urokinase, Streptokinase (all IV)
How do we treat acute coronary syndrome?
300 mg aspirin immediately
Dual therapy (aspirin+ADP receptor inhibitor) after PCI
Heparin (unfractionated) in addition for patients undergoing primary PCI with radial access
Fibrinolysis is only offered to people with acute STEMI presenting within 12 hours of onset of symptoms if primary PCI cannot be delivered within 2hrs
How do we treat atrial fibrillation?
New onset AF→ Heparin
If valvular AF→ transition to warfarin (DOAC not recommended)
If non-valvular AF→ DOAC
** anticoagulation should be offered for stroke prevention to all patients with a CHA2DS2 VASc score of 2 or above
How do we treat pulmonary embolism?
If hemodynamically unstable:
Continuous unfractionated heparin infusion + thrombolytic therapy
If hemodynamically stable: Start on anti-coagulants
Start with heparin
Transition to DOAC or warfarin
Adverse side effects of aspirin
Asthma, bronchospasm, dyspnoea (due to increased leukotrienes)
Gastrointestinal irritation (due to reduced PGE2)
Not prescribed to children younger than 16 years of age due to risk of Reye’s syndrome (increased ammonia and lactic acid)
Toxicity can lead to AGMA, respiratory alkalosis
Adverse side effects of ADP receptor inhibitors
Gastrointestinal ulceration
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (due to autoantibodies against ADAMTS13)
Fever, anaemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure, neurological symptoms
Adverse side effects of PDE-3 inhibitors
Can cause cerebral vasodilation→ press down on pain receptors→ headaches
Associated with increased mortality in CHF
Adverse side effects of heparin
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) (unfractionated heparin):
Heparin bind to platelet factor 4→ immunogenic→ antibodies produced→ binds to platelets→ activate platelet plugs→ thrombus formation→ arterial and venous circulation
Skin necrosis around subcutaneous injection site


What does aPTT test for?
measures how long it takes for blood to clot
tests intrinsic pathway and the common pathway
What does INR test for?
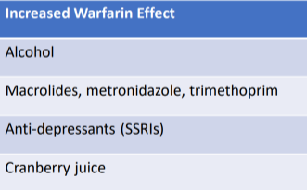
How does warfarin interact with other things?
Warfarin is metabolised by the cytochrome P450 system
If CYP450 is inhibited→ warfarin not metabolised→ Increased effect→ Bleeding
** Should not be used in patients with severe hepatic impairment