A&P - Respiratory System
5.0(2)Studied by 7 people
Card Sorting
1/230
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:39 PM on 6/26/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
231 Terms
1
New cards
what are the major functions of the respiratory system
* O2 delivery and CO2 removal to/from blood
* acid base regulation (blood pH)
* immune protection
* smell/olfaction
* speech production
* thermoregulation
* warm and humidify inhaled air
* CV regulation
* acid base regulation (blood pH)
* immune protection
* smell/olfaction
* speech production
* thermoregulation
* warm and humidify inhaled air
* CV regulation
2
New cards
what is respiration
process of supplying body with O2 and removing CO2 from the body
3
New cards
what are the 3 processes of respiration
pulmonary ventilation
external respiration
internal respiration
external respiration
internal respiration
4
New cards
pulmonary ventilation
actual breathing
movement of air between atmosphere and alveoli
movement of air between atmosphere and alveoli
5
New cards
inhalation/inspiration is ventilation of air from ------ to -------
atmosphere; alveoli
6
New cards
exhalation/expiration is ventilation of air from ------- to -------
alveoli; atmosphere
7
New cards
external respiration
gas exchange at the lungs (alveolar air sacs to pulmonary blood capillaries)
8
New cards
in external respiration ____ is moving from alveolar air sacs to pulmonary blood capillaries
O2
9
New cards
in external respiration ___ is moving from pulmonary blood capillaries to alveolar air sacs
CO2
10
New cards
internal respiration
gas exchange at the tissue level (systemic blood capillaries and tissue cells)
11
New cards
in internal inspiration ____ is moving from systemic blood capillaries to tissue cells
O2
12
New cards
in internal inspiration ___ is moving from tissue cells to systemic capillaries
CO2
13
New cards
what are the structural classifications of the respiratory system
upper or lower
14
New cards
what are the functional classifications of the respiratory system
conducting zone or respiratory zone
15
New cards
what structures/organs are part of the upper structural classification
* nose
* mouth
* pharynx
* mouth
* pharynx
16
New cards
what structures/organs are part of the lower structural classification
* larynx
* trachea
* primary bronchi
* secondary bronchi
* tertiary bronchi
* bronchioles
* terminal bronchioles
* respiratory bronchioles
* alveolar duct
* alveolar sac (alveoli)
* trachea
* primary bronchi
* secondary bronchi
* tertiary bronchi
* bronchioles
* terminal bronchioles
* respiratory bronchioles
* alveolar duct
* alveolar sac (alveoli)
17
New cards
conducting zone refers to the function of
movement of air
18
New cards
respiratory zone refers to the function of
work of gas exchange
19
New cards
what structures/organs are part of the conducting zone (functional classification)
nose/mouth/pharynx all the way to terminal bronchioles
20
New cards
what structures/organs are part of the respiratory zone (functional classification)
from respiratory bronchioles to alveolar sacs (alveoli)
21
New cards
characteristics of the conducting zone
* thicker layers of epithelium tissue
* goblet cells producing mucus/cilia → mucociliary clearance
* thicker cartilage to keep airway patent
* less smooth muscle
* goblet cells producing mucus/cilia → mucociliary clearance
* thicker cartilage to keep airway patent
* less smooth muscle
22
New cards
characteristics of respiratory zone
* thinner layers of epithelium tissue
* type I and type II alveolar cells
* immune protection from resident macrophages in alveoli
* little to no cartilage
* more smooth muscle
* type I and type II alveolar cells
* immune protection from resident macrophages in alveoli
* little to no cartilage
* more smooth muscle
23
New cards
where would nonkeratinized stratified squamous epi be in the system
* nose/mouth/pharynx
* larynx
* larynx
24
New cards
where would ciliated pseudostratified columnar epi be in the system
* nose
* pharynx
* larynx
* trachea
* primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchi
* pharynx
* larynx
* trachea
* primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchi
25
New cards
where would ciliated simple columnar epi be in the system
bronchioles
26
New cards
where would nonciliated simple columnar epi be in the system
terminal bronchioles
27
New cards
where would simple cuboidal epi be in the system
respiratory bronchioles
28
New cards
where would simple squamous epi be in the system
respiratory bronchioles and alveoli in alveolar sac
29
New cards
what are the 4 cells of the respiratory zone
* type I alveolar cells
* respiratory membranes
* type II alveolar cells
* macrophages
* respiratory membranes
* type II alveolar cells
* macrophages
30
New cards
alveolar cells can also be known as
pneumocytes
31
New cards
what do resident macrophages derive from
monocytes
32
New cards
what function do resident macrophages derive from, where do they reside
immune protection, alveolar
33
New cards
characteristics of type I alveolar cells
* simple squamous epi cells
* site of gas exchange
* more numerous alveoli cell
* site of gas exchange
* more numerous alveoli cell
34
New cards
characteristics of respiratory membrane
very thin fusion of alveolar (mainly type I) epithelium cells and pulmonary capillary endothelial cells
35
New cards
characteristics of type II alveolar cells
* less numerous than type I
* produce a fluid called surfactant
* reduces surface tension of alveoli to help maintain patency
* maintain patency and openness
* produce a fluid called surfactant
* reduces surface tension of alveoli to help maintain patency
* maintain patency and openness
36
New cards
what to membranes make of the serous membrane
parietal pleura and visceral pleura
37
New cards
parietal pleura lines the
thoracic cavity
38
New cards
visceral pleura lines the
direct surface of the lung
39
New cards
what is between the two membranes in the serous membrane
serous fluid; helps reduce friction
40
New cards
what is a spirogram measure with
spirometer
41
New cards
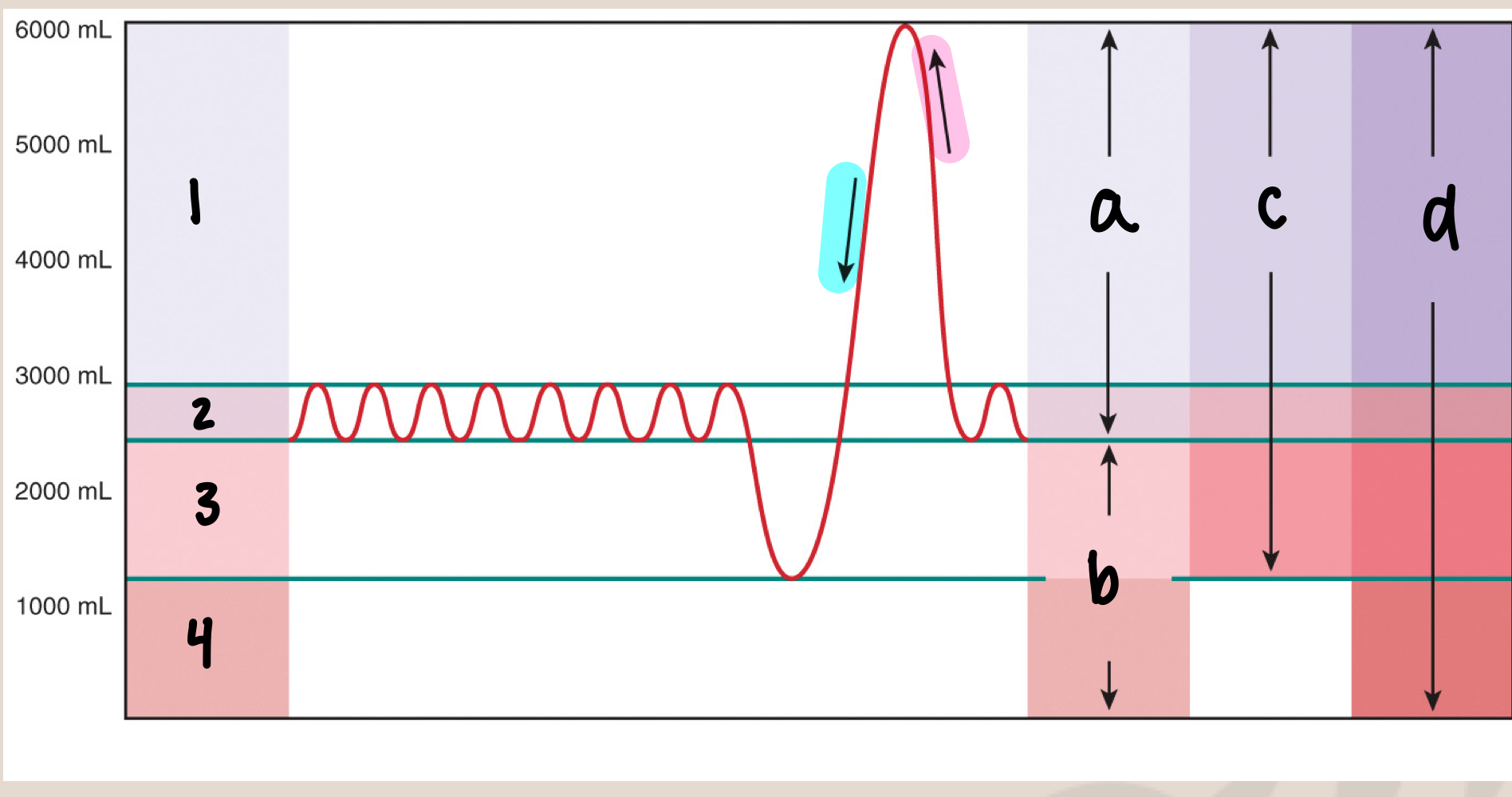
what is 1
inspiratory reserve volume/IRV (3000mL)
42
New cards
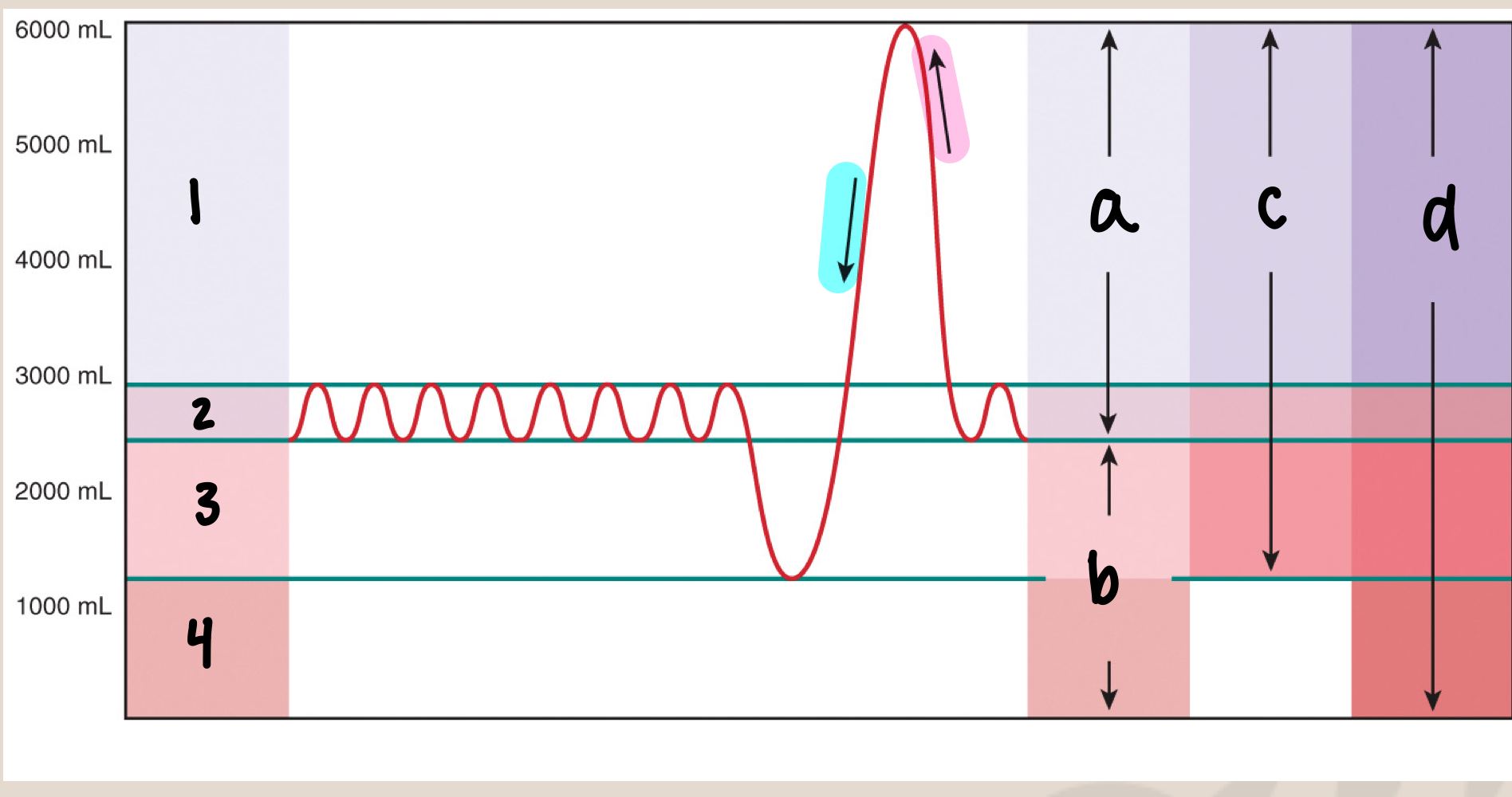
what is 2
tidal volume/Vt (500mL)
43
New cards
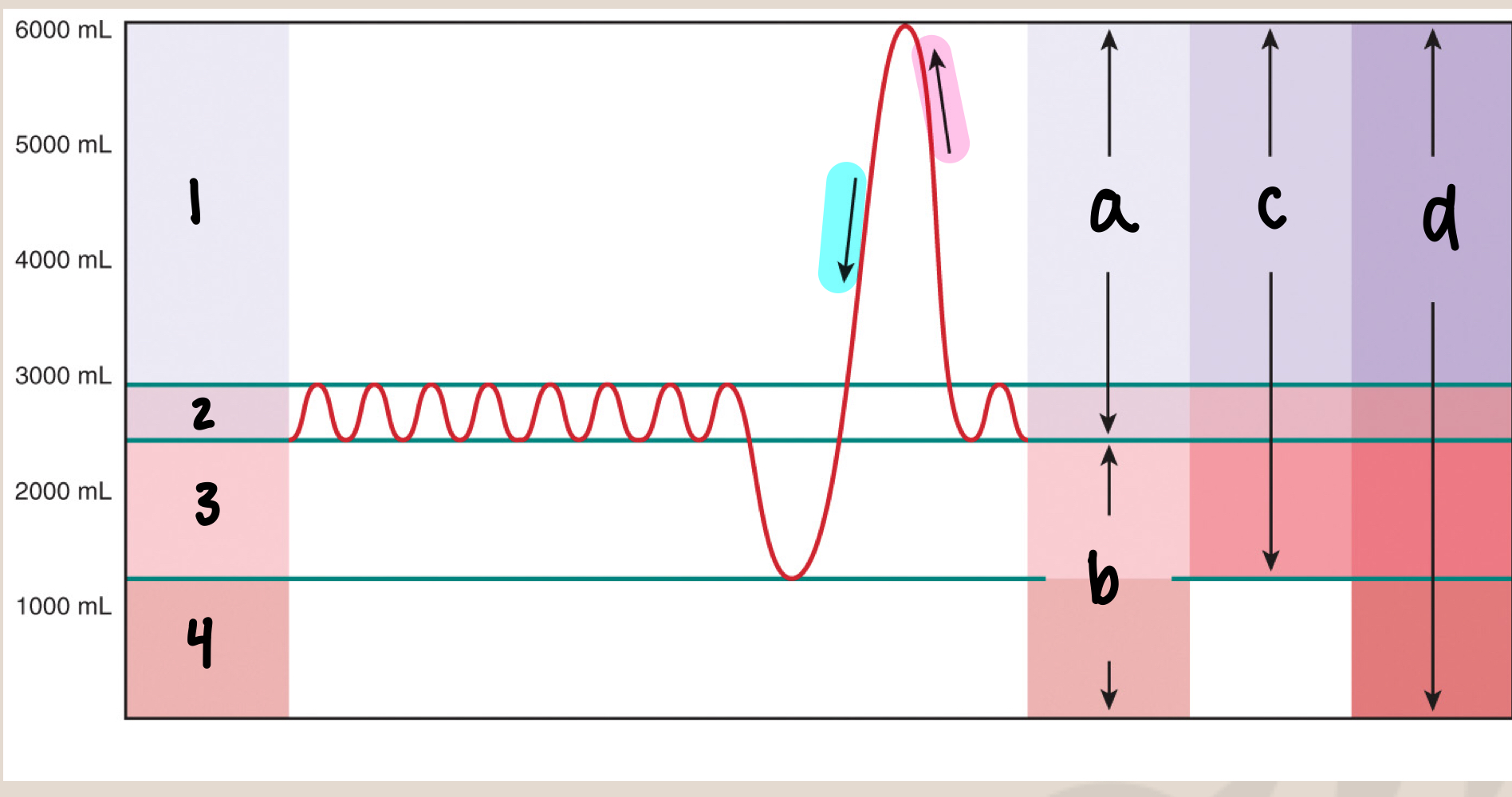
what is 3
expiratory reserve volume/ERV (1500mL)
44
New cards
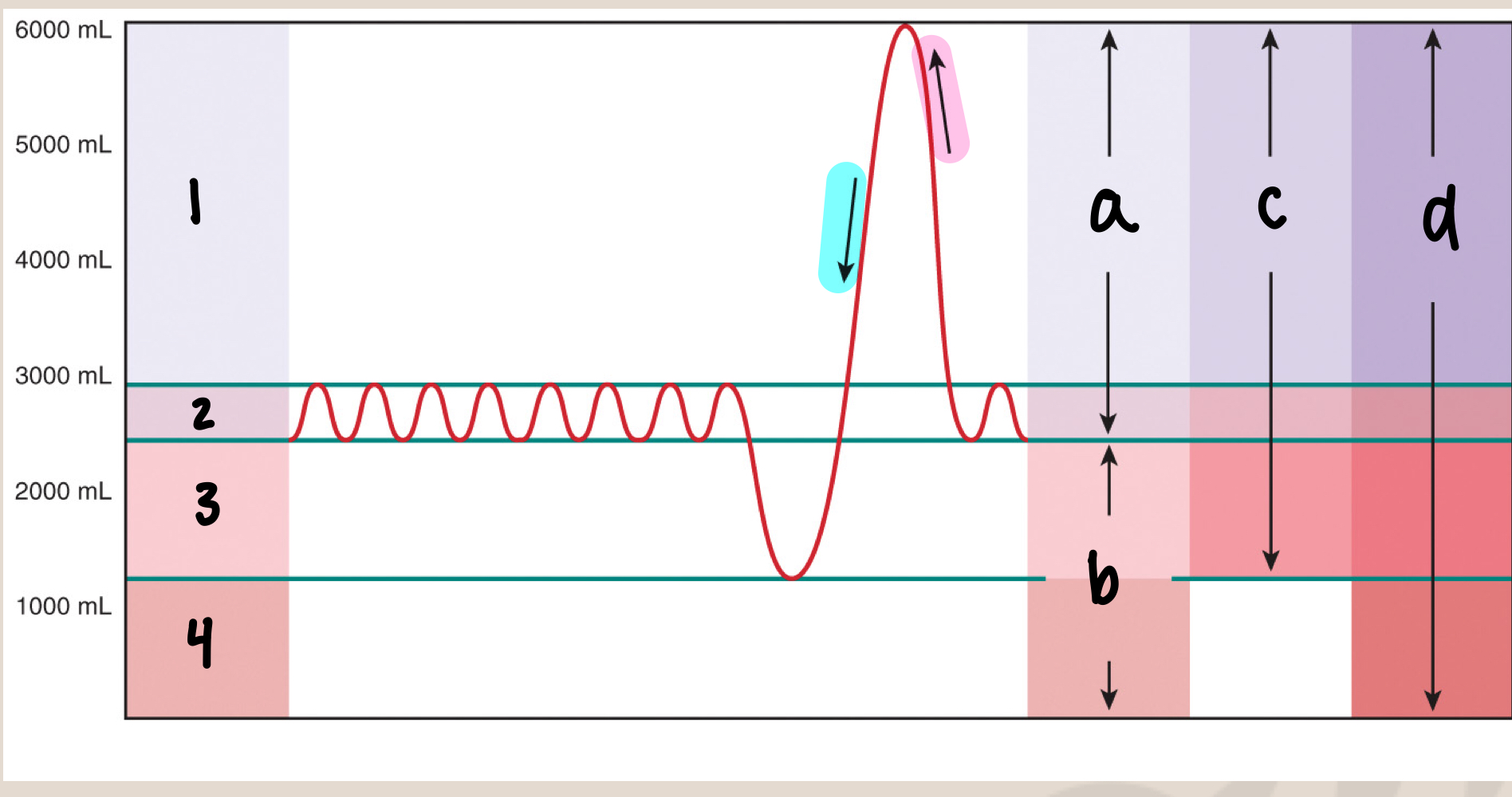
what is 4
residual volume (1000mL)
45
New cards
what is tidal volume
volume of air in lungs during restful breathing (500mL)
46
New cards
what is expiratory reserve volume/ERV
maximum exhale after normal exhale (1500mL)
47
New cards
what is inspiratory reserve volume/IRV
maximum inhale after normal inhale (3000mL)
48
New cards
what is residual volume/RV
amount of air remaining after maximum exhale because we never get rid of all volume in lungs (1000mL)
49
New cards
what are the 4 lung volumes
* IRV
* Tidal Volume (Vt)
* ERV
* Residual volume
* Tidal Volume (Vt)
* ERV
* Residual volume
50
New cards
what are the 4 lung capacities
* Inspiratory capacity
* functional reserve capacity
* vital capacity
* total lung capacity
* functional reserve capacity
* vital capacity
* total lung capacity
51
New cards
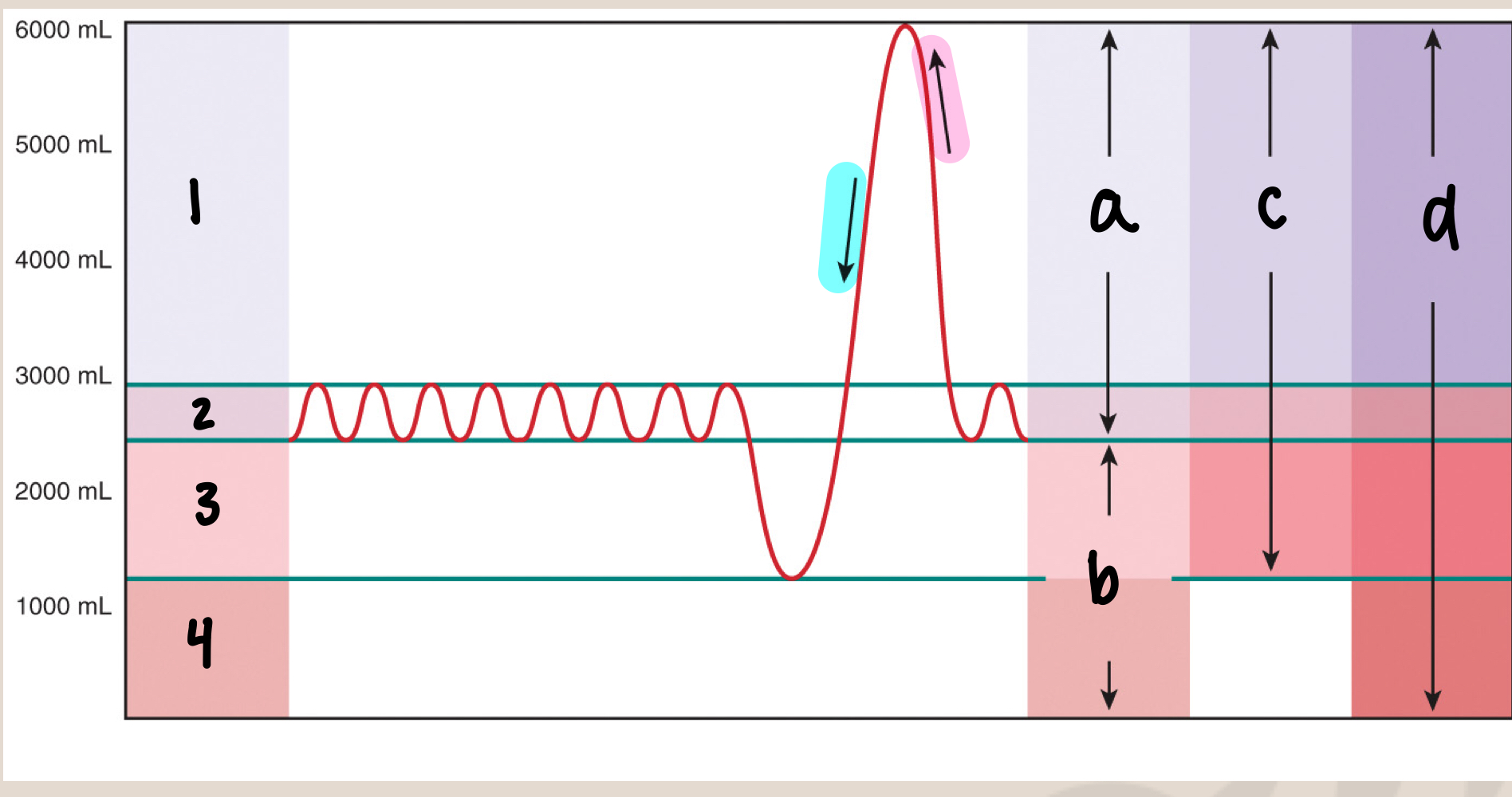
what is a
inspiratory capacity/IC (3500mL)
52
New cards
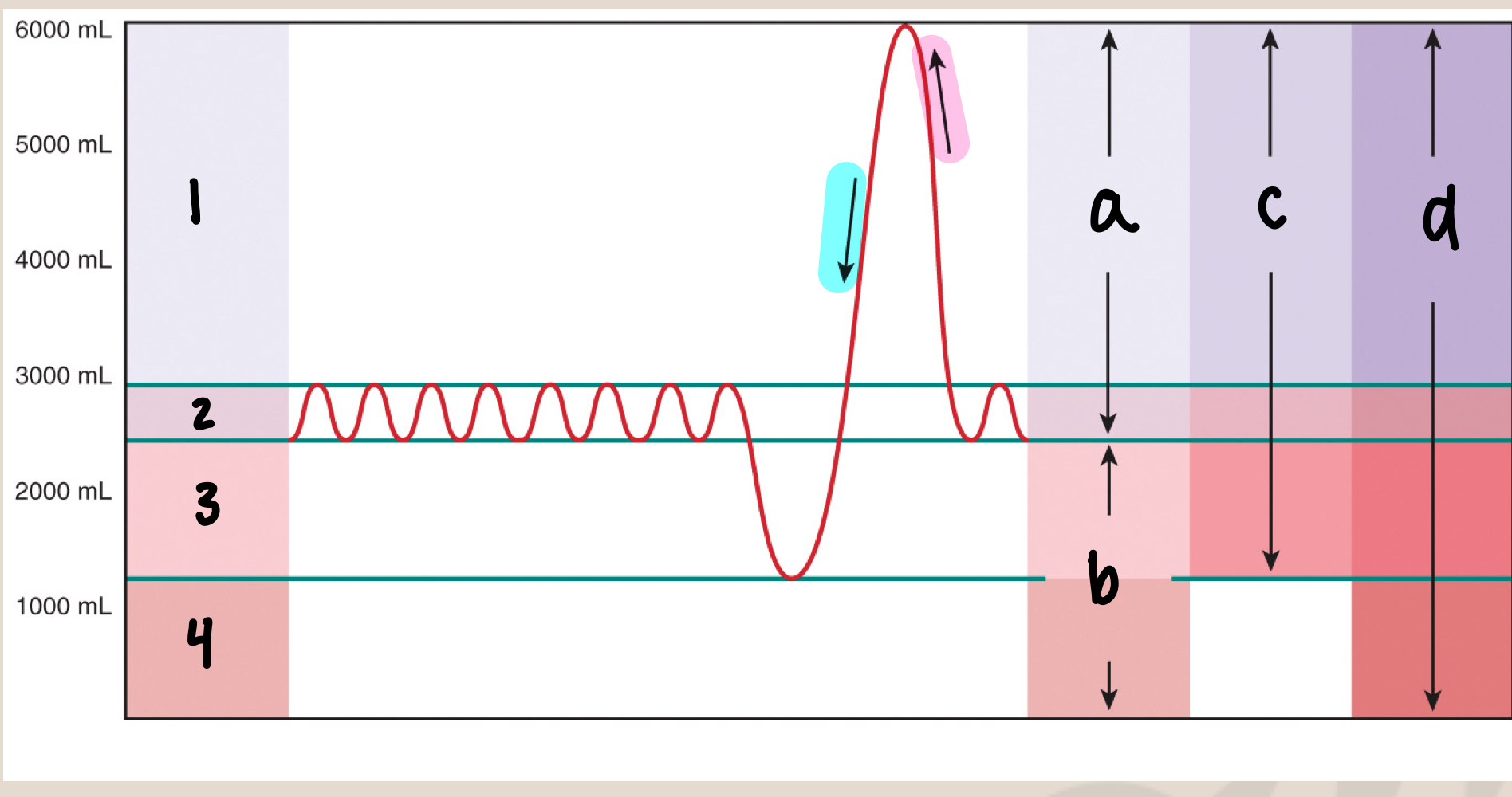
what is b
functional residual capacity/FRC (2500mL)
53
New cards
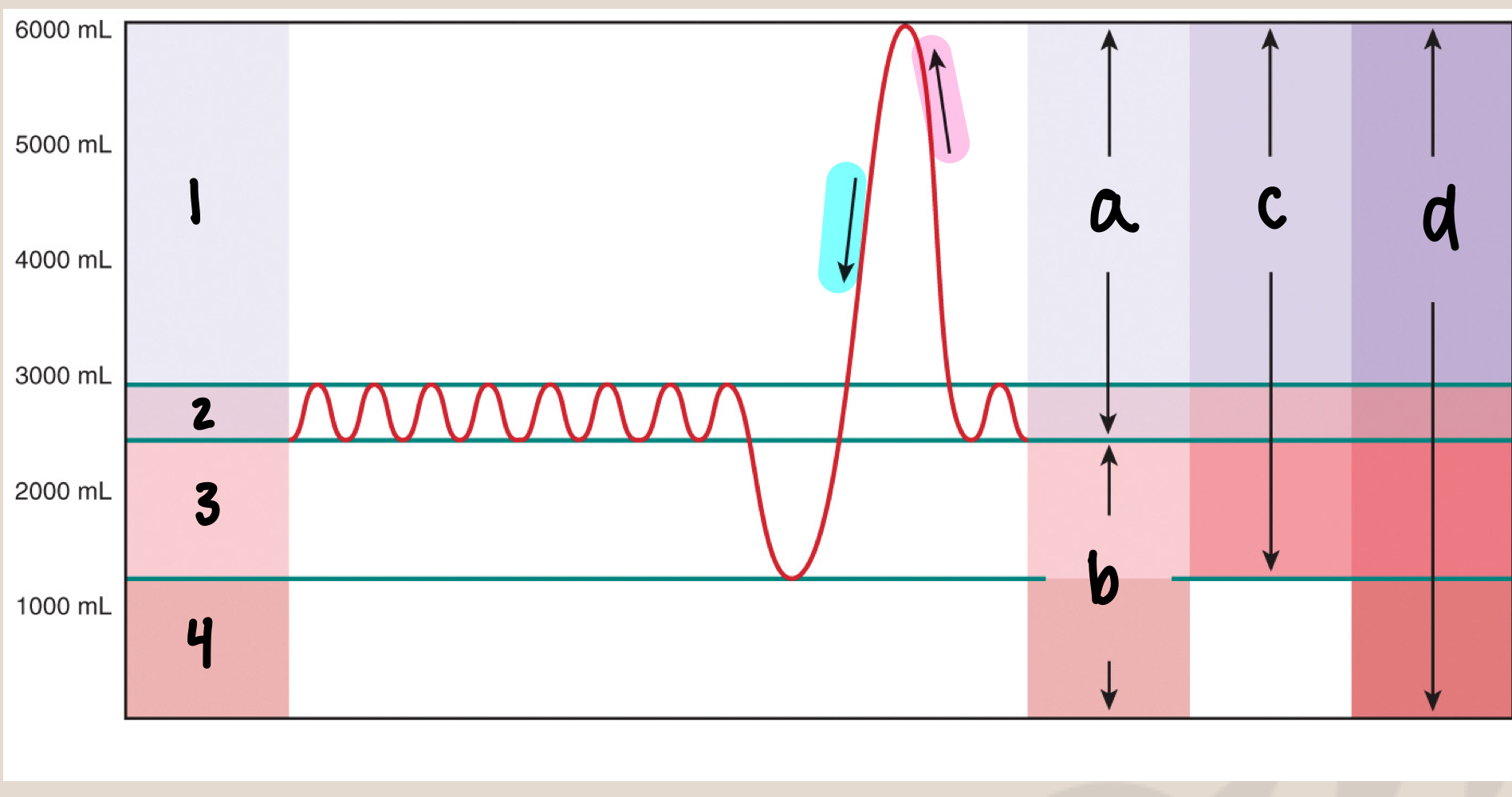
what is c
vital capacity/VC (5000mL)
54
New cards
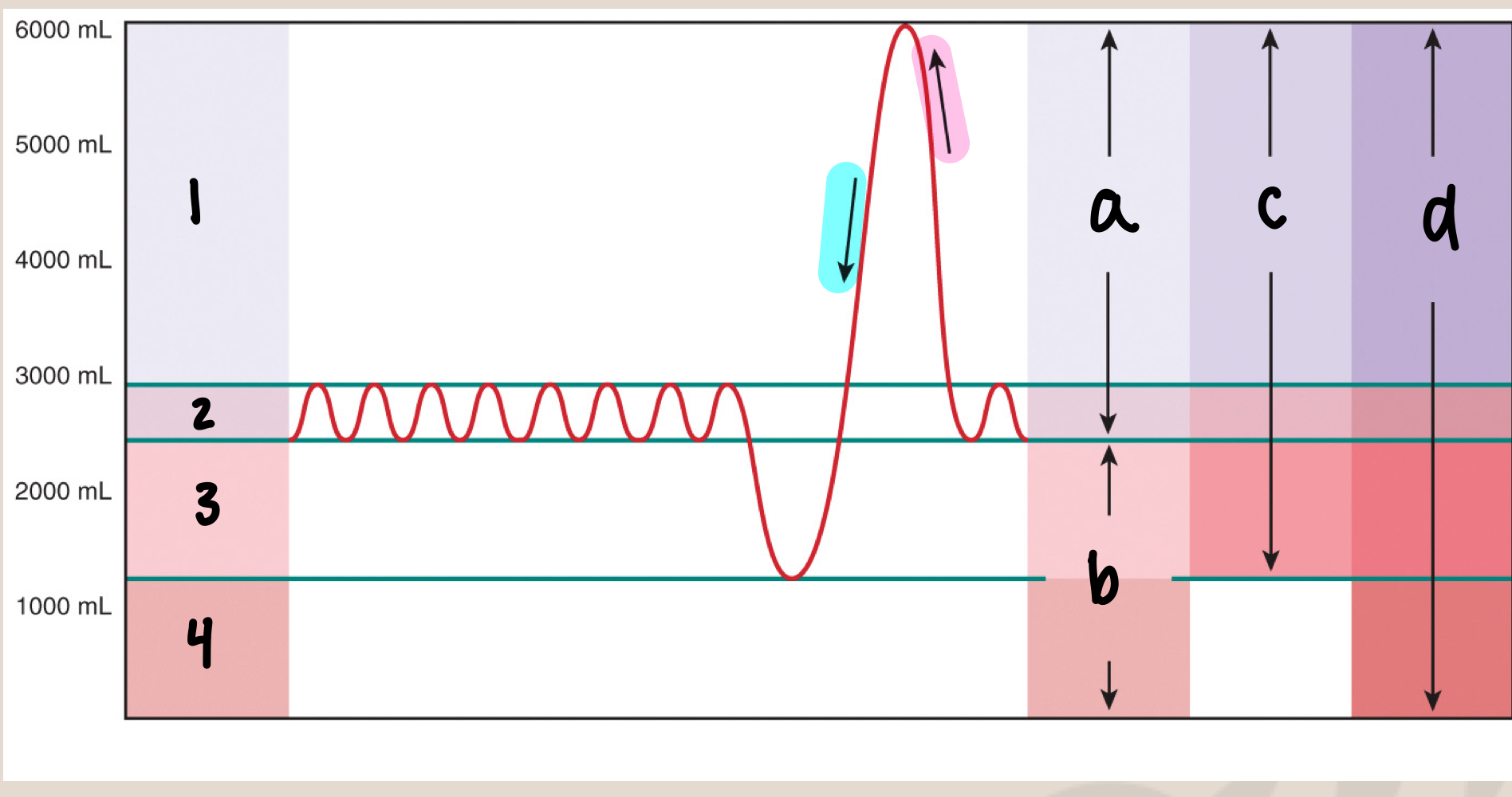
what is d
total lung capacity/TLC (6000mL)
55
New cards
what is inspiratory capacity/IC
max inhale after normal exhale (3500mL)
56
New cards
equation for inspiratory capacity/IC
IC=Vt+IRV
57
New cards
what is functional residual capacity/FRC
amount of air in lungs after normal exhale (2500mL), before the next inhale (slight pause)
58
New cards
equation for functional residual capacity/FRC
FRC=ERV+RV
59
New cards
what is vital capacity/VC
max inhale → max exhale (5000mL)
60
New cards
equation for vital capacity/VC
VC=IRV+Vt+ERV
61
New cards
what is total lung capacity/TLC
sum of all volumes
62
New cards
equation for total lung capacity/TLC
TLC=IRV+Vt+ERV+RV
63
New cards
what is minute ventilation
amount of air flow in 1 minute to the lungs
64
New cards
equation for minute ventilation
minute ventilation Vb=Vt x fb (tidal volume\*respiratory rate)
65
New cards
what is fb
breathing frequency/respiratory rate
66
New cards
what is alveolar ventilation
amount of “fresh air” reaching alveoli in 1 minute
67
New cards
what is dead space volume/Vd
amount of air in conducting zone
approximately equal to one’s ideal body weight (mL)
approximately equal to one’s ideal body weight (mL)
68
New cards
equation for alveolar ventilation
Va= minute ventilation - (breathing frequency\*dead space volume)
69
New cards
what is boyle’s law
pressure and volume are inversely related
70
New cards
what is airflow equation
change in pressure (Patm-Palv) / resistance
71
New cards
what is airflow at FRC
0
72
New cards
what is Patm
atmospheric pressure
approx. 760 mmHg at sea level
0 mmHg at FRC
approx. 760 mmHg at sea level
0 mmHg at FRC
73
New cards
what is Palv
alveolar pressure
approx. 760 mmHg at sea level
0 mmHg at FRC
approx. 760 mmHg at sea level
0 mmHg at FRC
74
New cards
what is Pip
interpleural pressure
approx. 756 mmHg at sea level
\-4 mmHg at FRC
approx. 756 mmHg at sea level
\-4 mmHg at FRC
75
New cards
what allows the pleura layers to move together when thoracic cavity increases or decreases
\-4 mmHg results in a vacuum suction
76
New cards
what happens to the lungs if the size of the thoracic cavity increases
lungs expand
77
New cards
what happens to the lungs if the size of the thoracic cavity decreases
lungs recoil/get smaller
78
New cards
primary muscles involved in respiratory breathing
* diaphragm
* external intercostals
* external intercostals
79
New cards
accessory muscles for forced inhalation/inspiration
* sternocleidomastoid
* scalenes
* scalenes
80
New cards
accessory muscles for forced exhalation/expiration
* internal intercostals
* external abdominal oblique
* internal abdominal oblique
* transverse abdominis
* rectus abdominis
* external abdominal oblique
* internal abdominal oblique
* transverse abdominis
* rectus abdominis
81
New cards
upon contraction the diaphragm moves ----- and ------ the size of the thoracic cavity
down; increases
82
New cards
upon relaxation the diaphragm moves ------ and ------ the size of the thoracic cavity
up; decreases
83
New cards
4 steps of restful inhalation/inspiration
1. neural input to skeletal muscles of inspiration
2. contraction of inspiratory muscles
3. lungs expand
4. air moves down its pressure gradient into lungs
84
New cards
4 steps of restful exhalation/expiration
1. withdrawal of neural input to inspiratory muscles
2. relaxation of diaphragm and external intercostals
3. lungs recoil
4. air moves down pressure gradient
85
New cards
what nerve innervates the diaphragm
phrenic nerve
86
New cards
what nerve innervates the external intercostals
intercostal nerves
87
New cards
upon contraction the external intercostals ------ ribs and ------ the size of the thoracic cavity
elevates; increases
88
New cards
an increase in thoracic cavity size during inhalation causes the -------- ------- to --------
alveolar volume; increase
89
New cards
if alveolar volume increases, alveolar pressure -------
decreases
90
New cards
once lung expand in inhalation what is the pressure relation
Patm > Palv
91
New cards
when Patm > Palv air moves where
into the lungs
92
New cards
relaxation of diaphragm and external intercostals causes the size of the thoracic cavity to ------
decrease
93
New cards
if thoracic cavity size decreases, then alveolar pressure -------
increases
94
New cards
once lungs recoil in exhalation, what is the pressure relation
Palv > Patm
95
New cards
when Palv > Patm air moves where
out of the lungs
96
New cards
3 factors affecting ventilation
* alveolar surface tension
* lung compliance
* airway resistance
* lung compliance
* airway resistance
97
New cards
if alveolar surface tension increases, work of breathing -----
increases
98
New cards
what reduces alveolar surface tension
surfactant (type II cells)
* breaks up H20 from sticking
* breaks up H20 from sticking
99
New cards
what is lung compliance
stretchability of the lung
100
New cards
increase in lung compliance means longs are more or less elastic/flexible
more flexible